"持梦行文本编辑器" 作为一款轻量高效的命令行文本处理工具,其核心优势在于精简的架构设计与实用的功能实现。本文将从项目架构入手,详细解析十大核心功能的技术实现,结合关键代码片段深入说明设计思路,为C/C++学习者提供可复用的文本编辑工具开发参考。
一、项目整体架构设计
1. 架构概览
项目采用 "核心控制 + 功能模块" 的分层设计,整体架构分为三层:

2. 核心类关系
项目通过三个核心类实现功能解耦:
Manage:核心控制类,聚合Edit和MyFile,协调各功能模块执行,处理用户交互流程;Edit:文本数据管理类,基于双向链表存储文本行,提供行级操作接口;MyFile:文件操作类,封装文件打开、读取、写入等底层 IO 操作;MyString:字符串工具类,提供字符串转整数等辅助功能,支撑用户输入验证。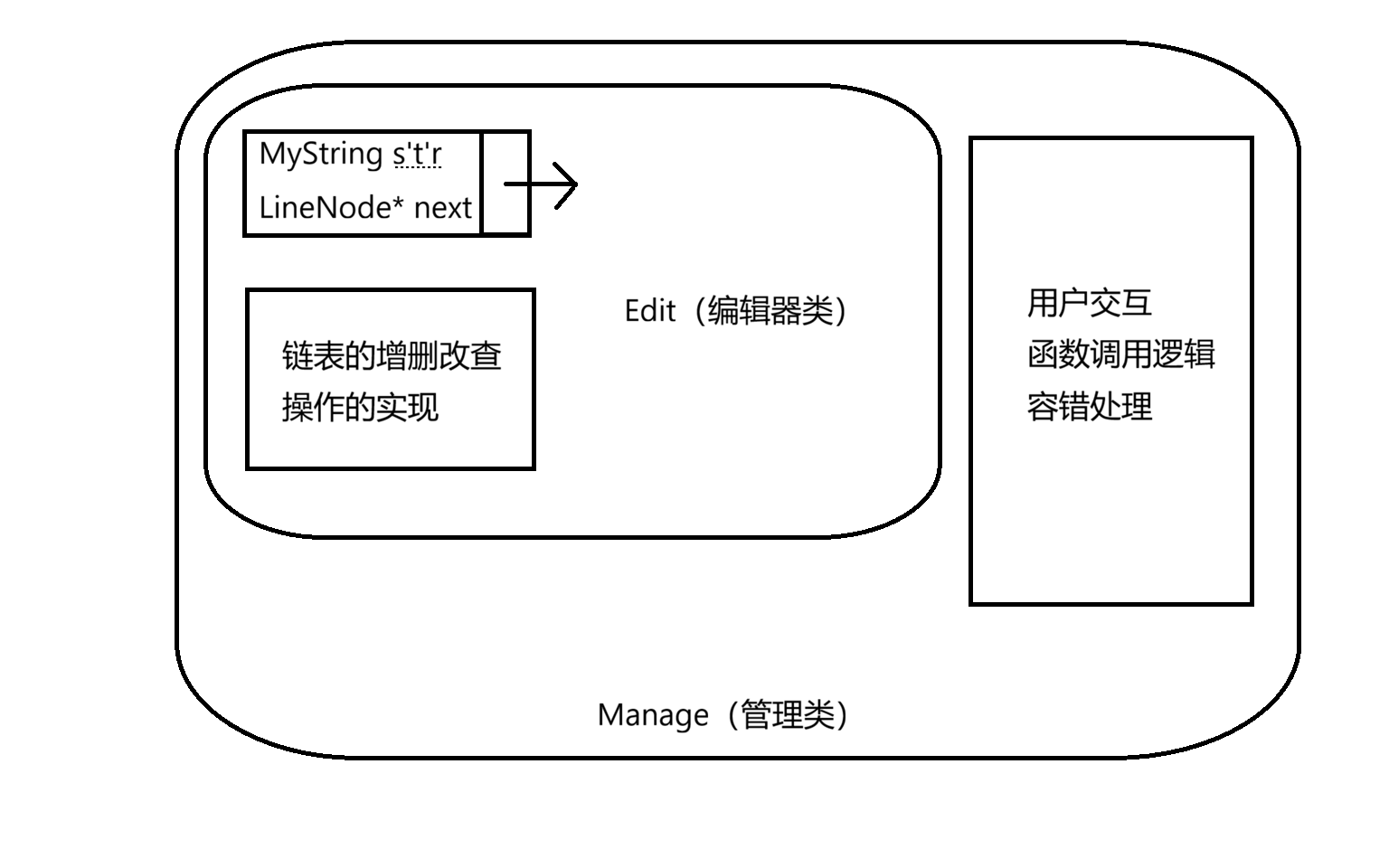
类关系图简化如下:
┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐
│ Manage │◄──────┤ Edit │ │ MyString │
└───────────┘ └───────────┘ └───────────┘
▲
│
▼
┌───────────┐
│ MyFile │
└───────────┘二、十大核心功能实现详解
1. 文件打开(openFile)
功能作用 :读取本地文本文件内容到编辑器,支持.txt、.md等纯文本格式。
实现思路:
- 接收用户输入的文件路径;
- 通过
MyFile类打开文件并读取内容; - 按行分割内容,通过
Edit类插入到双向链表中; - 更新文件状态标记(
isOpenExistFile、hasChoosedFile)。
核心代码:
管理类处理文件路径
cpp
void Manage::openFile()
{
if (hasntModify == false&&hasChoosedFile)
{
//file has been modified
puts("文件已修改,是否保存?");
char c = _getch();
if (c == 'y' || c == 'Y')
{
saveFile();
MessageBox(NULL, "文件已保存,即将打开新文件!", "提示", MB_OK);
}
else
{
MessageBox(NULL, "文件未保存,即将打开新文件!", "提示", MB_OK);
}
}
cls();
puts("请在磁盘中选择您要打开的文件/文件夹");
MyFile t;
t.FileChoose();
if (!t.Get_filePath().empty())
{
hasChoosedFile = true;
if (t.IsFileExist())
{
isOpenExistFile = true;
}
else
{
isOpenExistFile = false;
hasntModify = false;
puts("您只选择了路径,请您输入文件名(不用输入后缀):");
MyString s;
cin >> s;
t.SetFilePath(t.Get_filePath() + s.c_str()+".txt");
}
}
else
{
puts("您取消了路径选择,使用默认输出路径,请您输入文件名(不用输入后缀):");
MyString s;
cin >> s;
t.SetFilePath(t.Get_filePath() + s.c_str() + ".txt");
hasntModify = false;
}
file = t;
//file.SetFilePath("test/test.txt");
edit.edit_openFile(file);
hasFileToSave = true;
pause();
}编辑器类处理文件读取
cpp
void Edit::edit_openFile(MyFile &file) {
if (file.IsFileExist()) {
// 清空链表
_clearLineList();
// 读取文件内容到链表
std::fstream fs;
fs.open(file.Get_filePath(), std::ios::in);
if (!fs.is_open()) {
std::cout << "文件打开失败!请设置存储内容的文件名:" << std::endl;
return;
}
char str[MAXLINESIZE] = { 0 };
tail; // 尾指针(避免每次遍历)
while (fs.getline(str, sizeof(str))) { // 按行读取
if (str!="")
{
LineNode* newNode = _createLineNode(str);//创建节点
tail->next = newNode;
tail = tail->next;
line++;
memset(str, 0, sizeof(str)); // 清空缓冲区
}
}
fs.close();
std::cout << "文件打开成功,共" << line << "行" << std::endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "您没有选择文件,已使用默认路径!" << std::endl;
}
}设计亮点:
- 逐行读取避免大文件一次性加载导致的内存占用过高;
- 通过状态标记(
hasChoosedFile)记录当前是否有打开的文件,为后续保存操作提供依据。
2. 文本显示(showText)
功能作用:将当前编辑器中的文本内容按行号显示,方便用户查看整体结构。
实现思路:
- 遍历
Edit类中的链表; - 逐行输出文本内容,并附加行号;
- 处理空文本场景(提示 "当前文本为空")。
核心代码:
cpp
//行链表的定义
struct LineNode //每行的内容链表
{
MyString text;
LineNode* next;
public:
LineNode()
{
next = NULL;
}
LineNode(MyString str)
{
text=str;
next = NULL;
}
void setTest(MyString str)
{
this->text = str;
}
void showText(int line)
{
printf("%4d:%s\n", line, text.c_str());
}
};
typedef LineNode* pLineNode; //行链表
void Edit::edit_showText()
{
pLineNode p = head->next;
int k = 1;
if (p == NULL)
{
cout << "您的内容被外星人偷了!快快创建内容吧!" << endl;
return;
}
while (p)
{
p->showText(k);
p = p->next;
k++;
}
}设计亮点:
- 基于链表遍历实现,时间复杂度为 O (n),适合中等规模文本;
- 行号从 1 开始计数,符合用户使用习惯(而非 0 基索引)。
3. 插入行文本(insertLineText)
功能作用:在指定行号插入新文本,支持在已有行前、后或末尾插入。
实现思路:
- 获取用户输入的目标行号和待插入文本;
- 验证行号合法性(必须为数字且在有效范围);
- 调用
Edit类的链表插入方法,在目标位置插入新节点。
核心代码:
cpp
void Manage::insertLineText()
{
cls();
int a, n;
puts("在a行后插入n行,请输入a和n:");
showCursor();
input:
cout << file.Get_filePath() << ">";
cin >> a >> n;
if (a < 0 || n < 1)
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
printf("输入有误,请重新输入");
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
Sleep(1000);
return;
}
if (a > edit.getline())
{
a = edit.getline();
puts("你输入的区间已经超出文件末尾,已自动调整为文件末尾插入!");
}
bool ret=edit.edit_insertLineText(a,n);
if (ret)
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLUE);
cout<<"在第"<<a<<"行后插入了"<<n<<"行"<<endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
hasntModify = false;
}
else
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
cout << "插入失败!" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
}
pause();
}
bool Edit::edit_insertLineText(int lineNum, int insertLineNum)
{
if (lineNum < 0)return false;
if (lineNum >= line)
{
lineNum = line;
HANDLE handle = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle,TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLUE);
cout << "插入位置超出文件末尾,已插入到文件末尾!" << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
}
pLineNode pInsertPos = _findLine(lineNum);
//pInsertPos->showText(lineNum);
pLineNode pInsertPos_next=pInsertPos->next;
//构建新的链表
pLineNode insertHead = new LineNode, insertTail = insertHead;//构建头链表
pLineNode p = insertHead;
MyString s;
cout << "new" << 1 << ":";
getchar();
s.getline_n();
insertHead->setTest(s);//设置表头
for (int i = 1; i < insertLineNum; i++)
{
MyString t;
cout << "new" << i+1 << ":";
t.getline_n();
pLineNode newNode = new LineNode(t);
p->next = newNode;
p = p->next;
insertTail = p;
}
//将新的链表插入到edit
pInsertPos->next = insertHead;
insertTail->next = pInsertPos_next;
_updateLineCount();
return true;
}设计亮点:
- 实现输入验证,防止非法输入让程序崩溃;
- 支持插入到 "最后一行 + 1" 的位置(即末尾追加),提升操作灵活性。
4. 删除行文本(deleteLineText)
功能作用:删除指定行号的文本,自动调整后续行号索引。
实现思路:
- 验证当前文本非空;
- 获取并验证用户输入的行号;
- 调用
Edit类的链表删除方法,移除目标节点并调整指针。
核心代码:
cpp
void Manage::deleteLineText()
{
cls();
showCursor();
int a, b;
puts("请输入您要删除的行区间[a,b]:");
cout << file.Get_filePath() << ">";
cin >> a >> b;
if (a > edit.getline()|| a > b)
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
puts("区间输入错误!");
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
Sleep(1000);
return;
}
if (b > edit.getline())
{
b = edit.getline();
puts("你输入的区间已经超出文件末尾,已自动调整为文件末尾删除!");
}
bool ret = edit.edit_deleteLineText(a, b);
if (ret)
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLUE);
cout << "成功删除了[" << a << "," << b << "]区间的行" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
hasntModify = false;
}
else
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
cout << "删除失败!" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
}
pause();
}
bool Edit::edit_deleteLineText(int a, int b)
{
if (b > line)return false;
pLineNode pleft_pre = _findLine(a - 1);
if (a == 0)
{
pleft_pre = &dummy;
}
pLineNode pleft = pleft_pre->next;
pLineNode pright = _findLine(b);
pLineNode deleteHead = pleft,pright_next=pright->next;
//开始删除
pleft_pre->next = pright_next;
pright->next = NULL;
//清除删除的链表
while (deleteHead)
{
pLineNode p = deleteHead;
deleteHead = p->next;
delete p;
}
_updateLineCount();
return true;
}设计亮点:
- 删除前检查文本是否为空,避免空链表操作错误;
- 链表节点删除后自动回收内存(
Edit类内部实现),防止内存泄漏。
5. 复制行文本(copyLineText)
功能作用:复制指定行的内容到剪贴板(此处简化为临时变量存储),支持后续粘贴。
实现思路:
- 验证目标行号合法性;
- 从
Edit链表中读取目标行内容; - 存储到
Manage类的剪贴板变量(未在代码片段中显示,实际实现需添加)。
核心代码:
cpp
void Manage::copyLineText()
{
cls();
showCursor();
int a, b, dest;
puts("请输入您要拷贝的行区间[a,b]:");
cout << file.Get_filePath() << ">";
cin >> a >> b;
if (a < 0 || b < a||b>edit.getline()||a>edit.getline())
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
cout << "输入区间不合法!" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
Sleep(1000);
return;
}
puts("请输入您要粘贴的目标行:(超出现有行,将自动粘贴至末尾)");
cout << file.Get_filePath() << ">";
cin >> dest;
if (dest > edit.getline())
{
dest = edit.getline();
}
bool ret = edit.edit_copyLineText(a, b,dest);
if (ret)
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLUE);
cout << "成功拷贝了[" << a << "," << b << "]区间的内容到第" << dest << "行后" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
hasntModify = false;
}
else
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
cout << "拷贝失败!" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
}
pause();
}
bool Edit::edit_copyLineText(int a, int b, int dest)
{
if (a>line ||b > line || a > b || a < 1 || dest < 0)
return false;
// 查找区间[a,b]
pLineNode pleft = _findLine(a);
pLineNode pright = _findLine(b);
// 创建拷贝缓存区
pLineNode p = pleft;
pLineNode copyHead = nullptr; // 局部变量,需要改为成员变量或返回值
pLineNode copyTail = nullptr;
pLineNode copy_p = nullptr;
while (p != nullptr && p != pright->next)
{
pLineNode newNode = new LineNode(p->text);
if (copyHead == nullptr) {
// 第一个节点
copyHead = newNode;
copyTail = newNode;
}
else {
// 连接到链表尾部
copyTail->next = newNode;
copyTail = newNode;
}
p = p->next;
}
// 检查是否成功拷贝
if (copyHead == nullptr) return false;
// 将拷贝的链表插入到dest位置
pLineNode pdest = _findLine(dest);
if (dest > line)return false;
if (pdest == nullptr) {
// 处理尾部插入的情况
pdest = tail;
tail->next = copyHead;
tail = copyTail;
_updateLineCount();
return false;
}
pLineNode pdest_next = pdest->next;
// 开始插入
pdest->next = copyHead;
copyTail->next = pdest_next;
// 更新行数
_updateLineCount();
return true;
}设计亮点:
- 通过
getLineAt方法封装链表节点访问,隐藏底层数据结构细节; - 剪贴板内容暂存于内存,适合轻量使用场景(复杂场景可扩展为系统剪贴板交互)。
6. 修改行文本(modifyLineText)
功能作用:替换指定行的全部内容,支持对已有文本进行修改。
实现思路:
- 验证目标行号合法性;
- 获取用户输入的新内容;
- 调用
Edit类的方法替换目标节点的文本数据。
核心代码:
cpp
bool Edit::edit_modifyLineText(int lineNum)
{
pLineNode p = _findLine(lineNum);
if (!p)return false;
printf("%4d:%s(原内容)\n", lineNum, p->text.c_str());
MyString s;
puts("请输入修改后的内容:");
getchar();
s.getline_n();
p->text = s;
return true;
}设计亮点:
- 直接修改链表节点的
data字段,无需删除再插入,提升效率; - 与插入功能共享行号验证逻辑,保证输入安全性。
7. 查找字符串(findString)
功能作用:在文本中搜索指定字符串,返回所有包含该字符串的行号及上下文。
实现思路:
- 获取用户输入的目标字符串;
- 遍历
Edit链表的每一行,调用字符串匹配函数(如strstr); - 记录并输出所有匹配行的行号和内容。
核心代码:
查找逻辑
cpp
void Manage::findString()
{
cls();
showCursor();
MyString fstr;
puts("请输入您要查找的字符串:");
cout << file.Get_filePath() << ">";
fstr.getline_n();
bool ret=edit.edit_findString(fstr);
if (!ret)
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
cout << "找不到与\""<<fstr<<"\"匹配的字符串" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
}
pause();
}
bool Edit::edit_findString(MyString str)
{
pLineNode p = head->next;
int k = 1;
bool hasFinded = false;
while (p)
{
int pos=p->text.findString(str);
if (pos >= 0)
{
hasFinded = true;
HANDLE handle = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_GREEN);
cout << "在" << k << "行" << pos << "列查找到" <<"\""<<str<<"\""<< endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
p->showText(k);
}
p=p->next;
k++;
}
return hasFinded;
}字符串查找算法(MyString::findString)
cpp
// 如果允许访问私有成员,可以直接使用,避免拷贝
int MyString::findString(MyString& substr) // 添加const
{
int len1 = size(); // 当前字符串长度
int len2 = substr.size(); // 子串长度
if (len2 == 0) return 0; // 空子串通常认为在位置0
for (int i = 0; i <= len1 - len2; i++) {
int j = 0;
while (j < len2 && (*this)[i + j] == substr[j]) {
j++;
}
if (j == len2) {
return i; // 完全匹配
}
}
return -1;
}设计亮点:
- 基于标准库
strstr实现高效字符串匹配,兼顾性能与开发效率; - 输出匹配行上下文,帮助用户定位具体位置。
8. 替换字符串(replaceString)
功能作用:将文本中所有指定字符串替换为新字符串,支持全局替换。
实现思路:
- 获取用户输入的旧字符串和新字符串;
- 遍历每一行文本,对包含旧字符串的行执行替换;
- 更新链表中对应行的内容,记录替换次数。
核心代码:
替换预处理逻辑
cpp
void Manage::replaceString()
{
cls();
showCursor();
MyString fstr,rp;
puts("请输入待替换的字符串:");
cout << file.Get_filePath() << ">";
fstr.getline_n();
puts("您要将它替换为:");
cout << file.Get_filePath() << ">";
rp.getline_n();
bool ret = edit.edit_replaceString(fstr,rp);
if (!ret)
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
cout << "替换失败" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
}
else hasntModify = false;
pause();
}
bool Edit::edit_replaceString(MyString str, MyString rp)
{
//cout << str << rp << endl;
pLineNode p = head->next;
int k = 1;
bool hasFinded = false;
bool isContinue = true;
bool isReplaceAll = false;
while (p&&isContinue)
{
int pos = p->text.findString(str);
if (pos >= 0)
{
hasFinded = true;
HANDLE handle = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_GREEN);
cout << "在" << k << "行" << pos << "列查找到" << "\"" << str << "\"" << endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
p->showText(k);
if (!isReplaceAll)
{
printf("请输入操作:\n1.替换\n2.跳过\n3.全部替换\n4.退出替换\n注:默认跳过\n");
switch (_getch())
{
case '1':
p->text.Replace(pos, str.size(), rp);
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_GREEN);
cout << "在" << k << "行" << pos << "列查找到" <<str<<"并替换成了"<<rp<< endl;
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
case '2':
p = p->next;
k++;
continue;
case '3':
isReplaceAll = true;
case '4':
isContinue = false;
default:
continue;
break;
}
}
}
p = p->next;
k++;
}
return hasFinded;
return false;
}替换逻辑
cpp
MyString& MyString::Replace(int start, int wide, MyString s)
{
// 参数有效性检查
if (str == nullptr) {
return *this;
}
if (start < 0) {
start = 0; // 负的start视为从0开始
}
// 处理start超出长度的情况
if (start > len) {
// 在末尾追加
return *this += s;
}
// 计算要删除的实际长度
int deleteLen = wide;
if (deleteLen < 0) {
deleteLen = 0; // 负的宽度视为0
}
// 确保不越界
if (start + deleteLen > len) {
deleteLen = len - start;
}
// 特殊情况:如果不需要删除且替换字符串为空,直接返回
if (deleteLen == 0 && s.len == 0) {
return *this;
}
// 特殊情况:如果不需要删除,直接插入
if (deleteLen == 0) {
// 在start位置插入s
int newLen = len + s.len;
char* newStr = new char[newLen + 1];
// 拷贝三部分
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < start; i++) {
newStr[idx++] = str[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.len; i++) {
newStr[idx++] = s.str[i];
}
for (int i = start; i < len; i++) {
newStr[idx++] = str[i];
}
newStr[newLen] = '\0';
delete[] str;
str = newStr;
len = newLen;
return *this;
}
// 一般情况:删除并替换
int newLen = len - deleteLen + s.len;
char* newStr = new char[newLen + 1];
int idx = 0;
// 第一部分:start之前
for (int i = 0; i < start; i++) {
newStr[idx++] = str[i];
}
// 第二部分:替换字符串
for (int i = 0; i < s.len; i++) {
newStr[idx++] = s.str[i];
}
// 第三部分:删除部分之后
for (int i = start + deleteLen; i < len; i++) {
newStr[idx++] = str[i];
}
newStr[newLen] = '\0';
delete[] str;
str = newStr;
len = newLen;
return *this;
}设计亮点:
- 逐行构建替换后的新内容,避免直接修改原字符串导致的内存溢出;
- 记录总替换次数,为用户提供操作反馈。
9. 保存文件(saveFile)
功能作用:将当前编辑器中的文本内容写入本地文件,支持覆盖原文件或另存为新文件。
实现思路:
- 若已有打开的文件,默认覆盖;否则提示输入新路径;
- 通过
MyFile类打开文件(写入模式); - 遍历
Edit链表,逐行写入文件。
核心代码:
cpp
void Manage::saveFile()
{
cls();
if (hasFileToSave)
{
bool ret = edit.edit_saveFile(file);
if (ret)
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_GREEN);
cout << "成功将" << edit.getline() << "行内容保存到" << file.Get_filePath() << "中" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
hasntModify = true;
}
else
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
cout << "文件保存失败" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
}
}
else
{
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
cout << "请选择文件后再保存!" << endl;
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
}
pause();
}
bool Edit::edit_saveFile(MyFile& file)
{
//保存文件
fstream fs;
fs.open(file.Get_filePath(), std::ios::out);
if (!fs.is_open())return false;
pLineNode p = head->next;
while (p)
{
fs << p->text.c_str() << endl;
p = p->next;
}
fs.close();
return true;
}设计亮点:
- 区分 "新文件" 和 "已有文件" 场景,已有文件需二次确认,防止误操作;
- 逐行写入与打开文件时的逐行读取对称,保证数据一致性。
10. 退出应用(exitApplication)
功能作用:安全退出编辑器,若存在未保存的修改,提示用户确认。
实现思路:
- 检查文本是否有未保存的修改(通过
hasntModify标记); - 若有未保存修改,提示用户选择 "保存""不保存" 或 "取消退出";
- 确认退出后,释放链表内存,终止程序运行。
核心代码:
cpp
void Manage::exitApplication()
{
cls();
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_RED);
puts("您确定要放弃编辑吗?(强制退出文件将不被保存)");
setColor(TEXT_COLOR_WHITE_BLACK);
char op;
op = _getch();
if (op == 'y' || op == 'Y')
{
isRunning = false;
}
else
{
puts("已取消,即将返回主页面!");
}
}设计亮点:
- 通过状态标记
hasntModify快速判断是否需要提示,减少冗余操作; - 提供三级选择(保存 / 不保存 / 取消),符合用户操作习惯,降低数据丢失风险。
三、辅助功能:控制台句柄颜色控制
功能作用:控制文字输出的颜色,让用户看起来更清晰
核心代码(已简化注释):
tools.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<windows.h>
#include <string>
using std::string;
namespace win//系统调用
{
///函数声明
//1、初始化句柄
void inlitHandle();
//2、设置颜色
void setColor(int color);
//3、设置光标位置
void setPos(int x, int y);
//4、隐藏光标
void hideCursor();
//5、显示光标
void showCursor();
}
HANDLE handle;//全局句柄
void win::inlitHandle()
{
handle = GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE);
}
void win::setColor(int color)
{
SetConsoleTextAttribute(handle, color);
}
void win::setPos(int x, int y)
{
COORD coord = { x * 2,y };
SetConsoleCursorPosition(handle, coord);
}
void win::hideCursor()
{
CONSOLE_CURSOR_INFO info;
info.bVisible = false;//设置光标是否可见
info.dwSize = 1;//设置光标是否可见
SetConsoleCursorInfo(handle, &info);
}
void win::showCursor()
{
CONSOLE_CURSOR_INFO info;
info.bVisible = true;//设置光标是否可见
info.dwSize = 1;//设置光标是否可见
SetConsoleCursorInfo(handle, &info);
}资源文件(res.h)定义常用的颜色
设计亮点:
- 颜色资源宏定义,便于资源管理;
- 控制文字颜色,使得界面更美观清晰。
四、总结与扩展方向
"持梦行文本编辑器" 通过简洁的架构设计(Manage为核心控制器,Edit和MyFile分工协作)和高效的链表数据结构,实现了文本编辑的十大核心功能。每个功能均围绕 "轻量、可靠" 的目标设计,例如通过状态标记管理文件状态、通过输入验证提升鲁棒性、通过逐行处理优化内存占用。