提到自动驾驶开发,C++ 曾经是绝对的王者。但近年来,凭借着内存安全、零成本抽象和极高的并发性能,Rust 正迅速成为机器人和自动驾驶领域的新宠。
今天,我们要搞点硬核的。我将手把手带大家在 Mac M1 环境下,使用 Rust 配合当下最火的机器人数据流框架 dora-rs ,以及 Webots 仿真器,搭建一个自动驾驶的模拟仿真 Demo。
重要声明:本项目基于 Rust、dora-rs 和 Webots 开发,仅用于自动驾驶的模拟仿真和演示目的。系统为 Demo 版本,不涉及真实的自动驾驶系统的开发与应用,请勿将仿真结果直接应用于实际驾驶场景。
01 为什么选择这套技术栈?
1. Rust:安全与性能的完美平衡
自动驾驶系统容不得半点内存泄漏或空指针引用。Rust 的所有权机制在编译阶段就扼杀了这些 bug,同时在 M1 芯片上运行效率极高,完美契合对实时性要求极高的仿真场景。
2. dora-rs:下一代机器人中间件
传统的 ROS 在处理大数据流(如图像、点云)时往往有延迟。dora-rs 是一个基于 Rust 编写的低延迟数据流框架,利用共享内存技术,让节点间通信快如闪电,架构清晰且极易扩展。
3. Webots:轻量级仿真利器
Webots 是一个开源、跨平台、功能强大的机器人仿真器,支持物理引擎、传感器模型、复杂环境等,并且对 macOS M1 支持极好(原生运行)且安装简单。在本项目中,我们将利用 Webots 模拟真实的驾驶环境,包括车辆、交通流量、环境等。
️02 环境搭建:Mac M1 避坑指南
在 M1 上配置环境主要要注意架构兼容性。以下是我的实测步骤:
1. 基础环境安装
首先确保你安装了 Rust 工具链:
bash
# 安装 Rust
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh接着安装 dora-rs 的 CLI 工具:
bash
# 安装 Dora 命令行工具
cargo install dora-cli2. Webots 与 SUMO 交通流
Webots : 下载链接 下载对应 macOS (Universal/Arm64) 的版本并安装。
SUMO : 用于生成复杂的交通路网。下载链接 安装后必须配置环境变量。 由于 SUMO 最新的版本采用的GUI的方式,不推荐使用 homebrew 安装,直接从官网下载安装包。
修改环境变量:
bash
# 编辑 ~/.zshrc 文件
vim ~/.zshrc
# 增加下面2行内容
# 针对 1.25.0 PKG 安装版的正确路径
export SUMO_HOME="/Library/Frameworks/EclipseSUMO.framework/Versions/Current/EclipseSUMO/share/sumo"
# 将 bin 目录加入 PATH 以后,你就可以直接在终端输入 sumo, netedit 等命令
export PATH="$SUMO_HOME/bin:$PATH"Webots 配置 : 打开 Webots,在车辆模型上添加传感器设备:Lidar (激光雷达) 和 Camera (摄像头) 等。 本项目使用的 city_traffic.wbt 已默认配置了 Camera 传感器 , Lidar 传感器 需要手动添加。 选中车辆后,在左侧找到 Slot 节点,点击添加 Lidar 传感器, 如下图:
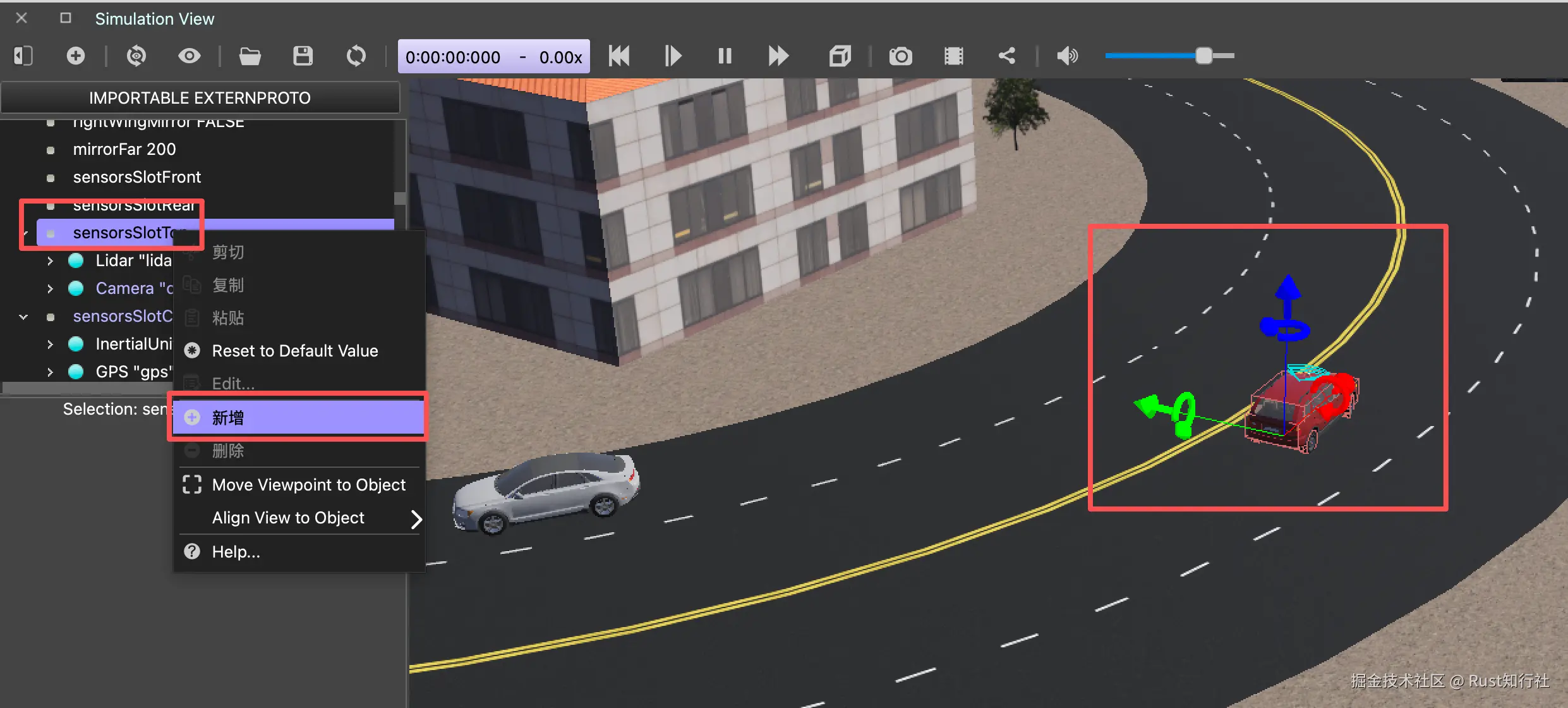 车辆的
车辆的 controller 项必须配置为:extern, 这样才能在 Rust 中调用 Webots 的 C 接口, 实现对车辆的控制。
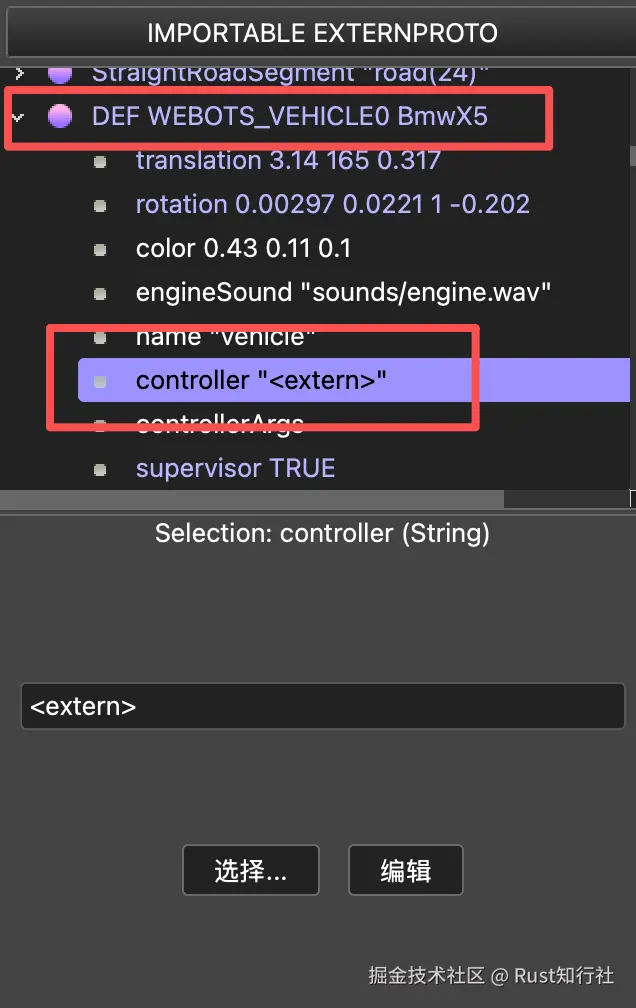
Webots 配置
重点提示 :直接点击图标启动 Webots 不会读取系统环境变量,需要 从终端启动 Webots , 如下所示:
arduino
open /Applications/Webots.app03 核心代码实战
我们的目标是构建一个基于 dora-rs 的 Dataflow 系统,整个项目全部使用 Rust 编写!
先看一下运行效果:
1 搞定 Webots 绑定 (webots-sys)
创建 webots-sys 绑定库项目:
sql
cargo new --lib webots-sys配置 build.rs: Webots 提供的是 C/C++ 接口,需要用 Rust 的 FFI 进行绑定。在 build.rs 中告诉 Cargo 去哪里找库:
rust
// build.rs
use std::env;
use std::path::PathBuf;
use std::process::Command;
fn main() {
// 1. 定义路径
let webots_home = "/Applications/Webots.app/Contents";
let lib_path = format!("{}/lib/controller", webots_home);
let include_path = format!("{}/include/controller/c/", webots_home);
let webots_app_root = "/Applications/Webots.app";
// 2. 告诉 Cargo 如何链接库文件
println!("cargo:rustc-link-search=native={}", lib_path);
println!("cargo:rustc-link-lib=dylib=Controller");
println!("cargo:rustc-link-lib=dylib=driver"); // 必须添加这一行
println!("cargo:rustc-link-arg=-Wl,-rpath,{}", webots_app_root);
println!("cargo:rustc-link-arg=-Wl,-rpath,{}", lib_path);
// 获取 macOS SDK 路径
let sdk_path = String::from_utf8(
Command::new("xcrun")
.args(&["--show-sdk-path"])
.output()
.expect("failed to get sdk path")
.stdout,
)
.unwrap()
.trim()
.to_string();
let bindings = bindgen::Builder::default()
.header("wrapper.h")
.clang_arg(format!("-I{}", include_path))
.clang_arg(format!("-isysroot{}", sdk_path))
.clang_arg("-target")
.clang_arg("arm64-apple-macos")
.allowlist_function("wb_.*")
.allowlist_function("wbu_.*") // 关键:允许 driver 函数
.allowlist_type("Wb.*")
.allowlist_var("WB_.*")
.prepend_enum_name(false)
.parse_callbacks(Box::new(bindgen::CargoCallbacks::new()))
.generate()
.expect("Unable to generate bindings");
let out_path = PathBuf::from(env::var("OUT_DIR").unwrap());
bindings
.write_to_file(out_path.join("bindings.rs"))
.expect("Couldn't write bindings!");
}lib.rs : 导入 Webots 机器人的 API 接口:
rust
// lib.rs
#![allow(non_upper_case_globals)]
#![allow(non_camel_case_types)]
#![allow(non_snake_case)]
// 引入 build.rs 生成的代码
include!(concat!(env!("OUT_DIR"), "/bindings.rs"));
mod robot;
pub use robot::WebotsRobot;实现 WebotsRobot 结构体: 对 Webots 机器人的接口进行封装,为机器人的传感器和驱动电机提供安全的 Rust 接口。
rust
// robot.rs
pub struct WebotsRobot {
pub time_step: i32,
pub camera: WbDeviceTag,
pub lidar: WbDeviceTag,
pub gps: WbDeviceTag,
// 改为存储所有驱动轮,确保动力充足
pub drive_motors: Vec<WbDeviceTag>,
pub steering_wheel: WbDeviceTag,
pub brakes: Vec<WbDeviceTag>,
pub imu: WbDeviceTag,
pub opendrive_data: String,
}
impl WebotsRobot {
pub fn get_device_list() {
unsafe {
let count = wb_robot_get_number_of_devices();
println!("Total devices found: {}", count);
for i in 0..count {
let tag = wb_robot_get_device_by_index(i);
// 尝试这个最原始的 C 函数名
let name_ptr = wb_device_get_name(tag);
if !name_ptr.is_null() {
let name = std::ffi::CStr::from_ptr(name_ptr).to_string_lossy();
println!("Device Index {}: {}", i, name);
}
}
}
}
pub fn new() -> Self {
unsafe {
wb_robot_init();
wbu_driver_init();
let time_step = wb_robot_get_basic_time_step() as i32;
// WebotsRobot::get_device_list();
// 1. 基础传感器 (保持不变)
let camera = Self::get_device("camera");
if camera != 0 {
wb_camera_enable(camera, time_step);
}
let gps = Self::get_device("gps");
if gps != 0 {
wb_gps_enable(gps, time_step);
}
// 2. 初始化驱动电机
let motor_names = ["left_front_wheel", "right_front_wheel"];
let mut drive_motors = Vec::new();
for name in motor_names {
let motor = Self::get_device(name);
if motor != 0 {
wb_motor_set_position(motor, f64::INFINITY);
wb_motor_set_velocity(motor, 100.0);
drive_motors.push(motor);
}
}
// 3. 初始化转向电机
let steering_wheel = Self::get_device("steering_wheel_motor");
if steering_wheel != 0 {
wb_motor_set_position(steering_wheel, 0.0);
}
// 4. 彻底释放刹车 (Brakes)
let brake_names = [
"left_front_brake",
"right_front_brake",
"left_rear_brake",
"right_rear_brake",
];
let mut brakes = Vec::new();
for name in brake_names {
let tag = Self::get_device(name);
if tag != 0 {
// 关键:将阻尼设为 0,防止物理阻力
wb_brake_set_damping_constant(tag, 0.0);
brakes.push(tag);
}
}
// Lidar 初始化
let lidar = Self::get_device("lidar"); // 确保 Webots 里设备名叫 "lidar"
if lidar != 0 {
wb_lidar_enable(lidar, time_step);
// 【关键步骤】必须显式开启点云生成,否则 get_point_cloud 会返回 null
wb_lidar_enable_point_cloud(lidar);
}
let imu = Self::get_device("inertial unit"); // 注意:请检查你名单里的实际名称,有时叫 "imu"
if imu != 0 {
unsafe {
wb_inertial_unit_enable(imu, time_step);
}
}
// 尝试加载 OpenDrive 文件(确保该文件已放在项目根目录)
let current_dir = env::current_dir().expect("Failed to get current working directory");
let relative_path = "webots-sys/data/sumo_map.xodr";
let path = current_dir.join(relative_path);
let opendrive_data = std::fs::read_to_string(path).unwrap_or_else(|_| {
println!("Warning: world_map.xodr not found. Using empty string.");
"".to_string()
});
Self {
time_step,
camera,
lidar,
gps,
drive_motors,
steering_wheel,
brakes,
imu,
opendrive_data,
}
}
}
......
}
impl Drop for WebotsRobot {
fn drop(&mut self) {
unsafe { wb_robot_cleanup() };
}
}2 Webots-Bridge 节点
这是连接仿真世界和算法世界的桥梁,此节点负责双向通信。
此节点中实现了以下功能:
- 初始化 Webots 机器人和传感器。
- 接收来自控制节点的控制指令。
- 读取摄像头图像、Lidar 点云和 GPS 位置、IMU 数据及 OpenDrive 地图。
- 将数据发送到下游节点(如路径规划器)。
rust
// main.rs
use dora_node_api::{
arrow::array::{Float32Array, StringArray, UInt8Array},
dora_core::config::DataId,
DoraNode, Event, Parameter,
};
use std::error::Error;
use webots_sys::WebotsRobot;
fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn Error>> {
let (mut node, mut events) = DoraNode::init_from_env()?;
// 强制设置 Webots 控制器地址
std::env::set_var("WEBOTS_CONTROLLER_URL", "tcp://127.0.0.1:1234");
let robot = WebotsRobot::new();
// 预先解析 Waypoints
let road_ids = (230..=401)
.map(|id| id.to_string())
.collect::<Vec<String>>();
let mut all_waypoints = Vec::new();
for id in road_ids {
let road_waypoints = robot.get_waypoints_from_opendrive(&id);
if !road_waypoints.is_empty() {
// 提取 [x, y, z] 并推入全局列表
for pt in road_waypoints {
all_waypoints.push(pt);
}
}
}
let global_waypoints = all_waypoints;
// 将 [ [x,y], [x,y] ] 展平为 [x1, y1, x2, y2, ...] 方便发送
let waypoints_flat: Vec<f32> = global_waypoints.into_iter().flatten().collect();
if waypoints_flat.is_empty() {
println!("Warning: No waypoints extracted from Road ");
} else {
println!(
"Successfully loaded {} waypoints from OpenDRIVE",
waypoints_flat.len() / 2
);
}
while let Some(event) = events.recv() {
match event {
Event::Input { id, metadata, data } => match id.as_str() {
"tick" => {
if !robot.step() {
break;
}
// 1. Camera Image
let image = robot.get_camera_image();
let w = robot.get_camera_width();
let h = robot.get_camera_height();
let mut params = metadata.parameters.clone();
params.insert("width".into(), Parameter::Integer(w as i64));
params.insert("height".into(), Parameter::Integer(h as i64));
node.send_output(
DataId::from("image".to_owned()),
params,
UInt8Array::from(image.to_vec()),
)?
// 2. Lidar Point Cloud
let pc = robot.get_lidar_points();
node.send_output(
DataId::from("lidar_pc".to_owned()),
metadata.parameters.clone(),
Float32Array::from(pc),
)?;
// 3. Position & Attitude (6DOF: x, y, z, r, p, y)
let pos = robot.get_gps_position();
let att = robot.get_attitude();
let full_pose = vec![pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], att[0], att[1], att[2]];
node.send_output(
DataId::from("position".to_owned()),
metadata.parameters.clone(),
Float32Array::from(full_pose),
)?;
// 4. Speed
let speed = vec![robot.get_speed()];
node.send_output(
DataId::from("speed".to_owned()),
metadata.parameters.clone(),
Float32Array::from(speed),
)?;
// 5. OpenDrive Raw Data
let opendrive = robot.get_opendrive();
node.send_output(
DataId::from("opendrive".to_owned()),
metadata.parameters.clone(),
StringArray::from(vec![opendrive]),
)?;
// 发送解析后的 Objective Waypoints
node.send_output(
DataId::from("objective_waypoints".to_owned()),
metadata.parameters.clone(),
Float32Array::from(waypoints_flat.clone()),
)?;
}
// 在 webots_bridge 的 main 循环中添加对 control_command 的处理
"control_command" => {
let array = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<Float32Array>().unwrap();
let cmd = array.values();
let steering = cmd[0] as f64;
let speed = cmd[1] as f64;
// 应用到 Webots 电机
robot.set_steering(steering);
robot.set_drive_speed(speed);
}
other => eprintln!("Received unknown input: {:?}", other),
},
_ => {}
}
}
Ok(())
}waypoint生成 :Webots 项目使用 sumo.net.xml 描述路网,通过 netconvert 工具解析并转换为 ODX 格式:
sumo.net.xml 文件一般位于与 wbt 文件同级同名的目录下,比如 city_traffic.wbt 对应的 sumo.net.xml 文件路径为 city_traffic/sumo.net.xml 找到 sumo.net.xml 文件后,运行以下代码将其转换为 ODX 格式的 waypoint 文件:
css
netconvert --sumo-net-file sumo.net.xml --opendrive-output sumo_map.xodr3 YOLO 目标检测节点
与上一篇的智能目标检测节点类似,只是数据处理部分不同。
rust
// object-detection/main.rs
while let Some(event) = events.recv() {
match event {
Event::Input { id, metadata, data } => match id.as_str() {
"frame" => {
// 从 metadata 中提取 width 和 height
// 尝试获取 width
let cols = match metadata.parameters.get("width") {
Some(Parameter::Integer(v)) => *v as i32,
_ => 640, // 默认值
};
// 尝试获取 height
let rows = match metadata.parameters.get("height") {
Some(Parameter::Integer(v)) => *v as i32,
_ => 480, // 默认值
};
// 将接收到的字节数据转换为 OpenCV Vector
// 1. 将 Arrow trait 对象强转为具体的 UInt8Array
let uint8_array = data
.as_any()
.downcast_ref::<UInt8Array>()
.context("Arrow data is not UInt8Array (expected byte array)")?;
// 2. 提取 UInt8Array 的字节切片
let byte_slice = uint8_array.values(); // 返回 &[u8]
if byte_slice.len() != (rows * cols * 4) as usize {
eprintln!(
"Data size mismatch! Expected {}, got {}",
rows * cols * 4,
byte_slice.len()
);
continue;
}
// 关键点:将 &[u8] 转换为 &[Vec4b]
// Vec4b 代表一个由 4 个 u8 组成的像素点
let (head, vec4_slice, tail) = unsafe { byte_slice.align_to::<Vec4b>() };
if !head.is_empty() || !tail.is_empty() {
// 如果数据不是 4 的倍数,可能会进到这里
eprintln!("Warning: Byte slice alignment issue");
}
// 因为 vec4_slice 的长度刚好是 byte_slice.len() / 4
let frame_raw = Mat::new_rows_cols_with_data(
rows, // 128 (行)
cols, // 64 (列)
vec4_slice, // 32768字节的 u8 切片现在变成了 8192长度的 Vec4b 切片
)?;
let mut frame = Mat::default();
// 注意:Webots 的颜色顺序可能是 BGRA,如果颜色不对,请尝试 COLOR_BGRA2RGB
imgproc::cvt_color(
&frame_raw,
&mut frame,
imgproc::COLOR_BGRA2BGR,
0,
AlgorithmHint::ALGO_HINT_DEFAULT,
)?;
if frame.empty() {
eprintln!("Warning: Decoded frame is empty. Skipping this iteration.");
continue; // 跳过当前循环,不进入 preprocess_image
}
// 步骤 A: 图像预处理 (OpenCV -> Candle Tensor)
let (processed_tensor, ratio, pad_w, pad_h) =
preprocess_image(&frame, &device)?;
// 步骤 B: 模型推理
let predictions = model.forward(&processed_tensor)?;
// 步骤 C: 后处理 (NMS)
// predictions 维度通常是 (1, 84, 8400) -> (Batch, Classes+Coords, Anchors)
let preds = predictions.squeeze(0)?;
let (bboxes, keypoints) = report_detect(&preds, &frame, ratio, pad_w, pad_h)?;
let arrow_array = bboxes_to_arrow(bboxes)?;
node.send_output(output.clone(), metadata.parameters, arrow_array)?;
}
other => eprintln!("Received input `{other}`"),
},
_ => {}
}
}4 障碍物定位节点
接收激光雷达点云和相机检测结果、当前车辆位置,计算障碍物的3D位置。
ini
// obstacle_location/main.rs
while let Some(event) = events.recv() {
match event {
Event::Input { id, data, metadata } => match id.as_str() {
"lidar_pc" => {
let array = data
.as_any()
.downcast_ref::<Float32Array>()
.context("Lidar data is not Float32Array")?;
let raw_points = array.values();
current_pc = raw_points
.chunks_exact(3)
.map(|c| {
let p = nalgebra::Vector3::new(c[0], c[1], c[2]);
let transformed = velodyne_to_camera * p;
[transformed[0], transformed[1], transformed[2]]
})
// 优化过滤:排除车体自身点(1.0m内)以及高于路面的点(p[1]是高度)
.filter(|p| p[2] > 1.0 && p[2] < 60.0 && p[1] < 1.2)
.collect();
camera_pc = utils::project_to_camera(¤t_pc, &intrinsic);
}
"position" => {
let array = data
.as_any()
.downcast_ref::<Float32Array>()
.context("Position data is not Float32Array")?;
extrinsic_matrix = utils::get_projection_matrix(array.values());
}
"obstacles_bbox" => {
let mut obstacles_3d = Vec::new();
let struct_array = data
.as_any()
.downcast_ref::<StructArray>()
.context("Input is not a StructArray")?;
let received_bboxes = utils::arrow_to_bboxes(struct_array)?;
for (name, rect, conf) in received_bboxes {
let min_x = rect.x as f32;
let max_x = (rect.x + rect.w) as f32;
let min_y = rect.y as f32;
let max_y = (rect.y + rect.h) as f32;
let mut pts_in_bbox: Vec<usize> = Vec::new();
for (i, cam_p) in camera_pc.iter().enumerate() {
// 增加深度约束,防止 BBox 误匹配背景噪点
if cam_p[0] > min_x
&& cam_p[0] < max_x
&& cam_p[1] > min_y
&& cam_p[1] < max_y
{
pts_in_bbox.push(i);
}
}
if !pts_in_bbox.is_empty() {
// 取 1/4 分位数点,这是车辆后表面的稳健估计
pts_in_bbox.sort_by(|&a, &b| {
camera_pc[a][2].partial_cmp(&camera_pc[b][2]).unwrap()
});
let idx = pts_in_bbox[pts_in_bbox.len() / 4];
let local_pos = current_pc[idx];
let world_pos = extrinsic_matrix
* Vector4::new(local_pos[0], local_pos[1], local_pos[2], 1.0);
obstacles_3d.push(world_pos[0]);
obstacles_3d.push(world_pos[1]);
obstacles_3d.push(world_pos[2]);
obstacles_3d.push(conf);
obstacles_3d.push(label_to_id(&name)); // 存入对应的物体 ID
}
}
node.send_output(
DataId::from("obstacles".to_owned()),
metadata.parameters,
Float32Array::from(obstacles_3d),
)?;
}
_ => {}
},
_ => {}
}
}5 路径规划节点
基于当前位置、目标点和障碍物信息,实时生成目标路径。
ini
// planning_op/main.rs
while let Some(event) = events.recv() {
match event {
Event::Input { id, data, metadata } => match id.as_str() {
"position" => {
let array = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<Float32Array>().unwrap();
let val = array.values();
current_pose = Vector3::new(val[0], val[1], val[5]);
}
"objective_waypoints" => {
let array = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<Float32Array>().unwrap();
global_waypoints = array
.values()
.chunks_exact(2)
.map(|c| Vector2::new(c[0], c[1]))
.collect();
}
"tick" => {
if global_waypoints.is_empty() {
continue;
}
let mut path = Vec::new();
let car_pos = Vector2::new(current_pose.x, current_pose.y);
// 1. 找最近点
let (closest_idx, min_dist) = global_waypoints
.iter()
.enumerate()
.map(|(i, wp)| (i, (wp - car_pos).norm()))
.min_by(|a, b| a.1.partial_cmp(&b.1).unwrap())
.unwrap();
// 2. 速度决策
let is_far = min_dist > 5.0;
let capture_speed = 12.0f32; // 追路速度
let cruise_speed = 22.0f32; // 巡航速度 (~80km/h)
// 3. 生成局部路径片段
let lookahead_dist = 50.0;
let mut accumulated_dist = 0.0;
for i in closest_idx..global_waypoints.len() {
let wp = global_waypoints[i];
let remaining = global_waypoints.len() - i;
// 动态速度规划
let v = if is_far {
capture_speed
} else if remaining < 15 {
5.0 // 终点前速度从3.0提高到5.0
} else if remaining < 40 {
15.0 // 接近终点速度从10.0提高到15.0
} else {
cruise_speed
};
path.push(TrajectoryPoint {
x: wp.x,
y: wp.y,
v,
});
if i > closest_idx {
accumulated_dist +=
(global_waypoints[i] - global_waypoints[i - 1]).norm();
}
if accumulated_dist > lookahead_dist || path.len() >= 30 {
break;
}
}
// 发送数据
let mut output = Vec::new();
for p in path {
output.push(p.x);
output.push(p.y);
output.push(p.v);
}
node.send_output(
DataId::from("waypoints".to_owned()),
metadata.parameters,
Float32Array::from(output),
)?;
}
_ => {}
},
_ => {}
}
}6 控制节点
接收路径指令,结合当前车辆位置,控制车辆运动。
ini
// control_op/main.rs
while let Some(event) = events.recv() {
match event {
Event::Input { id, data, metadata } => match id.as_str() {
"position" => {
let array = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<Float32Array>().unwrap();
current_pose.copy_from_slice(array.values());
}
"waypoints" => {
let array = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<Float32Array>().unwrap();
planned_path = array
.values()
.chunks_exact(3)
.map(|c| [c[0], c[1], c[2]])
.collect();
}
"tick" => {
if planned_path.is_empty() {
continue;
}
let x = current_pose[0];
let y = current_pose[1];
let yaw = current_pose[5];
// 1. 全局搜索最近点(去掉局部搜索,防止掉头时索引卡死)
let (closest_idx, min_dist) = planned_path
.iter()
.enumerate()
.map(|(i, p)| (i, ((p[0] - x).powi(2) + (p[1] - y).powi(2)).sqrt()))
.min_by(|a, b| a.1.partial_cmp(&b.1).unwrap())
.unwrap();
// 2. 动态预瞄距离
let ld = if min_dist > 20.0 { 3.0f32 } else { 6.0f32 };
// 3. 计算 Alpha
let target_pt = planned_path[closest_idx]; // 掉头时直接瞄准最近点,确保转弯半径最小
let target_angle = (target_pt[1] - y).atan2(target_pt[0] - x);
let mut alpha = target_angle - yaw;
......
let target_speed: f32;
let target_steer: f32;
// 4. 核心状态机逻辑优化
if alpha.abs() > 1.2 {
// 【掉头模式】
if uturn_lock == 0.0 {
uturn_lock = if alpha > 0.0 { 1.0 } else { -1.0 };
}
target_steer = uturn_lock * MAX_STEER_ANGLE;
// 关键:大幅降低掉头速度,防止转圈过猛
target_speed = 1.2;
} else if uturn_lock != 0.0 {
// 【掉头保持模式】
if alpha.abs() < 0.3 {
uturn_lock = 0.0; // 角度很小时才解除锁定
target_steer = 0.0;
} else {
target_steer = uturn_lock * MAX_STEER_ANGLE * 0.8;
}
target_speed = 2.0;
} else {
// 【正常循迹模式】
let curvature = 2.0 * alpha.sin() / ld;
target_steer = (curvature * WHEEL_BASE).atan();
target_speed = 4.0;
}
// 5. 转向处理(解决右转过快问题)
let mut final_steer = target_steer.clamp(-MAX_STEER_ANGLE, MAX_STEER_ANGLE);
......
last_steering = final_steer;
node.send_output(
DataId::from("control_command".to_owned()),
metadata.parameters.clone(),
Float32Array::from(vec![final_steer, final_speed]),
)?;
}
_ => {}
},
_ => {}
}
}7 可视化节点 (Viewer)
使用 opencv 实时显示所有数据流,包括相机图像、检测框、障碍物、路径等。
rust
// viewer/main.rs
while let Some(event) = events.recv() {
match event {
Event::Input { id, metadata, data } => match id.as_str() {
// A. 接收 YOLO 检测框
"detections" => {
if let Some(struct_array) = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<StructArray>() {
if let Ok(received_bboxes) = arrow_to_bboxes(struct_array) {
bboxes = received_bboxes;
}
}
}
// B. 接收 3D 障碍物位置
"obstacles" => {
if let Some(array) = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<Float32Array>() {
// 格式: [x, y, z, conf, label, ...]
obstacles_3d = array
.values()
.chunks_exact(5)
.map(|c| [c[0], c[2]]) // 提取 X 和 Z
.collect();
}
}
// C. 接收自车位姿
"position" => {
if let Some(array) = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<Float32Array>() {
if array.len() >= 6 {
current_position.copy_from_slice(array.values());
}
}
}
// D. 接收规划路径
"waypoints" => {
if let Some(array) = data.as_any().downcast_ref::<Float32Array>() {
// 格式: [x, y, v, ...]
println!("Received {} waypoints", array.len() / 3);
planned_path = array
.values()
.chunks_exact(3)
.map(|c| [c[0], c[1]])
.collect();
}
}
// F. 核心渲染逻辑:处理图像输入
"frame" => {
let cols = match metadata.parameters.get("width") {
Some(Parameter::Integer(v)) => *v as i32,
_ => 640,
};
let rows = match metadata.parameters.get("height") {
Some(Parameter::Integer(v)) => *v as i32,
_ => 480,
};
let uint8_array = data
.as_any()
.downcast_ref::<UInt8Array>()
.context("Expected UInt8Array for image")?;
let byte_slice = uint8_array.values();
if byte_slice.len() != (rows * cols * 4) as usize {
continue;
}
// 1. BGRA 转 BGR
let (_head, vec4_slice, _tail) = unsafe { byte_slice.align_to::<Vec4b>() };
let frame_raw = Mat::new_rows_cols_with_data(rows, cols, vec4_slice)?;
let mut display_frame = Mat::default();
imgproc::cvt_color(
&frame_raw,
&mut display_frame,
imgproc::COLOR_BGRA2BGR,
0,
AlgorithmHint::ALGO_HINT_DEFAULT,
)?;
// 2. 绘制 YOLO 2D 检测框
for (classname, bbox, conf) in &bboxes {
imgproc::rectangle(
&mut display_frame,
*bbox,
Scalar::new(0.0, 255.0, 0.0, 0.0),
2,
8,
0,
)?;
let label = format!("{}: {:.2}", classname, conf);
imgproc::put_text(
&mut display_frame,
&label,
Point::new(bbox.x, bbox.y - 5),
imgproc::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.5,
Scalar::new(0.0, 255.0, 0.0, 0.0),
1,
8,
false,
)?;
}
// 3. 绘制 HUD 仪表盘文本
let hud_color = Scalar::new(255.0, 255.0, 255.0, 0.0);
let pos_info = format!(
"GPS: X:{:.1} Y:{:.1} Yaw:{:.2}",
current_position[0], current_position[1], current_position[5]
);
imgproc::put_text(
&mut display_frame,
&pos_info,
Point::new(20, 30),
imgproc::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6,
hud_color,
2,
8,
false,
)?;
......
// 4.2 绘制规划路径
let step = 2;
for wp in planned_path.iter().step_by(step) {
// 计算相对坐标
let dx = (wp[0] - current_position[0]) * scale;
let dy = (wp[1] - current_position[1]) * scale;
let p = Point::new(center.x + dx as i32, center.y - dy as i32);
if map_rect.contains(p) {
imgproc::circle(
&mut display_frame,
p,
2,
Scalar::new(0.0, 255.0, 255.0, 0.0),
-1,
8,
0,
)?;
}
}
......
// 5. 显示并刷新
highgui::imshow(win_name, &display_frame)?;
if highgui::wait_key(1)? == 27 {
break;
} // ESC 退出
}
_ => {}
},
_ => {}
}
}04 DataFlow 配置:一个文件串联所有节点
dora-rs 最酷的地方就是不需要写复杂的网络连接代码,只需要一个 .yml 文件就能把所有 Rust 节点串联起来。
数据流图:
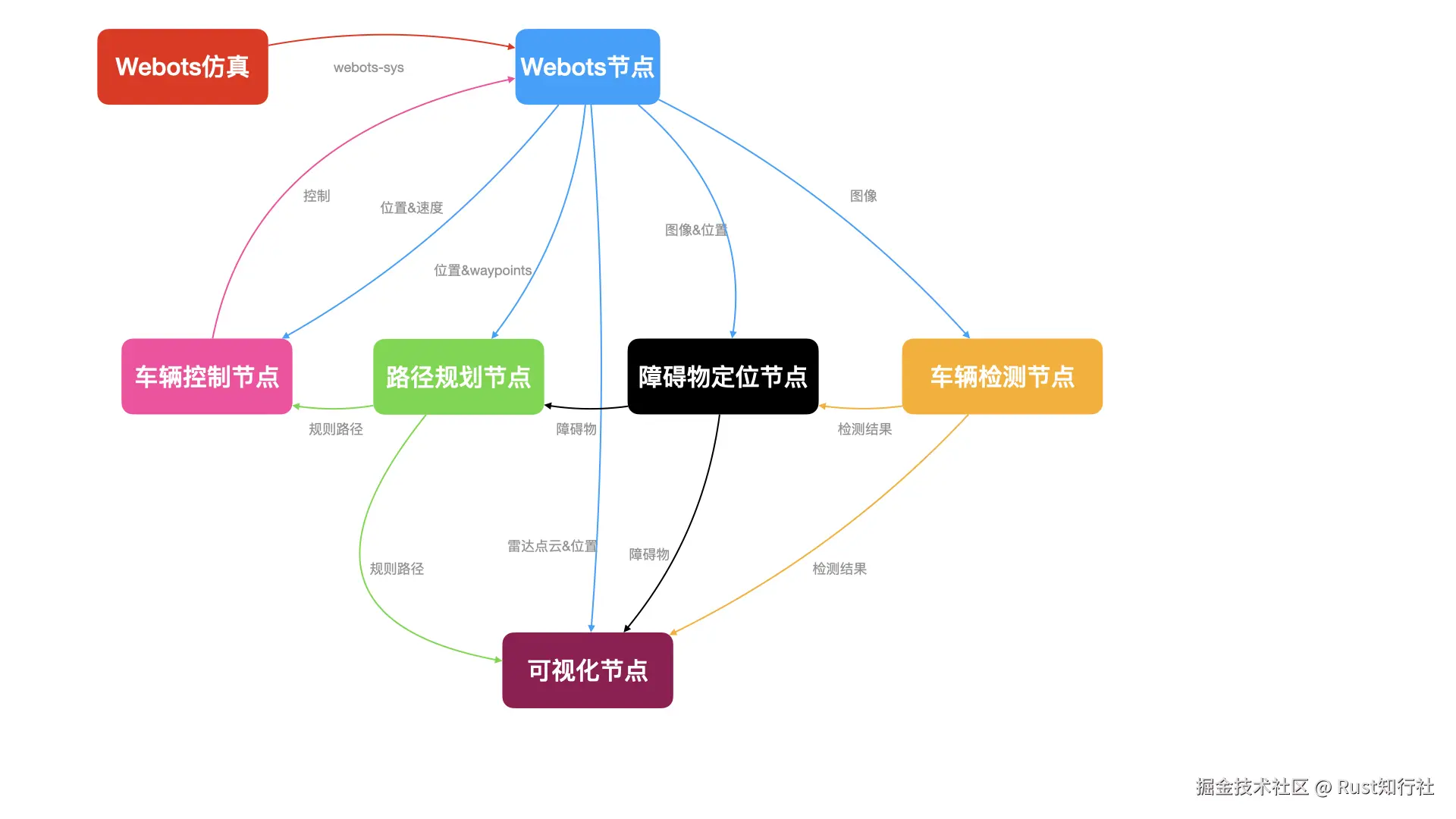 yml配置:
yml配置:
less
nodes:
- id: webots_bridge
build: cargo build -p webots-bridge
path: target/debug/webots-bridge
inputs:
tick: dora/timer/millis/100
control_command: control_op/control_command
outputs:
- image
- lidar_pc
- position
- speed
- opendrive
- objective_waypoints
- id: object_detection
build: cargo build -p object-detection
path: target/debug/object-detection
inputs:
frame: webots_bridge/image
outputs:
- detections
- id: viewer
build: cargo build -p viewer
path: target/debug/viewer
inputs:
detections: object_detection/detections
frame: webots_bridge/image
obstacles: obstacle_location/obstacles
position: webots_bridge/position
waypoints: planning_op/waypoints
control: control_op/control_command
- id: obstacle_location
build: cargo build -p obstacle-location
path: target/debug/obstacle-location
inputs:
lidar_pc: webots_bridge/lidar_pc
position: webots_bridge/position
obstacles_bbox: object_detection/detections
outputs:
- obstacles
- id: planning_op
build: cargo build -p planning-op
path: target/debug/planning-op
inputs:
position: webots_bridge/position
objective_waypoints: webots_bridge/objective_waypoints
obstacles: obstacle_location/obstacles
tick: dora/timer/millis/100
outputs:
- waypoints
- id: control_op
build: cargo build -p control-op
path: target/debug/control-op
inputs:
position: webots_bridge/position
speed: webots_bridge/speed
waypoints: planning_op/waypoints
tick: dora/timer/millis/100
outputs:
- control_command04 构建与运行
构建运行
perl
# 1. 启动 Webots 仿真
open /Applications/Webots.app
# 2. 构建所有 Rust 节点
dora build dataflow.yml
# 3. 启动数据流
dora run dataflow.ymlWebots 输出
less
INFO: sumo_supervisor: Starting controller: /usr/bin/python3 -u sumo_supervisor.py --no-gui --no-netconvert --max-vehicles=100 --port=8873 --seed=1 --step=200 --radius=-1 --maximum-lateral-speed=2.5 --maximum-angular-speed=3 --lane-change-delay=3
INFO: 'vehicle' extern controller: Waiting for local or remote connection on port 1234 targeting robot named 'vehicle'.
INFO: generic_traffic_light: Starting controller: /Users/gustaf/webots/wbt/controllers/generic_traffic_light/generic_traffic_light 10 10 r
INFO: crossroads_traffic_lights: Starting controller: /Users/gustaf/webots/wbt/controllers/crossroads_traffic_lights/crossroads_traffic_lightsdora-rs 输出
vbnet
planning_op: INFO daemon node is ready
viewer: INFO daemon node is ready
webots_bridge: INFO daemon node is ready
obstacle_location: INFO daemon node is ready
control_op: INFO daemon node is ready
object_detection: INFO daemon node is ready
INFO daemon all nodes are ready, starting dataflow
object_detection: stdout Loading YOLOv8 model...
object_detection: stdout 🚀 Using Metal device.
object_detection: stdout Model loaded successfully.
webots_bridge: stdout Initialized: 2 motors, 4 brakes, 16 lidar, 18 imu, opendrive.
webots_bridge: stdout Webots Bridge 优化版已启动...
webots_bridge: stdout Extracted 37 waypoints from Road 230
viewer: stdout Plot operator initialized. Waiting for data...
......总结
通过这个项目,我们验证了 Rust + dora-rs 在机器人开发中的强大潜力:
- 开发体验爽 :
Cargo包管理让依赖处理变得异常简单。 - 运行效率高:在 Mac M1 上跑这套仿真,CPU 占用率极低,通信几乎无延迟。
- 架构清晰:Dataflow 的设计让每个节点各司其职,解耦得非常彻底。
如果你也是自动驾驶或机器人爱好者,强烈建议尝试一下 Rust 生态!
源码传送门
本项目完整代码已开源,欢迎 Star ⭐ 和 Fork: 👉 github: rust-zhixingshe-examples