一、char类型的符号性
在C++中,
char类型的符号性是由实现定义的:
可能是
signed char(有符号字符)可能是
unsigned char(无符号字符)具体取决于编译器和目标平台
二、三种char类型的区别
cpp
char foo; // 可能是signed,也可能是unsigned,由实现定义
unsigned char bar; // 明确是无符号的
signed char snark; // 明确是有符号的三、数值范围和行为差异
数值范围对比
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
void rangeComparison() {
cout << "=== Numeric Ranges ===" << endl;
cout << "signed char range: "
<< (int)numeric_limits<signed char>::min() << " to "
<< (int)numeric_limits<signed char>::max() << endl;
cout << "unsigned char range: "
<< (int)numeric_limits<unsigned char>::min() << " to "
<< (int)numeric_limits<unsigned char>::max() << endl;
cout << "char range: "
<< (int)numeric_limits<char>::min() << " to "
<< (int)numeric_limits<char>::max() << endl;
// 使用climits中的宏定义
cout << "\nUsing climits macros:" << endl;
cout << "SCHAR_MIN: " << SCHAR_MIN << endl;
cout << "SCHAR_MAX: " << SCHAR_MAX << endl;
cout << "UCHAR_MAX: " << UCHAR_MAX << endl;
cout << "CHAR_MIN: " << CHAR_MIN << endl;
cout << "CHAR_MAX: " << CHAR_MAX << endl;
}四、代码示例
示例1:基本数值操作
cpp
void basicNumericOperations() {
cout << "\n=== Basic Numeric Operations ===" << endl;
// signed char 示例
signed char sc1 = 100;
signed char sc2 = 50;
signed char sc_result = sc1 + sc2;
cout << "signed char 100 + 50 = " << (int)sc_result << endl;
// unsigned char 示例
unsigned char uc1 = 200;
unsigned char uc2 = 100;
unsigned char uc_result = uc1 + uc2;
cout << "unsigned char 200 + 100 = " << (int)uc_result << endl;
// 溢出行为演示
signed char sc_overflow = 127 + 1;
cout << "signed char 127 + 1 = " << (int)sc_overflow << " (overflow!)" << endl;
unsigned char uc_overflow = 255 + 1;
cout << "unsigned char 255 + 1 = " << (int)uc_overflow << " (overflow!)" << endl;
}示例2:存储大数值
cpp
void storingLargeValues() {
cout << "\n=== Storing Large Values ===" << endl;
// 尝试存储大于127的值
int large_value = 200;
// 使用unsigned char可以安全存储
unsigned char uc_large = large_value;
cout << "unsigned char storing 200: " << (int)uc_large << endl;
// 使用signed char会有问题(实现定义的行为)
signed char sc_large = large_value;
cout << "signed char storing 200: " << (int)sc_large << " (unexpected!)" << endl;
// 普通char的行为取决于实现
char c_large = large_value;
cout << "char storing 200: " << (int)c_large << " (implementation defined)" << endl;
}示例3:ASCII字符处理
cpp
void asciiCharacterHandling() {
cout << "\n=== ASCII Character Handling ===" << endl;
// 对于标准ASCII字符(0-127),所有char类型都适用
char regular_char = 'A';
signed char signed_char = 'B';
unsigned char unsigned_char = 'C';
cout << "char 'A': " << regular_char << " (value: " << (int)regular_char << ")" << endl;
cout << "signed char 'B': " << signed_char << " (value: " << (int)signed_char << ")" << endl;
cout << "unsigned char 'C': " << unsigned_char << " (value: " << (int)unsigned_char << ")" << endl;
// 扩展ASCII字符(128-255)的处理
unsigned char extended_ascii = 200;
cout << "Extended ASCII 200 as unsigned char: '" << extended_ascii
<< "' (value: " << (int)extended_ascii << ")" << endl;
// 使用signed char处理扩展ASCII会有问题
signed char extended_signed = 200;
cout << "Extended ASCII 200 as signed char: '" << extended_signed
<< "' (value: " << (int)extended_signed << ")" << endl;
}示例4:二进制数据处理
cpp
#include <bitset>
void binaryDataHandling() {
cout << "\n=== Binary Data Handling ===" << endl;
// 对于原始二进制数据,通常使用unsigned char
unsigned char binary_data[] = {0x48, 0x65, 0x6C, 0x6C, 0x6F}; // "Hello" in hex
cout << "Binary data as hex: ";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << hex << uppercase << (int)binary_data[i] << " ";
}
cout << dec << endl;
cout << "Binary data as characters: ";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << binary_data[i];
}
cout << endl;
// 位操作演示
unsigned char flags = 0b10101010; // 170 decimal
cout << "Flags: " << bitset<8>(flags) << " (decimal: " << (int)flags << ")" << endl;
// 设置位
flags |= 0b00000001; // 设置最低位
cout << "After setting bit 0: " << bitset<8>(flags) << " (decimal: " << (int)flags << ")" << endl;
// 清除位
flags &= ~0b10000000; // 清除最高位
cout << "After clearing bit 7: " << bitset<8>(flags) << " (decimal: " << (int)flags << ")" << endl;
}示例5:类型转换和比较
cpp
void typeConversionAndComparison() {
cout << "\n=== Type Conversion and Comparison ===" << endl;
signed char sc = -50;
unsigned char uc = 200;
char c = 'X';
// 隐式转换
int sc_to_int = sc;
int uc_to_int = uc;
cout << "signed char -50 to int: " << sc_to_int << endl;
cout << "unsigned char 200 to int: " << uc_to_int << endl;
// 比较操作
cout << "Comparison examples:" << endl;
cout << "signed char -50 < unsigned char 200: " << (sc < uc) << endl;
cout << "But be careful: (int)sc = " << (int)sc << ", (int)uc = " << (int)uc << endl;
// 显式转换
unsigned char explicit_convert = static_cast<unsigned char>(sc);
cout << "signed char -50 to unsigned char: " << (int)explicit_convert << endl;
}示例6:实际应用场景
cpp
// 场景1:图像像素处理(通常使用unsigned char)
class ImageProcessor {
private:
unsigned char* pixel_data;
int width, height;
public:
ImageProcessor(int w, int h) : width(w), height(h) {
pixel_data = new unsigned char[width * height * 3]; // RGB
}
~ImageProcessor() {
delete[] pixel_data;
}
void setPixel(int x, int y, unsigned char r, unsigned char g, unsigned char b) {
int index = (y * width + x) * 3;
pixel_data[index] = r;
pixel_data[index + 1] = g;
pixel_data[index + 2] = b;
}
void brighten(int amount) {
for (int i = 0; i < width * height * 3; i++) {
// 防止溢出
int new_value = pixel_data[i] + amount;
if (new_value > 255) new_value = 255;
if (new_value < 0) new_value = 0;
pixel_data[i] = static_cast<unsigned char>(new_value);
}
}
};
// 场景2:网络数据包处理
class PacketHandler {
public:
static void processPacket(const unsigned char* data, int length) {
cout << "Processing packet of length " << length << ":" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < length && i < 16; i++) { // 只显示前16字节
cout << hex << uppercase << (int)data[i] << " ";
}
cout << dec << endl;
// 检查包类型(第一个字节)
unsigned char packet_type = data[0];
cout << "Packet type: 0x" << hex << (int)packet_type << dec << endl;
}
};
void practicalUseCases() {
cout << "\n=== Practical Use Cases ===" << endl;
// 图像处理示例
ImageProcessor img(2, 2);
img.setPixel(0, 0, 255, 0, 0); // 红色
img.setPixel(1, 0, 0, 255, 0); // 绿色
img.setPixel(0, 1, 0, 0, 255); // 蓝色
img.setPixel(1, 1, 255, 255, 255); // 白色
cout << "Image processor created with unsigned char pixel data" << endl;
// 网络数据包示例
unsigned char packet[] = {0x01, 0x02, 0x03, 0x04, 0x05, 0xAB, 0xCD, 0xEF};
PacketHandler::processPacket(packet, sizeof(packet));
}示例7:检测当前系统的char符号性
cpp
void detectCharSign() {
cout << "\n=== Detecting char Sign on This System ===" << endl;
char test_char = -1;
if (static_cast<unsigned char>(test_char) == 255) {
cout << "char is UNSIGNED on this system" << endl;
} else if (static_cast<signed char>(test_char) == -1) {
cout << "char is SIGNED on this system" << endl;
} else {
cout << "char sign is UNDETERMINED" << endl;
}
// 另一种检测方法
cout << "CHAR_MIN = " << CHAR_MIN << endl;
if (CHAR_MIN < 0) {
cout << "char is SIGNED (CHAR_MIN < 0)" << endl;
} else {
cout << "char is UNSIGNED (CHAR_MIN == 0)" << endl;
}
}五、完整演示程序
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <limits>
#include <climits>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "=== C++ signed char vs unsigned char Demonstration ===" << endl;
rangeComparison();
basicNumericOperations();
storingLargeValues();
asciiCharacterHandling();
binaryDataHandling();
typeConversionAndComparison();
practicalUseCases();
detectCharSign();
cout << "\n=== Best Practices Summary ===" << endl;
cout << "1. Use plain char for ASCII text" << endl;
cout << "2. Use unsigned char for:" << endl;
cout << " - Binary data processing" << endl;
cout << " - Values above 127" << endl;
cout << " - Bit manipulation" << endl;
cout << "3. Use signed char only when explicitly needed for negative values" << endl;
cout << "4. Be explicit about signedness for portability" << endl;
return 0;
}六、编译和运行
cpp
g++ -o char_demo char_demo.cpp
./char_demo七、关键要点总结
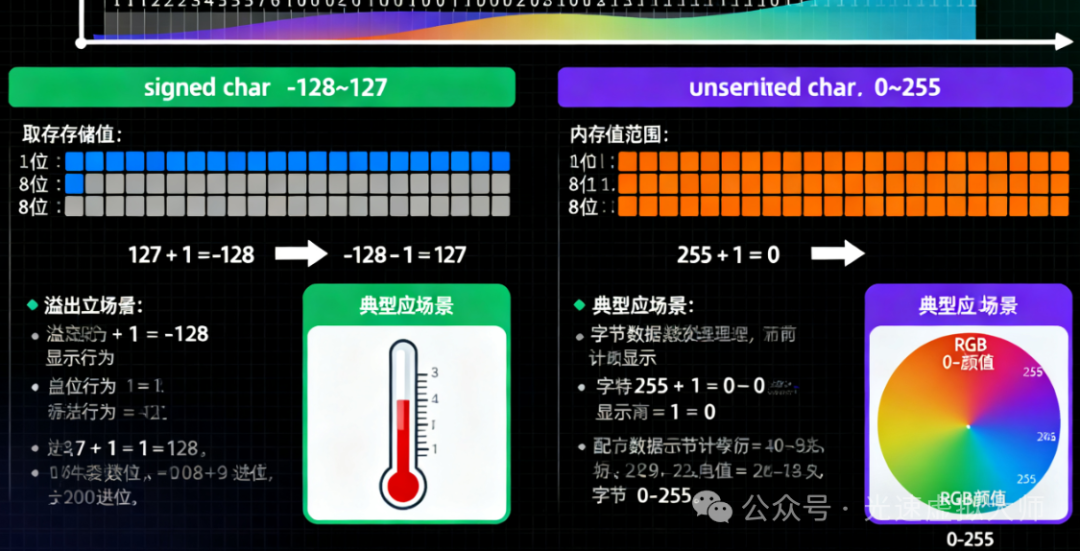
char的符号性 :默认
char的符号性由实现定义,不可移植数值范围:
signed char: -128 到 127
unsigned char: 0 到 255使用场景:
ASCII字符:使用
char大数值(>127):使用
unsigned char二进制数据:使用
unsigned char需要负值:使用
signed char最佳实践:明确指定符号性以提高代码可移植性
这个全面的示例展示了signed char和unsigned char的区别、使用场景和最佳实践,帮助您在不同情况下做出正确的类型选择。