作者:来自 Elastic JINA

新的 0.6B - parameter 的 listwise reranker ,在单个 context window 中同时考虑 query 和所有 candidate documents 。
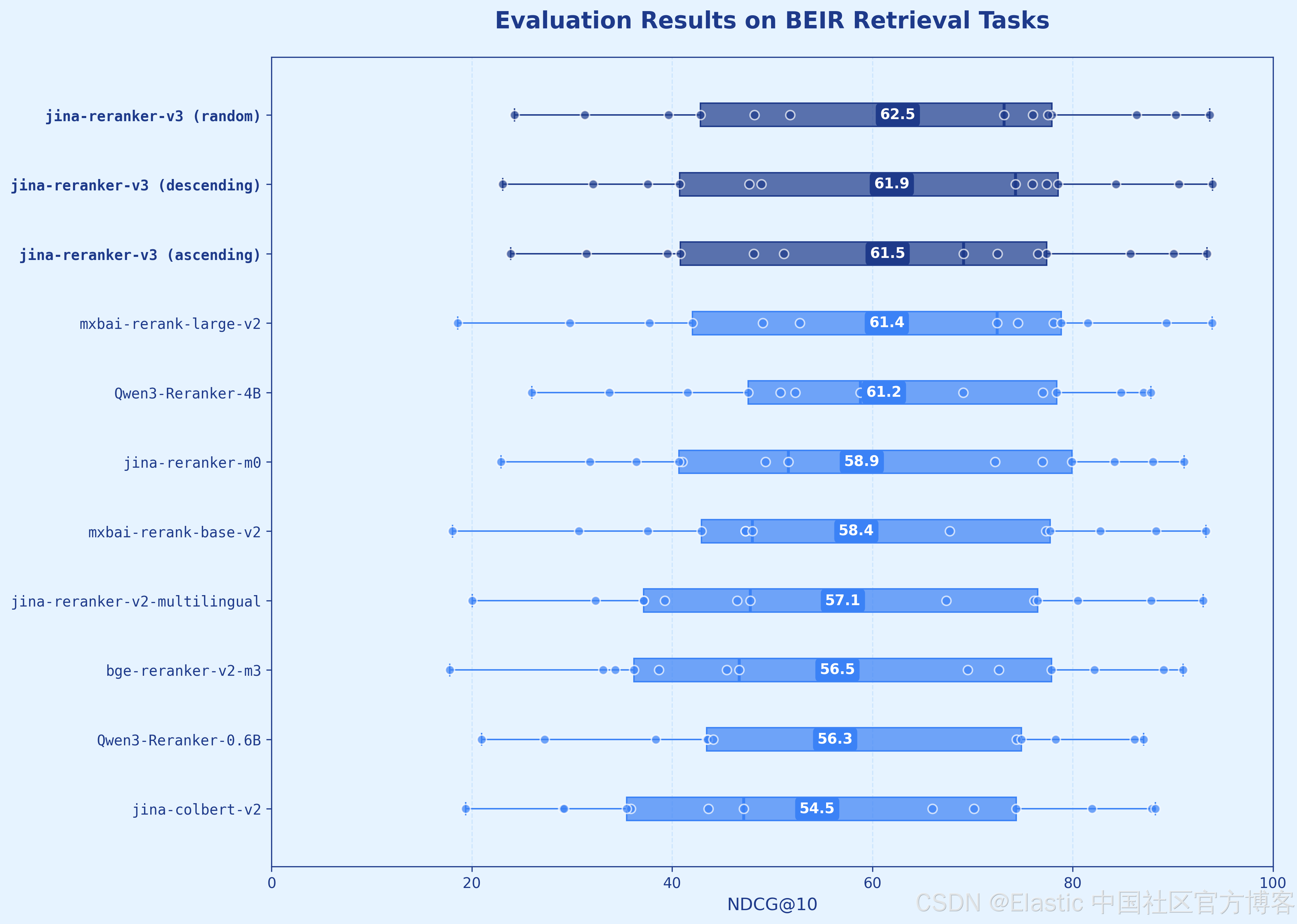
我们很高兴发布 jina-reranker-v3 ,这是我们最新一代的 reranker ,在多语言检索基准上提供最先进的性能。这个 0.6B - parameter 的 document reranker 引入了一种新的 last but not late interaction(最后但不迟的交互) ,与现有方法采取了根本不同的方式。 jina-reranker-v3 以 listwise 方式工作:它在单个 context window 内对 query 和所有 candidate documents 应用 causal attention ,在从每个 document 的 final token 提取 contextual embeddings 之前,实现丰富的跨 document 交互。我们的新模型在 BEIR 上达到了 61.94 nDCG@10 ,性能超过 Qwen3-Reranker-4B ,同时模型体积小 6× 。
| Model | Size | BEIR | MIRACL | MKQA | CoIR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| jina-reranker-v3 | 0.6B | 61.94 | 66.83 | 67.92 | 70.64 |
| jina-reranker-v2 | 0.3B | 57.06 | 63.65 | 67.90 | 56.14 |
| jina-reranker-m0 | 2.4B | 58.95 | 66.75 | 68.19 | 63.55 |
| bge-reranker-v2-m3 | 0.6B | 56.51 | 69.32 | 67.88 | 36.28 |
| mxbai-rerank-base-v2 | 0.5B | 58.40 | 55.32 | 64.24 | 65.71 |
| mxbai-rerank-large-v2 | 1.5B | 61.44 | 57.94 | 67.06 | 70.87 |
| Qwen3-Reranker-0.6B | 0.6B | 56.28 | 57.70 | 65.34 | 65.18 |
| Qwen3-Reranker-4B | 4.0B | 61.16 | 67.52 | 67.52 | 73.91 |
| jina-code-embeddings-0.5b | 0.5B | - | - | - | 73.94 |
模型架构
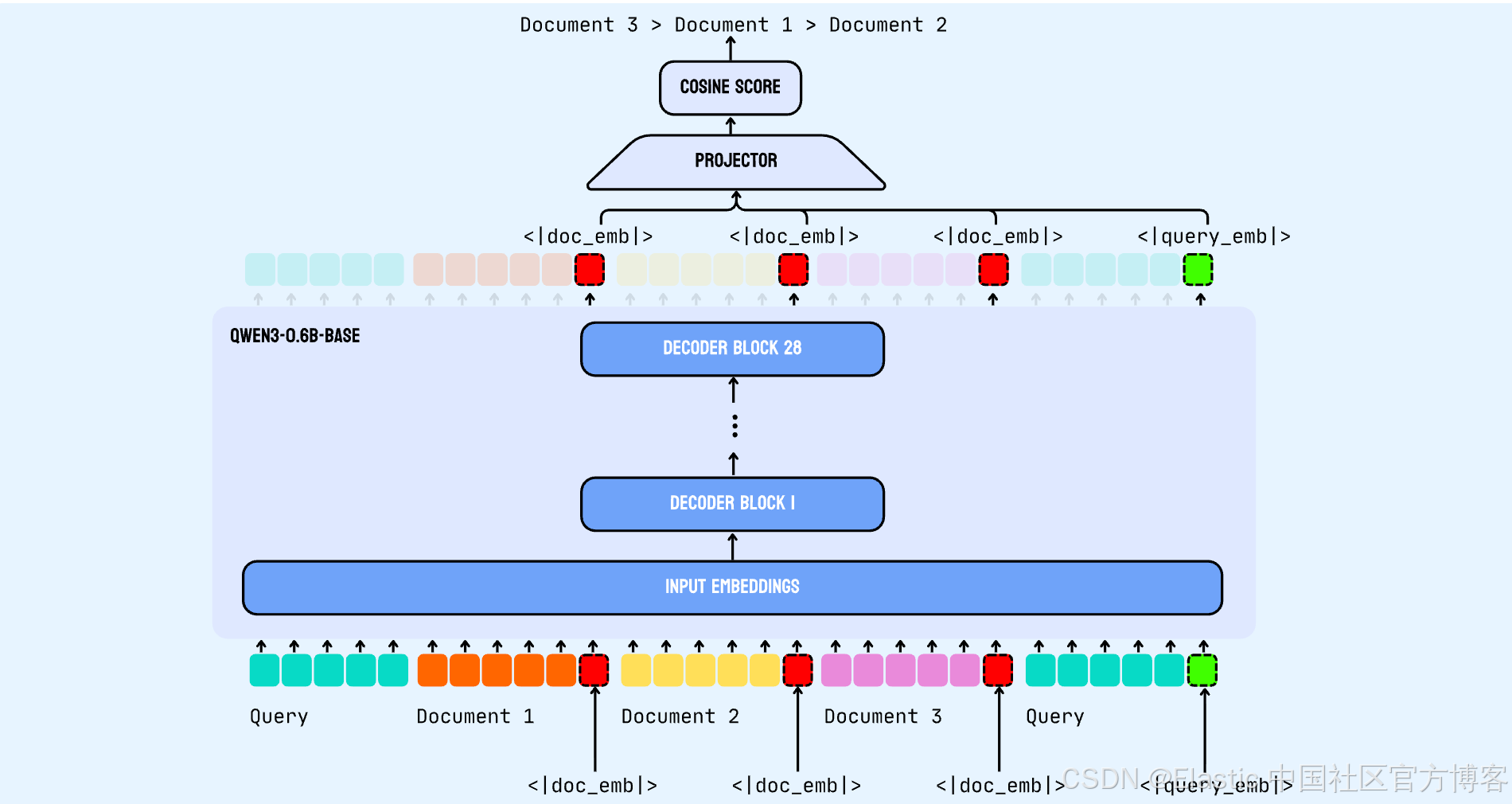
jina-reranker-v3 构建在 Qwen3-0.6B backbone 上,这是一个仅 decoder 的 transformer 模型,带有 causal self-attention。该模型同时处理多个 documents 和 query,在指定的 token 位置提取 contextual embeddings,以实现高效的相似度计算。
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Parameters | 0.6B |
| Non-Embedding Parameters | 0.44B |
| Hidden Size | 1,024 |
| Number of Layers | 28 |
| Attention Heads (Q/KV) | 16/8 (GQA) |
| Context Length | 131,072 |
| MLP Projector | 1024→512→256 |
| Final Embedding Size | 256 |
给定一个 query 和一组 candidate documents ,jina-reranker-v3 使用一个专门的 prompt template 处理 reranking 任务,该模板在单次 forward pass 中实现跨 document 交互。输入构建遵循特定格式:
<|im_start|>system
You are a search relevance expert who can determine
a ranking of passages based on their relevance to the query.
<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
I will provide you with k passages, each indicated by a numerical identifier.
Rank the passages based on their relevance to query: [QUERY]
<passage id="1">
[DOCUMENT_1]<|doc_emb|>
</passage>
<passage id="2">
[DOCUMENT_2]<|doc_emb|>
</passage>
...
<passage id="k">
[DOCUMENT_k]<|doc_emb|>
</passage>
<query>
[QUERY]<|query_emb|>
</query>
<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
<think></think>在输入结构中,query 出现两次------ 一次在开头用于任务指令,一次在末尾用于最终 attention 处理。这种双重位置使得最终的 query 位置可以通过 causal attention 关注所有前面的 documents。两个关键的特殊 token 标记了 embedding 提取位置:<|doc_emb|> token 放在每个 document 之后,用于标记 document embedding 的提取点,而 <|query_emb|> token 放在最终的 query 之后,用于标记 query embedding 的提取点。这些 embeddings 通过共享的 causal self-attention 机制捕捉了局部 document 语义和全局跨 document 上下文。
我们称这种 query-document 交互为 "last but not late"。之所以叫 "last",是因为 <|doc_emb|> 放在每个 document 的最后一个 token。之所以叫 "not late",是因为与 ColBERT 等 late interaction 模型不同,那些模型在多向量匹配前会单独编码 documents,而我们在 forward pass 中在同一个 context window 内实现了 query-document 和 document-document 交互。
最后,一个带 ReLU 激活的两层 MLP projector 将 1024 维的 hidden states 映射到 256 维的 ranking space。相关性评分通过投影后的 query embedding 与每个投影后的 document embedding 之间的 cosine similarity 计算,从而为输入集合中的每个 document 生成相关性分数。
入门
通过 API
使用 jina-reranker-v3 最简单的方法是通过我们的 Search Foundation API 。我们可以参考之前的文章 "Jina-VLM:小型多语言视觉语言模型" 来获取一个 API key。然后,我们使用如下的命令来定义一个环境变量:
export JINA_API_KEY=<Your JIAN API KEY>
curl -X POST \
https://api.jina.ai/v1/rerank \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer JINA_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "jina-reranker-v3",
"query": "slm markdown",
"documents": [
...
],
"return_documents": false
}'比如:
curl -X POST \
https://api.jina.ai/v1/rerank \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $JINA_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "jina-reranker-v3",
"query": "阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司是哪一年成立的?",
"documents": [
"阿里巴巴是全球领先的B2B电子商务网上贸易平台",
"阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司成立于2007年03月26日,法定代表人蒋芳"
],
"return_documents": false
}' | jq .
$ curl -X POST \
> https://api.jina.ai/v1/rerank \
> -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
> -H "Authorization: Bearer $JINA_API_KEY" \
> -d '{
> "model": "jina-reranker-v3",
> "query": "阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司是哪一年成立的?",
> "documents": [
> "阿里巴巴是全球领先的B2B电子商务网上贸易平台",
> "阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司成立于2007年03月26日,法定代表人蒋芳"
> ],
> "return_documents": false
> }' | jq .
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 494 100 168 100 326 194 377 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 571
{
"model": "jina-reranker-v3",
"object": "list",
"usage": {
"total_tokens": 218
},
"results": [
{
"index": 1,
"relevance_score": 0.55301309
},
{
"index": 0,
"relevance_score": -0.05146404
}
]
}很显然,文档 index 为 1 的文档和 "阿里巴巴(中国)有限公司是哪一年成立的?" 更为贴近。
通过 transformers
from transformers import AutoModel
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
'jinaai/jina-reranker-v3',
dtype="auto",
trust_remote_code=True,
)
model.eval()现在你可以使用模型的 rerank 函数来计算 query 和一组 documents 的相关性分数:
query = "What are the health benefits of green tea?"
documents = [
"Green tea contains antioxidants called catechins that may help reduce inflammation and protect cells from damage.",
"El precio del café ha aumentado un 20% este año debido a problemas en la cadena de suministro.",
"Studies show that drinking green tea regularly can improve brain function and boost metabolism.",
"Basketball is one of the most popular sports in the United States.",
"绿茶富含儿茶素等抗氧化剂,可以降低心脏病风险,还有助于控制体重。",
"Le thé vert est riche en antioxydants et peut améliorer la fonction cérébrale.",
]
# Rerank documents
results = model.rerank(query, documents)
# Results are sorted by relevance score (highest first)
for result in results:
print(f"Score: {result['relevance_score']:.4f}")
print(f"Document: {result['document'][:100]}...")
print()完整的代码:
$ python transformer.py
modeling.py: 10.4kB [00:00, 11.6MB/s]
A new version of the following files was downloaded from https://huggingface.co/jinaai/jina-reranker-v3:
- modeling.py
. Make sure to double-check they do not contain any added malicious code. To avoid downloading new versions of the code file, you can pin a revision.
model.safetensors: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 1.19G/1.19G [00:54<00:00, 21.8MB/s]
generation_config.json: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 202/202 [00:00<00:00, 1.46MB/s]
tokenizer_config.json: 10.7kB [00:00, 17.9MB/s]
tokenizer.json: 100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 11.4M/11.4M [00:04<00:00, 2.41MB/s]
added_tokens.json: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 795/795 [00:00<00:00, 6.74MB/s]
special_tokens_map.json: 100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 777/777 [00:00<00:00, 2.29MB/s]
Score: 0.2966
Document: Green tea contains antioxidants called catechins that may help reduce inflammation and protect cells...
Score: 0.2262
Document: 绿茶富含儿茶素等抗氧化剂,可以降低心脏病风险,还有助于控制体重。...
Score: 0.1911
Document: Studies show that drinking green tea regularly can improve brain function and boost metabolism....
Score: 0.1645
Document: Le thé vert est riche en antioxydants et peut améliorer la fonction cérébrale....
Score: -0.1602
Document: El precio del café ha aumentado un 20% este año debido a problemas en la cadena de suministro....
Score: -0.1699
Document: Basketball is one of the most popular sports in the United States....结论
jina-reranker-v3 是一个新的 0.6B parameter 多语言 listwise reranker,引入了 last but not late interaction,以实现高效的 document reranking。Documents 在编码过程中可以互相关注,建立交互,从而影响最终排序。
一个主要关注点是这种交互是否对输入顺序的变化具有鲁棒性------也就是说,如果我们打乱输入顺序,排名是否保持不变?我们用一个 query 对 110 个 candidate documents 进行了随机排列测试,并在下图中绘制了每个排名位置的方差。
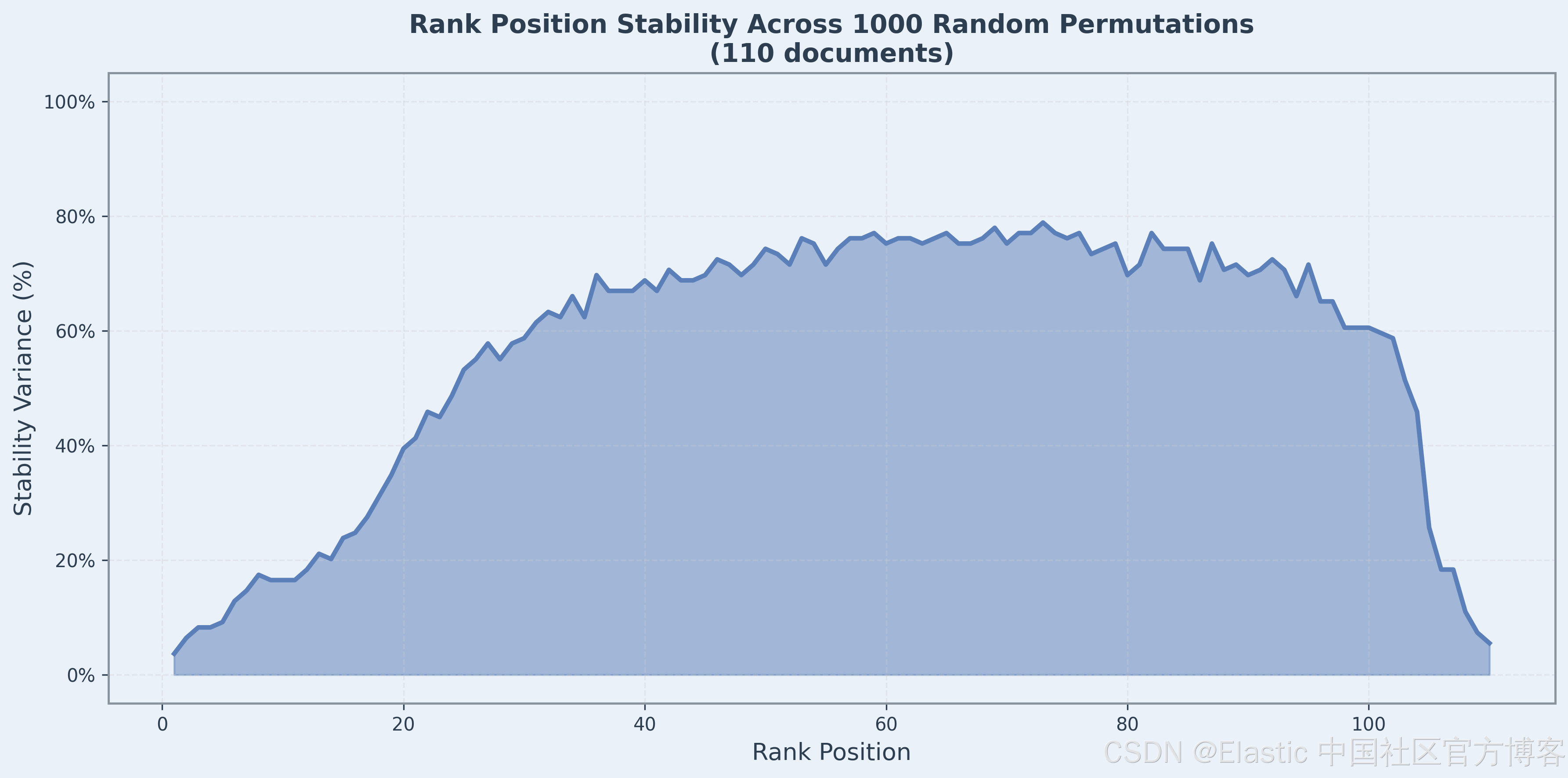
关键发现是,排名靠前的位置表现出极好的稳定性。排名 1-10 的方差最小,最相关的 documents 无论输入顺序如何,都能稳定排在顶部。这对于 nDCG@10 和类似的 top-k 指标至关重要。无关的 documents 一直排在底部,清晰区分了相关内容和无关内容。
中间部分显示了明显的位置交换,这是预期且可接受的。模型使用 causal self-attention,并根据序列中前面的内容编码不同的上下文信息。
在实际应用中,我们关心的是最顶部的结果,这种行为完全可以接受。我们的评估显示 jina-reranker-v3 的性能优于早期版本,包括 jina-reranker-v2-base-multilingual 和 jina-colbert-v2,以及更大的替代模型如 Qwen3-Reranker-4B 和 jina-reranker-m0 ,进一步证实了这一点。
原文:https://jina.ai/news/jina-reranker-v3-0-6b-listwise-reranker-for-sota-multilingual-retrieval/