前文中我们了解了 Flink 的数据交互过程,上游的 Task 将数据写入到 ResultSubpartition 的 buffers 队列中。下游的 Task 通过 LocalInputChannel 和 RemoteInputChannel 消费上游的数据。
LocalInputChannel 是上下游的 Task 部署在同一个 TaskManager 时使用的,在本地即可完成数据交换,无需网络通信。当上下游的 Task 部署在不同的 TaskManager 时,就需要用到 RemoteInputChannel,Flink 利用 Netty 来进行数据交互。本文我们来一起梳理一下 Netty 相关的源码。
初始化
我们先来看 NettyServer 和 NettyClient 的初始化过程。

Netty 的初始化阶段是在 TaskManager 启动的过程中执行的。在 TaskManagerServices.fromConfiguration 方法中,会创建并启动 ShuffleEnvironment。
java
public static TaskManagerServices fromConfiguration(
TaskManagerServicesConfiguration taskManagerServicesConfiguration,
PermanentBlobService permanentBlobService,
MetricGroup taskManagerMetricGroup,
ExecutorService ioExecutor,
ScheduledExecutor scheduledExecutor,
FatalErrorHandler fatalErrorHandler,
WorkingDirectory workingDirectory)
throws Exception {
...
final ShuffleEnvironment<?, ?> shuffleEnvironment =
createShuffleEnvironment(
taskManagerServicesConfiguration,
taskEventDispatcher,
taskManagerMetricGroup,
ioExecutor,
scheduledExecutor);
final int listeningDataPort = shuffleEnvironment.start();
...
}我们顺着调用链路可以一直找到 NettyShuffleServiceFactory.createNettyShuffleEnvironment 方法,这个方法中创建了 NettyConnectionManager,在 NettyConnectionManager 中有几个很重要的对象。
java
public NettyConnectionManager(
NettyBufferPool bufferPool,
ResultPartitionProvider partitionProvider,
TaskEventPublisher taskEventPublisher,
NettyConfig nettyConfig,
boolean connectionReuseEnabled) {
this.server = new NettyServer(nettyConfig);
this.client = new NettyClient(nettyConfig);
this.bufferPool = checkNotNull(bufferPool);
this.partitionRequestClientFactory =
new PartitionRequestClientFactory(
client, nettyConfig.getNetworkRetries(), connectionReuseEnabled);
this.nettyProtocol =
new NettyProtocol(
checkNotNull(partitionProvider), checkNotNull(taskEventPublisher));
}server 和 client 不需要多介绍,就是 Netty 的服务端和客户端。bufferPool 是缓冲池,用于存储要传输的数据。nettyProtocol 提供了 NettyClient 和 NettyServer 引导启动注册的 Channel Handler。
后面就是创建 NettyShuffleEnvironment 及其需要的对象了。在创建完成后,会调用它的 start 方法启动。这个启动方法就是调用了 connectionManager.start,在 NettyConnectionManager 中,就是初始化客户端和服务端。
java
public int start() throws IOException {
client.init(nettyProtocol, bufferPool);
return server.init(nettyProtocol, bufferPool);
}client 初始化
client 的初始化过程是先创建并初始化 Bootstrap。
java
private void initEpollBootstrap() {
// Add the server port number to the name in order to distinguish
// multiple clients running on the same host.
String name =
NettyConfig.CLIENT_THREAD_GROUP_NAME + " (" + config.getServerPortRange() + ")";
EpollEventLoopGroup epollGroup =
new EpollEventLoopGroup(
config.getClientNumThreads(), NettyServer.getNamedThreadFactory(name));
bootstrap.group(epollGroup).channel(EpollSocketChannel.class);
config.getTcpKeepIdleInSeconds()
.ifPresent(idle -> bootstrap.option(EpollChannelOption.TCP_KEEPIDLE, idle));
config.getTcpKeepInternalInSeconds()
.ifPresent(
interval -> bootstrap.option(EpollChannelOption.TCP_KEEPINTVL, interval));
config.getTcpKeepCount()
.ifPresent(count -> bootstrap.option(EpollChannelOption.TCP_KEEPCNT, count));
}初始化过程重要设置 EventLoopGroup 和 channel,可以用 epoll 的话就用 epoll,否则就用 nio。设置好这些后就是设置了一些通道参数(连接超时时间、Bufffer 池等)。
到这里 client 的初始化其实并没有结束,还需要设置 Handler 流水线,这些工作是在 Task 启动时执行了。
server 初始化
server 的初始化过程是先创建并初始化了 ServerBootstrap。之后同样也是设置 EventLoopGroup 和 channel,以及通道相关的各种参数。
设置好之后,会添加 ChannelHandler 流水线,这里的 ChannelHandler 流水线就是我们前面创建的 NettyProtocol 提供的。
java
public ChannelHandler[] getServerChannelHandlers() {
PartitionRequestQueue queueOfPartitionQueues = new PartitionRequestQueue();
PartitionRequestServerHandler serverHandler =
new PartitionRequestServerHandler(
partitionProvider, taskEventPublisher, queueOfPartitionQueues);
return new ChannelHandler[] {
messageEncoder,
new NettyMessage.NettyMessageDecoder(),
serverHandler,
queueOfPartitionQueues
};
}流水线上包含了消息编码器、解码器、PartitionRequestServerHandler 请求服务端处理器和 PartitionRequestQueue 分区请求队列。
这些都设置好之后,就开始启动 NettyServer 服务了。
java
Iterator<Integer> portsIterator = config.getServerPortRange().getPortsIterator();
while (portsIterator.hasNext() && bindFuture == null) {
Integer port = portsIterator.next();
LOG.debug("Trying to bind Netty server to port: {}", port);
bootstrap.localAddress(config.getServerAddress(), port);
try {
bindFuture = bootstrap.bind().syncUninterruptibly();
} catch (Exception e) {
// syncUninterruptibly() throws checked exceptions via Unsafe
// continue if the exception is due to the port being in use, fail early
// otherwise
if (isBindFailure(e)) {
LOG.debug("Failed to bind Netty server", e);
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
if (bindFuture == null) {
throw new BindException(
"Could not start rest endpoint on any port in port range "
+ config.getServerPortRange());
}
localAddress = (InetSocketAddress) bindFuture.channel().localAddress();客户端请求远端子分区
服务端和客户端初始化之后,在 Task 运行时,会先完成 Client 的 ChannelHandler 的配置,然后请求 Netty 远端服务。
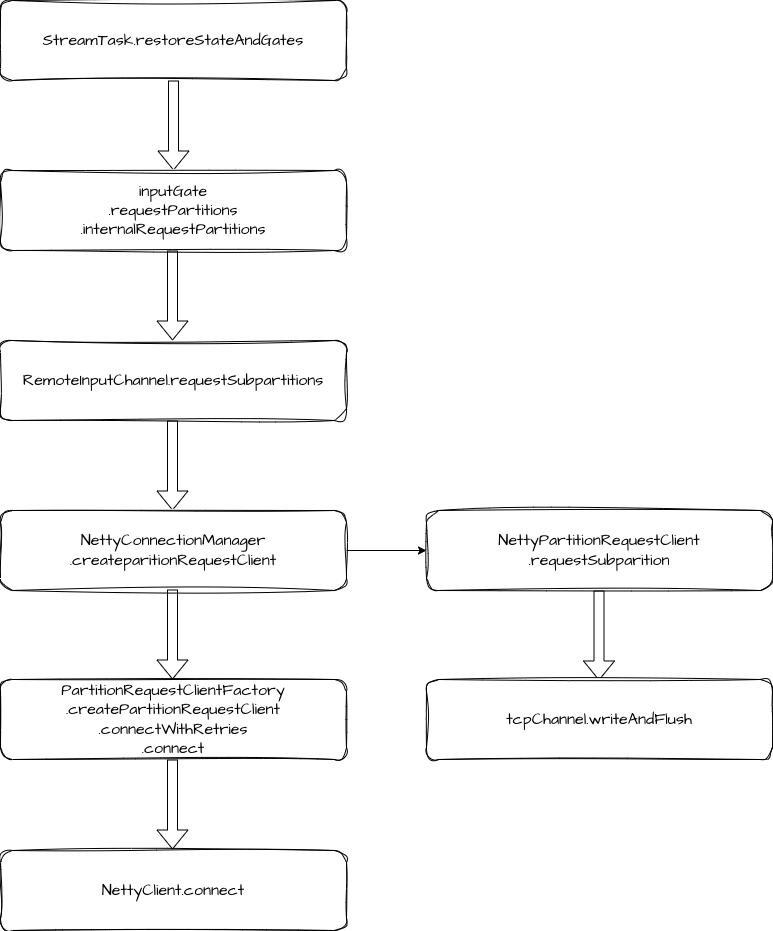
我们来看具体过程,在 Task 初始化时,会调用 StreamTask.invoke 方法,其内部会调用 StreamTask.restoreStateAndGate 方法,这里会便利 Task 的所有 InputGate,然后调用 requestPartitions。在 InputGate 的 requestPartitions 逻辑中,又便利所有的 InputChannel,调用 requestSubpartitions。
java
for (InputGate inputGate : inputGates) {
recoveredFutures.add(inputGate.getStateConsumedFuture());
inputGate
.getStateConsumedFuture()
.thenRun(
() ->
mainMailboxExecutor.execute(
inputGate::requestPartitions,
"Input gate request partitions"));
}
private void internalRequestPartitions() {
for (InputChannel inputChannel : inputChannels()) {
try {
inputChannel.requestSubpartitions();
} catch (Throwable t) {
inputChannel.setError(t);
return;
}
}
}我们来看 RemoteInputChannel.requestSubpartitions 的逻辑。
java
public void requestSubpartitions() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
if (partitionRequestClient == null) {
LOG.debug(
"{}: Requesting REMOTE subpartitions {} of partition {}. {}",
this,
consumedSubpartitionIndexSet,
partitionId,
channelStatePersister);
// Create a client and request the partition
try {
partitionRequestClient =
connectionManager.createPartitionRequestClient(connectionId);
} catch (IOException e) {
// IOExceptions indicate that we could not open a connection to the remote
// TaskExecutor
throw new PartitionConnectionException(partitionId, e);
}
partitionRequestClient.requestSubpartition(
partitionId, consumedSubpartitionIndexSet, this, 0);
}
}这里主要有两个步骤,先是创建 partitionRequestClient,然后调用 requestSubpartition。
创建请求客户端
PartitionRequestClient 是在 PartitionRequestClientFactory.connect 中创建的。先调用了 NettyClient.connect,同步等待客户端连接到服务端,这个过程中会进行 ChannelHandler 配置,也就是我们在初始化的过程中介绍的,NettyClient 没有完成的步骤。
java
public ChannelHandler[] getClientChannelHandlers() {
NetworkClientHandler networkClientHandler = new CreditBasedPartitionRequestClientHandler();
return new ChannelHandler[] {
messageEncoder,
new NettyMessageClientDecoderDelegate(networkClientHandler),
networkClientHandler
};
}Handler 包括了消息编码器、解码器和 CreditBasedPartitionRequestClientHandler 这个基于 Credit 的分区请求客户端处理器。Handler 配置好之后会利用 bootstrap 连接到服务端。
在获取到 Channel 和 NetworkClientHandler 之后,就直接创建了 NettyPartitionRequestClient。
请求子分区数据
让我们再回到 RemoteInputChannel 的 requestSubpartitions 方法中,现在我们创建好了 NettyPartitionRequestClient,接下来就是调用它的 requestSubpartition 方法来发起请求。
这里逻辑也比较简单:
-
向 NetworkClientHandler 注册当前 RemoteInputChannel。
-
构造请求对象 PartitionRequest,这里包含了分区 ID、子分区索引、inputChannel ID 以及初识的 Credit。
-
调用
tcpChannel.writeAndFlush发起请求,并添加请求失败的监听。 -
如果请求失败,移除当前 inputChannel。
服务端响应
现在数据到了服务端,我们来看服务端处理的具体过程。
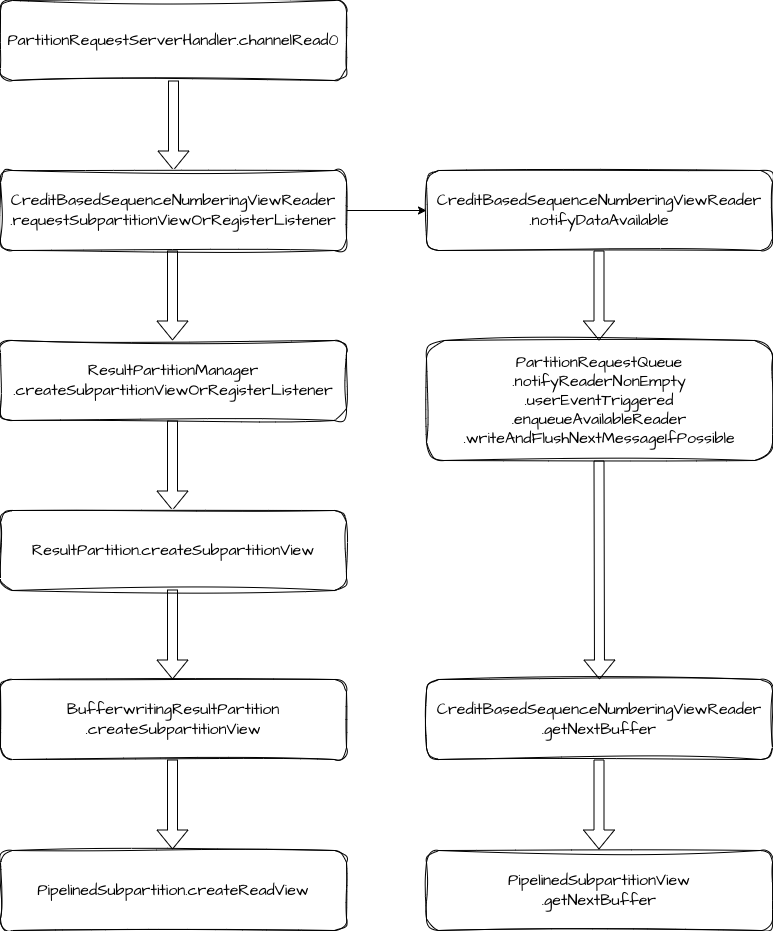
在 NettyServer 初始化的过程中,我们添加了两个重要的 Handler,分别是 PartitionRequestServerHandler 和 PartitionRequestQueue。服务端响应数据的过程就是这两个 Handler 在发挥作用。
PartitionRequestServerHandler 负责处理 Client 端通过 PartitionRequestClient 发送的请求,处理过程是先创建 CreditBasedSequenceNumberingViewReader 类型的 reader,然后将它放入 PartitionRequestQueue 维护的 reader 队列中。PartitionRequestQueue 会监听 Netty Channel 的可写入状态,当 Netty Channel 可写入时,会消费数据并写入网络。
下面我们来看具体的源码。
服务端的响应入口在 PartitionRequestServerHandler.channelRead0 方法,这里在处理 PartitionRequest 请求时,先是创建 CreditBasedSequenceNumberingViewReader,然后调用 requestSubpartitionViewOrRegisterListener。
requestSubpartitionViewOrRegisterListener 的逻辑是创建 ResultSubpartitionView,并提醒 PartitionRequestQueue 有数据可用。
java
Optional<ResultSubpartitionView> subpartitionViewOptional =
partitionProvider.createSubpartitionViewOrRegisterListener(
resultPartitionId,
subpartitionIndexSet,
this,
partitionRequestListener);
...
notifyDataAvailable(subpartitionView);ResultSubpartitionView 就是用来消费 ResultSubpartition 的数据。
notifyDataAvailable 内部调用了 notifyReaderNonEmpty,notifyReaderNonEmpty 又触发了 userEventTriggered,这里调用 enqueueAvailableReader 将 reader 放入到可用队列 availableReaders 中。
java
private void enqueueAvailableReader(final NetworkSequenceViewReader reader) throws Exception {
if (reader.isRegisteredAsAvailable()) {
return;
}
ResultSubpartitionView.AvailabilityWithBacklog availabilityWithBacklog =
reader.getAvailabilityAndBacklog();
if (!availabilityWithBacklog.isAvailable()) {
int backlog = availabilityWithBacklog.getBacklog();
if (backlog > 0 && reader.needAnnounceBacklog()) {
announceBacklog(reader, backlog);
}
return;
}
// Queue an available reader for consumption. If the queue is empty,
// we try trigger the actual write. Otherwise this will be handled by
// the writeAndFlushNextMessageIfPossible calls.
boolean triggerWrite = availableReaders.isEmpty();
registerAvailableReader(reader);
if (triggerWrite) {
writeAndFlushNextMessageIfPossible(ctx.channel());
}
}如果 reader 是队列中的第一个元素,会触发数据写入网络。
writeAndFlushNextMessageIfPossible 的处理步骤如下:
-
取出可用 reader。
-
调用
reader.getNextBuffer获取数据。 -
如果 reader 仍然可用,将其加回队列。
-
向下游写入数据并添加下次写入的监听。
java
public BufferAndAvailability getNextBuffer() throws IOException {
BufferAndBacklog next = subpartitionView.getNextBuffer();
if (next != null) {
if (next.buffer().isBuffer() && --numCreditsAvailable < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("no credit available");
}
final Buffer.DataType nextDataType = getNextDataType(next);
return new BufferAndAvailability(
next.buffer(), nextDataType, next.buffersInBacklog(), next.getSequenceNumber());
} else {
return null;
}
}在 getNextBuffer 方法中,会将 credit 值减 1,并判断是否小于 0。如果小于 0 会抛出异常,reader 是否可用也是根据 numCreditsAvailable 是否大于 0 来判断的。
客户端接收数据
NettyClient 在消费数据时,同样也是以 ChannelHandler 作为入口。这里的入口方法是 CreditBasedPartitionRequestClientHandler.channelRead 。

在 decodeMsg 方法中,先解码 msg,判断 InputChannel 是否可用,如果不可用,则取消当前 InputChannel 的订阅。如果可用,继续调用 decodeBufferOrEvent 进行处理。decodeBufferOrEvent 的核心逻辑是调用 RemoteInputChannel.onBuffer 方法,将数据加入到 receivedBuffers 队列。
如果 receivedBuffers 队列在此之前处于空闲状态,会调用 notifyChannelNonEmpty,将当前 RemoteInputChannel 加入到 inputChannelsWithData 队列中,同时还会唤醒 inputChannelsWithData 上的阻塞线程,让 inputGate 可以消费 RemoteInputChannel 的数据。
java
private boolean queueChannelUnsafe(InputChannel channel, boolean priority) {
assert Thread.holdsLock(inputChannelsWithData);
if (channelsWithEndOfPartitionEvents.get(channel.getChannelIndex())) {
return false;
}
final boolean alreadyEnqueued =
enqueuedInputChannelsWithData.get(channel.getChannelIndex());
if (alreadyEnqueued
&& (!priority || inputChannelsWithData.containsPriorityElement(channel))) {
// already notified / prioritized (double notification), ignore
return false;
}
// 当前 inputChannel 加入到 inputChannelsWithData
inputChannelsWithData.add(channel, priority, alreadyEnqueued);
if (!alreadyEnqueued) {
enqueuedInputChannelsWithData.set(channel.getChannelIndex());
}
return true;
}
// 唤醒线程
public void notifyDataAvailable() {
availabilityMonitor.notifyAll();
toNotify = inputGate.availabilityHelper.getUnavailableToResetAvailable();
}如果客户端有积压,还需要根据积压申请 Buffer 并更新 Credit 值。这里申请的 buffer 数量为积压数量+初识 Credit 值。
java
public void onSenderBacklog(int backlog) throws IOException {
notifyBufferAvailable(bufferManager.requestFloatingBuffers(backlog + initialCredit));
}如果 RemoteInputChannel 没有足够的 buffer,则会向 LocalBufferPool 申请新的 buffer,如果申请不到,会加一个监听,等 LocalBufferPool 有空闲时再触发申请 buffer。
java
private int tryRequestBuffers() {
assert Thread.holdsLock(bufferQueue);
int numRequestedBuffers = 0;
while (bufferQueue.getAvailableBufferSize() < numRequiredBuffers
&& !isWaitingForFloatingBuffers) {
BufferPool bufferPool = inputChannel.inputGate.getBufferPool();
Buffer buffer = bufferPool.requestBuffer();
if (buffer != null) {
bufferQueue.addFloatingBuffer(buffer);
numRequestedBuffers++;
} else if (bufferPool.addBufferListener(this)) {
isWaitingForFloatingBuffers = true;
break;
}
}
return numRequestedBuffers;
}当 RemoteInputChannel 申请到了需要的 buffer 之后,就会向 NettyServer 发送 AddCredit 消息,请求更新 Credit 值。
java
private void notifyCreditAvailable() throws IOException {
checkPartitionRequestQueueInitialized();
partitionRequestClient.notifyCreditAvailable(this);
}
public void notifyCreditAvailable(RemoteInputChannel inputChannel) {
sendToChannel(new AddCreditMessage(inputChannel));
}NettyServer 收到请求后,会将对应的 Credit 值进行更新。
java
else if (msgClazz == AddCredit.class) {
AddCredit request = (AddCredit) msg;
outboundQueue.addCreditOrResumeConsumption(
request.receiverId, reader -> reader.addCredit(request.credit));
}
void addCreditOrResumeConsumption(
InputChannelID receiverId, Consumer<NetworkSequenceViewReader> operation)
throws Exception {
if (fatalError) {
return;
}
NetworkSequenceViewReader reader = obtainReader(receiverId);
operation.accept(reader);
enqueueAvailableReader(reader);
}
public void addCredit(int creditDeltas) {
numCreditsAvailable += creditDeltas;
}此外,Flink 还有两种场景会更新 Credit 值。
一种是 LocalBufferPool 回收空闲 buffer 时,会将 buffer 分配给申请者,分配之后会调用对应 InputChannel 的 notifyBufferAvailable 方法通知更新 Credit。
另一种是 RemoteInputChannel 独占的 buffer 队列释放 buffer 时,会触发 Credit 更新。

反压
通过前面的学习,我们其实已经理解了反压的机制了。当前 Flink 的反压就是通过 Credit 来实现反压的,如果下游数据处理速度慢,Credit 会被耗尽,上游也就不会继续处理和下发数据了。直到下游处理完成,有了空闲的 buffer,此时向上游反馈更新 Credit 值,上游就会继续处理数据。
总结
最后我们总结一下,本文我们一起梳理了 Flink Netty 相关的源码。包括 NettyClient 和 NettyServer 的初始化,初始化过程中会创建一系列 ChannelHandler,之后利用这些Handler 处理数据,数据处理包括 Client 端的发送和接收消息,Server 端处理消息的过程。中间还穿插着 Credit 的处理。Flink 的反压逻辑就是依赖于 Credit 来实现的。