
8.3.3 实现D* Lite算法
文件d_star_lite.py实现了 D* Lite 算法的关键部分,包括计算路径、更新路径、扫描障碍物、移动并重新扫描等功能。具体来说,文件d_star_lite.py定义了计算 D* Lite 算法中路径的函数,包括计算顶部键、启发式函数、更新顶点、计算最短路径、寻找下一个最短路径、扫描障碍物、移动并重新扫描等功能。这些函数可以实现在动态环境中实时更新路径规划,并根据环境变化进行路径的调整和优化。
(1)函数topKey(queue)用于获取优先队列中最小键值的元素,它首先对队列进行排序,然后返回排序后队列中的第一个元素的前两个值作为键值。如果队列为空,则返回无穷大的键值。
python
def topKey(queue):
queue.sort()
# print(queue)
if len(queue) > 0:
return queue[0][:2]
else:
# print('empty queue!')
return (float('inf'), float('inf'))(2)函数heuristic_from_s(graph, id, s)用于计算启发式值,根据当前节点id和目标节点s的坐标,计算它们在x和y方向上的距离差,然后返回其中较大的值作为启发式值。
python
def heuristic_from_s(graph, id, s):
x_distance = abs(int(id.split('x')[1][0]) - int(s.split('x')[1][0]))
y_distance = abs(int(id.split('y')[1][0]) - int(s.split('y')[1][0]))
return max(x_distance, y_distance)(3)函数calculateKey(graph, id, s_current, k_m)用于计算D* Lite算法中的关键值,通过结合节点的g值、rhs值以及启发式函数的值,再加上一个修正因子k_m,计算出节点的关键值,并返回计算得到的关键值。
python
def calculateKey(graph, id, s_current, k_m):
return (min(graph.graph[id].g, graph.graph[id].rhs) + heuristic_from_s(graph, id, s_current) + k_m, min(graph.graph[id].g, graph.graph[id].rhs))(4)函数updateVertex(graph, queue, id, s_current, k_m)用于更新节点的信息,包括计算节点的rhs值、更新优先队列中的节点位置。首先,根据节点的子节点信息,计算出节点的rhs值;然后,将节点从优先队列中移除;最后,如果节点的rhs值与g值不相等,则重新计算节点的关键值,并将节点重新加入优先队列中。
python
def updateVertex(graph, queue, id, s_current, k_m):
s_goal = graph.goal
if id != s_goal:
min_rhs = float('inf')
for i in graph.graph[id].children:
min_rhs = min(
min_rhs, graph.graph[i].g + graph.graph[id].children[i])
graph.graph[id].rhs = min_rhs
id_in_queue = [item for item in queue if id in item]
if id_in_queue != []:
if len(id_in_queue) != 1:
raise ValueError('more than one ' + id + ' in the queue!')
queue.remove(id_in_queue[0])
if graph.graph[id].rhs != graph.graph[id].g:
heapq.heappush(queue, calculateKey(graph, id, s_current, k_m) + (id,))(5)函数computeShortestPath(graph, queue, s_start, k_m)用于计算最短路径,并更新节点的g值。在函数中,通过检查优先队列中的最小关键值是否小于当前节点的关键值,以及当前节点的rhs值是否等于g值,来决定是否需要继续计算最短路径。在计算过程中,根据节点的g值和rhs值的关系,以及节点的子节点信息,更新节点的g值,并更新优先队列中相关节点的位置。
python
def computeShortestPath(graph, queue, s_start, k_m):
while (graph.graph[s_start].rhs != graph.graph[s_start].g) or (topKey(queue) < calculateKey(graph, s_start, s_start, k_m)):
# print(graph.graph[s_start])
# print('topKey')
# print(topKey(queue))
# print('calculateKey')
# print(calculateKey(graph, s_start, 0))
k_old = topKey(queue)
u = heapq.heappop(queue)[2]
if k_old < calculateKey(graph, u, s_start, k_m):
heapq.heappush(queue, calculateKey(graph, u, s_start, k_m) + (u,))
elif graph.graph[u].g > graph.graph[u].rhs:
graph.graph[u].g = graph.graph[u].rhs
for i in graph.graph[u].parents:
updateVertex(graph, queue, i, s_start, k_m)
else:
graph.graph[u].g = float('inf')
updateVertex(graph, queue, u, s_start, k_m)
for i in graph.graph[u].parents:
updateVertex(graph, queue, i, s_start, k_m)
# graph.printGValues()(6)函数nextInShortestPath(graph, s_current)用于寻找最短路径中的下一个节点。首先检查当前节点的rhs值是否为无穷大,如果是,则打印提示信息。否则,遍历当前节点的子节点,计算子节点的代价,并找到具有最小代价的子节点作为下一个节点。若成功找到下一个节点,则返回该节点的ID,否则抛出数值错误。
python
def nextInShortestPath(graph, s_current):
min_rhs = float('inf')
s_next = None
if graph.graph[s_current].rhs == float('inf'):
print('You are done stuck')
else:
for i in graph.graph[s_current].children:
# print(i)
child_cost = graph.graph[i].g + graph.graph[s_current].children[i]
# print(child_cost)
if (child_cost) < min_rhs:
min_rhs = child_cost
s_next = i
if s_next:
return s_next
else:
raise ValueError('could not find child for transition!')(7)函数scanForObstacles(graph, queue, s_current, scan_range, k_m)用于扫描当前节点周围的区域以检测障碍物。首先,根据扫描范围,初始化要更新的状态集合,并从当前节点的子节点开始更新。然后,循环迭代扫描范围,逐步扩展更新状态集合。在扫描过程中,如果发现有状态的值小于0,则表示发现了障碍物,需要进行处理,包括更新障碍物状态、更新相关节点的子节点信息,并更新优先队列中相关节点的位置。最后,返回是否发现新障碍物的标志。
python
def scanForObstacles(graph, queue, s_current, scan_range, k_m):
states_to_update = {}
range_checked = 0
if scan_range >= 1:
for neighbor in graph.graph[s_current].children:
neighbor_coords = stateNameToCoords(neighbor)
states_to_update[neighbor] = graph.cells[neighbor_coords[1]
][neighbor_coords[0]]
range_checked = 1
# print(states_to_update)
while range_checked < scan_range:
new_set = {}
for state in states_to_update:
new_set[state] = states_to_update[state]
for neighbor in graph.graph[state].children:
if neighbor not in new_set:
neighbor_coords = stateNameToCoords(neighbor)
new_set[neighbor] = graph.cells[neighbor_coords[1]
][neighbor_coords[0]]
range_checked += 1
states_to_update = new_set
new_obstacle = False
for state in states_to_update:
if states_to_update[state] < 0: # found cell with obstacle
# print('found obstacle in ', state)
for neighbor in graph.graph[state].children:
# first time to observe this obstacle where one wasn't before
if(graph.graph[state].children[neighbor] != float('inf')):
neighbor_coords = stateNameToCoords(state)
graph.cells[neighbor_coords[1]][neighbor_coords[0]] = -2
graph.graph[neighbor].children[state] = float('inf')
graph.graph[state].children[neighbor] = float('inf')
updateVertex(graph, queue, state, s_current, k_m)
new_obstacle = True
# elif states_to_update[state] == 0: #cell without obstacle
# for neighbor in graph.graph[state].children:
# if(graph.graph[state].children[neighbor] != float('inf')):
# print(graph)
return new_obstacle(8)函数moveAndRescan(graph, queue, s_current, scan_range, k_m)用于执行移动并重新扫描操作。首先检查当前节点是否为目标节点,如果是,则返回 'goal' 和修正因子 k_m。否则,根据当前节点获取下一个节点,并检查下一个节点是否遇到新的障碍物。如果是,则暂停移动操作,执行障碍物扫描和路径重新规划。最后,返回下一个节点的ID和修正因子 k_m。
python
def moveAndRescan(graph, queue, s_current, scan_range, k_m):
if(s_current == graph.goal):
return 'goal', k_m
else:
s_last = s_current
s_new = nextInShortestPath(graph, s_current)
new_coords = stateNameToCoords(s_new)
if(graph.cells[new_coords[1]][new_coords[0]] == -1): # just ran into new obstacle
s_new = s_current # need to hold tight and scan/replan first
results = scanForObstacles(graph, queue, s_new, scan_range, k_m)
# print(graph)
k_m += heuristic_from_s(graph, s_last, s_new)
computeShortestPath(graph, queue, s_current, k_m)
return s_new, k_m(9)函数initDStarLite(graph, queue, s_start, s_goal, k_m)用于初始化D* Lite算法。首先,将目标节点的rhs值设为0,并将其加入优先队列;然后,执行最短路径计算。最后,返回更新后的图、优先队列和修正因子 k_m。
python
def initDStarLite(graph, queue, s_start, s_goal, k_m):
graph.graph[s_goal].rhs = 0
heapq.heappush(queue, calculateKey(
graph, s_goal, s_start, k_m) + (s_goal,))
computeShortestPath(graph, queue, s_start, k_m)
return (graph, queue, k_m)8.3.4 路径规划可视化
文件main.py是一个基于Pygame库实现的D* Lite路径规划算法的可视化程序,创建了一个网格世界,并允许用户点击屏幕上的单元格来设置障碍物。算法将在屏幕上显示网格状态,并使用红色圆圈表示移动的机器人。当用户按下空格键时,机器人将沿最短路径移动,并根据其视野范围重新扫描环境。直到达到目标位置为止,算法将持续运行。
python
# 导入必要的库
# 定义颜色
BLACK = (0, 0, 0) # 黑色
WHITE = (255, 255, 255) # 白色
GREEN = (0, 255, 0) # 绿色
RED = (255, 0, 0) # 红色
GRAY1 = (145, 145, 102) # 灰色1
GRAY2 = (77, 77, 51) # 灰色2
BLUE = (0, 0, 80) # 蓝色
colors = {
0: WHITE, # 未探索区域
1: GREEN, # 障碍物
-1: GRAY1, # 未知区域
-2: GRAY2 # 已知障碍物
}
# 设置每个网格位置的宽度和高度
WIDTH = 40
HEIGHT = 40
# 设置每个单元格之间的间距
MARGIN = 5
# 创建一个二维数组,存储网格状态
grid = []
for row in range(10):
grid.append([]) # 添加一个空数组,用于存储行中的单元格
for column in range(10):
grid[row].append(0) # 添加一个单元格,初始状态为0
# 将第1行第5个单元格设为1(表示障碍物,行和列编号从0开始)
grid[1][5] = 1
# 初始化Pygame
pygame.init()
X_DIM = 12 # X轴维度
Y_DIM = 12 # Y轴维度
VIEWING_RANGE = 3 # 机器人的可视范围
# 设置屏幕的宽度和高度
WINDOW_SIZE = [(WIDTH + MARGIN) * X_DIM + MARGIN,
(HEIGHT + MARGIN) * Y_DIM + MARGIN]
screen = pygame.display.set_mode(WINDOW_SIZE)
# 设置屏幕标题
pygame.display.set_caption("D* Lite路径规划")
# 退出标志
done = False
# 用于控制屏幕更新速度
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建网格世界
graph = GridWorld(X_DIM, Y_DIM)
# 设置起点和终点
s_start = 'x1y2'
s_goal = 'x5y4'
goal_coords = stateNameToCoords(s_goal)
graph.setStart(s_start)
graph.setGoal(s_goal)
k_m = 0 # 初始化修正参数
s_last = s_start # 初始化上一个状态
queue = [] # 初始化优先队列
# 初始化D* Lite算法
graph, queue, k_m = initDStarLite(graph, queue, s_start, s_goal, k_m)
s_current = s_start # 设置当前状态为起点
pos_coords = stateNameToCoords(s_current) # 获取当前状态坐标
basicfont = pygame.font.SysFont('Comic Sans MS', 36) # 设置基本字体
# -------- 主程序循环 -----------
while not done:
for event in pygame.event.get(): # 用户操作
if event.type == pygame.QUIT: # 点击关闭按钮
done = True # 退出循环
elif event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_SPACE:
# 调用移动和重新扫描函数
s_new, k_m = moveAndRescan(
graph, queue, s_current, VIEWING_RANGE, k_m)
if s_new == 'goal':
print('Goal Reached!') # 达到目标点
done = True
else:
s_current = s_new # 更新当前状态
pos_coords = stateNameToCoords(s_current) # 更新当前状态坐标
elif event.type == pygame.MOUSEBUTTONDOWN:
# 鼠标点击事件,设置网格状态
pos = pygame.mouse.get_pos()
column = pos[0] // (WIDTH + MARGIN)
row = pos[1] // (HEIGHT + MARGIN)
if(graph.cells[row][column] == 0):
graph.cells[row][column] = -1
# 设置屏幕背景色
screen.fill(BLACK)
# 绘制网格
for row in range(Y_DIM):
for column in range(X_DIM):
pygame.draw.rect(screen, colors[graph.cells[row][column]],
[(MARGIN + WIDTH) * column + MARGIN,
(MARGIN + HEIGHT) * row + MARGIN, WIDTH, HEIGHT])
node_name = 'x' + str(column) + 'y' + str(row)
if(graph.graph[node_name].g != float('inf')):
text = basicfont.render(
str(graph.graph[node_name].g), True, (0, 0, 200))
textrect = text.get_rect()
textrect.centerx = int(
column * (WIDTH + MARGIN) + WIDTH / 2) + MARGIN
textrect.centery = int(
row * (HEIGHT + MARGIN) + HEIGHT / 2) + MARGIN
screen.blit(text, textrect)
# 绘制目标点
pygame.draw.rect(screen, GREEN, [(MARGIN + WIDTH) * goal_coords[0] + MARGIN,
(MARGIN + HEIGHT) * goal_coords[1] + MARGIN, WIDTH, HEIGHT])
# 绘制移动的机器人
robot_center = [int(pos_coords[0] * (WIDTH + MARGIN) + WIDTH / 2) +
MARGIN, int(pos_coords[1] * (HEIGHT + MARGIN) + HEIGHT / 2) + MARGIN]
pygame.draw.circle(screen, RED, robot_center, int(WIDTH / 2) - 2)
# 绘制机器人的可视范围
pygame.draw.rect(
screen, BLUE, [robot_center[0] - VIEWING_RANGE * (WIDTH + MARGIN), robot_center[1] - VIEWING_RANGE * (HEIGHT + MARGIN), 2 * VIEWING_RANGE * (WIDTH + MARGIN), 2 * VIEWING_RANGE * (HEIGHT + MARGIN)], 2)
# 限制帧率为20
clock.tick(20)
# 更新屏幕显示
pygame.display.flip()
# 关闭Pygame
pygame.quit()运行文件main.py后显示一个可视化网格图,可以通过单击鼠标来添加或删除障碍物。按下空格键将启动D* Lite路径规划算法,每次按下空格键机器人会重新扫描环境,如图8-3所示。当机器人到达目标点时,程序将结束。
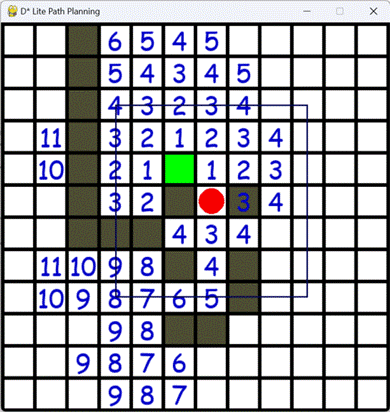
图8-3 执行效果