week8-8
二叉树的前序遍历:
cpp
void preOrder(treeNode* root) {
treeNode* cur=nullptr;
stack<treeNode*>st;
st.push(root);
while(!st.empty()){
cur=st.top();
st.pop();
cout<<cur->data<<" ";
if(cur->right){
st.push(cur->right);
}
if(cur->left){
st.push(cur->left);
}
}
}思路:先将root压栈,然后进入循环,对于每一次循环,输出当前栈顶元素,然后先压右孩子入栈,再压左孩子,因为栈先进后出嘛
中序遍历
核心思路
当前节点 = root
while 当前节点不为空 或者 栈不为空:
while 当前节点不为空:
将当前节点入栈
当前节点 = 当前节点.left
弹出栈顶 → visit(输出)
当前节点 = 栈顶.right
老是想不好要怎么写
cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int>res;
if(!root)return res;
stack<TreeNode*>st;
//st.push(root);
TreeNode* cur=root;
while (cur != nullptr || !st.empty()) {
// 一路向左
while (cur != nullptr) {
st.push(cur);
cur = cur->left;
}
// 弹栈访问
cur = st.top();
st.pop();
res.push_back(cur->val);
// 转向右子树
cur = cur->right;
}
return res;
}
};线索化二叉树的中序遍历(不是很会)
cpp
#include "solution.h"
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
ThreadedTreeNode* Solution::threaded(ThreadedTreeNode* root){
if(!root)return nullptr;
ThreadedTreeNode* cur=root;
stack<ThreadedTreeNode*>st;
vector<ThreadedTreeNode*>order;
while(cur||!st.empty()){
while(cur){
st.push(cur);
cur=cur->left;
}
cur=st.top();
order.push_back(cur);
st.pop();
cur=cur->right;
}
// 构建线索
for (int i = 0; i < (int)order.size(); ++i) {
ThreadedTreeNode* node = order[i];
if (!node->left) {
node->ltag = 1;
node->left = (i == 0 ? nullptr : order[i - 1]);
}
if (!node->right) {
node->rtag = 1;
node->right = (i == order.size() - 1 ? nullptr : order[i + 1]);
}
}
return root;
}
vector<int> Solution::inorderTraversal(ThreadedTreeNode* root){
vector<int> ans;
if (!root) return ans;
ThreadedTreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur && cur->ltag == 0) cur = cur->left;
while (cur) {
ans.push_back(cur->val);
if (cur->rtag == 1)
cur = cur->right;
else {
cur = cur->right;
while (cur && cur->ltag == 0)
cur = cur->left;
}
}
return ans;
}构建线索的时候i=0和i=n-1的细节要注意
遍历线索二叉树是重点
首先先得到第一个节点
之后以此开始按遇到的情况来讨论,进入循环后:
首先直接输出当前节点
之后看tag,如果rtag==1,说明这个右节点是之前已经遍历过的,直接输出就好
如果rtag==0,那么这个右节点就是不能马上输出的
要cur先变成右节点,然后不停的往left找,注意此时的条件是
while (cur && cur->ltag == 0)cur = cur->left;
这样才能干脆的找到下一个要输出的节点
W8-6计算前缀和
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m,n;
cin>>m>>n;
vector<vector<long long>>matrix(m+1,vector<long long >(n+1,0));
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
cin>>matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j]=matrix[i][j]+matrix[i][j-1]+matrix[i-1][j]-matrix[i-1][j-1];
}
}
int q;
cin>>q;
while(q--){
int l1,r1,l2,r2;
cin>>l1>>r1>>l2>>r2;
l1++;
r1++;
l2++;
r2++;
long long sum=matrix[r1][r2]-matrix[r1][l2-1]-matrix[l1-1][r2]+matrix[l1-1][l2-1];
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
}通过预处理的小技巧来算出前缀和
pre[i][j]=pre[i−1][j]+pre[i][j−1]−pre[i−1][j−1]+A[i][j]
w8-5左孩子右兄弟遍历
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int>f(n+1,-1);
vector<vector<int>>ch(n+1);
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
cin>>f[i];
ch[f[i]].push_back(i);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
sort(ch[i].begin(),ch[i].end());
}
queue<int>q;
q.push(1);
while(!q.empty()){
int cur=q.front();q.pop();
cout<<cur<<" ";
if(!ch[cur].empty()){
q.push(ch[cur][0]);
}
if(f[cur]!=-1){
int bro=-1;
for(unsigned int i=0;i<=ch[f[cur]].size();i++){
if(ch[f[cur]][i]>cur){
bro=ch[f[cur]][i];
break;
}
}
if(bro!=-1)q.push(bro);
}
}
}最长交错路径

cpp
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
//public:
// int maxlen=0;
// void dfs(TreeNode* root,int l,int r){
// if(!root)return;
// maxlen=max(maxlen,max(l,r));
// dfs(root->right,r+1,0);
// dfs(root->left,0,l+1);
// }
// int longestZigZag(TreeNode* root) {
// if(!root)return 0;
// dfs(root,0,0);
// return maxlen;
// }
int ans=0;
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int dir,int dis){//(当前结点,左/右孩子,路径长度)
if(!root)return;//空结点返回
ans=max(ans,dis);//更新最大值
if(dir){//如果当前结点是其父结点的右孩子
dfs(root->left,0,dis+1);//搜索其左孩子时,满足ZigZig,路径长度+1
dfs(root->right,1,1);//搜索其右孩子时,不满足ZigZig,路径长度置为1
}
else{//如果当前结点是其父结点的左孩子
dfs(root->left,0,1);//搜索其左孩子时,不满足ZigZig,路径长度置为1
dfs(root->right,1,dis+1);//搜索其右孩子时,满足ZigZig,路径长度+1
}
}
public:
int longestZigZag(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root->left,0,1);//0左节点
dfs(root->right,1,1);//1右结点
return ans;
}
};w8-9 逐层删除二叉树叶子节点
思路就是按高度来划分分组
cpp
int dfs(TreeNode* root ,vector<vector<int>>&res){
if(!root)return -1;
int l=dfs(root->left,res);
int r=dfs(root->right,res);
int height=max(l,r)+1;
if (res.size() <= height)
res.push_back({});
res[height].push_back(root->val);
return height;
}
vector<vector<int>> findLeaves(TreeNode* root){
vector<vector<int>> res;
dfs(root,res);
return res;
}小根堆(Min Heap)的定义:
小根堆是一种完全二叉树 ,并且满足下面的堆序性质:
任意一个节点的值 ≤ 它的左右孩子节点的值
也就是说:
-
堆顶(根节点)是整个堆中最小的元素
-
每个父节点都不大于它的子节点
cpp#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<queue> using namespace std; int main(){ int t; cin>>t; while(t--){ int n; cin>>n; vector<int>heap(n); for(int i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>heap[i]; queue<int>q; q.push(0); bool isp=true; while(!q.empty()){ int cur=q.front(); q.pop(); int l=2*cur+1; int r=2*cur+2; if(l<n){ if(heap[cur]>heap[l]){ isp=false; break; } else q.push(l); } if(r<n){ if(heap[cur]>heap[r]){ isp=false; break; } else q.push(r); } } if(isp)cout<<"YES"<<endl; else cout<<"NO"<<endl; } }
W9-3 哈夫曼树
哈夫曼树是一棵"越重要(权值越大)的叶子,离根越近"的二叉树
思路:用一个优先级队列存储哈夫曼树里面的元素(最小的在前面),每次取两个出来,然后创建一个新的节点,权重等于二者相加,这个玩意作为根节点,再放进优先级队列
W10-4 最大对称子二叉树
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
vector<int> weight;
vector<pair<int,int>> child;
int n;
int ans=1;
bool ismirror(int a,int b){
//cout<<111<<endl;
queue<int>qa;
queue<int>qb;
qa.push(a);
qb.push(b);
while(!qa.empty()&&!qb.empty()){
int ca=qa.front();qa.pop();
int cb=qb.front();qb.pop();
if (ca == -1 && cb == -1) continue;
if (ca == -1 || cb == -1) return false;
if (weight[ca] != weight[cb]) return false;
qa.push(child[ca].first);
qa.push(child[ca].second);
qb.push(child[cb].second);
qb.push(child[cb].first);
}
if(qa.empty()&&qb.empty())return true;
else return false;
}
int count(int a){
queue<int>q;
q.push(a);
int cnt=0;
while(!q.empty()){
int cur=q.front();
q.pop();
if(cur!=-1)cnt++;
else continue;
q.push(child[cur].first);
q.push(child[cur].second);
}
return cnt;
}
void max_mirror(int root){
if(root==-1)return;
if(ismirror(child[root].first,child[root].second)){
//cout<<root<<endl;
ans=max(count(root),ans);
return;
}
else{
max_mirror(child[root].first);
max_mirror(child[root].second);
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
weight.resize(n+1);
child.resize(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>weight[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>child[i].first>>child[i].second;
}
max_mirror(1);
//cout<<111<<endl;
cout<<ans;
}犯了两个致命的错误:
1、不明晰对称二叉树的定义:以根节点为轴两边对称的就是对称二叉树,子树不需要对称,被题目误导了
2、没有去关心越界的问题,这里有根节点为权值为-1的情况,导致数组下标越界,这点老是没注意
W11-1 删木成林
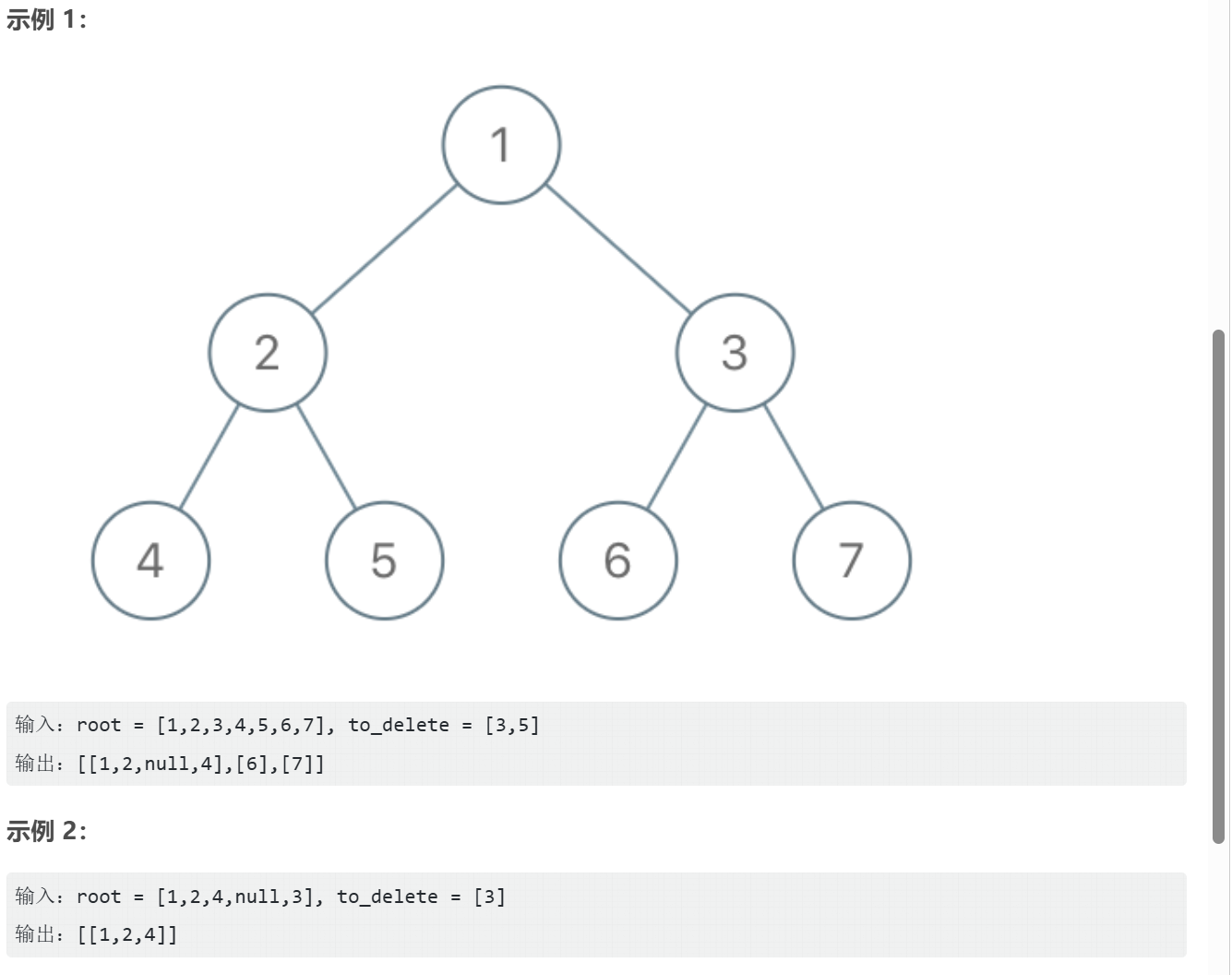
cpp
#include "tree.h"
#include<algorithm>
vector<TreeNode*> ans;
unordered_set<int> del;
TreeNode* dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root){
return nullptr;
}
root->left=dfs(root->left);
root->right=dfs(root->right);
if(del.count(root->val)){
if (root->left) ans.push_back(root->left);
if (root->right) ans.push_back(root->right);
return nullptr;//!!!!!!
}
return root;
}
bool cmp(TreeNode* a,TreeNode* b){
return a->val<b->val;
}
vector<TreeNode*> solve(TreeNode* root, const vector<int>& to_delete) {
for(auto p:to_delete){
del.insert(p);
}
root=dfs(root);
if(root)ans.push_back(root);//!!!!!!
sort(ans.begin(),ans.end(),cmp);
return ans;
}有两个点是要注意的
1、删掉某个点之后要妥善处理它的儿子女儿
同时这个点已经置为了nullptr,因此返回的要是nullptr
2、根节点特殊处理
W11-2 合并多棵二叉搜索树

cpp
#include "tree.h"
#include<algorithm>
#include<climits>
unordered_map<int,TreeNode*>treemap;
unordered_set<int>treeset;
void insertT(TreeNode* root,vector<TreeNode*>&trees){
queue<TreeNode*>q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
TreeNode* cur=q.front();q.pop();
if(cur->left){
if(treemap[cur->left->val]){
cur->left=treemap[cur->left->val];
}
q.push(cur->left);
}
if(cur->right){
if(treemap[cur->right->val]){
cur->right=treemap[cur->right->val];
}
q.push(cur->right);
}
}
}
TreeNode* canMerge(vector<TreeNode*>& trees) {
treemap.clear();
treeset.clear();
for(auto t:trees){
treemap.insert({t->val,t});
treeset.insert(t->val);
}
//找到不能当儿子,只能当爹的节点
for(auto t:trees){
if(t->left){
treeset.erase(t->left->val);
}
if(t->right){
treeset.erase(t->right->val);
}
}
int num=treeset.size();
if(num>=2)return nullptr;
TreeNode* root=nullptr;
for(auto p:treeset){
root=treemap[p];
break;
}
insertT(root,trees);
return root;
}关键的关键:
找到最顶上的根节点
最大生成森林

cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Unionset{
public:
vector<int>parent;
vector<int>size;
Unionset(int n){
parent.resize(n);
size.resize(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
parent[i]=i;
size[i]=1;
}
}
int find(int x){
if(parent[x]==x)return x;
else return parent[x]=find(parent[x]);
}
void unite(int x,int y){
int rx=find(x),ry=find(y);
if(rx==ry)return ;
if(size[rx]>size[ry]){
parent[ry]=rx;
}
else if(size[rx]<size[ry]){
parent[rx]=ry;
}
else{
parent[rx]=ry;
size[ry]++;
}
}
};
struct Edge {
int u, v, w;
};
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<Edge> edges(m);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> edges[i].u >> edges[i].v >> edges[i].w;
}
// 按权值从大到小排序(最大生成树)
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end(), [](const Edge &a, const Edge &b){
return a.w > b.w;
});
Unionset uf(n);
long long total=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
if(uf.find(edges[i].u)!=uf.find(edges[i].v)){
uf.unite(edges[i].u,edges[i].v);
total+=edges[i].w;
}
//uf.unite(edges[i].u,edges[i].v);
}
cout<<total<<endl;
}
}给定一个无向图 G,它可能是一个非连通图的,你的任务是找到最大生成森林
理解:既然是无向图,又是森林,必然想到的是并查集
首先对于一连通的树,从哪个节点开始生成最大树是无所谓的,因为这个树必然会连接这个连通分量的所有节点
那么就先对所有的边的权值进行排序,排完序再每次取最大的进行生成,并且用并查集来连接
快速排序
cpp
void mysort(vector<int>&a,int l,int r){
if (l >= r) return;
int pivot = a[l];
int i = l, j = r;
while (i <= j) {
while (a[i] < pivot) i++;
while (a[j] > pivot) j--;
if (i <= j) {
swap(a[i], a[j]);
i++;
j--;
}
}
if (l < j) mysort(a,l,j);
if (i < r) mysort(a,i,r);
}
cpp
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
vector<vector<int>>g(n);
vector<int>degin(n,0);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
g[a].push_back(b);
degin[b]++;
}
queue<int>q;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(degin[i]==0){
q.push(i);
}
}
while(!q.empty()){
int cur=q.front();
q.pop();
for(auto p:g[cur]){
degin[p]--;
if(degin[p]==0){
q.push(p);
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(degin[i]!=0){
cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
}求第n位数字(梦魇来了孩子)
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int func1(long long n) {
long long standnumber = 1;
long long standnextnumber = 10;
long long standstr = 0;
long long standnextstr = 9;
int slen = 1;
while (standnextstr < n) {
standstr = standnextstr;
standnumber = standnextnumber;
standnextnumber *= 10;
slen++;
standnextstr += (standnextnumber - standnumber) * slen;
}
long long num = (n - standstr - 1) / slen + standnumber;
int numsite=(n-standstr-1)%slen;
for(int i=0;i<slen-numsite-1;i++){
num/=10;
}
return num%10;
}
int main() {
long long n;
cin >> n;
cout << func1(n) << endl;
return 0;
}最近公共祖先
cpp
TreeNode* lcr(int p,int q,TreeNode* root){
if(!root)return nullptr;
if(root->val==p||root->val==q){
return root;
}
TreeNode* l=lcr(p,q,root->left);
TreeNode* r=lcr(p,q,root->right);
if(l&&r)return root;
else return l?l:r;
}DAG松弛关键路径关键实践拿下
cpp
#include<queue>
#include<climits>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
vector<vector<int>>g(n+1);
vector<int>degin(n+1,0);
vector<int>time(n+1,0);
vector<int>realtime(n+1,0);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>time[i];
realtime[i]=time[i];
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
g[u].push_back(v);
degin[v]++;
}
queue<int>q;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(degin[i]==0){
q.push(i);
}
}
while(!q.empty()){
int cur=q.front();q.pop();
for(auto p:g[cur]){
realtime[p]=max(realtime[cur]+time[p],realtime[p]);
degin[p]--;
if(degin[p]==0)q.push(p);
}
}
int max=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(max<realtime[i])max=realtime[i];
}
cout<<max;
}