本系列介绍增强现代智能体系统可靠性的设计模式,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。本系列一共 14 篇文章,这是第 13 篇。原文:Building the 14 Key Pillars of Agentic AI[1]
优化智能体解决方案需要软件工程确保组件协调、并行运行并与系统高效交互。例如预测执行[2],会尝试处理可预测查询以降低时延 ,或者进行冗余执行[3],即对同一智能体重复执行多次以防单点故障。其他增强现代智能体系统可靠性的模式包括:
- 并行工具:智能体同时执行独立 API 调用以隐藏 I/O 时延。
- 层级智能体:管理者将任务拆分为由执行智能体处理的小步骤。
- 竞争性智能体组合:多个智能体提出答案,系统选出最佳。
- 冗余执行:即两个或多个智能体解决同一任务以检测错误并提高可靠性。
- 并行检索和混合检索:多种检索策略协同运行以提升上下文质量。
- 多跳检索:智能体通过迭代检索步骤收集更深入、更相关的信息。
还有很多其他模式。
本系列将实现最常用智能体模式背后的基础概念,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。
所有理论和代码都在 GitHub 仓库里:🤖 Agentic Parallelism: A Practical Guide 🚀[4]
代码库组织如下:
agentic-parallelism/
├── 01_parallel_tool_use.ipynb
├── 02_parallel_hypothesis.ipynb
...
├── 06_competitive_agent_ensembles.ipynb
├── 07_agent_assembly_line.ipynb
├── 08_decentralized_blackboard.ipynb
...
├── 13_parallel_context_preprocessing.ipynb
└── 14_parallel_multi_hop_retrieval.ipynb并行上下文预处理以提升准确度
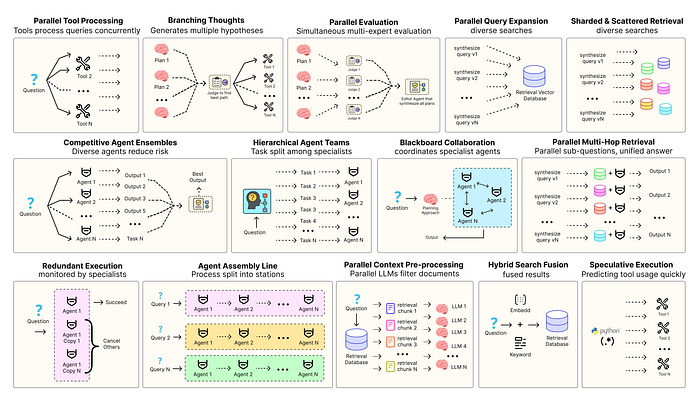
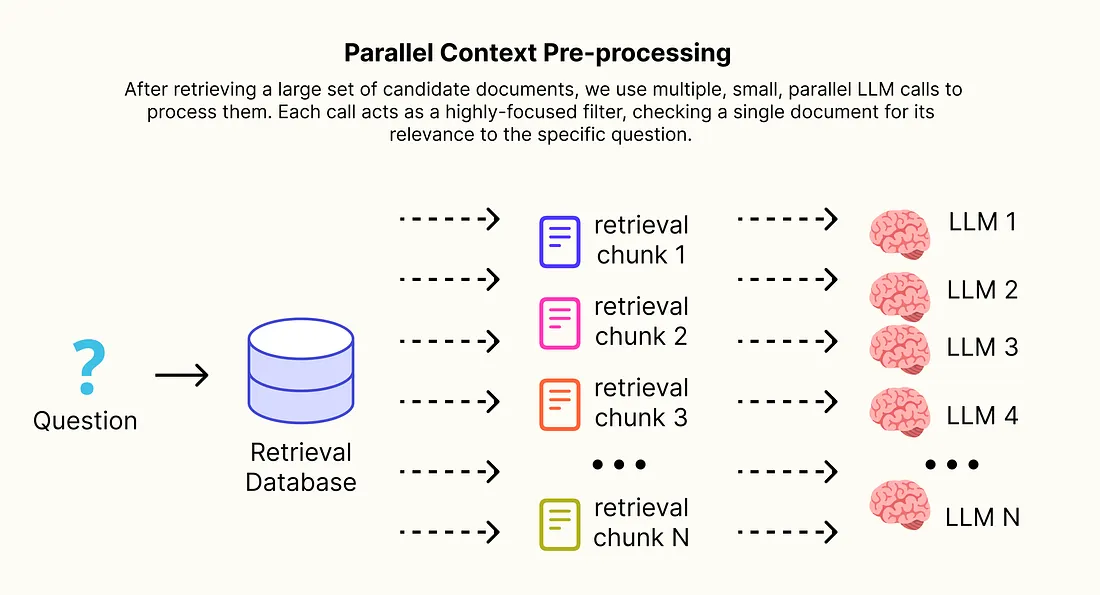
之前探索的 RAG 模式主要集中于改进初始检索步骤,以找到更多正确文档。而并行上下文预处理则关注检索之后发生的事情,最大化召回率的一个常见策略是检索大量候选文档(k=10 或更多)。
然而,将大量且通常嘈杂的文档集合直接输入到最终生成器 LLM 的上下文窗口中是有问题的。
 并行上下文处理
并行上下文处理
速度很慢,而且成本很高(由于需要更多 token),并且实际上无关信息会淹没模型从而损害准确性,即发生"中间丢失"问题。
解决方案是引入中间的"蒸馏"步骤。在检索到大量候选文档后,使用多个、小型的并行 LLM 调用来处理。每个调用作为一个高度专注的过滤器,检查单个文档与其和特定问题的相关性。只有通过这个检查的文档才会被包含在最终、经过"蒸馏"的上下文中,该上下文将被发送到主生成器。
我们将构建并比较两个 RAG 系统,一个使用大型原始上下文,另一个使用并行预处理步骤,以展示可衡量的改进。
首先定义结构化并行"蒸馏器"代理输出的 Pydantic 模型。
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
class RelevancyCheck(BaseModel):
"""蒸馏/过滤的结构化输出 Pydantic 模型"""
# 对文档相关性进行明确的二元决策。
is_relevant: bool = Field(description="True if the document contains information that directly helps answer the question.")
# 对该决定的简明解释
brief_explanation: str = Field(description="A one-sentence explanation of why the document is or is not relevant.")RelevancyCheck 模式是蒸馏器代理的合约。通过强制每个并行调用返回 is_relevant 布尔值,创建了一个快速可靠的过滤机制。brief_explanation 对于调试和理解文档被包含或排除的原因非常有价值。
接下来定义 GraphState 和高级系统的核心节点:distill_context_node。该节点将协调并行预处理。
from typing import TypedDict, List
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
class RAGGraphState(TypedDict):
question: str
raw_docs: List[Document]
distilled_docs: List[Document]
final_answer: str
# 针对每个文档并行运行的链
distiller_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Given the user's question, determine if the following document is relevant for answering it. "
"Provide a brief explanation.\n\n"
"Question: {question}\n\nDocument:\n{document}"
)
distiller_chain = distiller_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(RelevancyCheck)
def distill_context_node(state: RAGGraphState):
"""该模式的核心:并行扫描所有检索到的文档,以过滤相关性"""
print(f"--- [Distiller] Pre-processing {len(state['raw_docs'])} raw documents in parallel... ---")
relevant_docs = []
# 通过 ThreadPoolExecutor 在每个文档上并发运行 'distiller_chain'
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=5) as executor:
# 为每个要检查的文档创建一个future
future_to_doc = {executor.submit(distiller_chain.invoke, {"question": state['question'], "document": doc.page_content}): doc for doc in state['raw_docs']}
for future in as_completed(future_to_doc):
doc = future_to_doc[future]
try:
result = future.result()
# 如果蒸馏剂将文件标记为相关的,就保留
if result.is_relevant:
print(f" - Doc '{doc.metadata['source']}' IS relevant. Reason: {result.brief_explanation}")
relevant_docs.append(doc)
else:
# 否则就丢弃
print(f" - Doc '{doc.metadata['source']}' is NOT relevant. Reason: {result.brief_explanation}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing doc {doc.metadata['source']}: {e}")
print(f"--- [Distiller] Distilled context down to {len(relevant_docs)} documents. ---")
return {"distilled_docs": relevant_docs}distill_context_node 是"质量控制"节点,在高召回率的检索步骤中获取大量 raw_docs 后,这个节点充当过滤器,利用 ThreadPoolExecutor 将工作分散,将每个文档发送到各自的小型独立 LLM。
这种并行处理至关重要,这意味着提炼 10 份文档的时间大致与提炼一份文档的时间相同。该节点随后只收集被认为符合 is_relevant 标准的文档,为最终生成器产生一个更小、更干净、更有力的 distilled_docs 列表。
然后组装完整的图,将新的 distill 节点放置在 retrieve 和 generate 步骤之间。
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
workflow = StateGraph(RAGGraphState)
# 给流水线添加三个节点
workflow.add_node("retrieve", retrieval_node)
workflow.add_node("distill", distill_context_node)
workflow.add_node("generate", generation_node)
# 定义线性工作流:检索->提取->生成
workflow.set_entry_point("retrieve")
workflow.add_edge("retrieve", "distill")
workflow.add_edge("distill", "generate")
workflow.add_edge("generate", END)
advanced_rag_app = workflow.compile() 并行上下文预处理
并行上下文预处理
进行最终的直接对比分析,对同一查询运行简单(大上下文)和高级(蒸馏上下文)的 RAG 系统,并仔细比较两者的准确性、时延和 token 开销。
import tiktoken
def count_tokens(text: str) -> int:
"""为成本分析计算令牌的辅助函数"""
encoding = tiktoken.get_encoding("cl100k_base")
return len(encoding.encode(text))
# --- 分析设置 ---
context_tokens_simple = count_tokens(context_simple)
context_tokens_advanced = count_tokens(context_advanced)
token_improvement = (context_tokens_simple - context_tokens_advanced) / context_tokens_simple * 100
latency_improvement = (gen_time_simple - gen_time_advanced) / gen_time_simple * 100
# --- 打印结果 ---
print("="*60)
print(" ACCURACY & QUALITY ANALYSIS")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print("**Simple RAG's Answer (from Large, Noisy Context):**")
print(f'"{simple_answer}"\n')
print("**Advanced RAG's Answer (from Distilled, Focused Context):**")
print(f'"{advanced_answer}"\n')
print("="*60)
print(" LATENCY & COST (TOKEN) ANALYSIS")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print("| Metric | Simple RAG (Large Context) | Advanced RAG (Distilled Context) | Improvement |")
print("|-----------------------------|----------------------------|----------------------------------|-------------|")
print(f"| Context Size (Tokens) | {context_tokens_simple:<26} | {context_tokens_advanced:<32} | **-{token_improvement:.0f}%** |")
print(f"| Final Generation Time | {gen_time_simple:<24.2f} seconds | {gen_time_advanced:<32.2f} seconds | **-{latency_improvement:.0f}%** |")分析结果如下......
#### 输出 ####
============================================================
ACCURACY & QUALITY ANALYSIS
============================================================
**Simple RAG Answer (from Large, Noisy Context):**
"Based on the context, a power supply unit of at least 1200W is recommended for the QLeap-V4 processor. The QLeap-V3 chip had a recommended power supply of 800W."
**Advanced RAG Answer (from Distilled, Focused Context):**
"Based on the provided context, a power supply unit of at least 1200W is recommended for the QLeap-V4 processor."
**Analysis:** The Simple RAG answer, while technically correct, includes irrelevant information about the previous generation product (QLeap-V3). This happened because the large, noisy context included documents about both products. The Advanced RAG answer is **more accurate and precise**. The parallel distillation step correctly filtered out the irrelevant document about the QLeap-V3, providing a clean, focused context to the generator, which then produced a perfect, concise answer.
============================================================
LATENCY & COST (TOKEN) ANALYSIS
============================================================
| Metric | Simple RAG (Large Context) | Advanced RAG (Distilled Context) | Improvement |
|-----------------------------|----------------------------|----------------------------------|-------------|
| Context Size (Tokens) | 284 | 29 | **-90%** |
| Final Generation Time | 7.89 seconds | 2.15 seconds | **-73%** |最终分析提供了清晰的、数据驱动的结论,并行上下文预处理模式带来了三重显著改进。
- 更高的准确性:定性分析显示,高级系统产出了更精确和集中的答案。通过过滤掉关于旧版"QLeap-V3"的干扰性文档,蒸馏步骤防止了最终生成器包含不相关信息,直接提升了答案质量。
- 更低的成本:显著减少了 token 开销,输入到最终、昂贵的生成器的上下文减少了 90%。在一个处理数百万查询的生产系统中,直接转化为在 LLM 推理上的显著成本节约。
- 降低延迟:上下文大小的减少直接影响了最终生成步骤的性能,使其速度提高了 73%。虽然蒸馏步骤本身会增加一些开销,但通常这些开销会被最终计算最密集步骤的节省所抵消,从而使用户总体响应时间更快。
Hi,我是俞凡,一名兼具技术深度与管理视野的技术管理者。曾就职于 Motorola,现任职于 Mavenir,多年带领技术团队,聚焦后端架构与云原生,持续关注 AI 等前沿方向,也关注人的成长,笃信持续学习的力量。在这里,我会分享技术实践与思考。欢迎关注公众号「DeepNoMind」,星标不迷路。也欢迎访问独立站 www.DeepNoMind.com[5],一起交流成长。
参考资料 [1]
Building the 14 Key Pillars of Agentic AI: https://levelup.gitconnected.com/building-the-14-key-pillars-of-agentic-ai-229e50f65986
2
预测执行: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speculative_execution
3
4
🤖 Agentic Parallelism: A Practical Guide 🚀: https://github.com/FareedKhan-dev/agentic-parallelism
5
www.DeepNoMind.com: https://www.deepnomind.com
本文由mdnice多平台发布