目录
一.栈
1.系统栈

数据结构中的栈:
只允许从一端进行数据的插入和删除的线性存储结构,称之为栈结构
特点:先进后出: FILO
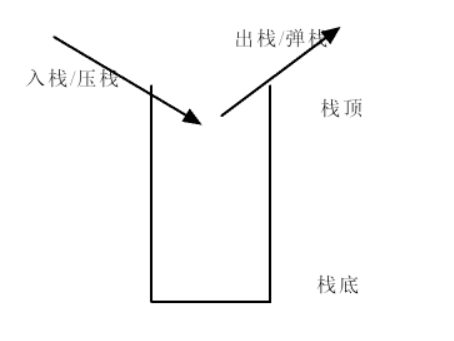
2.顺序表(数组)---》顺序栈
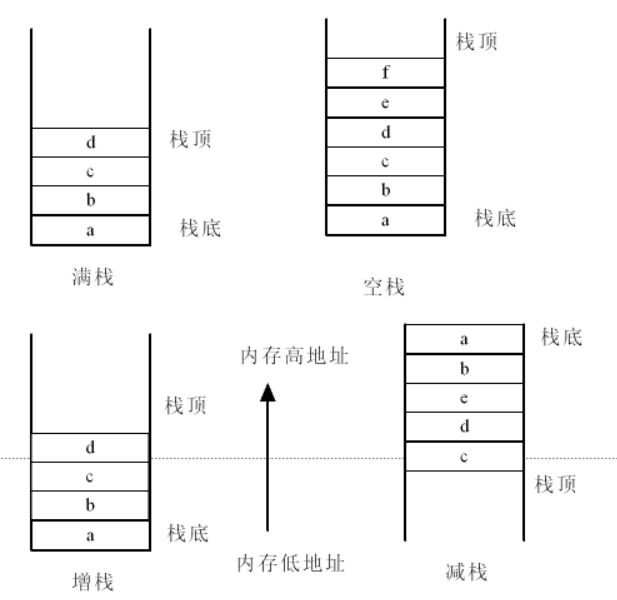
满增栈、满减栈、空增栈、空减栈
满栈、空栈:栈顶所在位置是否存在数据
增栈、减栈:按照栈的生长方向区分
3.链式栈:
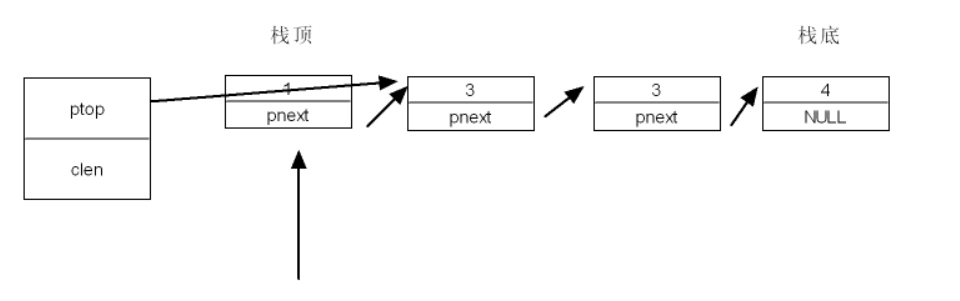
头文件
cpp
#ifndef __STACK_H__
#define __STACK_H__
typedef int Data_type_t;
typedef struct stnode
{
Data_type_t data;
struct stnode *pnext;
} STNode_t;
typedef struct stack
{
STNode_t *ptop;
int clen;
} Stack_t;
Stack_t *create_stack();
int is_empty_stack(Stack_t *pstack);
int push_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t data);
int pop_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t *pdata);
void stack_for_each(Stack_t *pstack);
int get_top_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t *pdata);
void destroy_stack(Stack_t **ppstack);
#endif创建链表
cpp
Stack_t *create_stack()
{
Stack_t *pstack = malloc(sizeof(Stack_t));
if (pstack == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
pstack->ptop = NULL;
pstack->clen = 0;
return pstack;
}入栈(压栈)
cpp
int push_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t data)
{
STNode_t *pnode = malloc(sizeof(STNode_t));
if (pnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return -1;
}
pnode->pnext = NULL;
pnode->data = data;
pnode->pnext = pstack->ptop;
pstack->ptop = pnode;
pstack->clen++;
}出栈(弹栈)
cpp
int pop_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t *pdata)
{
if (pstack->ptop == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
STNode_t *ptemp = pstack->ptop;
pstack->ptop = ptemp->pnext;
if (pdata != NULL)
{
*pdata = ptemp->data;
}
free(ptemp);
pstack->clen--;
return 0;
}
}获取栈顶元素
cpp
int get_top_stack(Stack_t *pstack, Data_type_t *pdata)
{
if (NULL == pstack->ptop)
{
return -1;
}
if (NULL == pdata)
{
return -1;
}
*pdata = pstack->ptop->data;
return 0;
}遍历
cpp
void stack_for_each(Stack_t *pstack)
{
STNode_t *ptemp = pstack->ptop;
while (ptemp != NULL)
{
printf("%d", ptemp->data);
ptemp = ptemp->pnext;
}
printf("\n");
}销毁链式栈
cpp
void destroy_stack(Stack_t **ppstack)
{
while (!is_empty_stack(*ppstack))
{
pop_stack(*ppstack, NULL);
}
free(*ppstack);
*ppstack = NULL;
}主函数
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "stack.h"
int main(void)
{
Data_type_t data;
Stack_t* pstack = create_stack();
if (NULL == pstack)
{
return -1;
}
push_stack(pstack, 0);
push_stack(pstack, 1);
push_stack(pstack, 2);
push_stack(pstack, 3);
push_stack(pstack, 4);
stack_for_each(pstack);
int ret = pop_stack(pstack, &data);
if (ret == 0)
{
printf("data = %d\n", data);
}
stack_for_each(pstack);
ret = get_top_stack(pstack, &data);
if (0 == ret)
{
printf("top : %d\n", data);
}
destroy_stack(&pstack);
}二.队列
允许从一端进行数据的插入,另一端进行数据的删除的线性存储结构,称为队列结构。
插入操作:入队操作,插入这端称为队列的队尾。
删除操作:出队操作,删除这端称为队列的队头。
特点:先进先出(FIFO)
应用:数据缓存
1.顺序队列
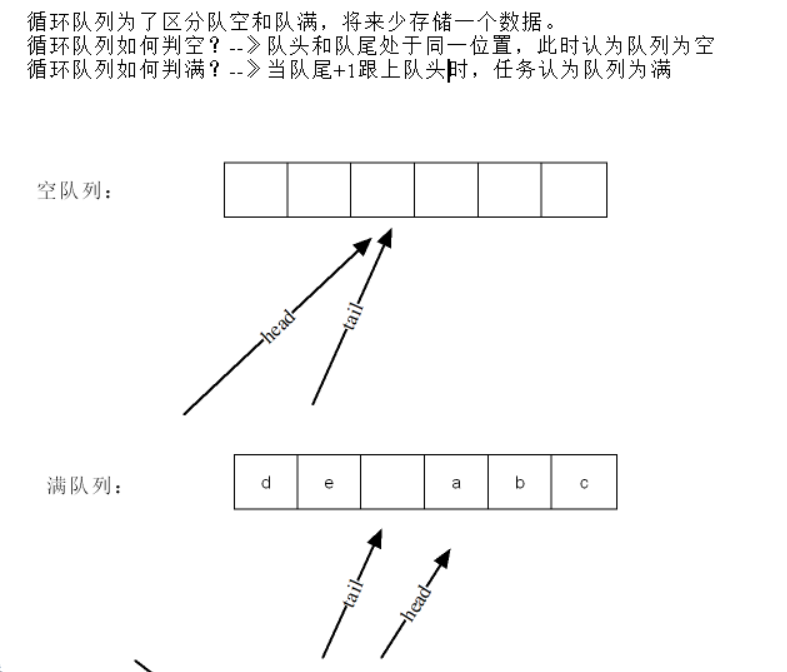
顺序表---->顺序队列---->假溢出问题---->循环队列
判空:队头,队尾处于同一位置
判满:当队尾+1跟上队头时
循环队列为了区分队空和队满,将少存储一个数据
2.链式队列
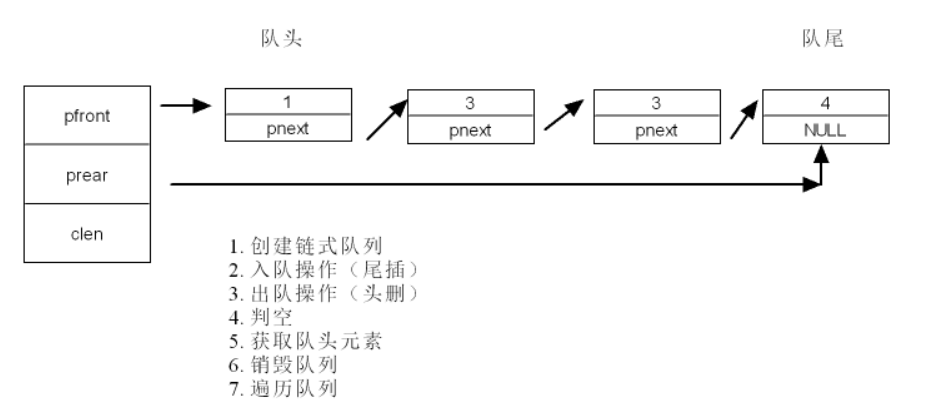
头文件
cpp
#ifndef __LQUEUE_H__
#define __LQUEUE_H__
typedef int Data_type_t;
typedef struct lqnode
{
Data_type_t data;
struct lqnode *pnext;
}LQNode_t;
typedef struct lqueue
{
LQNode_t *phead;
LQNode_t *ptail;
int clen;
}LQueue_t;
extern LQueue_t *create_link_queue();
extern void link_queue_for_each(LQueue_t *plq);
extern int push_link_queue(LQueue_t *plq, Data_type_t data);
extern int is_empty_link_queue(LQueue_t *plq);
extern int pop_link_queue(LQueue_t *plq, Data_type_t *pdata);
extern void destroy_link_queue(LQueue_t **pplq);
extern int get_queue_head(LQueue_t *plq, Data_type_t *pdata);
#endif创建队列
cpp
LQueue_t* create_lqueue()
{
LQueue_t* plqueue = malloc(sizeof(LQueue_t));
if (NULL == plqueue)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
plqueue->phead = NULL;
plqueue->ptail = NULL;
plqueue->clen = 0;
return plqueue;
}入队
cpp
int in_plqueue_tail(LQueue_t* plqueue, Data_type_t data)
{
LQNode_t* pnode = malloc(sizeof(LQNode_t));
if (pnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return -1;
}
pnode->pnext = NULL;
pnode->data = data;
if (is_empty_plqueue(plqueue))
{
plqueue->phead = pnode;
plqueue->ptail = pnode;
plqueue->clen++;
}
else
{
plqueue->ptail->pnext = pnode;
plqueue->ptail = pnode;
plqueue->clen++;
}
return 0;
}出队
cpp
int out_plqueue_head(LQueue_t* plqueue)
{
LQNode_t* ptemp = plqueue->phead;
if (is_empty_plqueue(plqueue))
{
return -1;
}
if (plqueue->phead == plqueue->ptail)
{
free(ptemp);
plqueue->phead = NULL;
plqueue->ptail = NULL;
plqueue->clen--;
}
else
{
plqueue->phead = ptemp->pnext;
free(ptemp);
plqueue->clen--;
}
}获取队头元素
cpp
int get_top_plqueue(LQueue_t* plqueue, Data_type_t* data)
{
if (is_empty_plqueue(plqueue))
{
return -1;
}
*data = plqueue->phead->data;
return 0;
}遍历
cpp
int plqueue_for_each(LQueue_t* plqueue)
{
LQNode_t* ptemp = plqueue->phead;
if (is_empty_plqueue(plqueue))
{
return -1;
}
while (ptemp != NULL)
{
printf("%2d", ptemp->data);
ptemp = ptemp->pnext;
}
printf("\n");
}销毁队列
cpp
int destory_plqueue(LQueue_t** pplqueue)
{
while (!is_empty_plqueue(*pplqueue))
{
out_plqueue_head(*pplqueue);
}
free(*pplqueue);
*pplqueue = NULL;
}主函数
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include "lqueue.h"
int main(void)
{
LQueue_t* plqueue = create_lqueue();
if (plqueue == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
in_plqueue_tail(plqueue, 0);
in_plqueue_tail(plqueue, 1);
in_plqueue_tail(plqueue, 2);
in_plqueue_tail(plqueue, 3);
in_plqueue_tail(plqueue, 4);
out_plqueue_head(plqueue);
plqueue_for_each(plqueue);
Data_type_t data;
int ret = get_top_plqueue(plqueue, &data);
if (ret == 0)
{
printf("top = %d\n", data);
}
destory_plqueue(&plqueue);
}3.循环队列
头文件
cpp
#ifndef __SEQQUE_H_
#define __SEQQUE_H_
#define SEQQUE_MAX_LEN 10
typedef int Data_type_t;
typedef struct seqque
{
Data_type_t *pbase;
int head;
int tail;
} Seqque_t;
extern Seqque_t *create_seqque();
extern int is_full_seqque(Seqque_t *psq);
extern int is_empty_seqque(Seqque_t *psq);
extern int push_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t data);
extern void seqque_for_each(Seqque_t *psq);
extern int out_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *data);
extern int get_head_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *data);
extern void destory_seqque(Seqque_t **psq);
#endif创建队列
cpp
Seqque_t *create_seqque()
{
Seqque_t *psq = malloc(sizeof(Seqque_t));
if (NULL == psq)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
psq->head = 0;
psq->tail = 0;
psq->pbase = malloc(sizeof(Data_type_t) * SEQQUE_MAX_LEN);
if (NULL == psq->pbase)
{
printf("malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
return psq;
}判空
cpp
int is_empty_seqque(Seqque_t *psq)
{
if (psq->head == psq->tail)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}判满
cpp
int is_full_seqque(Seqque_t *psq)
{
if ((psq->tail + 1) % SEQQUE_MAX_LEN == psq->head)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}入队
cpp
int push_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t data)
{
if (is_full_seqque(psq))
{
printf("seqque is full\n");
return -1;
}
psq->pbase[psq->tail] = data;
psq->tail = (psq->tail + 1) % SEQQUE_MAX_LEN;
return 0;
}出队
cpp
int out_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *data)
{
if (is_empty_seqque(psq) || NULL == data)
{
printf("seqque is empty\n");
return -1;
}
*data = psq->pbase[psq->head];
psq->head = (psq->head + 1) % SEQQUE_MAX_LEN;
return 0;
}遍历
cpp
void seqque_for_each(Seqque_t *psq)
{
for (int i = psq->head; i != psq->tail; i = (i + 1) % SEQQUE_MAX_LEN)
{
printf("%d ", psq->pbase[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}获取队头元素
cpp
int get_head_seqque(Seqque_t *psq, Data_type_t *data)
{
if (is_empty_seqque(psq) || NULL == data)
{
printf("seqque is empty\n");
return -1;
}
*data = psq->pbase[psq->head];
}销毁队列
cpp
void destory_seqque(Seqque_t **psq)
{
free((*psq)->pbase);
free(*psq);
*psq = NULL;
}主函数
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include "seqque.h"
int main(void)
{
Seqque_t *psq = create_seqque();
if (NULL == psq)
{
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
push_seqque(psq, i);
}
Data_type_t data;
seqque_for_each(psq);
out_seqque(psq, &data);
if (out_seqque(psq, &data) == 0)
{
printf("%d\n", data);
}
seqque_for_each(psq);
destory_seqque(&psq);
return 0;
}