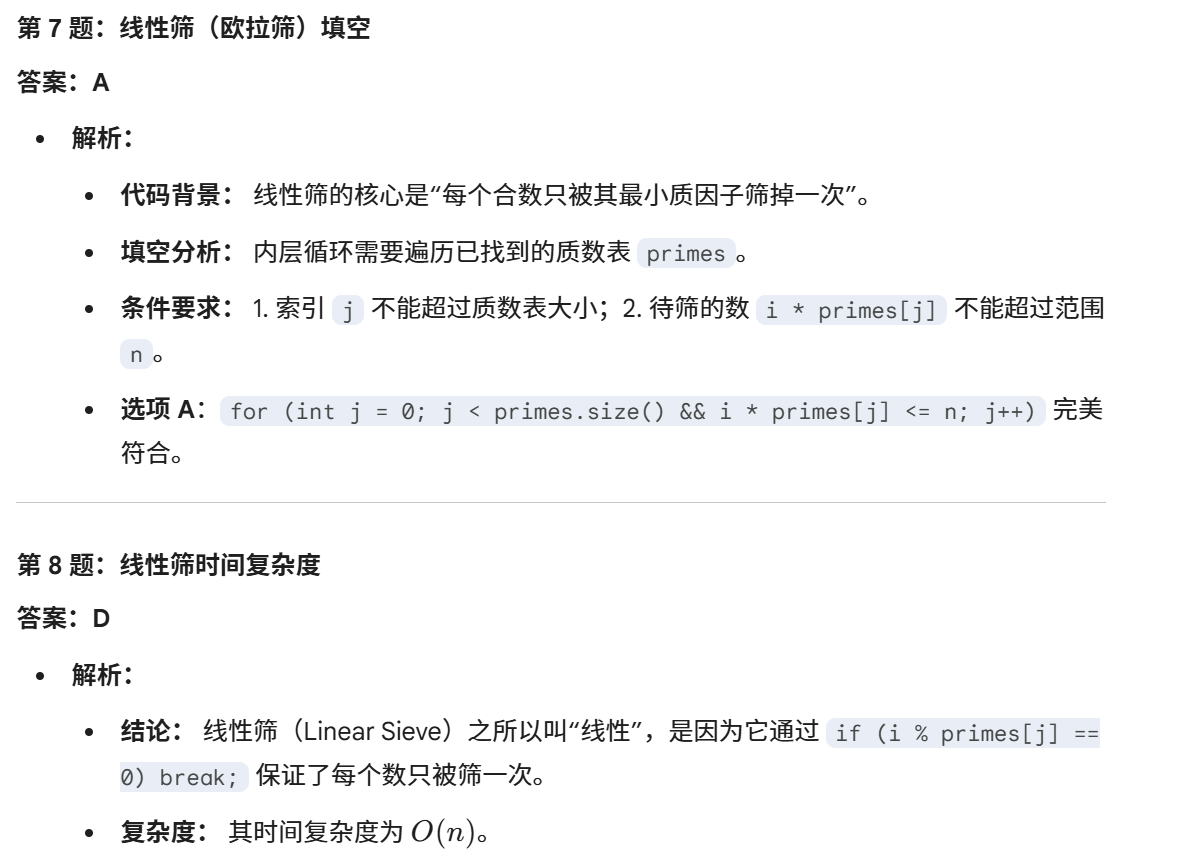
选择题








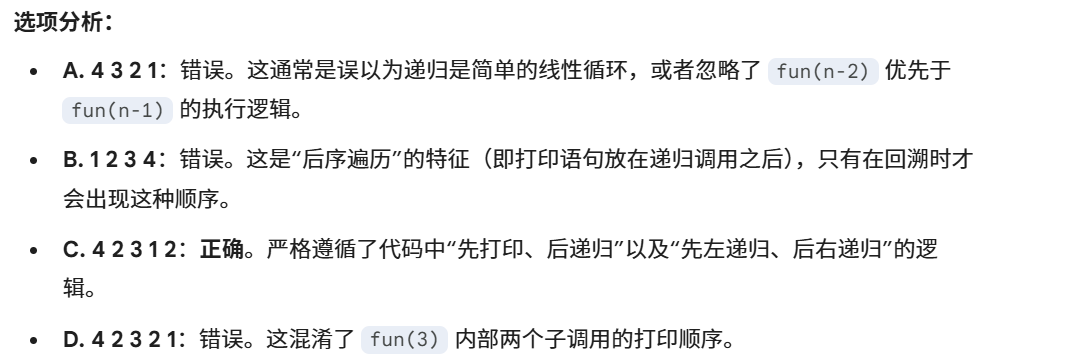
判断题






编程题
1. 黑白格

C++代码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// 根据数据范围 n, m <= 100,给定略大的常量
const int N = 110;
const int INF = 1e9;
int n, m, k;
int s[N][N]; // s[i][j] 表示第 j 列前 i 行黑格子的数量(列前缀和)
int main() {
// 优化输入效率(可选)
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
if (!(cin >> n >> m >> k)) return 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
string row;
cin >> row;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
int val = (row[j - 1] == '1' ? 1 : 0);
s[i][j] = s[i - 1][j] + val; // 预处理列前缀和
}
}
int ans = INF;
bool found = false;
// 枚举子矩形的上边界 i 和下边界 j
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j <= n; j++) {
int height = j - i + 1;
// 使用双指针(滑动窗口)维护列边界 l 和 r
int sum = 0;
for (int l = 1, r = 1; r <= m; r++) {
sum += (s[j][r] - s[i - 1][r]); // 累加当前列在 [i, j] 行区间内的黑格子数
// 当黑格子总数 >= k 时,尝试收缩左边界 l 以减小面积
while (sum >= k) {
found = true;
ans = min(ans, height * (r - l + 1));
sum -= (s[j][l] - s[i - 1][l]);
l++;
}
}
}
}
if (!found) cout << 0 << endl;
else cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
2. 小杨的幸运数字

C++代码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
// cnt[i] 存储数字 i 的不同质因子个数
int cnt[N];
int n;
// 类似埃氏筛的预处理函数
void precompute() {
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
// 如果 cnt[i] 仍为 0,说明 i 是一个质数
if (cnt[i] == 0) {
// 将该质数的所有倍数的质因子计数加 1
for (int j = i; j < N; j += i) {
cnt[j]++;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// 优化输入输出效率
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
// 执行预处理
precompute();
if (!(cin >> n)) return 0;
while (n--) {
int a;
cin >> a;
// 如果不同质因子个数恰好为 2,输出 1,否则输出 0
if (cnt[a] == 2) {
cout << 1 << "\n";
} else {
cout << 0 << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
C++代码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
// cnt[i] 存储数字 i 的不同质因子个数
int cnt[N];
int n;
// 类似埃氏筛的预处理函数
void precompute() {
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
// 如果 cnt[i] 仍为 0,说明 i 是一个质数
if (cnt[i] == 0) {
// 将该质数的所有倍数的质因子计数加 1
for (int j = i; j < N; j += i) {
cnt[j]++;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// 优化输入输出效率
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
// 执行预处理
precompute();
if (!(cin >> n)) return 0;
while (n--) {
int a;
cin >> a;
// 如果不同质因子个数恰好为 2,输出 1,否则输出 0
if (cnt[a] == 2) {
cout << 1 << "\n";
} else {
cout << 0 << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}