目录
[1.1 文件:存储的基本抽象](#1.1 文件:存储的基本抽象)
[1.2 目录树:层次化组织结构](#1.2 目录树:层次化组织结构)
[1.3 文件路径:定位机制](#1.3 文件路径:定位机制)
[1.4 文件类型与识别机制](#1.4 文件类型与识别机制)
[1.5 文件权限:访问控制模型](#1.5 文件权限:访问控制模型)
[2.1 File类:文件的Java抽象](#2.1 File类:文件的Java抽象)
[2.2 文件创建与删除的原子性](#2.2 文件创建与删除的原子性)
[2.3 Java IO流体系架构](#2.3 Java IO流体系架构)
[2.4 文件读取的三种模式](#2.4 文件读取的三种模式)
模式3:使用BufferedInputStream(自动缓冲)
[2.5 文本文件的正确读写](#2.5 文本文件的正确读写)
[2.6 高效文件写入模式](#2.6 高效文件写入模式)
[3.1 目录遍历算法实现](#3.1 目录遍历算法实现)
[3.2 文件搜索工具实现](#3.2 文件搜索工具实现)
[3.3 文件复制的高级实现](#3.3 文件复制的高级实现)
[4.1 IO性能优化策略](#4.1 IO性能优化策略)
[4.2 异常处理与资源管理](#4.2 异常处理与资源管理)
[4.3 大文件处理策略](#4.3 大文件处理策略)
[5.1 Java NIO.2 API概述](#5.1 Java NIO.2 API概述)
[传统IO vs NIO.2对比:](#传统IO vs NIO.2对比:)
[5.2 文件监控与变化检测](#5.2 文件监控与变化检测)
前言
在计算科学中,持久化存储 是一个核心概念。程序运行过程中产生的数据需要被长期保存,而不仅仅是驻留在易失性内存中。硬盘、固态硬盘等存储设备提供了这种能力,但直接操作物理存储介质极其复杂。因此,操作系统引入了文件系统这一抽象层,将存储设备组织成逻辑上独立且易于管理的单元------文件。本文将从理论出发,深入探讨文件系统的设计原理,并结合Java语言的具体实现,全面解析文件操作的各个方面。
一、文件系统理论基础
1.1 文件:存储的基本抽象
文件(File) 是操作系统对存储设备中数据的逻辑抽象。从用户视角看,文件是包含了特定信息的命名实体;从系统视角看,文件是存储在介质上的字节序列及其元数据的集合。
关键理论点:
文件是数据存储的最小逻辑单位
文件系统隐藏了物理存储的复杂性(如扇区、磁道等)
文件具有逻辑独立性,与物理存储位置无关
文件元数据(Metadata)
每个文件都包含两类信息:
数据内容:文件的实际信息
元数据:描述文件属性的信息
1.2 目录树:层次化组织结构
目录(Directory) 是一种特殊文件,其内容是文件系统中其他文件(包括子目录)的元数据索引。这种设计形成了树形结构,是文件系统组织的核心。
目录树结构图示:
/
├── bin/ # 系统可执行文件
│ ├── ls
│ ├── cat
│ └── grep
├── home/ # 用户主目录
│ ├── alice/
│ │ ├── Documents/
│ │ │ ├── report.docx
│ │ │ └── data.xlsx
│ │ └── Pictures/
│ └── bob/
├── etc/ # 系统配置文件
└── var/ # 可变数据
└── log/ # 日志文件理论意义:
-
路径解析:目录树结构使得路径寻址成为可能
-
命名空间管理:不同目录下的文件可以重名
-
访问控制:权限可以基于目录层级继承
1.3 文件路径:定位机制
路径(Path) 是文件系统中定位文件的唯一标识。路径解析是文件系统的核心功能之一。
绝对路径与相对路径对比表:
| 类型 | 定义 | 示例 | 起点 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绝对路径 | 从根目录开始的完整路径 | /home/user/docs/report.txt |
根目录 | 唯一确定,与当前位置无关 |
| 相对路径 | 相对于当前工作目录的路径 | ./docs/report.txt 或 ../shared/config.ini |
当前目录 | 简洁,便于移动整个目录结构 |
路径表示法图解:
文件系统树:
/
├── home/
│ └── user/
│ ├── current/ <-- 当前目录
│ │ └── file1.txt
│ ├── docs/
│ │ └── report.pdf
│ └── parent/
│ └── config.ini
绝对路径示例:
/home/user/docs/report.pdf
相对路径示例:
./file1.txt # 当前目录下的file1.txt
../docs/report.pdf # 兄弟目录docs下的report.pdf
../../etc/passwd # 向上两级后的etc/passwd1.4 文件类型与识别机制
文件可根据内容和用途分为多种类型,操作系统采用不同机制识别文件类型:
文件分类体系:
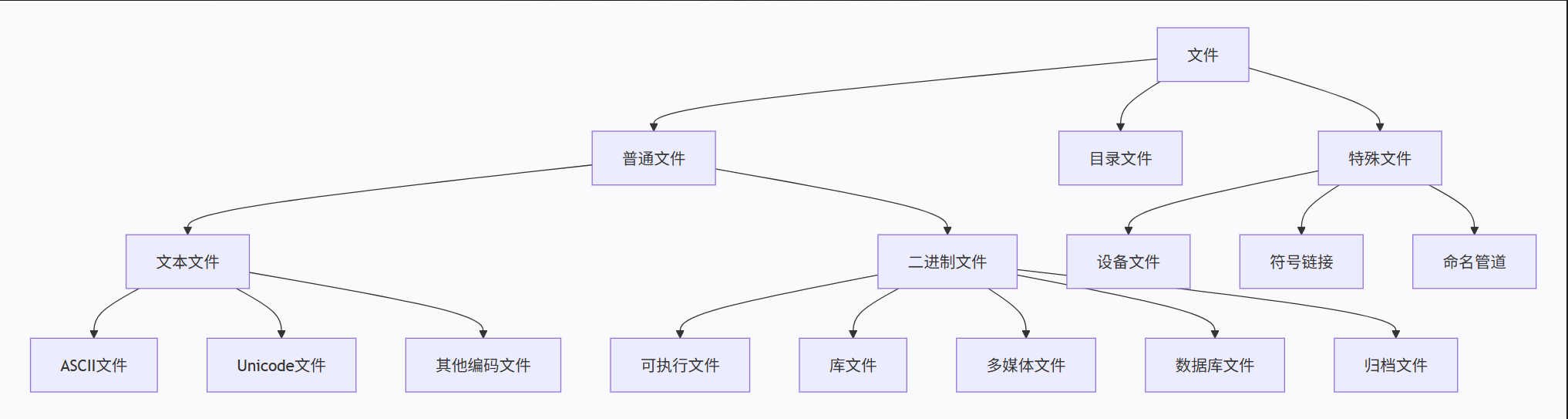
文件识别机制对比:
| 操作系统 | 主要识别方式 | 示例 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows | 文件扩展名 | .txt, .exe, .jpg |
用户友好,易于理解 |
| Linux/Unix | 文件头魔数(Magic Number) + 扩展名 | ELF可执行文件头部7F 45 4C 46 |
更准确,安全性更高 |
| macOS | 扩展名 + 文件类型元数据 | .app目录 + 特定元数据 |
结合多种方式 |
1.5 文件权限:访问控制模型
现代操作系统采用基于用户-组-其他的三级权限模型,确保系统安全。
UNIX权限位详解:
权限表示:rwx rwx rwx
↑ ↑ ↑
用户 组 其他
权限位含义:
r (read) = 4 = 可读取内容/列出目录内容
w (write) = 2 = 可修改内容/在目录中创建/删除文件
x (execute) = 1 = 可执行/可进入目录
权限计算示例:
rwxr-xr-- = 111 101 100 = 754二、Java文件操作API详解
2.1 File类:文件的Java抽象
java.io.File类提供了文件系统的抽象表示,它封装了路径操作和文件属性访问。
File类核心方法分类表:
| 方法类别 | 方法签名 | 功能说明 | 返回值说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 路径操作 | String getPath() |
返回构造时传入的路径 | 可能是相对或绝对路径 |
String getAbsolutePath() |
返回绝对路径表示 | 可能包含.或..符号 |
|
String getCanonicalPath() |
返回规范化的绝对路径 | 解析所有符号链接和相对引用 | |
| 属性查询 | boolean exists() |
检查文件/目录是否存在 | 文件不存在不代表路径无效 |
boolean isFile() |
是否为普通文件 | 非目录、非特殊文件 | |
boolean isDirectory() |
是否为目录 | 目录是一种特殊文件 | |
long length() |
文件大小(字节) | 目录返回值未定义 | |
| 文件操作 | boolean createNewFile() |
创建新空文件 | 原子操作,避免竞态条件 |
boolean delete() |
删除文件/空目录 | 不能删除非空目录 | |
boolean renameTo(File dest) |
重命名或移动文件 | 可能跨文件系统失败 | |
| 目录操作 | boolean mkdir() |
创建单级目录 | 父目录必须存在 |
boolean mkdirs() |
创建多级目录 | 自动创建不存在的父目录 | |
String[] list() |
列出目录内容(名称) | 不包括.和.. |
|
File[] listFiles() |
列出目录内容(File对象) | 便于进一步操作 |
路径解析示例代码分析:
java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class PathAnalysis {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 假设当前目录: /home/user/project
File file = new File("../docs/report.txt");
System.out.println("构造路径: " + file.getPath());
// 输出: ../docs/report.txt
System.out.println("绝对路径: " + file.getAbsolutePath());
// 输出: /home/user/project/../docs/report.txt
// 注意: 包含相对引用".."
System.out.println("规范路径: " + file.getCanonicalPath());
// 输出: /home/user/docs/report.txt
// 已解析所有相对引用
System.out.println("父目录: " + file.getParent());
// 输出: ../docs
System.out.println("文件名: " + file.getName());
// 输出: report.txt
}
}2.2 文件创建与删除的原子性
文件操作中的原子性至关重要,特别是在多线程或多进程环境中。
创建文件的正确模式:
java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class AtomicFileCreation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("data.txt");
// 错误方式:存在竞态条件
if (!file.exists()) {
// 此处可能有其他进程创建了文件
try {
file.createNewFile(); // 可能失败
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 正确方式:原子性操作
try {
if (file.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
} else {
System.out.println("文件已存在");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("创建失败: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}deleteOnExit()机制:
deleteOnExit()方法在JVM退出时删除文件,适用于临时文件清理:
java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DeleteOnExitDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File tempFile = File.createTempFile("temp_", ".dat");
System.out.println("临时文件: " + tempFile.getAbsolutePath());
// 标记为退出时删除
tempFile.deleteOnExit();
// 使用文件...
// 程序正常退出时自动删除
// 即使发生异常,只要JVM退出也会删除
}
}2.3 Java IO流体系架构
Java的IO系统基于流(Stream) 抽象,分为字节流和字符流两大类。
字节流与字符流的本质区别:
| 对比维度 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 处理单位 | 字节(8-bit) | 字符(16-bit Unicode) |
| 编码处理 | 不处理编码 | 自动处理字符编码转换 |
| 主要类 | InputStream/OutputStream | Reader/Writer |
| 适用场景 | 二进制文件(图片、视频等) | 文本文件 |
| 性能考虑 | 直接处理原始数据 | 需要编码/解码开销 |
2.4 文件读取的三种模式
模式1:单字节读取(低效,仅用于演示)
java
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class SingleByteRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("input.txt")) {
int byteRead;
int count = 0;
while ((byteRead = is.read()) != -1) {
// 每次读取1字节,性能极差
count++;
System.out.print((char) byteRead);
}
System.out.println("\n读取字节数: " + count);
}
}
}性能分析:每次系统调用只读取1字节,上下文切换开销巨大,不适用于生产环境。
模式2:缓冲区批量读取(推荐)
java
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class BufferedRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 缓冲区大小选择策略:
// 1. 默认8KB适合大多数场景
// 2. 大文件可适当增大(如64KB)
// 3. 内存敏感环境可减小
byte[] buffer = new byte[8192]; // 8KB缓冲区
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("largefile.dat")) {
int bytesRead;
long totalBytes = 0;
while ((bytesRead = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
totalBytes += bytesRead;
// 处理buffer[0..bytesRead-1]
processBuffer(buffer, bytesRead);
}
System.out.println("总读取字节: " + totalBytes);
}
}
private static void processBuffer(byte[] buffer, int length) {
// 实际业务处理
}
}缓冲区大小优化公式:
理想缓冲区大小 = min(可用内存/4, 文件大小, 系统页大小×N)
一般建议值:4KB ~ 64KB
模式3:使用BufferedInputStream(自动缓冲)
java
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class AutoBufferedRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// BufferedInputStream内部维护缓冲区
// 默认缓冲区大小8KB,可通过构造函数调整
try (InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("input.txt"), 65536)) { // 64KB缓冲区
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
// 处理数据
}
}
}
}2.5 文本文件的正确读写
处理文本文件时必须考虑字符编码,否则会出现乱码问题。
字符编码问题示例:
java
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class EncodingProblem {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String text = "你好,世界!"; // 包含中文字符
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("test.txt")) {
// 错误:使用平台默认编码(可能是GBK)
os.write(text.getBytes());
// 正确:明确指定UTF-8编码
os.write(text.getBytes("UTF-8"));
// 更优:使用字符流自动处理编码
// try (Writer writer = new OutputStreamWriter(os, "UTF-8")) {
// writer.write(text);
// }
}
}
}使用Scanner读取文本文件:
java
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TextFileScanner {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 场景1:逐词读取
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("article.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is, "UTF-8")) {
scanner.useDelimiter("[\\s\\p{Punct}]+"); // 按空格和标点分割
int wordCount = 0;
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
String word = scanner.next();
wordCount++;
System.out.println("单词 " + wordCount + ": " + word);
}
}
// 场景2:逐行读取(更常用)
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream("data.csv");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is, "UTF-8")) {
int lineNumber = 0;
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
lineNumber++;
// CSV解析示例
String[] columns = line.split(",");
System.out.printf("第%d行: %s%n", lineNumber,
String.join(" | ", columns));
}
}
}
}2.6 高效文件写入模式
模式比较表:
| 写入模式 | 实现类 | 缓冲区 | 自动刷新 | 编码处理 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原始字节流 | FileOutputStream | 无 | 无 | 无 | 二进制文件写入 |
| 缓冲字节流 | BufferedOutputStream | 有 | 手动flush | 无 | 二进制文件高效写入 |
| 字符输出流 | OutputStreamWriter | 可选 | 手动flush | 支持 | 文本文件基础写入 |
| 缓冲字符流 | BufferedWriter | 有 | 手动flush | 支持 | 文本文件高效写入 |
| 格式化输出 | PrintWriter | 有 | 可选autoFlush | 支持 | 格式化文本输出 |
PrintWriter的高级用法:
java
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class AdvancedPrintWriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("output.log");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os, "UTF-8");
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(osw, true)) { // autoFlush=true
// 1. 基本写入
writer.print("基本文本");
writer.println(); // 换行
// 2. 格式化输出
writer.printf("日期: %tF%n", System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.printf("价格: $%.2f%n", 19.99);
writer.printf("数量: %03d%n", 7);
// 3. 错误处理
writer.checkError(); // 检查是否发生IO错误
// 4. 追加模式(需在FileOutputStream中指定)
// new FileOutputStream("output.log", true)
}
}
}三、高级文件操作实践
3.1 目录遍历算法实现
递归深度优先遍历:
java
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class DirectoryTraversal {
/**
* 深度优先遍历目录
* @param root 根目录
* @return 所有文件的列表
*/
public static List<File> dfsTraversal(File root) {
List<File> result = new ArrayList<>();
dfsTraversal(root, result);
return result;
}
private static void dfsTraversal(File current, List<File> result) {
// 安全性检查
if (current == null || !current.exists()) {
return;
}
// 添加当前文件(如果是普通文件)
if (current.isFile()) {
result.add(current);
return;
}
// 遍历子目录
File[] children = current.listFiles();
if (children == null) {
// 权限不足或IO错误
return;
}
for (File child : children) {
dfsTraversal(child, result);
}
}
/**
* 广度优先遍历目录
* @param root 根目录
* @return 按层级排序的文件列表
*/
public static List<File> bfsTraversal(File root) {
List<File> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null || !root.exists()) {
return result;
}
Queue<File> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
File current = queue.poll();
if (current.isFile()) {
result.add(current);
} else {
File[] children = current.listFiles();
if (children != null) {
for (File child : children) {
queue.offer(child);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}目录遍历性能优化:
java
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.nio.file.attribute.BasicFileAttributes;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class EfficientDirectoryWalker {
/**
* 使用NIO Files.walkFileTree API(Java 7+)
* 性能更好,资源管理更安全
*/
public static List<Path> walkFileTree(String rootDir) throws IOException {
List<Path> result = new ArrayList<>();
Files.walkFileTree(Paths.get(rootDir), new SimpleFileVisitor<Path>() {
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFile(Path file, BasicFileAttributes attrs) {
result.add(file);
return FileVisitResult.CONTINUE;
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult visitFileFailed(Path file, IOException exc) {
// 处理访问失败的文件(如权限不足)
System.err.println("无法访问: " + file + ", 原因: " + exc.getMessage());
return FileVisitResult.CONTINUE;
}
@Override
public FileVisitResult postVisitDirectory(Path dir, IOException exc) {
if (exc != null) {
System.err.println("遍历目录失败: " + dir);
}
return FileVisitResult.CONTINUE;
}
});
return result;
}
}3.2 文件搜索工具实现
java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class FileSearchUtility {
/**
* 综合搜索:按文件名和内容搜索
*/
public static List<File> searchFiles(File rootDir,
String fileNamePattern,
String contentKeyword,
boolean caseSensitive) throws IOException {
List<File> result = new ArrayList<>();
searchFilesRecursive(rootDir, fileNamePattern, contentKeyword,
caseSensitive, result);
return result;
}
private static void searchFilesRecursive(File dir,
String fileNamePattern,
String contentKeyword,
boolean caseSensitive,
List<File> result) throws IOException {
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if (files == null) return;
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
// 递归搜索子目录
searchFilesRecursive(file, fileNamePattern, contentKeyword,
caseSensitive, result);
} else {
boolean matches = true;
// 1. 检查文件名匹配
if (fileNamePattern != null && !fileNamePattern.isEmpty()) {
String fileName = file.getName();
String pattern = caseSensitive ? fileNamePattern :
fileNamePattern.toLowerCase();
String nameToCheck = caseSensitive ? fileName :
fileName.toLowerCase();
if (!nameToCheck.contains(pattern)) {
matches = false;
}
}
// 2. 检查内容匹配
if (matches && contentKeyword != null && !contentKeyword.isEmpty()) {
if (!fileContainsKeyword(file, contentKeyword, caseSensitive)) {
matches = false;
}
}
if (matches) {
result.add(file);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 检查文件是否包含关键词
* 使用缓冲区提高性能
*/
private static boolean fileContainsKeyword(File file, String keyword,
boolean caseSensitive) throws IOException {
// 优化:先检查文件大小,避免读取过大文件
if (file.length() > 10 * 1024 * 1024) { // 10MB
System.out.println("文件过大,跳过内容搜索: " + file.getName());
return false;
}
String searchKeyword = caseSensitive ? keyword : keyword.toLowerCase();
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file), "UTF-8"))) {
char[] buffer = new char[8192];
int charsRead;
StringBuilder contentBuffer = new StringBuilder();
while ((charsRead = reader.read(buffer)) != -1) {
contentBuffer.append(buffer, 0, charsRead);
// 检查当前缓冲区是否包含关键词
String currentContent = caseSensitive ? contentBuffer.toString() :
contentBuffer.toString().toLowerCase();
if (currentContent.contains(searchKeyword)) {
return true;
}
// 滑动窗口:保留可能跨越缓冲区边界的关键词部分
int keepLength = Math.min(keyword.length() - 1, contentBuffer.length());
contentBuffer.delete(0, contentBuffer.length() - keepLength);
}
}
return false;
}
}3.3 文件复制的高级实现
分块复制与进度监控:
java
import java.io.*;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class AdvancedFileCopier {
public static void copyFileWithProgress(File source, File destination,
ProgressListener listener) throws IOException {
// 参数验证
if (!source.exists()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("源文件不存在: " + source.getPath());
}
if (!source.isFile()) {
throw new IOException("源路径不是文件: " + source.getPath());
}
// 创建目标目录(如果需要)
File parentDir = destination.getParentFile();
if (parentDir != null && !parentDir.exists()) {
if (!parentDir.mkdirs()) {
throw new IOException("无法创建目标目录: " + parentDir.getPath());
}
}
long fileSize = source.length();
long totalCopied = 0;
// 动态调整缓冲区大小(基于文件大小)
int bufferSize = calculateOptimalBufferSize(fileSize);
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferSize];
try (InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(source), bufferSize);
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destination), bufferSize)) {
int bytesRead;
long lastUpdateTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("0.00");
while ((bytesRead = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
totalCopied += bytesRead;
// 进度通知(限制频率)
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (listener != null && (currentTime - lastUpdateTime > 100 || bytesRead == -1)) {
float progress = (float) totalCopied / fileSize * 100;
float speed = calculateSpeed(totalCopied, lastUpdateTime, currentTime);
listener.onProgress(progress, speed, totalCopied, fileSize);
lastUpdateTime = currentTime;
}
}
os.flush();
if (listener != null) {
listener.onComplete(destination);
}
}
}
private static int calculateOptimalBufferSize(long fileSize) {
// 基于文件大小的缓冲区优化策略
if (fileSize < 1024 * 1024) { // < 1MB
return 4 * 1024; // 4KB
} else if (fileSize < 10 * 1024 * 1024) { // < 10MB
return 32 * 1024; // 32KB
} else if (fileSize < 100 * 1024 * 1024) { // < 100MB
return 64 * 1024; // 64KB
} else {
return 128 * 1024; // 128KB
}
}
private static float calculateSpeed(long bytesCopied, long startTime, long endTime) {
if (endTime <= startTime) return 0;
float elapsedSeconds = (endTime - startTime) / 1000.0f;
if (elapsedSeconds <= 0) return 0;
return bytesCopied / elapsedSeconds / 1024.0f; // KB/s
}
public interface ProgressListener {
void onProgress(float percentage, float speedKBps, long copied, long total);
void onComplete(File destination);
}
/**
* 使用NIO的零拷贝技术(Java 7+)
* 在某些情况下性能更好
*/
public static void copyFileWithTransferTo(File source, File destination) throws IOException {
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destination);
FileChannel sourceChannel = fis.getChannel();
FileChannel destChannel = fos.getChannel()) {
long position = 0;
long size = sourceChannel.size();
while (position < size) {
position += sourceChannel.transferTo(position, size - position, destChannel);
}
}
}
}四、性能优化与最佳实践
4.1 IO性能优化策略
缓冲区策略对比:
| 策略 | 缓冲区大小 | 适用场景 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 固定小缓冲区 | 1KB-4KB | 内存受限环境 | 内存占用小 | IO次数多,性能差 |
| 固定适中缓冲区 | 8KB-32KB | 通用场景 | 平衡性好 | 可能不是最优 |
| 动态缓冲区 | 基于文件大小调整 | 大文件操作 | 性能优化好 | 实现复杂 |
| 系统默认缓冲区 | 依赖实现 | 简单应用 | 无需配置 | 可能不是最优 |
性能测试框架示例:
java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class IOPerformanceBenchmark {
public static void benchmarkCopy(String methodName, Runnable copyTask) {
System.out.println("\n=== 测试方法: " + methodName + " ===");
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
try {
copyTask.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("测试失败: " + e.getMessage());
return;
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
long durationMs = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(endTime - startTime);
System.out.println("耗时: " + durationMs + "ms");
}
public static void createTestFile(String path, long sizeMB) throws IOException {
File testFile = new File(path);
System.out.println("创建测试文件: " + sizeMB + "MB");
try (OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream(testFile))) {
byte[] pattern = "0123456789ABCDEF".getBytes();
long bytesToWrite = sizeMB * 1024 * 1024;
long written = 0;
while (written < bytesToWrite) {
int toWrite = (int) Math.min(pattern.length, bytesToWrite - written);
os.write(pattern, 0, toWrite);
written += toWrite;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 准备测试文件
String sourceFile = "test_source.dat";
String destFile = "test_dest.dat";
createTestFile(sourceFile, 100); // 100MB测试文件
// 测试不同缓冲区大小
int[] bufferSizes = {1024, 4096, 8192, 32768, 65536, 131072};
for (int bufferSize : bufferSizes) {
benchmarkCopy("缓冲区大小=" + bufferSize + "字节", () -> {
try {
copyWithBuffer(sourceFile, destFile, bufferSize);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
}
// 清理测试文件
new File(sourceFile).delete();
new File(destFile).delete();
}
private static void copyWithBuffer(String source, String dest, int bufferSize)
throws IOException {
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream(source);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(dest)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferSize];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
}
}4.2 异常处理与资源管理
正确的资源管理模式:
java
import java.io.*;
public class ResourceManagement {
// 反模式:手动管理资源,容易泄露
public static void copyFileBad(File src, File dst) throws IOException {
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(src);
out = new FileOutputStream(dst);
byte[] buffer = new byte[8192];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
} finally {
// 可能忘记关闭,或者关闭时发生异常影响其他关闭
if (in != null) {
in.close();
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
}
}
}
// 正模式:try-with-resources(Java 7+)
public static void copyFileGood(File src, File dst) throws IOException {
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dst)) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[8192];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
// 资源自动关闭,即使发生异常
}
// 正确处理多个异常
public static void processFile(String path) {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(path))) {
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// 处理行
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("文件未找到: " + path);
// 可能创建新文件或提示用户
} catch (SecurityException e) {
System.err.println("没有权限访问文件: " + path);
// 提示权限问题
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("IO错误: " + e.getMessage());
// 记录日志或重试
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("未知错误: " + e.getMessage());
// 通用错误处理
}
}
}4.3 大文件处理策略
分块处理大文件:
java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class LargeFileProcessor {
/**
* 并行处理大文件
*/
public static void processLargeFileParallel(File largeFile, int chunkSizeMB,
FileProcessor processor)
throws IOException, InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
long fileSize = largeFile.length();
long chunkSize = chunkSizeMB * 1024L * 1024L;
int numChunks = (int) Math.ceil((double) fileSize / chunkSize);
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
);
List<Future<Void>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numChunks; i++) {
final int chunkIndex = i;
long startPos = i * chunkSize;
long endPos = Math.min(startPos + chunkSize, fileSize);
Future<Void> future = executor.submit(() -> {
processFileChunk(largeFile, startPos, endPos, processor, chunkIndex);
return null;
});
futures.add(future);
}
// 等待所有任务完成
for (Future<Void> future : futures) {
future.get();
}
executor.shutdown();
}
private static void processFileChunk(File file, long start, long end,
FileProcessor processor, int chunkIndex)
throws IOException {
try (RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r")) {
raf.seek(start);
byte[] buffer = new byte[8192];
long position = start;
while (position < end) {
int toRead = (int) Math.min(buffer.length, end - position);
int bytesRead = raf.read(buffer, 0, toRead);
if (bytesRead == -1) break;
processor.process(buffer, bytesRead, chunkIndex);
position += bytesRead;
}
}
}
public interface FileProcessor {
void process(byte[] data, int length, int chunkIndex);
}
}五、现代Java文件操作(NIO.2)
5.1 Java NIO.2 API概述
Java 7引入了NIO.2 API,提供了更现代、更强大的文件操作接口。
传统IO vs NIO.2对比:
java
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.file.*;
import java.nio.file.attribute.*;
import java.util.*;
public class NIO2Examples {
// 传统IO方式
public static void traditionalFileOps() throws IOException {
File file = new File("test.txt");
// 创建文件
file.createNewFile();
// 检查属性
boolean exists = file.exists();
boolean isFile = file.isFile();
long size = file.length();
// 列出目录
File[] files = new File(".").listFiles();
// 删除文件
file.delete();
}
// NIO.2方式
public static void nio2FileOps() throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get("test.txt");
// 创建文件(支持设置属性)
Files.createFile(path);
// 检查属性(更丰富)
boolean exists = Files.exists(path);
boolean isRegularFile = Files.isRegularFile(path);
long size = Files.size(path);
// 获取更多属性
BasicFileAttributes attrs = Files.readAttributes(
path, BasicFileAttributes.class);
FileTime creationTime = attrs.creationTime();
FileTime lastModified = attrs.lastModifiedTime();
// 列出目录(带过滤)
try (DirectoryStream<Path> stream = Files.newDirectoryStream(
Paths.get("."), "*.{txt,java}")) {
for (Path entry : stream) {
System.out.println(entry.getFileName());
}
}
// 删除文件(更多选项)
Files.delete(path); // 不存在时抛出异常
Files.deleteIfExists(path); // 不存在时不抛异常
}
}5.2 文件监控与变化检测
java
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.file.*;
import static java.nio.file.StandardWatchEventKinds.*;
public class FileChangeMonitor {
public static void watchDirectory(String directoryPath) throws IOException {
Path path = Paths.get(directoryPath);
try (WatchService watchService = FileSystems.getDefault().newWatchService()) {
// 注册感兴趣的事件类型
path.register(watchService,
ENTRY_CREATE,
ENTRY_MODIFY,
ENTRY_DELETE);
System.out.println("开始监控目录: " + directoryPath);
while (true) {
WatchKey key;
try {
key = watchService.take(); // 阻塞直到事件发生
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("监控被中断");
return;
}
for (WatchEvent<?> event : key.pollEvents()) {
WatchEvent.Kind<?> kind = event.kind();
// 处理OVERFLOW事件
if (kind == OVERFLOW) {
continue;
}
// 获取文件名
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
WatchEvent<Path> ev = (WatchEvent<Path>) event;
Path fileName = ev.context();
// 处理不同事件
if (kind == ENTRY_CREATE) {
System.out.println("文件创建: " + fileName);
} else if (kind == ENTRY_MODIFY) {
System.out.println("文件修改: " + fileName);
} else if (kind == ENTRY_DELETE) {
System.out.println("文件删除: " + fileName);
}
}
// 重置key,继续监听
boolean valid = key.reset();
if (!valid) {
System.out.println("监控目录已失效");
break;
}
}
}
}
}总结
-
文件抽象:操作系统将存储设备抽象为文件和目录的层次结构
-
路径解析:绝对路径和相对路径提供了文件的定位机制
-
权限系统:基于用户-组-其他模型保障文件安全
-
IO流模型:Java将输入输出抽象为字节流和字符流
-
缓冲机制:通过减少系统调用提高IO性能
-
资源管理:try-with-resources确保资源正确释放
-
异常处理:正确处理IO异常提高程序健壮性