The first week
追光的人永远光芒万丈
一.前言
寒假集训第一周,前三天去练科三了(虽然最后还是挂了),后面几天写了一些题单,回家后的cf一直在打,目前1397,希望今晚能变青色,寒假目标cf变蓝。
期末周搁置了两周再加上考试和放假,快一个月没动手了,这周就当调整状态了,下周开始猛猛干。
这周补了:快速幂取模,费马小定理求逆元,矩阵快速幂,素数筛,堆排序
二.部分题解与思路
1.Problem - C2 - Codeforces
题目复现
 解题思路
解题思路
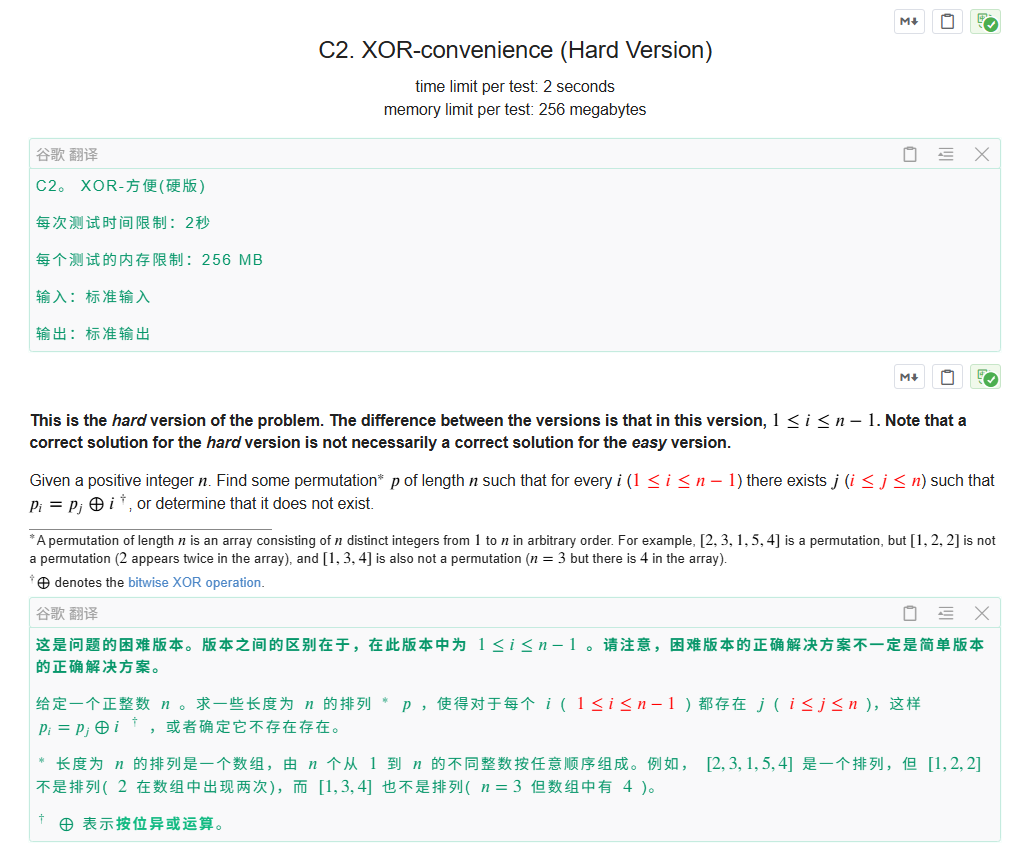
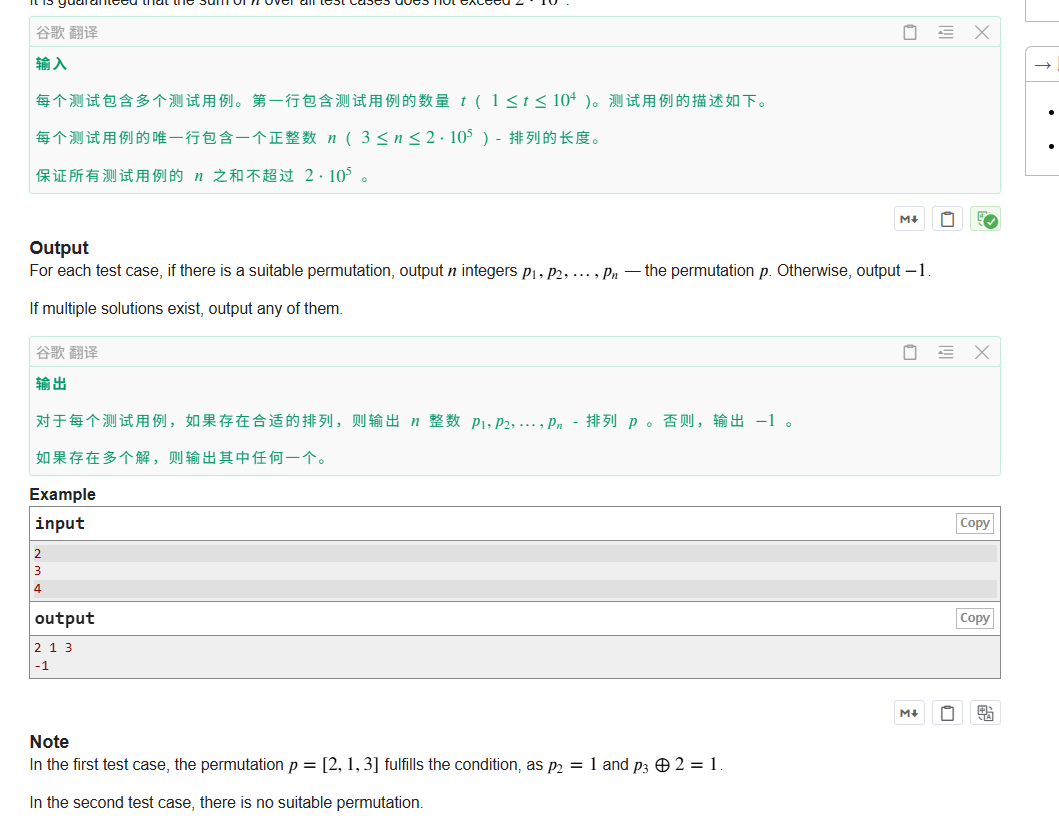
构造 1~n 的排列,满足每个位置 i 的数值 = 某位置 j 的数值 异或 i,且首位置数值需满足异或 1 约束,与Easy 版比存在偶数 n 构造冲突
n 为奇数直接用 Easy 版构造法 末位放 1,从 n-1 到 2 依次用末位数值 异或 当前位置得到对应数值,集合记录未用数,剩余数填充首位置,无冲突可直接得到合法排列;
n为偶数:用标记数组记录已占用的异或结果,遍历 2~n-1 位置,寻找首个可放置 n 的合法位置,
若找到合法位置,按规则填充剩余数值、集合补全首位置,完成构造;若未找到,直接输出 -1
code
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int tt;
cin >> tt;
while (tt--) {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> ans(n + 1);
if (n % 2 == 1) {
ans[n] = 1;
set<int> st;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
st.insert(i);
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 2; --i) {
ans[i] = ans[n] ^ i;
st.erase(ans[i]);
}
ans[1] = *st.begin();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
continue;
}
ans[n] = 1;
set<int> st;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
st.insert(i);
}
vector<bool> vis(n * 2 + 1, false);
vis[1 ^ n] = true;
bool found = false;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 2; --i) {
if (!found && vis[i]) {
ans[i] = n;
found = true;
} else {
ans[i] = ans[n] ^ i;
vis[ans[i] ^ n] = true;
}
st.erase(ans[i]);
}
ans[1] = *st.begin();
if (!found) {
cout << "-1\n";
continue;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}2.Problem - C2 - Codeforces Problem - D1 - Codeforces Problem - C2 - Codeforces
题目复现

解题思路
先判断字符串首尾是否为 0,若为 0 则直接输出 - 1,否则从第一个字符到倒数第二个字符遍历,遇到 1 则累乘 2、遇到 0 则累乘其对应位置的索引值,分别维护对 c 取模和对 1e9+7 取模的乘积,若对 c 取模的乘积为 0 则无符合条件的解输出 - 1,否则输出对 1e9+7 取模的乘积。
code
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const ll mod=1e9+7;
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n;
ll c;
cin>>n>>c;
string s;
cin>>s;
if(s[0]=='0'||s[n-1]=='0')
{
cout<<-1<<'\n';
continue;
}
ll pc=1,pm=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n-1;++i)
{
if(s[i-1]=='1')
{
pc=pc*2%c;
pm=pm*2%mod;
}
else
{
ll f=i-1;
pc=pc*f%c;
pm=pm*f%mod;
}
}
if(pc==0)cout<<-1<<'\n';
else cout<<pm<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}3.Problem - E - Codeforces Problem - D1 - Codeforces
题目复现
解题思路
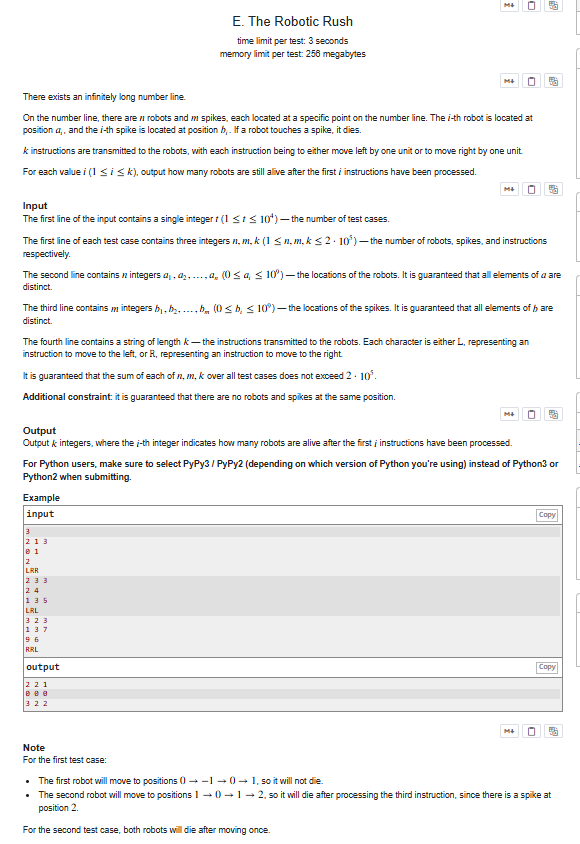
暴力模拟每个机器人移动会超时(Onk 复杂度),因此我们预处理每个机器人向左、向右移动的首次死亡步数:先对机器人与尖刺位置排序,用二分快速定位每个机器人左右最近的尖刺,得到 moveli(左移死亡步数)和 moveri(右移死亡步数)。用两个小根堆维护这些死亡步数,随着指令执行维护累计位移 d 及其最值 minx/maxx,当 d 超出当前范围时,动态弹出堆中满足死亡条件的机器人(右移步数≤d 或左移步数≤-d),并更新存活数。整体复杂度为 Onlogn + mlogm + klogn
code
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll inf=1e12;
ll t,n,m,k;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n>>m>>k;
vector<ll>a(n),b(m);
for(ll i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
sort(a.begin(),a.end());
for(ll j=0;j<m;j++){
cin>>b[j];
}
sort(b.begin(),b.end());
//计算机器人往左/往右多少步遇到钉子
vector<ll>movel(n,inf),mover(n,inf);
for(ll i=0;i<m;i++){
auto it=upper_bound(a.begin(),a.end(),b[i]);
if(it==a.begin())continue;
ll idx=it-a.begin();
idx--;
for(ll j=idx;j>=0;j--){
if(mover[j]<=b[i]-a[j])break;
mover[j]=b[i]-a[j];
}
}
for(ll i=m-1;i>=0;i--){
auto it=upper_bound(a.begin(),a.end(),b[i]);
if(it==a.end())continue;
ll idx=it-a.begin();
for(ll j=idx;j<n;j++){
if(movel[j]<=a[j]-b[i])break;
movel[j]=a[j]-b[i];
}
}
priority_queue<pair<ll,ll>,vector<pair<ll,ll>>,greater<pair<ll,ll>>>ml,mr;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(movel[i]!=inf)ml.push({movel[i],mover[i]});
if(mover[i]!=inf)mr.push({mover[i],movel[i]});
}
string s;
cin>>s;
ll d=0,minx=0,maxx=0,ans=n;
for(ll i=0;i<k;i++){
if(s[i]=='L')d--;
else d++;
if(d>=minx&&d<=maxx){
cout<<ans<<" ";
continue;
}
else{
if(d>maxx){
while(!mr.empty()){
auto [r,l]=mr.top();
if(r>d)break;
if(l>-minx){
ans--;
}
mr.pop();
}
}
if(d<minx){
while(!ml.empty()){
auto [l,r]=ml.top();
if(l>-d)break;
if(r>maxx){
ans--;
}
ml.pop();
}
}
minx=min(minx,d);
maxx=max(maxx,d);
}
cout<<ans<<" ";
}
cout<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}4.Problem - D1 - Codeforces
题目复现
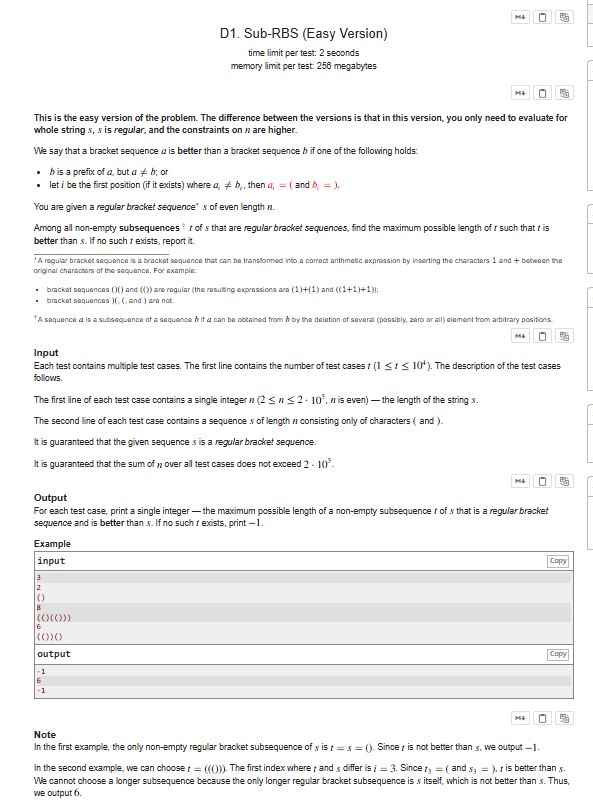
解题思路
首先对于括号序列 a 优于括号序列 b,题目中给的第一种情况完全是多余的,可以不用考虑;对于第二种情况,可以理解为将一个 "(" 向前移一位,即在前面删除一个 ")",为了保证括号序列是正确的,我们要在后面再删一个 "(",来保证括号序列的正确性,所以,当编号最前面的 ")" 后面还有至少两个 "(" 时,输出 n−2,否则输出 −1
code
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll = long long;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
int n;
string s;
cin >> n >> s;
bool ok = true;
// 检查前n/2 -1个字符是否均为左括号
for (int i = 0; i < n/2 - 1; ++i) {
if (s[i] != '(') {
ok = false;
break;
}
}
if (ok) {
cout << -1 << '\n';
} else {
cout << n - 2 << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}5.Problem - C - Codeforces
题目复现
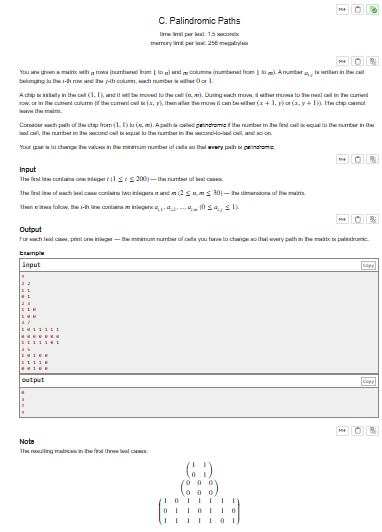
解题思路
从起点 (1,1) 到任意点 (i,j) 需要走的步数固定为 i+j-2,基于这个规律,我们可以把走 k 步能到达的所有点归为同一个集合,每个集合分别统计其中数字 1 和 0 的数量。整个路径的点集存在回文特性:走 k 步到达的点集,与走 n+m-2-k 步到达的点集完全对应,且对应位置的数字必须保持一致(要么同时为 1,要么同时为 0)。因此对于每一组回文对应的点集,只需计算将其统一转为全 1 或全 0 的两种代价,选择其中更小的那个,最后把所有组的最小代价累加,就是最终的总代价
code
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int t,n,m;
int vis[109][2],a[50][50];
int main()
{
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
cin>>n>>m;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
int shu=i+j-2,s=a[i][j];
vis[shu][s]++;
}
int len=n+m-2;
for(int i=0,j=len;j>i;i++,j--)
ans+=min(vis[i][0]+vis[j][0],vis[i][1]+vis[j][1]);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}6.Problem - C - Codeforces
题目复现
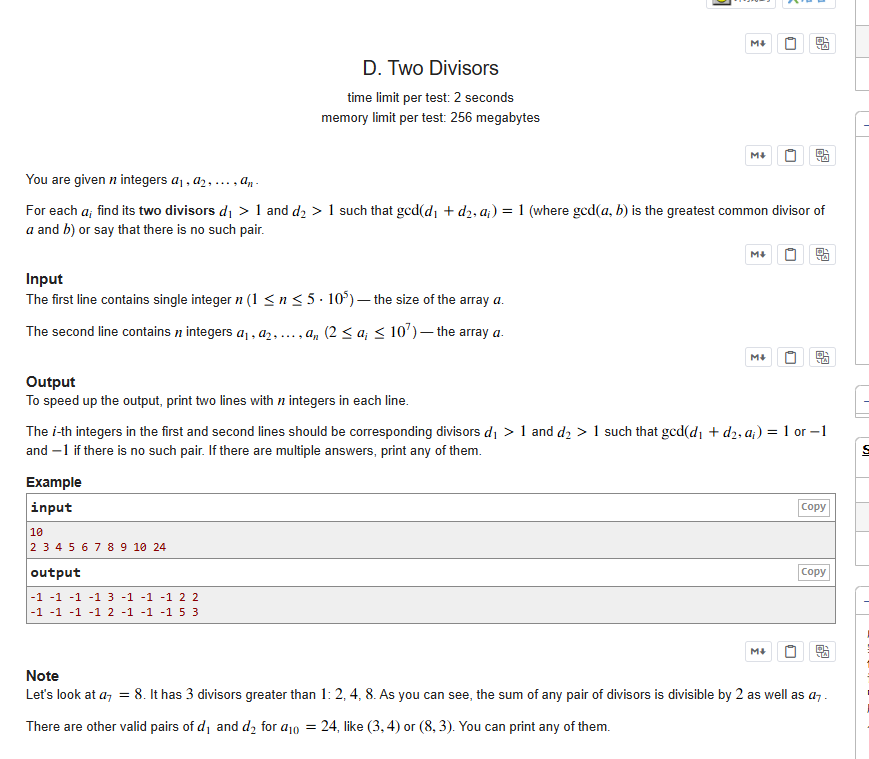
解题思路
利用 gcd 性质:若 gcd (d1,d2)=1,则 gcd (d1+d2,d1^n d2)=1。因此只需对 ai 找到互质因数 d1、d2(ai=d1^n d2),就能得到与 ai 互质的 d1+d2。通过埃氏筛预处理每个数的最小质因数 d1,再将 ai 不断除以 d1 得到 d2;若 d2=1 则无解,否则 d1、d2 即为满足条件的互质因数。
code
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int Max = 5e5 + 5;
int prim[Max*20], vis[Max*20], h[Max*20], x = 0;//h存储合数找到的第一个质因数
int a[Max], b[Max];
void eratos(int n)
{
for (int i = 2;i <= n;i++)
{
if (!vis[i])prim[++x] = i;
if (vis[i])continue;
for (int j = 1;j * i <= n;j++)
{
if(j!=1)vis[i * j] = 1;
h[i * j] = i;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n;cin >> n;
eratos(1e7+3);
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
int p;cin >> p;
if (vis[p] == 0)a[i] = -1, b[i] = -1;
else
{
int k = h[p];
while (p % k == 0)p /= k;
if (p == 1)a[i] = -1, b[i] = -1;
else a[i] = k, b[i] = p;
}
}
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)cout << a[i] << " ";cout << endl;
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)cout << b[i] << " ";
}7.Problem - C - Codeforces
题目复现
解题思路
先考虑两种特殊的情况:
- t=h,一步到位。
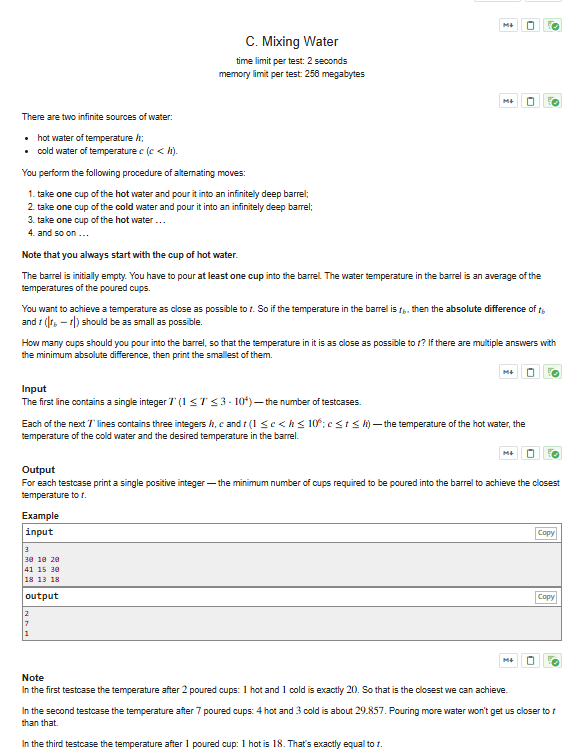
- t≤2h+c,那么肯定是平均温度最接近,答案为2。
接着考虑t>2h+c时的情况。假设我们已经加入了x轮热水和冷水,那么此时温度为2h+c,共有2x杯水。
所以我们再倒入热水的时候,温度就变为2x+1(x+1)h+xc,所以我们列出方程:2x+1(x+1)h+xc=t。
解得x=h+c−2tt−h,由于精度误差,我们再比较一下x和x+1即可。
code
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using ll=long long ;
const int N=2e6+5;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int tt;
cin>>tt;
while(tt--){
ll h,c,t;
cin>>h>>c>>t;
if(t==h){
cout<<1<<endl;
continue;
}
if((h+c)>>1>=t){
cout<<2<<endl;
continue;
}
ll x=(h-t)*1.0/(2*t-h-c);
double diff1=fabs(t-((x+1)*h+x*c)*1.0/(2*x+1));
double diff2=fabs(t-((x+2)*h+(x+1)*c)*1.0/(2*(x+1)+1));
if(diff1<=diff2){
cout<<2*x+1<<endl;
}else{
cout<<2*(x+1)+1<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}8.Problem - D - Codeforces
题目复现
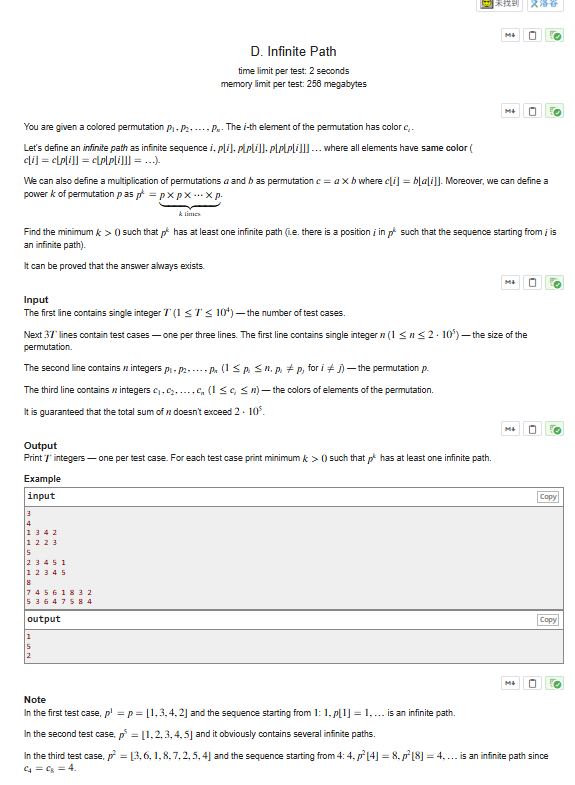
解题思路
首先把图搞出来,发现是很多环。显然对置换求幂不会让两个本不联通的环联通,所以可以对每个环单独考虑。
根据次幂的定义,可以得到,对一个环求幂,就是将环上每一个点指向他接下来的第 k 个点(废话)。那么,当 k 是环长 n 的约数时,pk 是 kn 个长度为 k 的小环。其余情况则与 k′=gcd(k,n) 的情况一致。所以只需枚举倍数判断环上是否同色即可。时间复杂度 O(nn)。
code
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
int p[MAXN], a[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN];
int b[MAXN], len;
inline bool check(int d) {
bool f1 = 0, f2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= d; i++) {
f2 = 1;
for (int j = i + d; j <= len; j += d)
f2 &= (b[i] == b[j]);
f1 |= f2;
}
return f1;
}
inline int solve(int k) {
int res = 0;
vis[k] = 1;
b[len = 1] = a[k];
for (int i = p[k]; i != k; i = p[i]) {
b[++len] = a[i];
vis[i] = 1;
}
res = len;
for (int i = 1; i <= len / i; i++) {
if (len % i == 0) {
if (check(i))
res = min(res, i);
if (i != len / i && check(len / i))
res = min(res, len / i);
}
}
return res;
}
int t, n, ans;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> t;
while (t--) {
cin >> n;
ans = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> p[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i])
ans = min(ans, solve(i));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
vis[i] = 0;
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}9.Problem - D - Codeforces
题目复现
解题思路
概率期望线性性先统计每个数字在所有集合中出现的总次数 sum [tmp],计算单个数字对所属集合的贡献为 sum [tmp]/n(mod 意义下用逆元实现除法),对每个集合累加其所有元素的贡献后除以集合大小得到该集合的期望贡献,最后将所有集合的期望贡献求和再除以总集合数 n,所有除法操作均通过模 998244353 的费马小定理求逆元完成,
code
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000005;
const int mod = 998244353;
typedef long long ll;
int n;
int si[N], sum[N];
vector<int> s[N];
ll qpow(ll a, ll b, ll p) {
ll res = 1, base = a;
while(b) {
if(b&1) res = res * base % p;
base = base * base % p;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
ll inv(ll a) {
return qpow(a, mod-2, mod);
}
ll ans;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
int tmp;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> si[i];
for(int j = 1; j <= si[i]; ++j) {
cin >> tmp;
sum[tmp]++, s[i].push_back(tmp);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ll res = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < si[i]; ++j)
res = (res + sum[s[i][j]] * inv(n) % mod) % mod;
ans = (ans + res * inv(si[i]) % mod) % mod;
}
cout << ans * qpow(n, mod-2, mod) % mod << endl;
return 0;
}三.总结
这周效率还算可以,下周继续猛猛干,寒假一定要猛猛上分,下周把贪心题单都写完,写一部分dp,继续打cf,加油吧。