链表OJ

前言
嗨,我是firdawn,因为我们前面已经学过链表相关的知识了,所以我们现在直接开始做链表OJ题来巩固链表相关知识。那么,让我们开始吧!
1.第一题
题目:给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。链表的中间结点
解题思路为:我们可以定义快慢指针去走这个链表,慢指针每走一步,快指针走两步。当快指针走到头时,慢指针所在节点为中间节点。解题代码如下:
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
//使用快慢指针判断链表中间节点
struct ListNode* fast=head,*slow=head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}2.第二题
题目:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。返回倒数第 k 个节点
解题思路为:这题的解题思路和第一题类似,我们可以定义两个快慢指针,快指针先走k步,当走到头时,也就是快指针指向NULL,慢指针所在节点为链表倒数第k个节点。 解题代码如下:
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
int kthToLast(struct ListNode* head, int k) {
//使用快慢指针,快指针比慢指针先走k步,快慢指针再同时走,快指针指向NULL时,慢指针就指向倒数第k个节点
struct ListNode* fast=head,*slow=head;
int num=k;
//慢指针先走
while(num--)
{
fast=fast->next;
}
//同时走
while(fast)
{
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow->val;
}3.第三题
题目:链表的回文结构。链表的回文结构
解题思路为:我们可以先找出链表的中间节点mid,将mid之后的链表逆置,这样,题目中给的链表的中间节点就变为rmid,然后让链表头指针head和链表中间节点rmid同时向前走,直到(headNULL || rmidNULL)结束,遍历链表过程中,如果( head->val != rmid->val ),则该链表不是回文结构,return false,如果能走完整个链表,说明两链表每个值都想等,该链表为回文结构。画图如下:
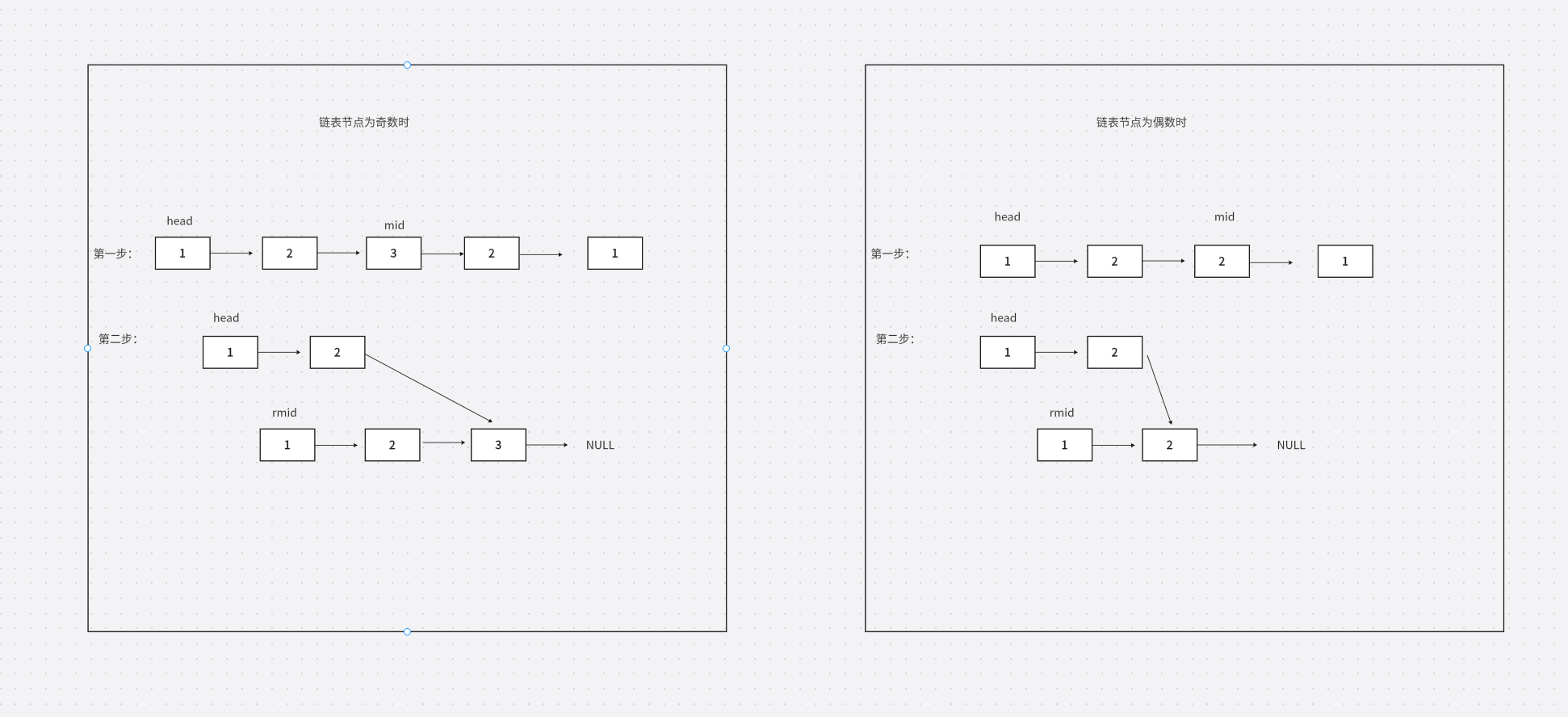
解题代码如下:
cpp
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
//使用快慢指针
struct ListNode* fast = head, *slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* cur=head;
struct ListNode* newhead=NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next=cur->next;
cur->next=newhead;
newhead=cur;
cur=next;
}
return newhead;
}
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(A);
struct ListNode* rmid = reverseList(mid);
while (A && rmid) {
if (A->val != rmid->val) {
return false;
}
A = A->next;
rmid = rmid->next;
}
return true;
// write code here
}
};4.第四题
题目:输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。相交链表
解题思路为:我们可以让两个指针从距离尾节点相同的地方走,当两指针指向的节点相同时,这两个指针就指向相交节点。定义 longList 和 shortList 两个指针,先用headA和headB分别遍历A链表和B链表,记录两链表的长度分别为lenA和lenB,让长链表的指针先向前走两链表长度差距步(abs(lenA - lenB)),然后两个链表的指针同时走,它们指向的节点相等时,该节点为两链表相交节点。画图如下:
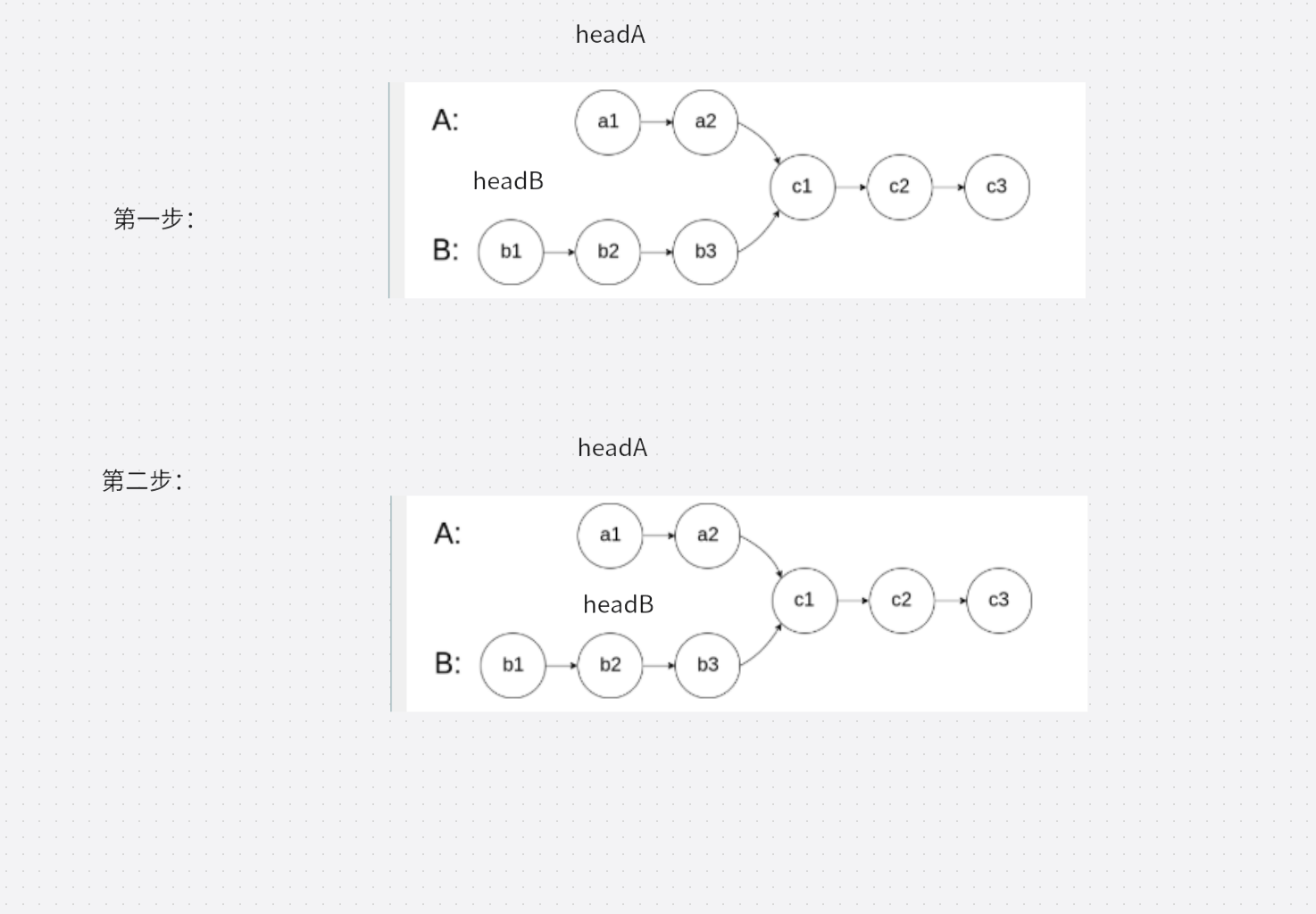
题目解题代码如下:
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
//判断是否相交:如果两个链表的尾节点指针相同则为相交,反之则不相交
//判断相交节点:使用longList和shortList两个指针,假设较短链表长度为shortlongth,对两个链表从距离尾节点shortlongth的距离,同时走,当节点指针第一次相同时,则为相交节点
//判断相交
struct ListNode* pA=headA,*pB=headB;//pA为A链表的尾指针,pB为B链表的尾指针
int lenA=1;
int lenB=1;
while(pA->next)
{
pA=pA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(pB->next)
{
pB=pB->next;
lenB++;
}
if(pA!=pB)
{
return NULL;
}
//链表相交,判断相交节点
int gap=abs(lenA-lenB);
struct ListNode* longList=headA,*shortList=headB;
if(lenA<lenB)
{
longList=headB;
shortList=headA;
}
while(gap--)
{
longList=longList->next;
}
while(longList!=shortList)
{
longList=longList->next;
shortList=shortList->next;
}
return shortList;
}5. 第五题
题目:给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。环形链表
解题思路为:我们可以定义快慢指针去走这个链表,慢指针每走一步,快指针走两步。当快慢指针相遇时,该链表带环,不相遇则不带环。解题代码如下:
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
//使用快慢指针解题,慢指针每走一步,快指针走两步。如果带环,慢指针会追上快指针,不带环则追不上。
struct ListNode* slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(fast==slow)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}6.第六题
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个结点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL。环形链表 II
解题思路为:这道题是上一题的升级版,先判断该链表有没有环,没有就返回NULL,有就继续下一步(判断链表带环的代码可以参考第五题)。如果链表带环,那使快慢指针相遇节点为meet,让该链表头指针head和meet指针同时走,它们的相遇点就是链表入环的第一个节点。为什么meet和head的相遇节点就是链表入环的第一个节点呢?证明如下图:
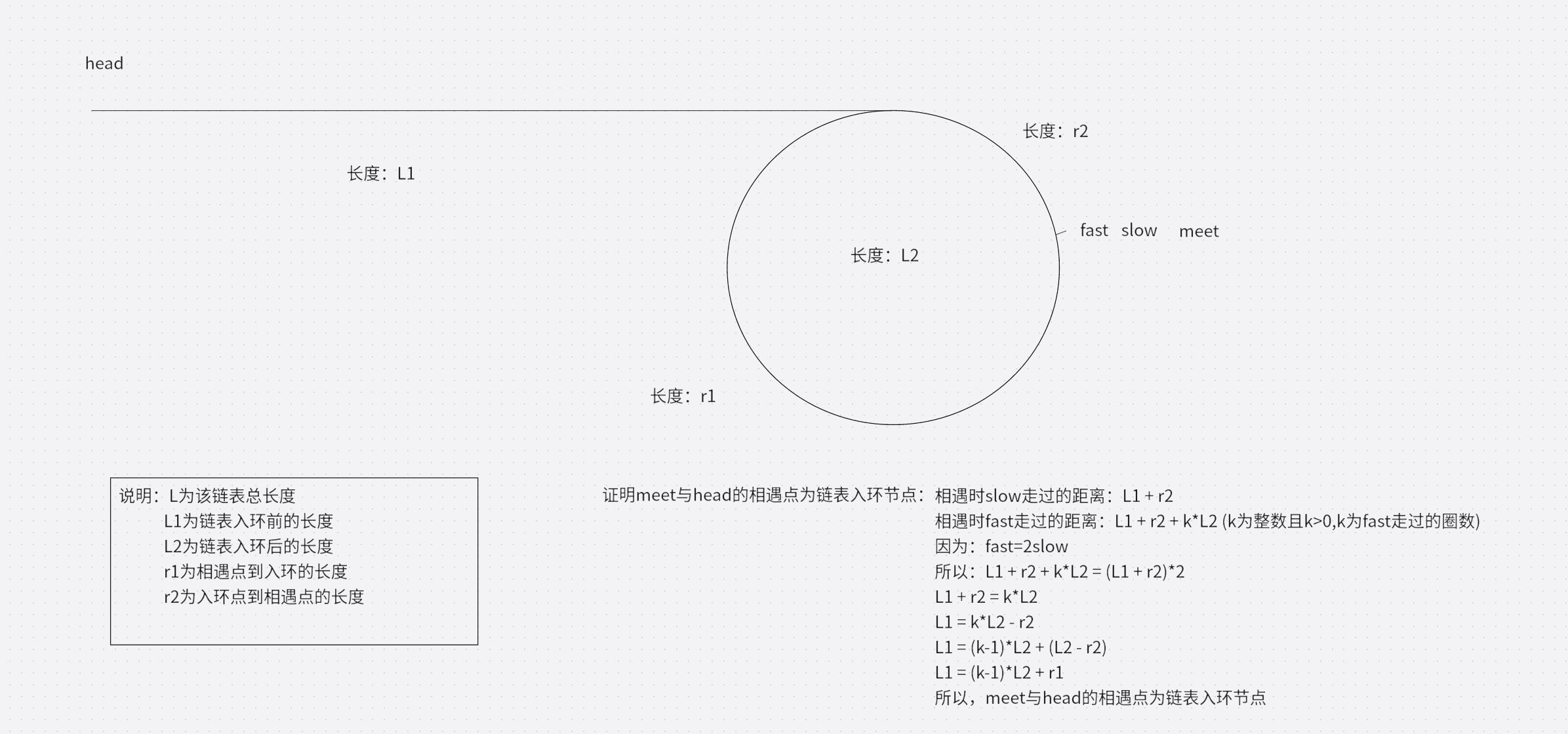
解题代码如下:
c
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
//判断链表是否为环形链表
struct ListNode* determineCycle(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(fast==slow)
{
return fast;
}
}
return NULL;
}
//判断环形链表的入环第一个节点
struct ListNode* enterCycleNode(struct ListNode* head,struct ListNode* meet)
{
while(head!=meet)
{
head=head->next;
meet=meet->next;
}
return head;
}
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
//使用快慢指针,通过它们是否可以相遇判断是否有环
//如果相遇,使相遇节点为meet,cur=head,meet和cur同时往前走,相遇点为链表入环的第一个节点
struct ListNode* meetNode=determineCycle(head);
if(meetNode==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
else
{
struct ListNode* enterNode=enterCycleNode(head,meetNode);
return enterNode;
}
}7.第七题
题目:给定一个链表,每个结点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何结点或空结点,要求返回这个链表的深度拷贝。随机链表的复制
解题思路为:先建立映射节点,使每个旧节点指向其复制节点,复制节点指向旧节点原本指向的下一个节点,通过旧节点与新节点的对应关系,赋值新节点的random,然后再将新节点连接起来。
解题代码如下:
c
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
//先建立映射节点,使每个旧节点指向其复制节点,复制节点指向旧节点原本指向的下一个节点,通过旧节点与新节点的对应关系,赋值新节点的random,然后再将新节点连接起来
//建立映射节点
if(head==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct Node* cur=head;
struct Node* next=head->next;
struct Node* newhead=NULL;
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copyNode=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
next=cur->next;
cur->next=copyNode;
copyNode->next=next;
copyNode->val=cur->val;
cur=next;
}
cur=head;
newhead=head->next;
//赋值新链表节点的random
while(cur)
{
struct Node* copyNode=cur->next;
if(cur->random)
{
copyNode->random=cur->random->next;
}
else
{
copyNode->random=NULL;
}
cur=cur->next->next;
}
cur=head;
//将新链表连接起来,并将旧链表恢复
while(cur->next)
{
struct Node* next=cur->next;
cur->next=cur->next->next;
cur=next;
}
return newhead;
}