在 PySide6 中,所有的窗口部件(QWidget 及其子类)都继承了事件处理机制(如鼠标右键、滚轮、窗口打开 / 关闭事件),可以通过重写这些事件来实现自定义功能,比如右键菜单、滚轮缩放等。要实现以上功能,核心是重写部件的事件处理方法 。事件方法名通常以 Event 结尾(如 mousePressEvent、wheelEvent),我们只需在自定义部件类中重新定义这些方法即可。
一、基本方法,以窗口打开事件为例
python
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QMessageBox
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setFixedSize(300, 200)
self.btn = QPushButton("关闭本窗口", self)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.close)
layout = QVBoxLayout(self)
layout.addWidget(self.btn)
# 重写showEvent方法(打开窗口时触发)
def showEvent(self, event):
# 调用父类方法,继承原有的showEvent方法
super().showEvent(event)
# 窗口第一次显示/从隐藏变为显示时触发
QMessageBox.information(self, "提示", "窗口即将打开!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = Window()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())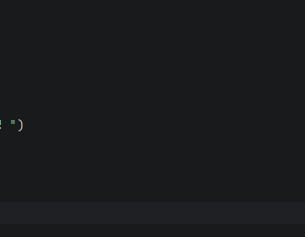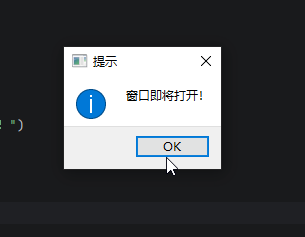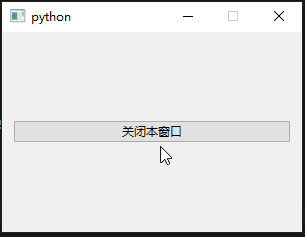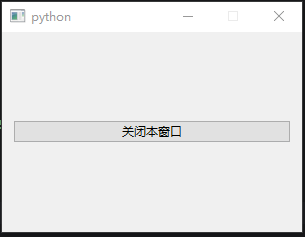
或:
python
import sys
from PySide6.QtCore import Qt
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QMessageBox, QErrorMessage
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setFixedSize(300, 200)
self.btn = QPushButton("关闭本窗口", self)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.close)
layout = QVBoxLayout(self)
layout.addWidget(self.btn)
# 重写showEvent方法(打开窗口时触发)
def showEvent(self, event):
# 调用父类方法,继承QWidget原有的showEvent方法
super().showEvent(event)
# 窗口第一次显示/从隐藏变为显示时触发
msg_box = QErrorMessage(self)
msg_box.showMessage("窗口已打开")
msg_box.setAttribute(Qt.WA_DeleteOnClose) # 关闭后自动删除
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = Window()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())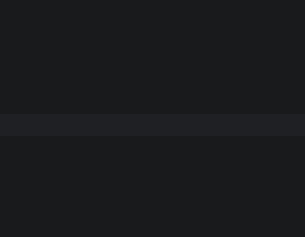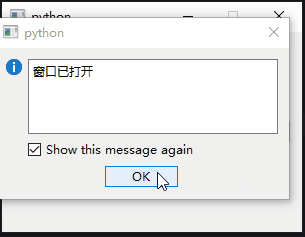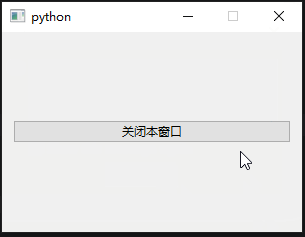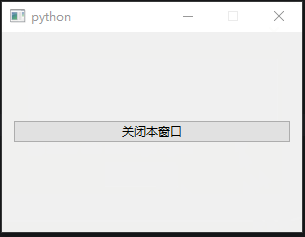
上面的代码重写showEvent()了,窗口首次显示或从隐藏恢复时触发,弹出打开提示框。这个功能在电气设计的hmi软件里很常见,比如当打开窗口时,对一些变量进行初始化,或者验证条件后再打开。代码中的super().showEvent(event),调用父类方法,继承QWidget原有的showEvent方法。
二、event.accept()和event.ignore()
除了super()继承父类方法,还有event.accept() :接受事件和event.ignore():忽略事件
python
def closeEvent(self, event):
# 弹出确认对话框
reply = QMessageBox.question(
self, "确认", "确定要关闭窗口吗?",
QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No,
QMessageBox.No # 默认选中No
)
# 根据用户选择决定是否关闭窗口
if reply == QMessageBox.Yes:
event.accept() # 接受关闭事件
else:
event.ignore() # 忽略关闭
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QMessageBox, QInputDialog
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setFixedSize(300, 200)
self.btn = QPushButton("关闭本窗口", self)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.close)
layout = QVBoxLayout(self)
layout.addWidget(self.btn)
# 重写closeEvent方法(关闭窗口时触发)
def closeEvent(self, event):
# 弹出确认对话框
reply = QMessageBox.question(
self, "确认", "确定要关闭窗口吗?",
QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No,
QMessageBox.No # 默认选中No
)
# 根据用户选择决定是否关闭窗口
if reply == QMessageBox.Yes:
event.accept() # 接受关闭事件
else:
event.ignore() # 忽略关闭事件(窗口不关闭)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = Window()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())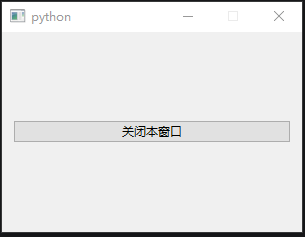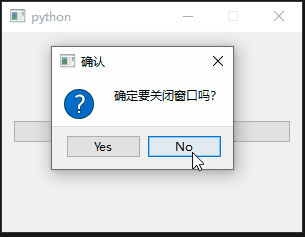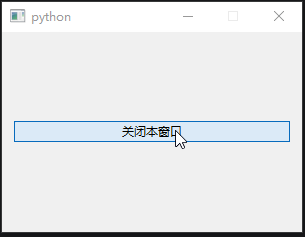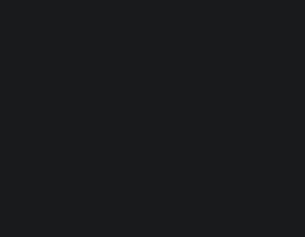
请注意,是有一些方法是"事后"方法,比如showEvent(),就是窗口即将显示 / 已经开始显示时触发的事件,在已经执行了show()之后才会启动该方法,所以就无法在方法中使用event.accept()和event.ignore()来控制程序。
下面的代码就是一个错误示范:
python
import sys
from PySide6.QtGui import QCloseEvent
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QMessageBox, QInputDialog
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setFixedSize(300, 200)
self.btn = QPushButton("关闭本窗口", self)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.close)
layout = QVBoxLayout(self)
layout.addWidget(self.btn)
# 重写showEvent方法(打开窗口时触发)
def showEvent(self, event):
super().showEvent(event)
while True:
text, ok = QInputDialog.getText(self, "输入密码", "请输入密码:")
if not ok:
pass_in = False
break
if text == "123456":
pass_in = True
break
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "错误", "密码错误")
if pass_in:
QMessageBox.information(self, "窗口即将打开", "密码正确")
event.accept()
else:
event.ignore()
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = Window()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())运行结果,当取消输入密码之后,页面还是正常显示了:
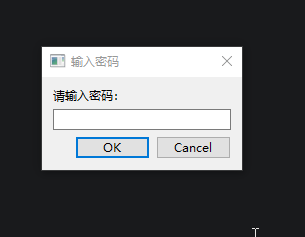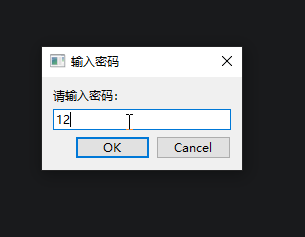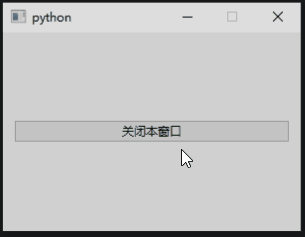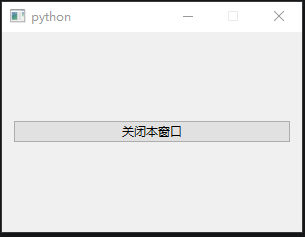
对于这种事后方法,可以将自定义功能放到该方法的事件"来源"里,比如showEvent()是由show()方法产生的,重写show()方法即可。
python
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QMessageBox, QInputDialog
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setFixedSize(300, 200)
self.btn = QPushButton("关闭本窗口", self)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.close)
layout = QVBoxLayout(self)
layout.addWidget(self.btn)
# 重写show方法,在show之前先验证密码
def show(self):
while True:
text, ok = QInputDialog.getText(self, "输入密码", "请输入密码:")
if not ok:
pass_in = False
break
if text == "123456":
pass_in = True
break
else:
QMessageBox.warning(self, "错误", "密码错误")
# 如果验证通过,则调用父类方法显示窗口
if pass_in:
super().show()
else:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = Window()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())三、鼠标事件示例
1、鼠标右键事件
python
import sys
from PySide6.QtGui import QCloseEvent, Qt, QAction
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QMessageBox, QInputDialog, QMenu
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setFixedSize(300, 200)
self.btn = QPushButton("关闭本窗口", self)
self.btn.clicked.connect(self.close)
layout = QVBoxLayout(self)
layout.addWidget(self.btn)
def mousePressEvent(self, event):
# 判断是否是鼠标右键按下
if event.button() == Qt.RightButton:
# 创建右键菜单
menu = QMenu(self)
# 添加菜单选项
action1 = QAction("关闭窗口", self)
action2 = QAction("关于", self)
# 绑定菜单点击事件
action1.triggered.connect(self.close)
action2.triggered.connect(self.show_about)
# 添加到菜单
menu.addAction(action1)
menu.addAction(action2)
# 在鼠标右键点击位置显示菜单
menu.exec(event.globalPosition().toPoint())
# 保留左键等其他事件的默认行为(可选)
super().mousePressEvent(event)
def show_about(self):
QMessageBox.about(self, "关于", "这是一个示例程序")
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = Window()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
2、鼠标滚轮事件
python
import sys
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QProgressBar
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setFixedSize(300, 200)
layout = QVBoxLayout(self)
self.progress_bar = QProgressBar(self)
self.progress_bar.setRange(0, 100)
self.progress_bar.setValue(0)
self.progress_bar.setFormat("当前进度:%p%")
layout.addWidget(self.progress_bar)
self.value = 0
def set_value(self):
if self.value < 0:
self.value = 0
elif self.value > 100:
self.value = 100
self.progress_bar.setValue(self.value)
def wheelEvent (self, event):
# 获取滚轮滚动方向(delta>0 向上滚,delta<0 向下滚)
delta = event.angleDelta().y() /120 # 我的鼠标每次滚动120度
self.value += delta
self.set_value()
# 保留默认滚轮行为(可选)
super().wheelEvent(event)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = Window()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
四、使用types.MethodType动态修改事件处理方法
python
import sys
import types
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QMessageBox
def close_event(widget, event):
# 弹出确认对话框
reply = QMessageBox.question(
widget, "确认", "确定要关闭窗口吗?",
QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No,
QMessageBox.No # 默认选中No
)
# 根据用户选择决定是否关闭窗口
if reply == QMessageBox.Yes:
event.accept() # 接受关闭事件
else:
event.ignore() # 忽略关闭
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = QWidget()
window.show()
window.closeEvent = types.MethodType(close_event, window) # 动态绑定关闭事件处理函数
sys.exit(app.exec())- PyQt/PySide 中,默认的
closeEvent是类的方法,比如使用window.closeEvent = close_event这样直接赋值普通函数会报错(因为普通函数没有绑定到对象,缺少self参数)。 types.MethodType解决了 "普通函数 → 对象方法" 的转换问题,让自定义函数能适配 GUI 库的方法调用规则。- 除了事件处理函数,
types.MethodType还可用于动态定义Qt部件其他的内置默认函数和新增函数,而不用重新定义Qt部件的类。 types.MethodType是针对单个实例 修改方法,不影响其他同类型部件(比如只改当前窗口的close,其他 QWidget 不受影响)。