思考问题:
1、当前目标点如何不断更新?按距离?如果存在动态障碍物占据全局路径该如何设置?
2、刹车距离如何预留?
输入全局规划器的轨迹(位置、朝向(曲线切线方向?))、车的当前位置(起点)、当前目标点和局部地图,输出车辆的线速度v和角速度w(控制器用其转换为车辆的油门和方向控制量,驱动车辆移动)。当前目标点需不断更新,引导车辆按全局规划的路径走向全局终点。局部地图一般是动态的,有些障碍物是不同移动的。局部路径优化的轨迹优化、避障算法与全局规划有相同之处,但由于直接输出给控制器使用,需要考虑车辆的运动模型;由于存在动态障碍物,还需预测障碍物的轨迹,增加时间约束。
ros navigation代码中,(父->子)nav_core/BaseLocalPlanner->(base_local_planner/TrajectoryPlannerROS、dwa_local_planner/DWAPlannerROS)
主要函数:
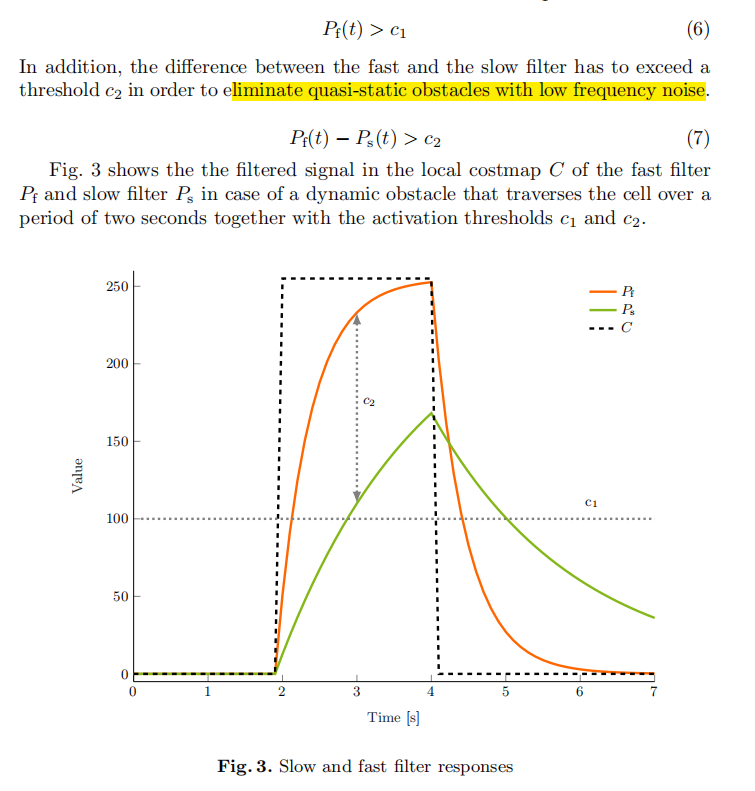
- setPlan:将global_planner规划路径plan输入
- computeVelocityCommands:根据plan计算角速度和线速度,输出给底盘控制器
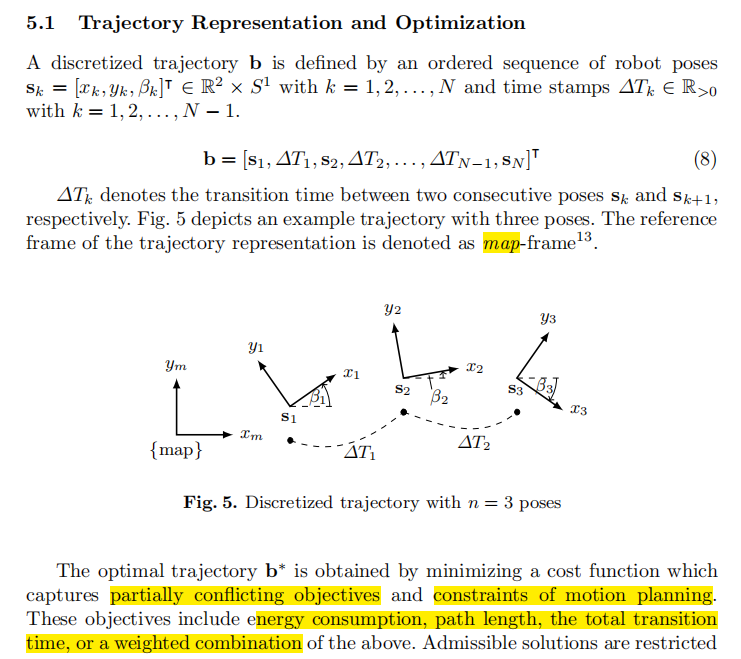
- isGoalReached:根据车辆当前位置和目标位置判断是否到达目标
一、局部路径规划算法
1、TrajectoryPlannerROS
代价函数:
1)方向角函数:轨迹终点方向角与当前目标点方向角(heading_scoring_);
2)距离评价函数:距离障碍物越远越好(occ_cost),贴合全局路径越近越好(path_dist、goal_dist);
base_local_planner/include/base_local_planner/trajectory_planner_ros.h
参考链接
- setPlan:将global_planner规划路径plan输入,赋给global_plan_
- computeVelocityCommands:根据plan计算角速度和线速度,输出给底盘控制器
1)将全局位置和plan变换到局部地图中transformed_plan,获取当前速度robot_vel
2)TrajectoryPlanner->updatePlan(transformed_plan):赋给global_plan_,轨迹最后一个点设为目标点,final_goal_x_/y_
3)TrajectoryPlanner->findBestPath(global_pose, robot_vel, drive_cmds):得到cmd_vel(drive_cmds),由createTrajectories(global_pose, robot_vel,acc_lim)得到Trajectory并返回。更新path_map_、goal_map_用于计算cost中Path/Goal_dist,path_map_记录各cell与全局规划路径上的cell之间的距离,goal_map_记录各cell与目标cell之间的距离。
4)TrajectoryPlanner->createTrajectories:Trajectory.cost需大于等0,cost计算公式如下,主要考虑occ_cost(障碍物)、path_dist(路径距离)、goal_dist(目标距离)和heading_diff(角度距离)等因素,返回cost最小的轨迹。holonomic_robot_表示全向机器人,一般为非全向,只有x和角速度、heading_scoring_表示是否为朝向打分,最大/小、线/角速度由当前速度加/减去最大加速度*sim_time_/sim_period_(dwa)。按最小/最大速度差/vx_samples_步长遍历所有前向速度和角速度(vx_samp、vy_samp和vtheta_samp),再遍历原地旋转轨迹,最后不行再生成逃逸轨迹。
5)TrajectoryPlanner::generateTrajectory:根据当前位置(x,y,theta)、速度(vx,vy,vtheta),使用最大加速度(acc_x,acc_y,acc_thea)达到期望速度(vx_samp,vy_samp,vtheta_samp),达到期望速度后匀速运动,总时间时间为sim_time_,!heading_scoring_时步数为num_steps = int(sim_time_ / sim_granularity_ + 0.5);heading_scoring_时num_steps = int(max((vmag * sim_time_) / sim_granularity_, fabs(vtheta_samp) / angular_sim_granularity_) + 0.5)。按dt = sim_time_ / num_steps进行加减速采样。最后输出的cmd_vel就是期望速度(vx_samp,vy_samp,vtheta_samp)。
cpp
void TrajectoryPlanner::generateTrajectory(
double x, double y, double theta,
double vx, double vy, double vtheta,
double vx_samp, double vy_samp, double vtheta_samp,
double acc_x, double acc_y, double acc_theta,
double impossible_cost,
Trajectory& traj) {
// make sure the configuration doesn't change mid run
boost::mutex::scoped_lock l(configuration_mutex_);
double x_i = x;
double y_i = y;
double theta_i = theta;
double vx_i, vy_i, vtheta_i;
vx_i = vx;
vy_i = vy;
vtheta_i = vtheta;
//compute the magnitude of the velocities
double vmag = hypot(vx_samp, vy_samp);
//compute the number of steps we must take along this trajectory to be "safe"
int num_steps;
if(!heading_scoring_) {
num_steps = int(max((vmag * sim_time_) / sim_granularity_, fabs(vtheta_samp) / angular_sim_granularity_) + 0.5);
} else {
num_steps = int(sim_time_ / sim_granularity_ + 0.5);
}
//we at least want to take one step... even if we won't move, we want to score our current position
if(num_steps == 0) {
num_steps = 1;
}
double dt = sim_time_ / num_steps;
double time = 0.0;
//create a potential trajectory
traj.resetPoints();
traj.xv_ = vx_samp;
traj.yv_ = vy_samp;
traj.thetav_ = vtheta_samp;
traj.cost_ = -1.0;
//initialize the costs for the trajectory
double path_dist = 0.0;
double goal_dist = 0.0;
double occ_cost = 0.0;
double heading_diff = 0.0;
for(int i = 0; i < num_steps; ++i){
//get map coordinates of a point
unsigned int cell_x, cell_y;
//we don't want a path that goes off the know map
if(!costmap_.worldToMap(x_i, y_i, cell_x, cell_y)){
traj.cost_ = -1.0;
return;
}
//check the point on the trajectory for legality
double footprint_cost = footprintCost(x_i, y_i, theta_i);
//if the footprint hits an obstacle this trajectory is invalid
if(footprint_cost < 0){
traj.cost_ = -1.0;
return;
//TODO: Really look at getMaxSpeedToStopInTime... dues to discretization errors and high acceleration limits,
//it can actually cause the robot to hit obstacles. There may be something to be done to fix, but I'll have to
//come back to it when I have time. Right now, pulling it out as it'll just make the robot a bit more conservative,
//but safe.
/*
double max_vel_x, max_vel_y, max_vel_th;
//we want to compute the max allowable speeds to be able to stop
//to be safe... we'll make sure we can stop some time before we actually hit
getMaxSpeedToStopInTime(time - stop_time_buffer_ - dt, max_vel_x, max_vel_y, max_vel_th);
//check if we can stop in time
if(fabs(vx_samp) < max_vel_x && fabs(vy_samp) < max_vel_y && fabs(vtheta_samp) < max_vel_th){
ROS_ERROR("v: (%.2f, %.2f, %.2f), m: (%.2f, %.2f, %.2f) t:%.2f, st: %.2f, dt: %.2f", vx_samp, vy_samp, vtheta_samp, max_vel_x, max_vel_y, max_vel_th, time, stop_time_buffer_, dt);
//if we can stop... we'll just break out of the loop here.. no point in checking future points
break;
}
else{
traj.cost_ = -1.0;
return;
}
*/
}
occ_cost = std::max(std::max(occ_cost, footprint_cost), double(costmap_.getCost(cell_x, cell_y)));
//do we want to follow blindly
if (simple_attractor_) {
goal_dist = (x_i - global_plan_[global_plan_.size() -1].pose.position.x) *
(x_i - global_plan_[global_plan_.size() -1].pose.position.x) +
(y_i - global_plan_[global_plan_.size() -1].pose.position.y) *
(y_i - global_plan_[global_plan_.size() -1].pose.position.y);
} else {
bool update_path_and_goal_distances = true;
// with heading scoring, we take into account heading diff, and also only score
// path and goal distance for one point of the trajectory
if (heading_scoring_) {
if (time >= heading_scoring_timestep_ && time < heading_scoring_timestep_ + dt) {
heading_diff = headingDiff(cell_x, cell_y, x_i, y_i, theta_i);
} else {
update_path_and_goal_distances = false;
}
}
if (update_path_and_goal_distances) {
//update path and goal distances
path_dist = path_map_(cell_x, cell_y).target_dist;
goal_dist = goal_map_(cell_x, cell_y).target_dist;
//if a point on this trajectory has no clear path to goal it is invalid
if(impossible_cost <= goal_dist || impossible_cost <= path_dist){
// ROS_DEBUG("No path to goal with goal distance = %f, path_distance = %f and max cost = %f",
// goal_dist, path_dist, impossible_cost);
traj.cost_ = -2.0;
return;
}
}
}
//the point is legal... add it to the trajectory
traj.addPoint(x_i, y_i, theta_i);
//calculate velocities
vx_i = computeNewVelocity(vx_samp, vx_i, acc_x, dt);
vy_i = computeNewVelocity(vy_samp, vy_i, acc_y, dt);
vtheta_i = computeNewVelocity(vtheta_samp, vtheta_i, acc_theta, dt);
//calculate positions
x_i = computeNewXPosition(x_i, vx_i, vy_i, theta_i, dt);
y_i = computeNewYPosition(y_i, vx_i, vy_i, theta_i, dt);
theta_i = computeNewThetaPosition(theta_i, vtheta_i, dt);
//increment time
time += dt;
} // end for i < numsteps
//ROS_INFO("OccCost: %f, vx: %.2f, vy: %.2f, vtheta: %.2f", occ_cost, vx_samp, vy_samp, vtheta_samp);
double cost = -1.0;
if (!heading_scoring_) {
cost = path_distance_bias_ * path_dist + goal_dist * goal_distance_bias_ + occdist_scale_ * occ_cost;
} else {
cost = occdist_scale_ * occ_cost + path_distance_bias_ * path_dist + 0.3 * heading_diff + goal_dist * goal_distance_bias_;
}
traj.cost_ = cost;
}
/**
* @brief Compute x position based on velocity
* @param xi The current x position
* @param vx The current x velocity
* @param vy The current y velocity
* @param theta The current orientation
* @param dt The timestep to take
* @return The new x position
*/
inline double computeNewXPosition(double xi, double vx, double vy, double theta, double dt){
return xi + (vx * cos(theta) + vy * cos(M_PI_2 + theta)) * dt;
}
/**
* @brief Compute y position based on velocity
* @param yi The current y position
* @param vx The current x velocity
* @param vy The current y velocity
* @param theta The current orientation
* @param dt The timestep to take
* @return The new y position
*/
inline double computeNewYPosition(double yi, double vx, double vy, double theta, double dt){
return yi + (vx * sin(theta) + vy * sin(M_PI_2 + theta)) * dt;
}
/**
* @brief Compute orientation based on velocity
* @param thetai The current orientation
* @param vth The current theta velocity
* @param dt The timestep to take
* @return The new orientation
*/
inline double computeNewThetaPosition(double thetai, double vth, double dt){
return thetai + vth * dt;
}
//compute velocity based on acceleration
/**
* @brief Compute velocity based on acceleration
* @param vg The desired velocity, what we're accelerating up to
* @param vi The current velocity
* @param a_max An acceleration limit
* @param dt The timestep to take
* @return The new velocity
*/
inline double computeNewVelocity(double vg, double vi, double a_max, double dt){
if((vg - vi) >= 0) {
return std::min(vg, vi + a_max * dt);
}
return std::max(vg, vi - a_max * dt);
}- isGoalReached:根据车辆当前位置和目标位置判断是否到达目标,初始化完成后返回reached_goal_
2、DWA(Dynamic Window Approach,动态窗口法)
DWA
参考链接1、参考链接2
采样不同v和w,根据运动学模型生成多条轨迹;再从中选取最好的1条轨迹,评价函数如下:
1)方向角函数:轨迹终点方向角与当前目标点方向角;
2)距离评价函数:距离障碍物越远越好,贴合全局路径越近越好;
3)速度评价函数:容许范围内越大越好
4)摆动打分
cpp
base_local_planner::OscillationCostFunction oscillation_costs_(摆动打分)
base_local_planner::ObstacleCostFunction obstacle_costs_(避障打分)
base_local_planner::MapGridCostFunction path_costs_(路径跟随打分)
base_local_planner::MapGridCostFunction goal_costs_(指向目标打分)
base_local_planner::MapGridCostFunction goal_front_costs_(前向点指向目标打分)
base_local_planner::MapGridCostFunction alignment_costs_(对齐打分)代码主要实现在base_local_planner::SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner类中,DWAPlanner初始化std::vector<base_local_planner::TrajectorySampleGenerator*> gen_list用于生成不同采样轨迹,std::vector<base_local_planner::TrajectoryCostFunction*> critics用于打分,包括以上6个打分规则,每项再用scale调节权重cost *= score_function_p->getScale()。以参数形式初始化SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner。
cpp
bool DWAPlannerROS::dwaComputeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::PoseStamped &global_pose, geometry_msgs::Twist& cmd_vel) {
// dynamic window sampling approach to get useful velocity commands
if(! isInitialized()){
ROS_ERROR("This planner has not been initialized, please call initialize() before using this planner");
return false;
}
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped robot_vel;
odom_helper_.getRobotVel(robot_vel);
/* For timing uncomment
struct timeval start, end;
double start_t, end_t, t_diff;
gettimeofday(&start, NULL);
*/
//compute what trajectory to drive along
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped drive_cmds;
drive_cmds.header.frame_id = costmap_ros_->getBaseFrameID();
// call with updated footprint,调研DWAPlanner::findBestPath
base_local_planner::Trajectory path = dp_->findBestPath(global_pose, robot_vel, drive_cmds);
//ROS_ERROR("Best: %.2f, %.2f, %.2f, %.2f", path.xv_, path.yv_, path.thetav_, path.cost_);
/* For timing uncomment
gettimeofday(&end, NULL);
start_t = start.tv_sec + double(start.tv_usec) / 1e6;
end_t = end.tv_sec + double(end.tv_usec) / 1e6;
t_diff = end_t - start_t;
ROS_INFO("Cycle time: %.9f", t_diff);
*/
//pass along drive commands
cmd_vel.linear.x = drive_cmds.pose.position.x;
cmd_vel.linear.y = drive_cmds.pose.position.y;
cmd_vel.angular.z = tf2::getYaw(drive_cmds.pose.orientation);
//if we cannot move... tell someone
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> local_plan;
if(path.cost_ < 0) {
ROS_DEBUG_NAMED("dwa_local_planner",
"The dwa local planner failed to find a valid plan, cost functions discarded all candidates. This can mean there is an obstacle too close to the robot.");
local_plan.clear();
publishLocalPlan(local_plan);
return false;
}
ROS_DEBUG_NAMED("dwa_local_planner", "A valid velocity command of (%.2f, %.2f, %.2f) was found for this cycle.",
cmd_vel.linear.x, cmd_vel.linear.y, cmd_vel.angular.z);
// Fill out the local plan
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < path.getPointsSize(); ++i) {
double p_x, p_y, p_th;
path.getPoint(i, p_x, p_y, p_th);
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped p;
p.header.frame_id = costmap_ros_->getGlobalFrameID();
p.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
p.pose.position.x = p_x;
p.pose.position.y = p_y;
p.pose.position.z = 0.0;
tf2::Quaternion q;
q.setRPY(0, 0, p_th);
tf2::convert(q, p.pose.orientation);
local_plan.push_back(p);
}
//publish information to the visualizer
publishLocalPlan(local_plan);
return true;
}
bool DWAPlannerROS::computeVelocityCommands(geometry_msgs::Twist& cmd_vel) {
// dispatches to either dwa sampling control or stop and rotate control, depending on whether we have been close enough to goal
if ( ! costmap_ros_->getRobotPose(current_pose_)) {
ROS_ERROR("Could not get robot pose");
return false;
}
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> transformed_plan;
if ( ! planner_util_.getLocalPlan(current_pose_, transformed_plan)) {
ROS_ERROR("Could not get local plan");
return false;
}
//if the global plan passed in is empty... we won't do anything
if(transformed_plan.empty()) {
ROS_WARN_NAMED("dwa_local_planner", "Received an empty transformed plan.");
return false;
}
ROS_DEBUG_NAMED("dwa_local_planner", "Received a transformed plan with %zu points.", transformed_plan.size());
// update plan in dwa_planner even if we just stop and rotate, to allow checkTrajectory
dp_->updatePlanAndLocalCosts(current_pose_, transformed_plan, costmap_ros_->getRobotFootprint());
// 到达目标点后的停止旋转运动控制类latchedStopRotateController_能到达终点就不用dwa了
if (latchedStopRotateController_.isPositionReached(&planner_util_, current_pose_)) {
//publish an empty plan because we've reached our goal position
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> local_plan;
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> transformed_plan;
publishGlobalPlan(transformed_plan);
publishLocalPlan(local_plan);
base_local_planner::LocalPlannerLimits limits = planner_util_.getCurrentLimits();
return latchedStopRotateController_.computeVelocityCommandsStopRotate(
cmd_vel,
limits.getAccLimits(),
dp_->getSimPeriod(),
&planner_util_,
odom_helper_,
current_pose_,
[this](auto pos, auto vel, auto vel_samples){ return dp_->checkTrajectory(pos, vel, vel_samples); });
} else {//使用dwaComputeVelocityCommands
bool isOk = dwaComputeVelocityCommands(current_pose_, cmd_vel);
if (isOk) {
publishGlobalPlan(transformed_plan);
} else {
ROS_WARN_NAMED("dwa_local_planner", "DWA planner failed to produce path.");
std::vector<geometry_msgs::PoseStamped> empty_plan;
publishGlobalPlan(empty_plan);
}
return isOk;
}
}
};
namespace base_local_planner {
SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner::SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner(std::vector<TrajectorySampleGenerator*> gen_list, std::vector<TrajectoryCostFunction*>& critics, int max_samples) {
max_samples_ = max_samples;
gen_list_ = gen_list; // DWAPlanner设置轨迹生成器
critics_ = critics; // DWAPlanner设置轨迹打分器
}
double SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner::scoreTrajectory(Trajectory& traj, double best_traj_cost) {
double traj_cost = 0;
int gen_id = 0;
// 每条轨迹遍历critics_进行打分
for(std::vector<TrajectoryCostFunction*>::iterator score_function = critics_.begin(); score_function != critics_.end(); ++score_function) {
TrajectoryCostFunction* score_function_p = *score_function;
if (score_function_p->getScale() == 0) {
continue;
}
double cost = score_function_p->scoreTrajectory(traj);
if (cost < 0) {
ROS_DEBUG("Velocity %.3lf, %.3lf, %.3lf discarded by cost function %d with cost: %f", traj.xv_, traj.yv_, traj.thetav_, gen_id, cost);
traj_cost = cost;
break;
}
if (cost != 0) {
cost *= score_function_p->getScale(); // 对每项打分进行加权
}
traj_cost += cost;
if (best_traj_cost > 0) {
// since we keep adding positives, once we are worse than the best, we will stay worse
if (traj_cost > best_traj_cost) {
break;
}
}
gen_id ++;
}
return traj_cost;
}
bool SimpleScoredSamplingPlanner::findBestTrajectory(Trajectory& traj, std::vector<Trajectory>* all_explored) {
Trajectory loop_traj;
Trajectory best_traj;
double loop_traj_cost, best_traj_cost = -1;
bool gen_success;
int count, count_valid;
for (std::vector<TrajectoryCostFunction*>::iterator loop_critic = critics_.begin(); loop_critic != critics_.end(); ++loop_critic) {
TrajectoryCostFunction* loop_critic_p = *loop_critic;
if (loop_critic_p->prepare() == false) {
ROS_WARN("A scoring function failed to prepare");
return false;
}
}
// 使用gen_list_遍历所有轨迹
for (std::vector<TrajectorySampleGenerator*>::iterator loop_gen = gen_list_.begin(); loop_gen != gen_list_.end(); ++loop_gen) {
count = 0;
count_valid = 0;
TrajectorySampleGenerator* gen_ = *loop_gen;
while (gen_->hasMoreTrajectories()) {
gen_success = gen_->nextTrajectory(loop_traj);// 生成下一条轨迹
if (gen_success == false) {
// TODO use this for debugging
continue;
}
// 对轨迹进行打分
loop_traj_cost = scoreTrajectory(loop_traj, best_traj_cost);
if (all_explored != NULL) {
loop_traj.cost_ = loop_traj_cost;
all_explored->push_back(loop_traj);
}
if (loop_traj_cost >= 0) {
count_valid++;
if (best_traj_cost < 0 || loop_traj_cost < best_traj_cost) {
best_traj_cost = loop_traj_cost;
best_traj = loop_traj;
}
}
count++;
if (max_samples_ > 0 && count >= max_samples_) {
break;
}
}
if (best_traj_cost >= 0) {
traj.xv_ = best_traj.xv_;
traj.yv_ = best_traj.yv_;
traj.thetav_ = best_traj.thetav_;
traj.cost_ = best_traj_cost;
traj.resetPoints();
double px, py, pth;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < best_traj.getPointsSize(); i++) {
best_traj.getPoint(i, px, py, pth);
traj.addPoint(px, py, pth);
}
}
ROS_DEBUG("Evaluated %d trajectories, found %d valid", count, count_valid);
if (best_traj_cost >= 0) {
// do not try fallback generators
break;
}
}
return best_traj_cost >= 0;
}
}// namespace3、TEB(Time Elastic Band ,时间弹力带)
TEB、代码
参考论文《Online Trajectory Optimization and Navigation
in Dynamic Environments in ROS》,TEB基于g2o库优化局部离散轨迹点(t,x,y, θ \theta θ)变量,根据相邻帧这些变量可以计算出v和w。由于增加了时间维度,便于根据障碍物预测轨迹进行避障。
检测动态物体步骤如下:
1)使用快滤波器Pf和慢滤波器Ps,当栅格有动态物体时占用概率会增大,Pf会快于Ps,而对于静态或无障碍物两者几乎相等
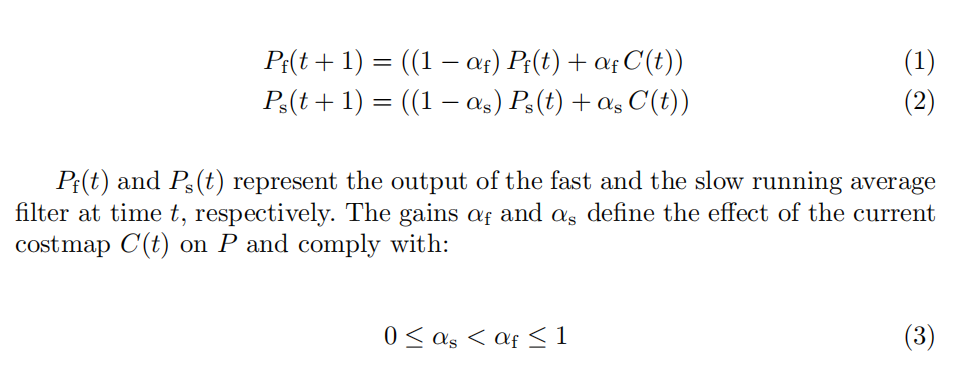
对于大障碍物公式可利用邻域栅格进行检测,belta用于调节中心栅格及相邻栅格权重:
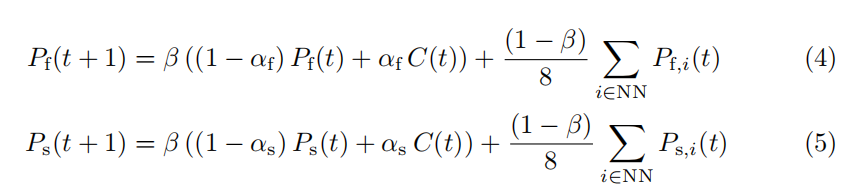
当两者满足如下条件时,认为栅格中为动态物体的点
2)由上一步得到动态和非动态的二值栅格图,进行腐蚀膨胀和聚类可得到动态物体,如白色块
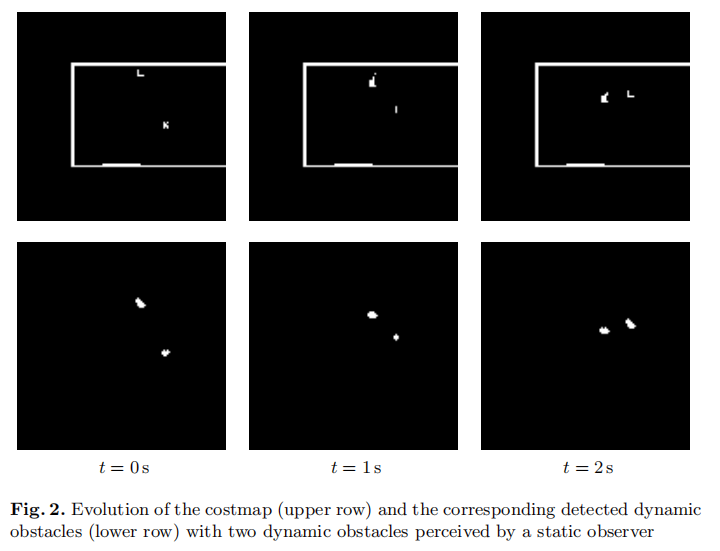

3)以栅格中心表示物体,使用匈牙利算法可对动态物体进行跟踪,估计障碍物速度、方向。从而可以得到和时间相关的动态栅格地图,用于避障
TEB结合了时间使用如下方式表示轨迹,
目标函数表示如下,fi(b)可以是如下几项
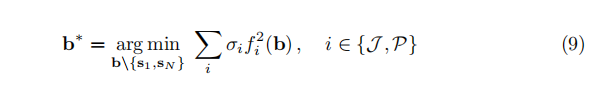
1)跟随路径约束和避障约束
距离障碍物越远越好,贴合全局路径越近越好
2)速度/角速度约束
约束相邻轨迹点的速度和加速度,使其不要超出容许范围
3)运动学越束
使轨迹尽可能平滑,更符合运动学模型
4)最快路径
到达目标点的时间尽可能短
参考论文主要有,基本是C. R¨osmann作者的
17\] C. R¨osmann, F. Hoffmann, T. Bertram. "Integrated online trajectory planning and optimization in distinctive topologies". In: Robotics and Autonomous Systems, Volume 88, pp. 142--153, 2017. \[18\] C. R¨osmann, F. Hoffmann, T. Bertram. "Online Trajectory Planning in ROS under Kinodynamic Constraints with Timed-Elastic-Bands". In: Robot Operating System (ROS) - The Complete Reference 2 (A. Koubaa, ed.), vol. 707 of Studies in Computational Intelligence, Springer International Publishing, 2017. 安装运行: 环境:Ubuntu 18.04 + ROS melodic ```bash $ mkdir -p ~/teb_ws/src $ cd ~/teb_ws/src $ catkin_init_workspace $ git clone https://github.com/rst-tu-dortmund/teb_local_planner.git $ git clone https://github.com/rst-tu-dortmund/teb_local_planner_tutorials.git $ git clone https://github.com/rst-tu-dortmund/costmap_converter.git $ git clone https://github.com/AMRobots/stage_ros.git $ cd ~/teb_ws $ catkin_make $ source devel/setup.bash # 检查是否正确安装 $ roslaunch teb_local_planner_tutorials dyn_obst_corridor_scenario.launch ``` 然后将teb_tutorials文件夹中文件拷到\~/teb_ws/src/teb_local_planner_tutorials对应文件夹下 dyn_obst_corridor_scenario_skew.launch -\> launch corridor_skew.yaml -\> maps move_obstacle.py - \> scripts (替换原文件) move_obstacle_skew_l.py - \> scripts move_obstacle_skew_r.py - \> scripts corridor_skew.world -\> stage ```bash $ roslaunch teb_local_planner_tutorials dyn_obst_corridor_scenario_skew.launch ``` 二、运动学模型 常见两轮差速和car_like汽车类模型大多车是非全向的,只有前向速度和旋转速度,而可以左右移动的全向移动的车才有y方向速度。根据运动学模型,由局部规划器输出的线速度v和角速度w,得到车辆控制量,控制车辆移动。 1)两轮差速模型:参考《ROS机器人编程》-表允晳 赵汉哲 郑黎蝹 林泰勋。无方向盘,通过左右轮差速控制方向,控制量一般是左右轮速度vl、vr。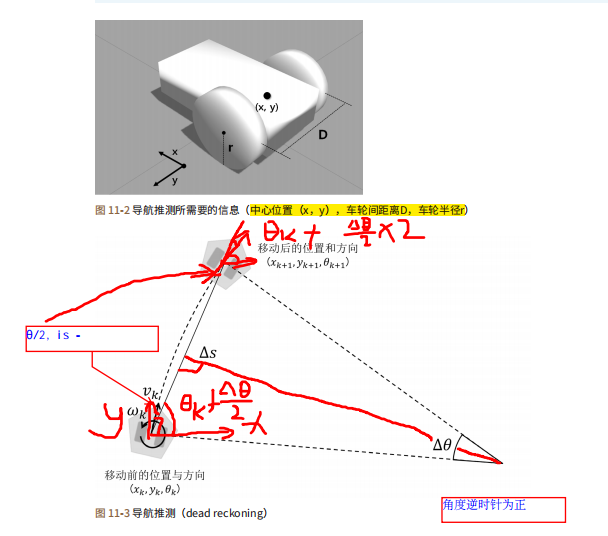 当局部规划器给出vk、wk后,可通过下式计算左右轮速度: 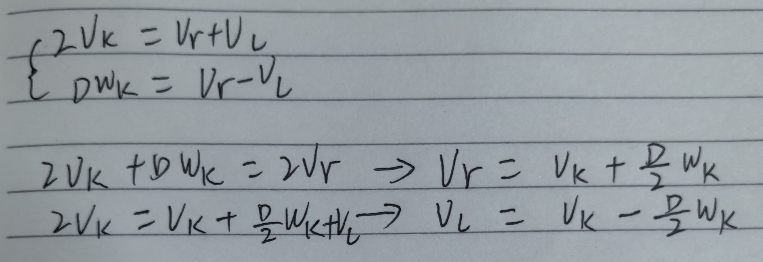 2)[汽车模型](https://www.jishulink.com/post/1879235) 汽车car-like可能是前驱、后驱或者四驱,可简化成Bicycle Model(自行车模型)。根据v和w输出油门(与后轮速度Vr(Vrear)直接相关)及方向盘转向角 θ \\theta θ控制量。一般使用Ackermann(阿克曼)转向结构几何来计算,转弯时四个轮子都必须绕同一个瞬时圆心转,圆半径不一样。如下图所示,L为前轮和后轮轴距,r为后轮转弯半径,w为后轮转速。 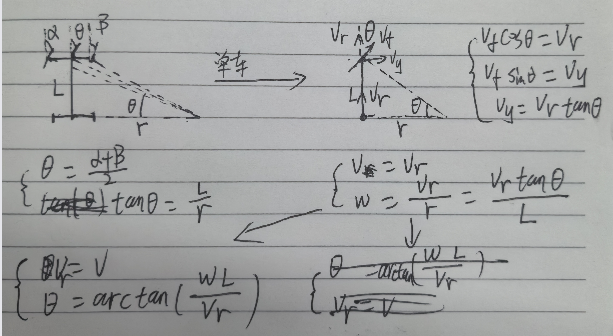 三、避障算法 静态障碍物避障与全局规划区一样,但动态障碍物需预测其轨迹进行避障。 1.车辆模型 使用四方形、圆形表示? 2.障碍物形状 以圆形表示比较简单,只需计算点或线与圆心距离。不规则轮廓或轨迹能否通过离散点计算? 3.距离计算 点-点、点-线距离。