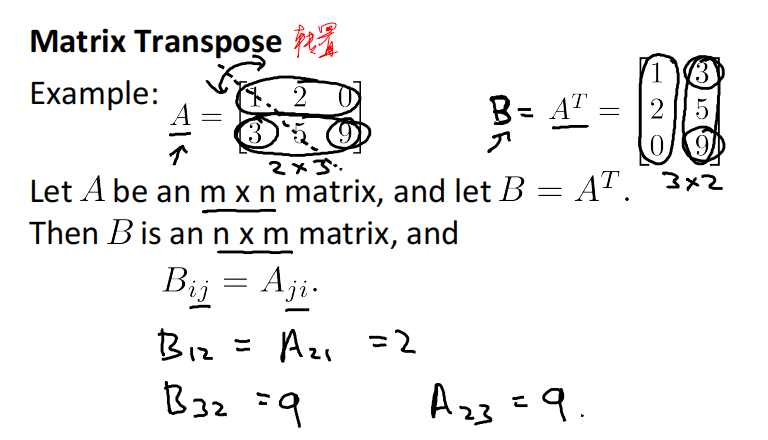关键词:
Matrices 矩阵
vector 向量
Matrix Addition 矩阵加法
Scalar Multiplication 标量乘法
Matrix-vector multiplication 矩阵向量乘法
Matrix-matrix multiplication 矩阵矩阵乘法
Not Commutative 不服从交换律
Associative 服从结合律
Identity Matrix 单位矩阵
Inverse and transcope 逆和转置
目录
[3.1 Matrices and vectors 矩阵和向量](#3.1 Matrices and vectors 矩阵和向量)
[3.1.1 Matrix: Rectangular array of numbers](#3.1.1 Matrix: Rectangular array of numbers)
[3.1.2 Matrix Elements (entries of matrix)](#3.1.2 Matrix Elements (entries of matrix))
[3.1.3 Vector: An n x1 matrix](#3.1.3 Vector: An n x1 matrix)
[3.2 Addition and scalar multiplication 矩阵加法和标量乘法](#3.2 Addition and scalar multiplication 矩阵加法和标量乘法)
[3.2.1 Matrix Addition](#3.2.1 Matrix Addition)
[3.2.2 Scalar Multiplication 标量乘法](#3.2.2 Scalar Multiplication 标量乘法)
[3.2.3 Combination of Operands](#3.2.3 Combination of Operands)
[3.3 Matrix-vector multiplication 矩阵向量乘法](#3.3 Matrix-vector multiplication 矩阵向量乘法)
[3.3.1 Example1](#3.3.1 Example1)
[3.3.2 Details](#3.3.2 Details)
[3.3.3 Example2](#3.3.3 Example2)
[3.3.4 矩阵向量乘法在线性回归中的应用举例](#3.3.4 矩阵向量乘法在线性回归中的应用举例)
[3.4 Matrix-matrix multiplication 矩阵矩阵乘法](#3.4 Matrix-matrix multiplication 矩阵矩阵乘法)
[3.4.1 Example](#3.4.1 Example)
[3.4.2 Details](#3.4.2 Details)
[3.4.3 Example2](#3.4.3 Example2)
[3.4.4 矩阵矩阵乘法在线性回归中的应用举例](#3.4.4 矩阵矩阵乘法在线性回归中的应用举例)
[3.5 Matrix multiplication properties 矩阵乘法的特性](#3.5 Matrix multiplication properties 矩阵乘法的特性)
[3.5.1 Not Commutative 不服从交换律](#3.5.1 Not Commutative 不服从交换律)
[3.5.2 Associative 服从结合律](#3.5.2 Associative 服从结合律)
[3.5.3 Identity Matrix 单位矩阵](#3.5.3 Identity Matrix 单位矩阵)
[3.6 Inverse and transcope 逆和转置](#3.6 Inverse and transcope 逆和转置)
[3.6.1 Matrix Inverse 矩阵的逆](#3.6.1 Matrix Inverse 矩阵的逆)
[3.6.2 Matrix Transcope 矩阵转置](#3.6.2 Matrix Transcope 矩阵转置)
正文
3.1 Matrices and vectors 矩阵和向量
3.1.1 Matrix: Rectangular array of numbers
Dimension of matrix: number of rows x number of columns
这是一个4x2矩阵,即4行2列:
A=
\\begin{bmatrix} 1402\&191\\\\ 1371\&821\\\\ 949\&1437\\\\ 147\&1448\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
记为R\^{4✖️2}.
这是一个2x3矩阵,即2行3列:
B=
\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&2\&3\\\\ 4\&5\&6\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
记为R\^{2✖️3}.
3.1.2 Matrix Elements (entries of matrix)
A_{ij} = "i,j entry" in the i\^{th} row, j\^{th} column.
such as:
A_{11}=1402
A_{12}=191
A_{32}=1437
A_{41}=147
A_{43}=undefined(error)
3.1.3 Vector: An n x1 matrix
这是一个4-dimensioned vector:
y=
\\begin{bmatrix} 460\\\\ 232\\\\ 315\\\\ 178\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
记为R\^4.
y_i=i\^{th} element, such as
y_1=460 , y_2=232, y_3=315
我们常用A, B, C, X 来表示矩阵matrix,用a, b, x, y 来表示数字number。
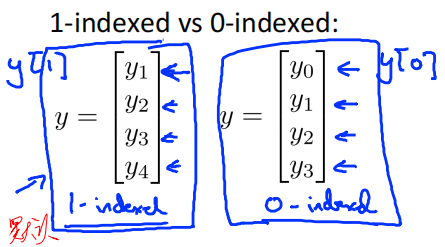
1-indexed vs 0-indexed:
向量下标从1开始还是从0开始?
默认从1开始!
3.2 Addition and scalar multiplication 矩阵加法和标量乘法
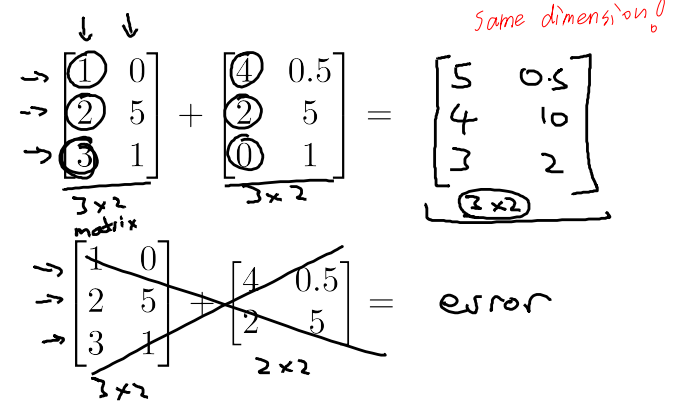
3.2.1 Matrix Addition
只有同型矩阵可以相加! same dimension!
对应位置的元素相加。
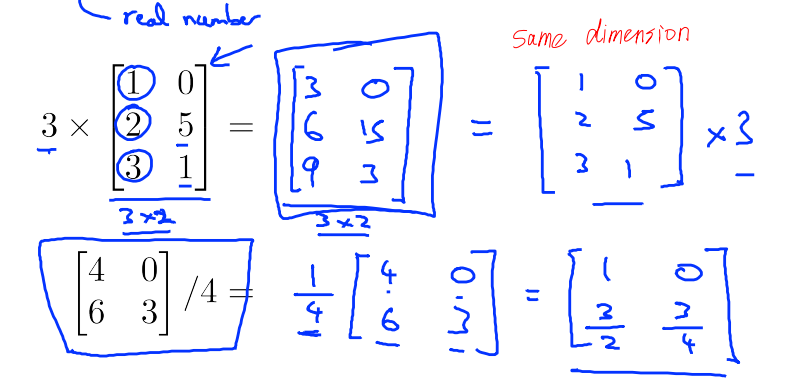
3.2.2 Scalar Multiplication 标量乘法
scalar: real number
计算前后矩阵的形状不变 same dimension!
每个元素都要乘
3.2.3 Combination of Operands
如下例子所示:
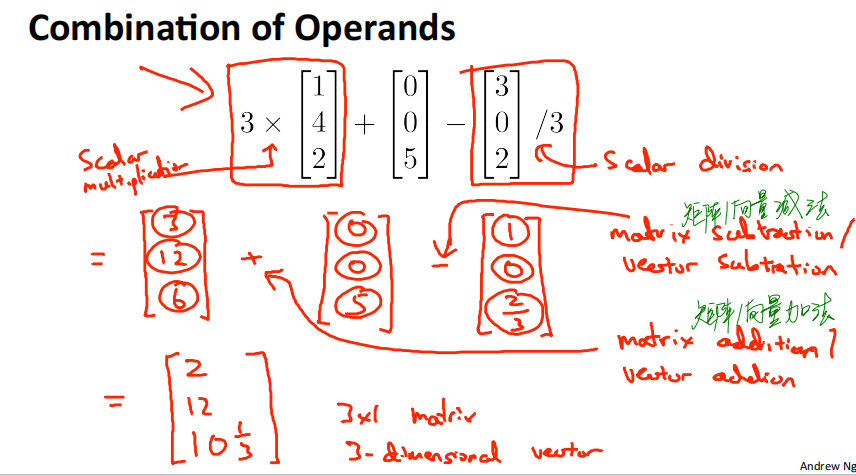
用到的运算:
scalar multiplication 标量乘法
scalar division 标量除法
matrix subtraction/ vector subtraction 矩阵/向量减法
matrix addition/ vector addition矩阵/向量加法
最终得到一个 3✖️1 matrix / 3-dimensioned vector
3.3 Matrix-vector multiplication 矩阵向量乘法
3.3.1 Example1
\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&3\\\\ 4\&0\\\\ 2\&1\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} 1\\\\ 5\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} 16\\\\ 4\\\\ 7\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
矩阵行和向量对应的元素分别相乘,然后相加
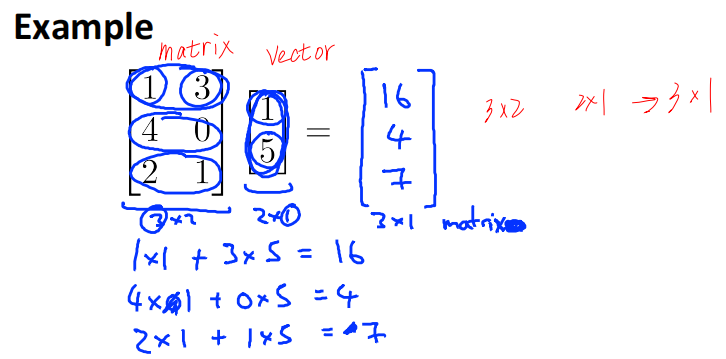
3.3.2 Details
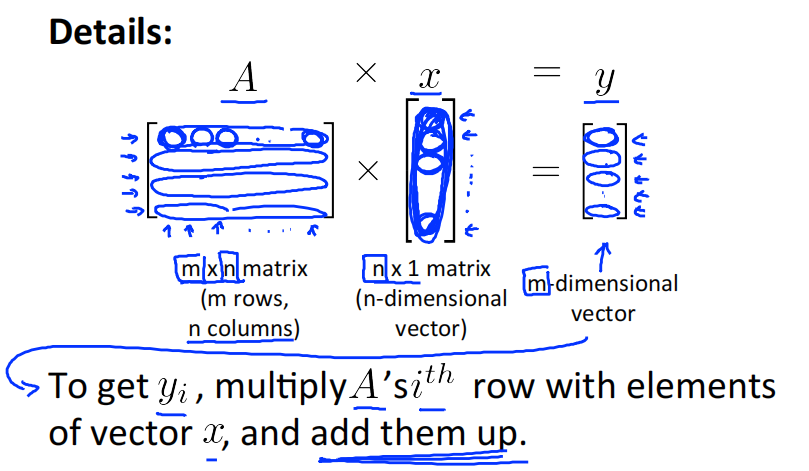
3.3.3 Example2
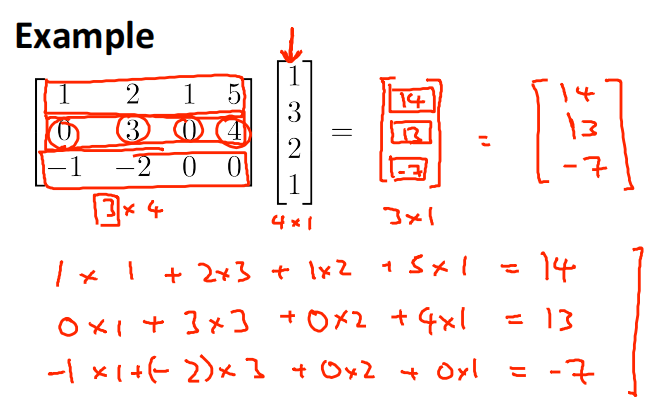
3.3.4 矩阵向量乘法在线性回归中的应用举例
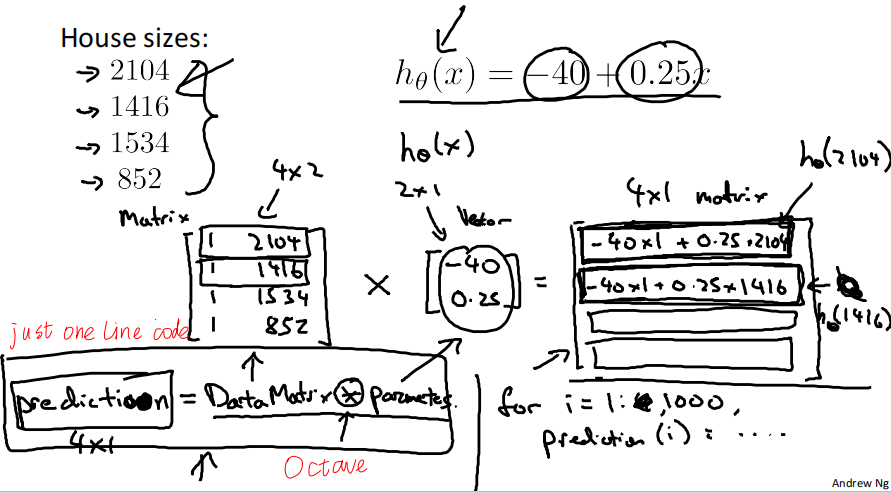
对于前面课程提到的假设函数ℎ_𝜃(𝑥) = -40 + 0.25x
可用矩阵向量乘法同时计算4个数据对应的ℎ_𝜃(𝑥) ,注意需要在第一个矩阵添加一列全1的向量。
we can just use one line code by using Octave to achieve this process:
prediction= DataMatrix \* parameters
而在其他语言中,需要使用for循环多行代码实现
3.4 Matrix-matrix multiplication 矩阵矩阵乘法
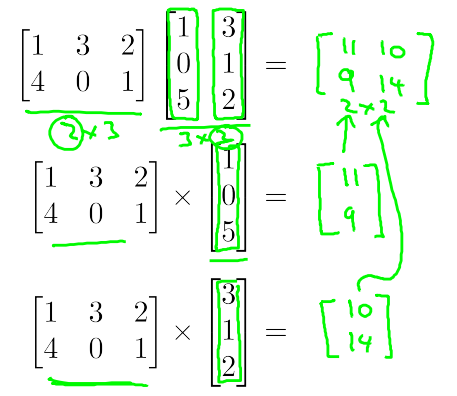
3.4.1 Example
矩阵的乘法可转化为多个矩阵与向量的乘法
\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&3\&2\\\\ 4\&0\&1\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} 1\&3\\\\ 0\&1\\\\ 5\&2\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} 11\&10\\\\ 9\&14\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
可转化为
\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&3\&2\\\\ 4\&0\&1\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} 1\\\\ 0\\\\ 5\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} 11\\\\ 9\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&3\&2\\\\ 4\&0\&1\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} 3\\\\ 1\\\\ 2\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} 10\\\\ 14\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
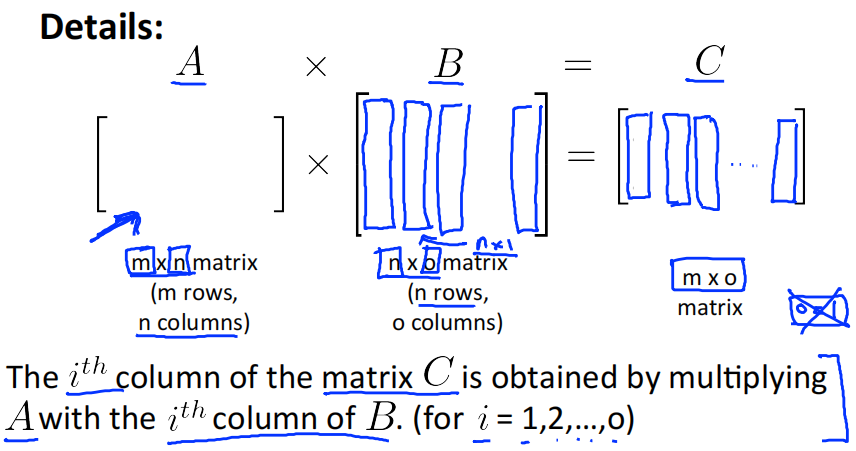
3.4.2 Details
The i\^{th} column of the matrix C is obtained by multiplying A with the i\^{th} column of B . (for i=1,2, ..., o)
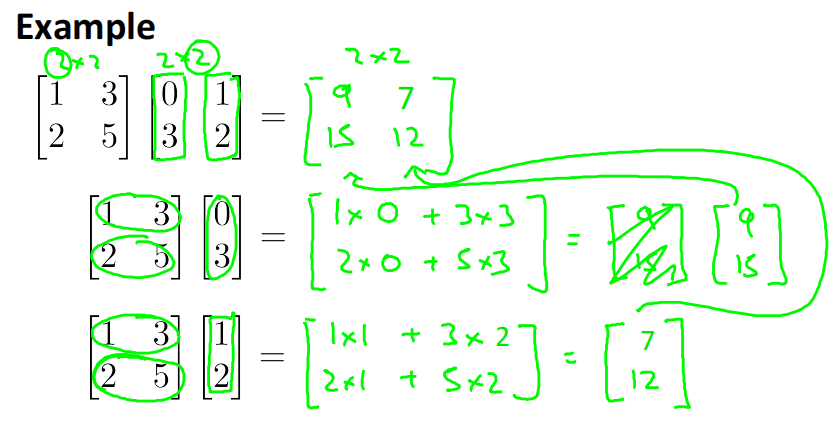
3.4.3 Example2
\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&2\\\\ 3\&5\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} 0\&1\\\\ 3\&2\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} = \\begin{bmatrix} 9\&7\\\\ 15\&12\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
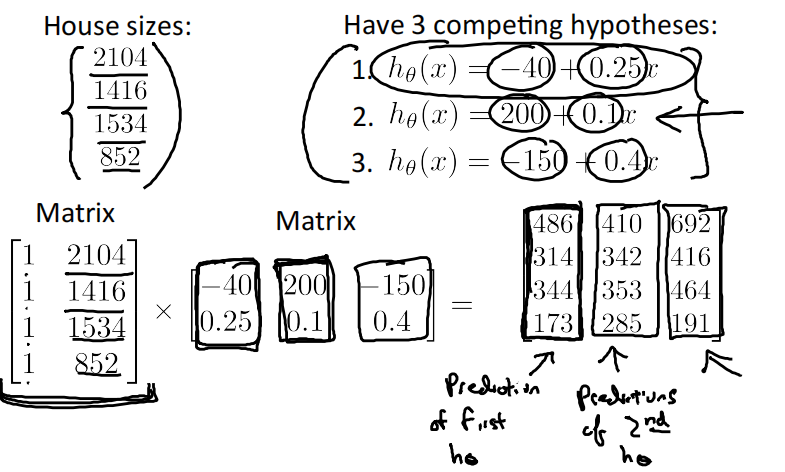
3.4.4 矩阵矩阵乘法在线性回归中的应用举例
如果我们有三个备选假设函数
-
ℎ_𝜃(𝑥) = -40 + 0.25x
-
ℎ_𝜃(𝑥) = 200 + 0.1x
-
ℎ_𝜃(𝑥) = -150 + 0.4x
可用矩阵矩阵乘法同时计算所有House sizes分别对应的4个ℎ_𝜃(𝑥) ,注意需要在第一个矩阵添加一列全1的向量:
3.5 Matrix multiplication properties 矩阵乘法的特性
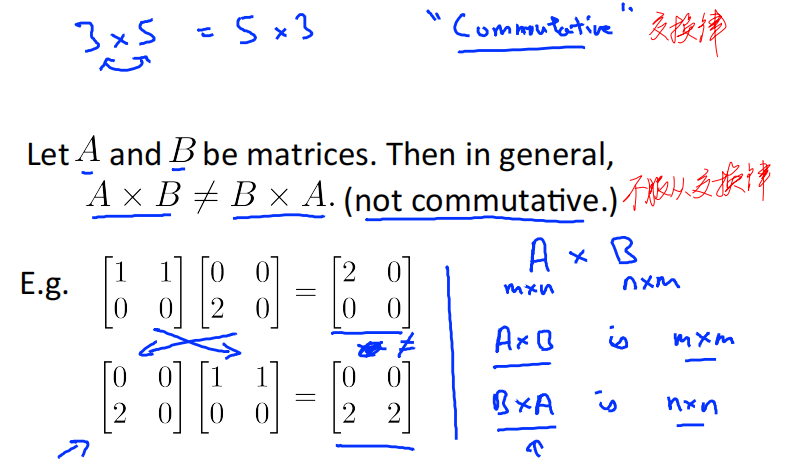
3.5.1 Not Commutative 不服从交换律
Let A and B be matrices. Then in general, A ✖️ B≠B ✖️ A. (not commuative)
3.5.2 Associative 服从结合律
Let A, B and C be matrices. Then in general, A ✖️ B✖️C=B ✖️ C✖️A. (associative)
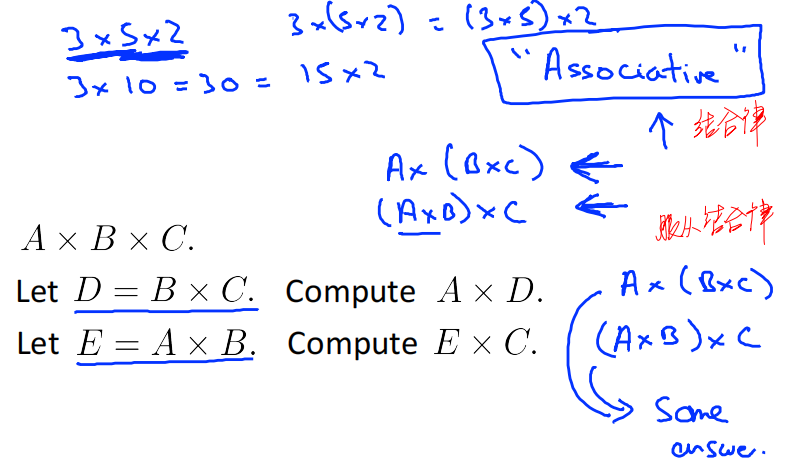
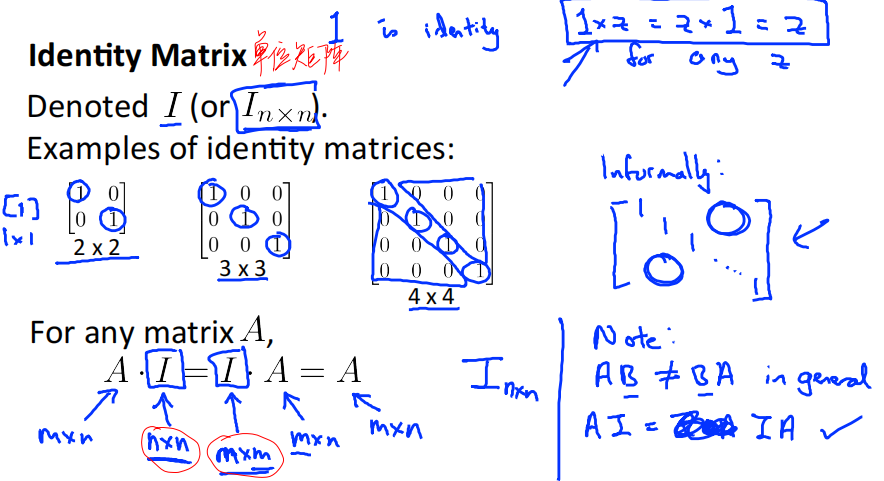
3.5.3 Identity Matrix 单位矩阵
Denoted I (or I_{n✖️n}).
Examples of identity matrixs:
\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&0\\\\ 0\&1\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} 1\&0\&0\\\\ 0\&1\&0\\\\ 0\&0\&1\\\\ \\end{bmatrix} \\begin{bmatrix} 1\&0\&0\&0\\\\ 0\&1\&0\&0\\\\ 0\&0\&1\&0\\\\ 0\&0\&0\&1 \\end{bmatrix}
For any matrix A, A·I=I·A=A
AB≠BA inn general, but AI=IA
3.6 Inverse and transcope 逆和转置
3.6.1 Matrix Inverse 矩阵的逆
类比实数中倒数的概念
Not all numbers have an inverse, alse not all numbers have an inverse.
Matrices that don't have an inverse are "singular" or "degenerate" 奇异矩阵或退化矩阵
Only square matrix (#rows= = #columns) can have a inverse.
If A is an m✖️m matrix, and if it has an inverse, then AA\^{-1}=A\^{-1}A=I. (I="identity")

3.6.2 Matrix Transcope 矩阵转置
Let A be an m✖️n matrix, and let B=A\^T. Then B is an n✖️m, and B_{ij}=A_{ji}.
Example:
A=\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&2\&0\\\\ 3\&5\&9\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}
A\^T=\\begin{bmatrix} 1\&3\\\\ 2\&5\\\\ 0\&9\\\\ \\end{bmatrix}