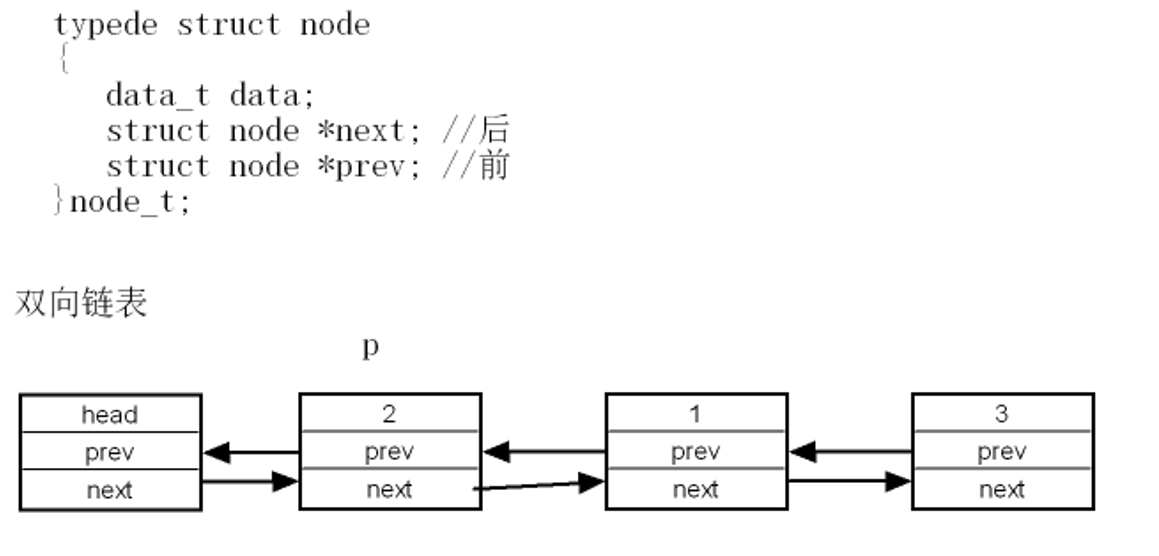
一、双向链表
双向链表是一种链式数据结构,其中每个节点包含三个部分:
-
数据域(存储数据)
-
前驱指针(指向上一个节点)
-
后继指针(指向下一个节点)
与单向链表相比,双向链表可以向前和向后遍历,但需要额外的内存空间存储前驱指针。
1.创建链表
cs
//1.创建头节点
node_t *create_doublelist(void)
{
node_t *head = malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d:malloc fail\n",__FILE__,__func__ ,__LINE__);
return NULL;
}
head -> next = NULL;
head -> prev = NULL;
return head;
}2.头插
cs
//2.头插
void doublelist_insert_head(node_t *phead ,data_t data)
{
//创建新节点并给值
node_t *p_new = malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if(p_new == NULL)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d:malloc fail\n",__FILE__,__func__ ,__LINE__);
return;
}
p_new -> data = data;
p_new -> next = NULL;
p_new -> prev = NULL;
//新节点的next指向原先首节点
p_new -> next = phead -> next;
//新节点的prev指向头节点
p_new -> prev = phead;
//头节点的next指向新节点
phead -> next = p_new;
//如果链表长度大于1
if(p_new -> next != NULL)
{
//原先首节点的prev指向新节点
p_new -> next -> prev = p_new;
}
}3.尾插
cs
//3.尾插
void doublelist_insert_tail(node_t *phead ,data_t data)
{
//创建新节点并给值
node_t *p_new = malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if(p_new == NULL)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d:malloc fail\n",__FILE__,__func__ ,__LINE__);
return;
}
p_new -> data = data;
p_new -> next = NULL;
p_new -> prev = NULL;
//找到尾节点
node_t *p = phead;
while(p -> next != NULL)
{
p = p -> next;
}
//将新节点给到原先尾节点的next
p -> next = p_new;
//将尾节点的位置给到新节点的prev
p_new -> prev = p;
}4.判断链表是否为空
cs
//4.判断链表是否为空
int is_empty(node_t *phead)
{
if(phead == NULL)
{
printf("linklist is empty!\n");
return -1;
}
return phead -> next == NULL;
}5.遍历打印(可选择正逆序)
cs
//5.遍历打印
int doublelist_print(node_t *phead,int dir)
{
if(phead == NULL || is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
printf("empty linklist!\n");
return -1;
}
if(dir == 1)
{
node_t *p = phead -> next;
while(p != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",p -> data);
p = p -> next;
}
}
else if( dir == -1)
{
node_t *p = phead -> next;
while(p -> next != NULL)
{
p = p -> next;
}
while(p != phead)
{
printf("%d ",p -> data);
p = p -> prev;
}
}
putchar('\n');
return 0;
}
6.计算链表长度
cs
//6.计算链表长度
int doublelist_long(node_t *phead)
{
if(is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
return 0;
}
node_t *p = phead -> next;
int cnt = 0;
while(p != NULL)
{
cnt++;
p = p -> next;
}
return cnt;
}7.遍历查找
cs
// 7.查找key并返回指向该节点的指针
node_t* doublelist_find_key(node_t *phead, data_t key)
{
if(is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
printf("empty linklist!\n");
return NULL;
}
node_t *p = phead -> next;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p -> data == key)
{
return p; // 返回找到的节点指针
}
p = p -> next;
}
// 未找到
printf("Key %d not found in linklist.\n", key);
return NULL;
}8.改值
cs
//8.改值
node_t* doublelist_find_update(node_t *phead, data_t old, data_t new)
{
if(is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
printf("empty linklist!\n");
return NULL;
}
node_t *p = phead -> next;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p -> data == old)
{
p -> data = new;
return p; // 返回找到的节点指针
}
p = p -> next;
}
return NULL;
}9.头删
cs
//9.头删
int doublelist_delate_head(node_t *phead)
{
if(is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
printf("%s: linklist empty!\n",__func__);
return -1;
}
//记录首节点地址
node_t *p = phead -> next;
//头节点的next指向次节点
phead -> next = p -> next;
//将此节点的prev指向头节点,重新链接
if(p -> next != NULL)
{
p -> next -> prev = phead;
}
//释放p所在的节点
free(p);
return 1;
}10.尾删
cs
//10.尾删
int doublelist_delete_tail(node_t *phead)
{
if(is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
printf("%s: linklist empty!\n",__func__);
return -1;
}
// 如果链表只有一个实际节点
if (phead -> next -> next == NULL)
{
free(phead -> next);
phead -> next = NULL;
return 0;
}
// 找到尾节点的前一个节点
node_t *p = phead -> next;
while (p -> next != NULL)
{
p = p -> next;
}
// 现在p指向节点
p -> prev -> next = NULL; // 将倒数第二个节点的next置为NULL
free(p); // 释放尾节点
return 1;
}11.插删
cs
//11.插删
int doublelist_delete_in(node_t *phead ,data_t key)
{
if(phead == NULL)
{
printf("%s:%s:%d:phead NULL!\n",__FILE__,__func__ ,__LINE__);
return -1;
}
if(is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
printf("%s: linklist empty!\n",__func__);
return -1;
}
node_t *p = phead -> next;
while (p != NULL)
{
//判断是否找到目标节点
if(p -> data == key)
{
p -> prev -> next = p -> next;
//判断该节点是否为头节点或者尾节点
if(p -> next != NULL)
{
p -> next -> prev = p -> prev;
}
//释放目标节点
free(p);
return 1;
}
p = p -> next;
}
return 0;
}12.销毁链表
cs
//12.销毁链表
int doublelist_destroy(node_t ** pphead)
{
//1.每个节点都删掉
//逐个释放
//p为NULL表示有效的数据节点释放完
if(is_empty(*pphead) == 1)
{
printf("%s: linklist empty!\n",__func__);
return -1;
}
node_t *p = (*pphead) -> next;
node_t *temp = NULL;
while( p != NULL)
{
temp = p;
p = p -> next;
free(temp);
}
//2.头节点释放掉
free (* pphead);
* pphead = NULL;//防止悬空指针
return 1;
}13.找中间位
cs
//13.找中间位
node_t * doublelist_find_mid(node_t *phead)
{
//空链表或只有头节点
if(phead == NULL || phead -> next == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
node_t * pfast = phead;
node_t * pslow = phead;
while(pfast != NULL && pfast -> next != NULL)
{
pfast = pfast -> next -> next;
pslow = pslow -> next;
}
return pslow;
}14.找倒数第K个节点
cs
//14.找倒数第K个节点
node_t * doublelist_find_key_tail(node_t *phead, data_t key)
{
//空链表或只有头节点
if(phead == NULL )
{
printf("%s:phead is NULL\n",__func__);
return NULL;
}
if(is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
printf("%s:linklist is empty!\n",__func__);
return NULL;
}
node_t * pfast = phead;
node_t * pslow = phead;
int i = 0;
for(i = 1 ; i <= key; i++ )
{
if(pfast == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
pfast = pfast -> next;
}
while(pfast != NULL)
{
pfast = pfast -> next;
pslow = pslow -> next;
}
return pslow;
}二、循环链表
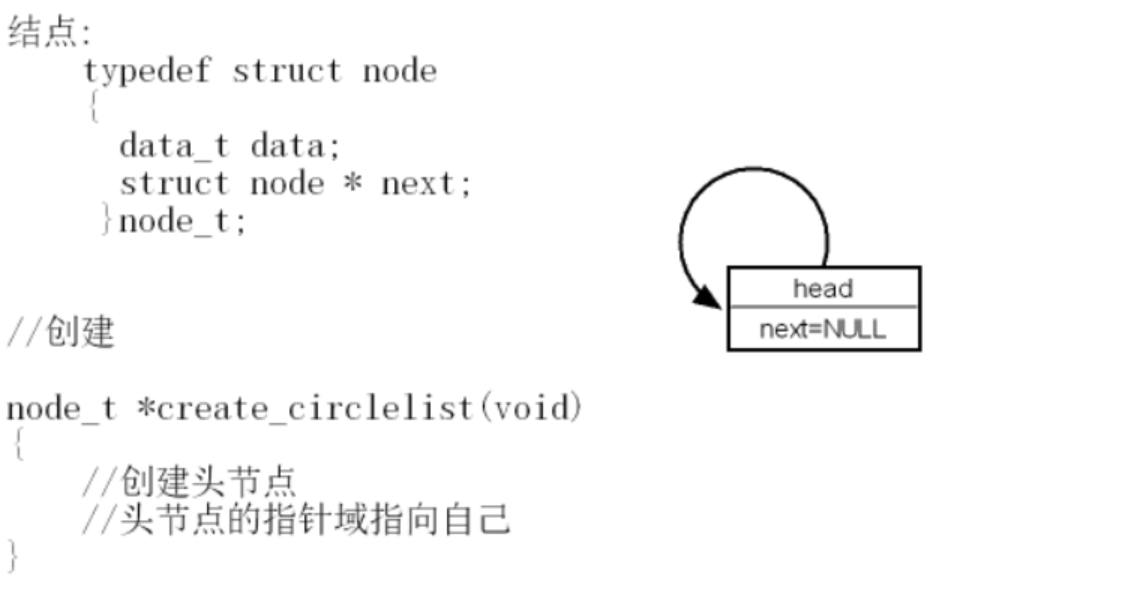
循环链表 是线性表链式存储结构的一种特殊形式,其特点是链表中最后一个结点的指针域指向头结点或第一个结点,使整个链表形成一个环。
循环链表可以分为两种:循环单链表和循环双链表。
-
循环单链表:
在单链表中,最后一个节点的指针域指向头节点(注意:不是第一个节点,而是头节点。如果是不带头节点的链表,则指向第一个节点)。这样,整个链表形成一个环。
循环单链表的操作与普通单链表类似,但在遍历时,循环的终止条件不再是节点指针为NULL,而是判断是否回到头节点(或开始节点)。
-
循环双链表:
在双链表中,最后一个节点的后继指针指向头节点,而头节点的前驱指针指向最后一个节点,形成一个双向的环。
循环链表的优点:
-
可以从任意节点出发遍历整个链表。
-
在某些应用中,如需要循环轮转的场景,使用循环链表非常方便。
循环链表的操作注意点:
-
在插入和删除节点时,需要特别注意更新指针,保持循环的特性。
-
遍历时,注意循环的终止条件,避免死循环。
cs
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "circlelist.h"
node_t *create_circlelist(void)
{
//创建头节点
node_t *head = malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("%s:malloc fail!\n",__func__);
return NULL;
}
//头节点的指针域指向自己
head->next = head;
return head;
}
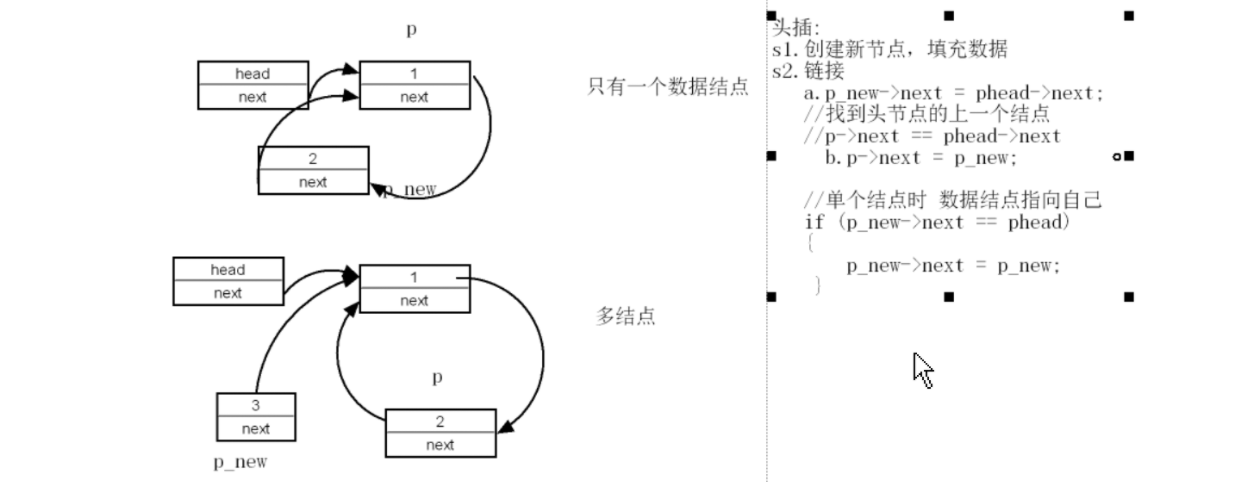
/*
头插:
s1.创建新节点,填充数据
s2.链接
a.p_new->next = phead->next;
//找到头节点的上一个结点
//p->next == phead->next
b.p->next = p_new;
//单个结点时 数据结点指向自己
if (p_new->next == phead)
{
p_new->next = p_new;
}
*/
node_t *circlelist_insert_head(node_t *phead,data_t data)
{
if (phead == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
node_t *p_new = malloc(sizeof(node_t));
if (p_new == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
p_new->data = data;
p_new->next = phead->next;
node_t *p = phead->next;
#if 0
do
{
p = p->next;
//printf("%d ",p);
}while (p->next != phead->next);
#endif
#if 1
while (p->next != phead->next)
{
p = p->next;
//printf("%d ",p);
}
#endif
p->next = p_new;
if (p_new->next == phead)
{
p_new->next = p_new;
}
return phead;
}
int is_empty(node_t *phead)
{
if (phead == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
return phead->next == phead;
}
int circlelist_print(node_t *phead)
{
if (phead == NULL || is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
return -1;
}
node_t *p = phead->next;
//node_t *p = phead;
do
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}while (p!= phead->next);
putchar('\n');
return 0;
}
node_t *circlelist_find(node_t * phead,data_t k)
{
if (phead == NULL || is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
return NULL;
}
node_t *p = phead->next;
do
{
if (p->data == k)
{
return p;
}
p = p->next;
}while (p != phead->next);
return NULL;
}
int circlelist_delete(node_t *phead)
{
if (phead == NULL || is_empty(phead) == 1)
{
return -1;
}
node_t *p = phead->next;
node_t *p_temp = p;
while (p->next != phead->next)
{
p = p->next;
}
phead->next = p_temp->next;
p->next = p_temp->next;
free(p_temp);
return 0;
}
int circlelist_destroy(node_t **phead)
{
if (phead == NULL || *phead == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
if (is_empty(*phead) == 1)
{
free(*phead);
*phead = NULL;
return 0;
}else
{
node_t *p = (*phead)->next->next;
while (p != (*phead)->next)
{
node_t *p_temp = p;
p = p->next;
free(p_temp);
}
free(p);
free(*phead);
*phead = NULL;
}
return 0;
}