一、什么是逻辑回归?
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)虽然名字带"回归",但本质是一个分类算法 ,尤其擅长解决二分类问题(也可扩展至多分类)。
核心思想
- 通过线性组合输入特征:
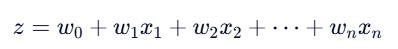
- 将 z 映射到 (0,1) 区间,表示属于正类的概率:
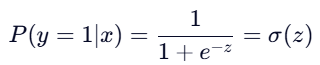
- 决策规则:若 P(y=1∣x)>0.5P(y=1∣x)>0.5 ,则预测为正类(1),否则为负类(0)。
优点 :模型简单、可解释性强(权重反映特征重要性)、训练高效。
局限:假设特征与对数几率(log-odds)线性相关,对非线性关系建模能力弱。
二、如何判断逻辑回归模型好不好?------ 关键评估指标
在不平衡数据中,准确率(Accuracy)是"毒药"!例如欺诈检测中,99.9% 的交易正常,模型全预测"正常"也能获得 99.9% 准确率,但毫无价值。
必看指标(基于混淆矩阵)
| 指标 | 意义 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| 召回率(Recall) | 查全率:有多少正样本被找出来了? | 欺诈检测、疾病筛查(宁可误报,不可漏报) |
| 精确率(Precision) | 查准率:预测为正的样本中有多少是真的? | 垃圾邮件过滤(避免误杀正常邮件) |
| F1-Score | 精确率与召回率的调和平均 | 综合评估 |
| AUC-ROC | 模型在不同阈值下的整体性能 | 通用,尤其适合不平衡数据 |
💡 银行老赖检测 :召回率是核心指标!目标是尽可能找出所有潜在老赖客户(即使误报一些正常交易)。
三、模型诊断:欠拟合 vs 过拟合
1. 欠拟合(Underfitting)
- 表现:训练集和测试集性能都很差(如 Recall < 0.5)
- 原因 :
- 特征太少或信息不足
- 正则化过强(C 值太小)
- 模型太简单(逻辑回归本身线性)
- 解决 :
- 增加特征(如多项式特征、交叉特征)
- 减小正则强度(增大
C参数) - 尝试更复杂模型(如随机森林)
2. 过拟合(Overfitting)
- 表现:训练集性能很好(Recall ≈ 1.0),但测试集性能差
- 原因 :
- 特征过多(尤其高维稀疏数据)
- 正则化不足(C 值太大)
- 训练数据太少
- 解决 :
- 增加正则化(减小
C,或使用 L1 正则) - 特征选择(L1 正则自动稀疏化)
- 增加训练数据(或使用过采样)
- 增加正则化(减小
🔍 诊断工具 :绘制学习曲线(Learning Curve),观察训练/验证分数随样本量的变化。
四、优化策略:提升召回率的关键技术
面对不平衡数据,单纯调参效果有限。必须结合采样技术 + 交叉验证。
1. 交叉验证
- 作用 :在训练阶段可靠评估模型泛化能力,指导超参数选择(如正则强度
C)。 - 陷阱 :若先对整个训练集采样再 CV,会导致数据泄露(每折验证集信息已用于生成合成样本)。
- 正确做法 :使用
imblearn.Pipeline,确保每折 CV 内部独立采样。
python
from imblearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
pipeline = Pipeline([
('smote', SMOTE(random_state=42)), # 每折内过采样
('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('lr', LogisticRegression(C=1.0))
])
# 安全的交叉验证
cv_scores = cross_val_score(pipeline, X_train, y_train, cv=5, scoring='recall')2. 下采样
- 原理:随机删除部分多数类样本,使正负样本平衡。
- 优点:训练快,实现简单。
- 缺点 :丢失大量有用信息,可能导致模型对正常样本欠拟合。
- 适用:数据量极大,计算资源紧张。
python
from imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler
undersampler = RandomUnderSampler(random_state=42)
X_res, y_res = undersampler.fit_resample(X_train, y_train)3. 过采样
- SMOTE(Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique) :
- 在特征空间中,基于 K 近邻合成新少数类样本。
- 例如:在两个0样本之间插值生成新0样本。
- 优点:保留全部原始数据,提升召回率效果显著。
- 缺点:可能过拟合(尤其高维数据),训练时间增加。
- 适用:中小规模数据,关注少数类检测。
python
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
smote = SMOTE(random_state=42)
X_res, y_res = smote.fit_resample(X_train, y_train)重要原则 :
采样仅用于训练!测试集必须保持原始分布,否则评估结果无效。
五、完整实战流程(以银行卡用户是否是老赖检测为例)
python
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, cross_val_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import recall_score, classification_report
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
from imblearn.pipeline import Pipeline
# 加载数据
data = pd.read_csv('creditcard.csv')
X = data.drop('Class', axis=1)
y = data['Class']
# 划分训练/测试集(测试集保持原始分布!)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42, stratify=y
)
X_train['Class'] = y_train
data_train = X_train
"""下采样解决样本不均衡问题"""
positive_eg = data_train[data_train['Class'] == 0] # 获取到了所有标签 (class) 为0的数据
negative_eg = data_train[data_train['Class'] == 1] # 获取到了所有标签(class)为1的数据
positive_eg = positive_eg.sample(len(negative_eg)) # sample表示随机从参数里面选择数据.
# 拼接数据 random.sample(10) random.choice()区别:
data_c = pd.concat([positive_eg, negative_eg]) # 是把两个pandas数据组合为一个
data_c_x = data_c.drop('Class', axis=1)
data_c_y = data_c['Class']
# 定义 C 参数范围
c_param_range = [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100]
scores = []
for c in c_param_range:
# 创建 Pipeline:先标准化,再逻辑回归
pipeline = Pipeline([
('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('lr', LogisticRegression(C=c, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000))
])
# 交叉验证(自动在每折内做标准化,无数据泄露)
cv_scores = cross_val_score(pipeline, data_c_x, data_c_y, cv=8, scoring='recall')
score_mean = cv_scores.mean()
scores.append(score_mean)
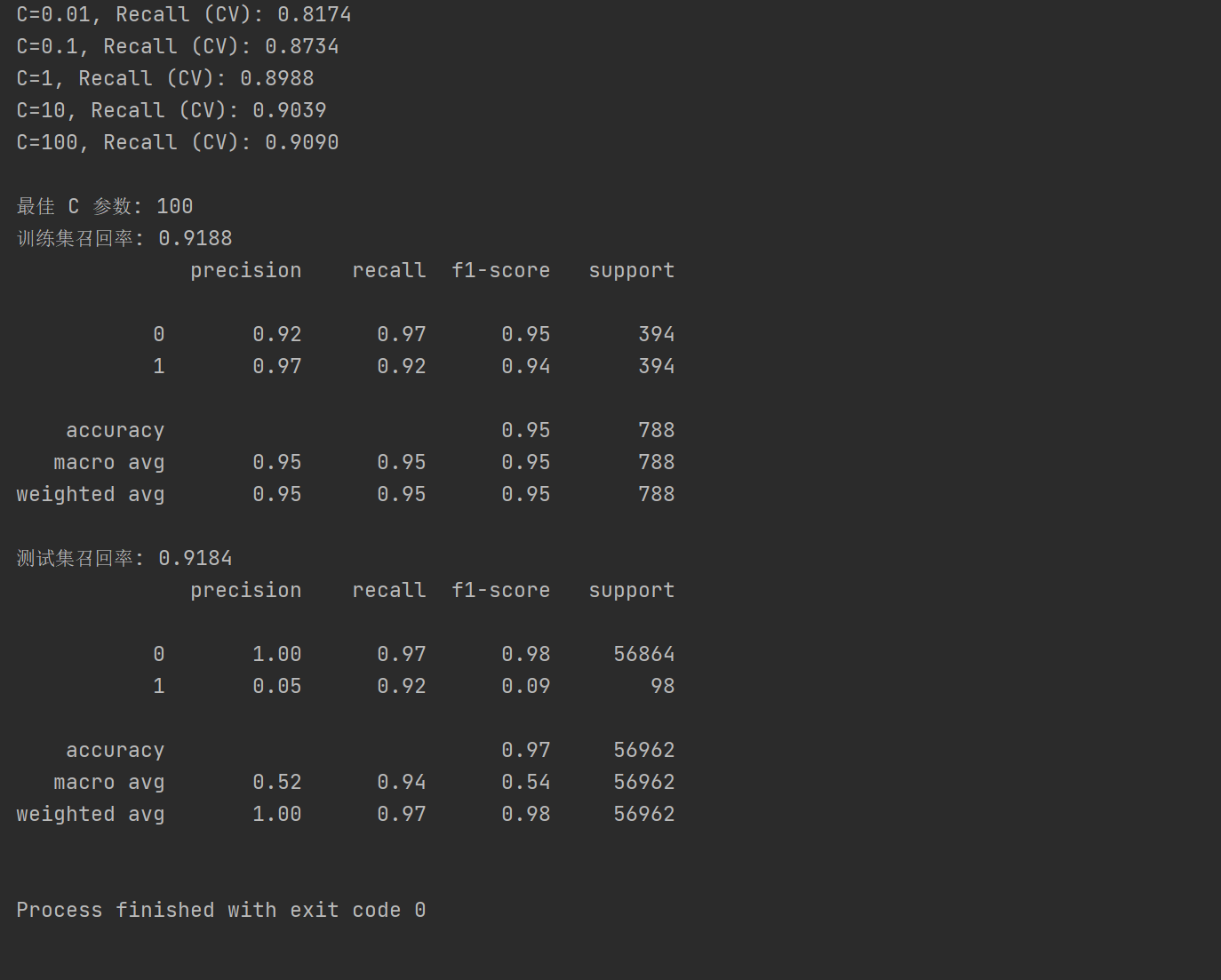
print(f"C={c}, Recall (CV): {score_mean:.4f}")
# 找到最佳 C
best_c = c_param_range[scores.index(max(scores))]
print(f"\n最佳 C 参数: {best_c}")
# 用最佳 C 训练最终模型
final_pipeline = Pipeline([
('scaler', StandardScaler()),
('lr', LogisticRegression(C=best_c, penalty='l2', solver='lbfgs', max_iter=1000))
])
# 模型训练
final_pipeline.fit(data_c_x, data_c_y)
# 训练集预测
data_c_pred = final_pipeline.predict(data_c_x)
train_recall = recall_score(data_c_y, data_c_pred)
print(f"训练集召回率: {train_recall:.4f}")
print(classification_report(data_c_y, data_c_pred))
# 测试集预测
y_pred = final_pipeline.predict(X_test)
test_recall = recall_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"测试集召回率: {test_recall:.4f}")
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))运行结果: