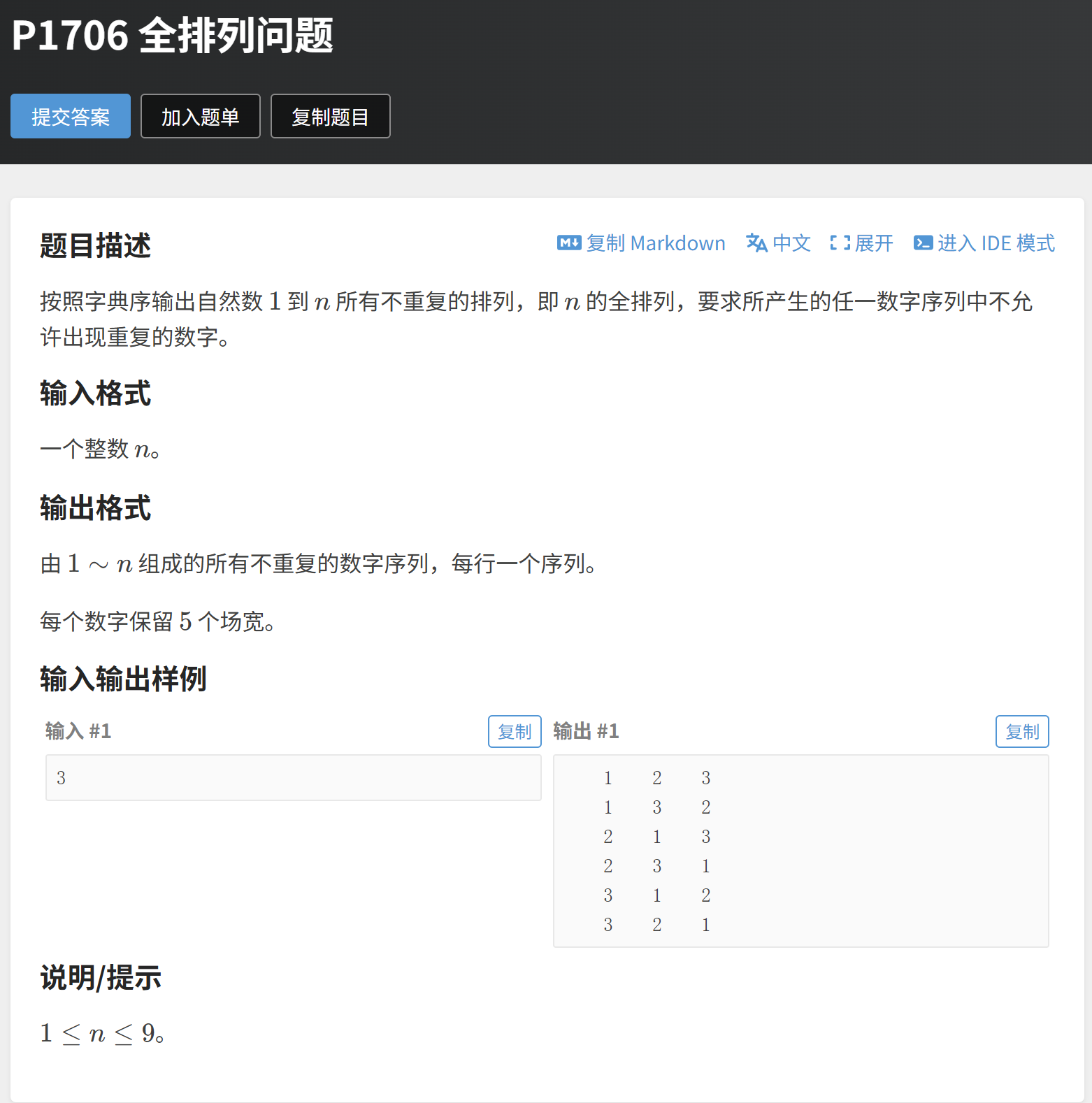
cpp
//1.手写dfs + hx哈希标记
//2.stl函数 next_permutation
//3.我开始错误的swap思路
//#include <iostream>
//#include <iomanip>
//#include <algorithm>
//using namespace std;
//#define int long long
//#define endl '\n'
//
//int n = 0;
//int arr[20];
//int hx[20];
//
//void dfs(int cnt){
// if(cnt == n + 1){ // cnt == n
// for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i){
// cout << setw(5) << arr[i];
// }
// cout << endl;
// return;
// }
//
// for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i){
// if(!hx[i]){
// arr[cnt] = i; // arr[cnt + 1] = i;
// hx[i] = 1;
// dfs(cnt + 1);
// hx[i] = 0;
// }
// }
//}
//
//signed main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
//
// cin >> n;
//
// dfs(1); // dfs(0);
//
// return 0;
//}
//
//
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
int n = 0;
int arr[20];
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i){
arr[i] = i;
}
do {
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i){
cout << setw(5) << arr[i];
}
cout << endl;
} while (next_permutation(arr + 1, arr + 1 + n)); // 它会自动把数组变成下一个更大的排列
return 0;
}
//#include <iostream>
//#include <iomanip>
//#include <algorithm>
//using namespace std;
//#define int long long
//#define endl '\n'
//
//int n = 0;
//int arr[20];
//
//void dfs(int left,int right){
// if(left == 0){
// return;
// }
//
// swap(arr[left],arr[right]);
// for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i){
// cout << setw(5) << arr[i];
// }
// cout << endl;
// swap(arr[left],arr[right]);
//
// if(right == n){
// dfs(left - 1,left);
// return;
// }
// else{
//// right++;
// dfs(left + 1,right + 1);
// return;
// }
//}
//
//signed main(){
// ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
// cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
//
// cin >> n;
//
// for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++i){
// arr[i] = i;
// cout << setw(5) << arr[i];
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// dfs(n-1,n);
//
// return 0;
//}

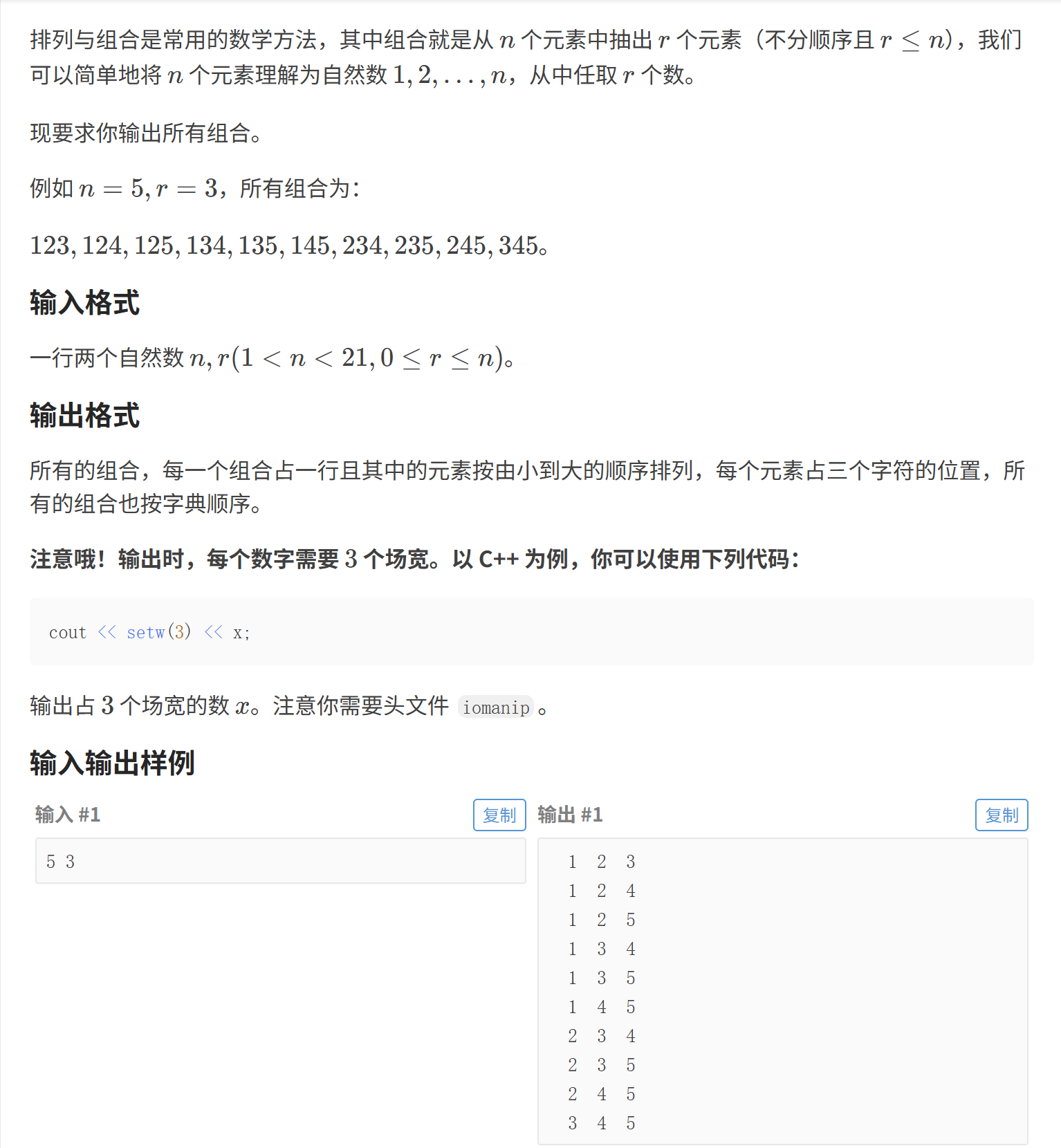
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
int n = 0,r = 0;
//int id = 1;
int jl[25];
void dfs(int start,int cnt){
if(cnt > r){
for(int i = 1 ; i <= r ; ++i){
cout << setw(3) << jl[i];
}
cout << endl;
// id = cnt - 1;
// cnt = 0;
return;
}
for(int i = start ; i <= n ; ++i){
// if(cnt <= r){
// cout << setw(3) << i;
// cout << "jl[" << cnt << "] = " << i << endl;
jl[cnt] = i;
dfs(i + 1,cnt + 1);
// }
}
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> r;
dfs(1,1);
return 0;
}刚刚那题全组合问题的重新理了一下思路:"
1.首先看题目数据,数据非常小说明出题人可能想让我们用枚举,也就是dfs。
2.好看回题目,确实我们人枚举也可以枚举出来,比如从三个数里面选两个数,我们很容易想到是12,13,和23。接着我们要把我们怎么想到这三种情况的告诉计算机。
3.首先从三个数里面选就得告诉计算机里现在有三个数为1,2,3,所以我们要用一个for循环,从1到3。
4.接着我们需要判断,是否已经够了两个数,所以我们需要给DFS一个变量为cnt来记录我们现在已经有了几个数。
(1)判断如果如果够了,你需要打印之前记录下来的数,并且返回,
所以我们需要一个数组记录我们之前记录下的数。
(2)如果没有够的话,比如我们先选1,判断1还没到两个数就应该进入下一层dfs(因为判断是在DFS的前面的用于返回,所以你应该进入下一层DFS,而不是直接记录for循环里面的i加加后的2),又因为要大于一,所以你应该把二传下去,还有cnt传下去,
所以现在需要一个变量start,作为DFS的参数。所以我们现在DFS为(int cnt,int start)进入(2,2)的时候,因为我们一开始说了for循环从一到n开始,现在发现我们有漏洞,我们要从start开始。
以上是我的完整思路。"



