[深度学习网络从入门到入土] 网络中的网络NiN
个人导航
知乎:https://www.zhihu.com/people/byzh_rc
CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_54636039
注:本文仅对所述内容做了框架性引导,具体细节可查询其余相关资料or源码
参考文章:各方资料
文章目录
- [[深度学习网络从入门到入土] 网络中的网络NiN](#[深度学习网络从入门到入土] 网络中的网络NiN)
- 个人导航
- 参考资料
- 背景
- 架构(公式)
-
-
-
- [1. MLPConv(卷积里的多层感知机)](#1. MLPConv(卷积里的多层感知机))
- [2. 全局平均池化(GAP)](#2. 全局平均池化(GAP))
-
-
- 创新点
-
-
-
- [1. 卷积内部引入非线性(MLPConv)](#1. 卷积内部引入非线性(MLPConv))
- [2. ==去全连接化(GAP)==](#2. ==去全连接化(GAP)==)
- [3. 端到端的"网络嵌套网络"思想](#3. 端到端的“网络嵌套网络”思想)
-
-
- 代码实现
- 项目实例
参考资料
Network In Network.
背景
在 AlexNet(2012) 之后,CNN 的基本范式逐渐固化:卷积层 → 非线性 → 池化 → 全连接
但这种结构有两个明显问题:
- 卷积层表达能力有限
- 标准卷积 = 对局部 patch 做 线性映射
- 通道间关系只能靠堆深网络"慢慢学"
- 全连接层参数量巨大
- 例如 AlexNet 中 FC 层参数占比超过 90%
- 易过拟合、显存和算力成本高
-> NiN 的核心问题意识:
- 为什么非线性只能放在层与层之间?
- 为什么不能让卷积本身更像一个小网络?
架构(公式)
完整:
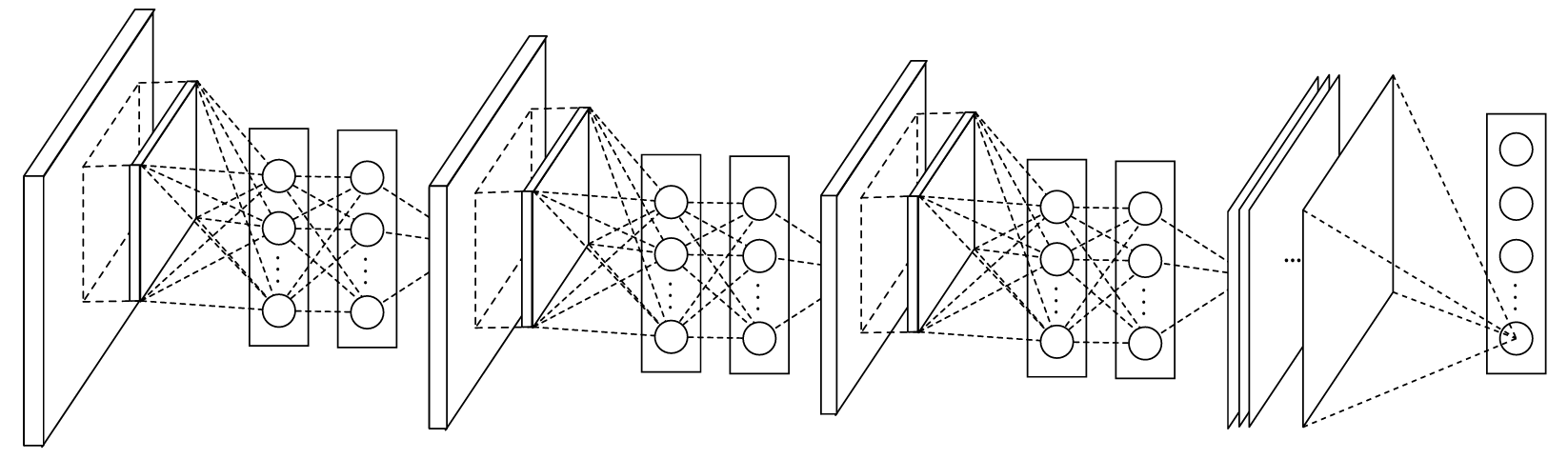
MLPConv结构:
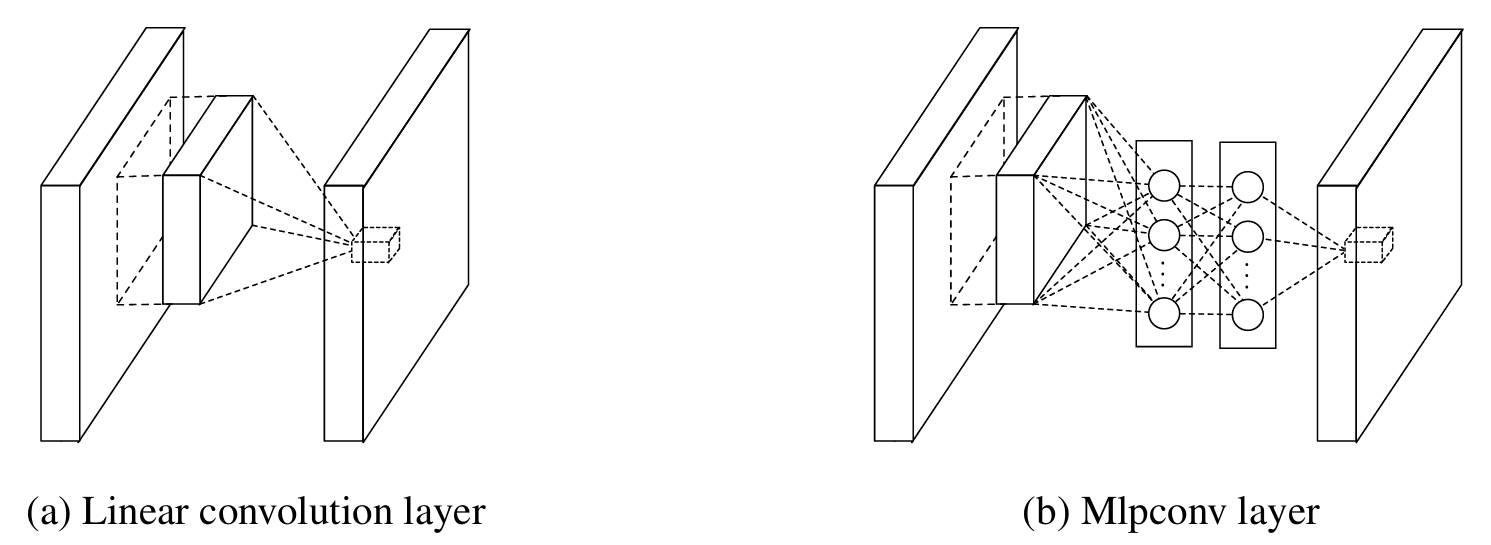
1. MLPConv(卷积里的多层感知机)
NiN 将一次卷积替换为一个 微型 MLP :
y i , j = f ( n ) ( ⋯ f ( 2 ) ( f ( 1 ) ( x i , j ) ) ) \mathbf{y}{i,j} = f^{(n)}( \cdots f^{(2)}( f^{(1)}(\mathbf{x}{i,j}) ) ) yi,j=f(n)(⋯f(2)(f(1)(xi,j)))
其中:
- x i , j \mathbf{x}_{i,j} xi,j:某个空间位置上的 通道向量
- f ( l ) f^{(l)} f(l):通常由 1 × 1 1\times1 1×1 卷积 + 非线性 组成
-> 实现形式非常关键:MLPConv = 普通卷积 + 多层 1×1 卷积
2. 全局平均池化(GAP)
NiN 彻底移除了全连接层 ,用 全局平均池化:
y k = 1 H × W ∑ i , j x i , j , k y_k = \frac{1}{H \times W} \sum_{i,j} x_{i,j,k} yk=H×W1i,j∑xi,j,k
作用:
- 每个通道 → 一个类别得分
- 无可学习参数
- 强结构先验,降低过拟合
创新点
1. 卷积内部引入非线性(MLPConv)
1×1 卷积 ≠ 降维工具, 本质是 通道维度上的全连接
-> 提升了局部特征的判别能力
2. 去全连接化(GAP)
- 用结构设计代替参数堆砌
- 分类结果与空间位置解耦(无关)
- 对尺度变化更鲁棒
3. 端到端的"网络嵌套网络"思想
从"堆层数"转向"提升单层表达力"的重要转折
代码实现
py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from byzh.ai.Butils import b_get_params
class MLPConv(nn.Module):
"""
NiN 的核心模块:MLPConv("卷积里的小网络")
结构:卷积(k×k) + ReLU -> 1×1卷积 + ReLU -> 1×1卷积 + ReLU
直观理解:
- 第一个 k×k 卷积负责提取局部空间特征(看邻域)
- 后面两层 1×1 卷积相当于对"通道维"做 MLP(增强通道间非线性组合能力)
"""
def __init__(self, in_ch, out_ch, k, s=1, padding=0):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
# 空间卷积:提取局部空间模式
nn.Conv2d(in_ch, out_ch, kernel_size=k, stride=s, padding=padding, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 1×1 卷积:等价于对每个像素位置的通道向量做一次"全连接"
nn.Conv2d(out_ch, out_ch, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
# 1×1 卷积:进一步增强非线性表达(模拟更深的 MLP)
nn.Conv2d(out_ch, out_ch, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
class B_NiN_Paper_CIFAR(nn.Module):
"""
CIFAR 版本(输入 32×32)的 NiN
论文风格要点:
- 多个 MLPConv 堆叠
- 中间用 pooling 下采样
- 用 Dropout 抑制过拟合
- 最后用 1×1 conv 输出类别通道 + 全局平均池化(GAP) 代替全连接
input shape: (N, 3, 224, 224)
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=10, dropout_p=0.5):
super().__init__()
# -------------------------
# Block 1
# 输入: 32×32
# conv(5,pad2) 后仍是 32×32
# maxpool(3, stride=2) -> 15×15(因为 (32-3)/2 + 1 = 15)
# -------------------------
self.block1 = nn.Sequential(
MLPConv(3, 192, k=5, s=1, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p),
)
# -------------------------
# Block 2
# 输入: 15×15
# conv(5,pad2) 后仍是 15×15
# avgpool(3, stride=2) -> 7×7(因为 (15-3)/2 + 1 = 7)
# -------------------------
self.block2 = nn.Sequential(
MLPConv(192, 192, k=5, s=1, padding=2),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p),
)
# -------------------------
# Block 3
# 输入: 7×7
# conv(3,pad1) 后仍是 7×7
# 通常最后一个大块可以不再下采样(直接为分类头服务)
# -------------------------
self.block3 = nn.Sequential(
MLPConv(192, 192, k=3, s=1, padding=1),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p),
)
# -------------------------
# 分类头:
# 1×1 conv 把通道数映射到 num_classes
# 然后用 GAP 把 H×W 平均成 1×1
# 相当于"无参数全连接",显著减少参数并缓解过拟合
# -------------------------
self.classifier = nn.Conv2d(192, num_classes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.block1(x)
x = self.block2(x)
x = self.block3(x)
# 输出:N, num_classes, H, W
x = self.classifier(x)
# 全局平均池化:把每个类别通道在空间维度做平均 -> N, num_classes, 1, 1
x = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, 1)
# 拉平为 N, num_classes
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
return x
class B_NiN_Paper_ImageNet(nn.Module):
"""
ImageNet 版本(输入 224×224)的 NiN(常见复现形态)
主要变化:
- 开头用更大的卷积核 + 更大的 stride,快速扩大感受野并降分辨率
- 通道数整体更大
- 同样保留:MLPConv + Dropout + 最终 1×1 conv + GAP
input shape: (N, 3, 224, 224)
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000, dropout_p=0.5):
super().__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
# -------------------------
# Stem:快速降采样
# 224×224 -> conv(11, stride=4, pad=2) -> 55×55
# 55×55 -> maxpool(3, stride=2) -> 27×27
# -------------------------
MLPConv(3, 96, k=11, s=4, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p),
# -------------------------
# 27×27 -> MLPConv(5,pad2) -> 27×27
# 27×27 -> maxpool(3, stride=2) -> 13×13
# -------------------------
MLPConv(96, 256, k=5, s=1, padding=2),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p),
# -------------------------
# 13×13 -> MLPConv(3,pad1) -> 13×13
# 13×13 -> maxpool(3, stride=2) -> 6×6
# -------------------------
MLPConv(256, 384, k=3, s=1, padding=1),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p),
# -------------------------
# 6×6 -> MLPConv(3,pad1) -> 6×6
# 这里不再 pool,直接交给分类头 + GAP
# -------------------------
MLPConv(384, 1024, k=3, s=1, padding=1),
nn.Dropout(p=dropout_p),
)
# 分类头:通道映射到类别数
self.classifier = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=1024, out_channels=num_classes,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
# N, num_classes, H, W
x = self.classifier(x)
# GAP:N, num_classes, 1, 1
x = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, 1)
# N, num_classes
return x.flatten(1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# -------------------------
# CIFAR 测试:输入 32×32
# -------------------------
model = B_NiN_Paper_CIFAR(num_classes=10)
x = torch.randn(4, 3, 32, 32)
y = model(x)
print(y.shape) # 期望输出: torch.Size([4, 10])
print(f"参数量: {b_get_params(model)}") # 1_492_618
# -------------------------
# ImageNet 测试:输入 224×224
# -------------------------
model = B_NiN_Paper_ImageNet(num_classes=1000)
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 224, 224)
y = model(x)
print(y.shape) # 期望输出: torch.Size([2, 1000])
print(f"参数量: {b_get_params(model)}") # 8_644_776项目实例
库环境:
numpy==1.26.4
torch==2.2.2cu121
byzh-core==0.0.9.21
byzh-ai==0.0.9.54
byzh-extra==0.0.9.12
...NiN训练MNIST数据集:
py
# copy all the codes from here to run
import torch
from byzh.ai.Btrainer import B_Classification_Trainer
from byzh.ai.Bdata import B_Download_CIFAR10, b_get_dataloader_from_tensor
# from uploadToPypi_ai.byzh.ai.Bmodel.study_cnn import B_NiN_Paper_CIFAR
from byzh.ai.Bmodel.study_cnn import B_NiN_Paper_CIFAR
from byzh.ai.Butils import b_get_device
##### hyper params #####
epochs = 10
lr = 1e-3
batch_size = 32
device = b_get_device(use_idle_gpu=True)
##### data #####
downloader = B_Download_CIFAR10(save_dir='D:/study_cnn/datasets/CIFAR10')
data_dict = downloader.get_data()
X_train = data_dict['X_train_standard']
y_train = data_dict['y_train']
X_test = data_dict['X_test_standard']
y_test = data_dict['y_test']
num_classes = data_dict['num_classes']
train_dataloader, val_dataloader = b_get_dataloader_from_tensor(
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test,
batch_size=batch_size
)
##### model #####
model = B_NiN_Paper_CIFAR(num_classes=num_classes)
##### else #####
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
##### trainer #####
trainer = B_Classification_Trainer(
model=model,
optimizer=optimizer,
criterion=criterion,
train_loader=train_dataloader,
val_loader=val_dataloader,
device=device
)
trainer.set_writer1('./runs/nin/log.txt')
##### run #####
trainer.train_eval_s(epochs=epochs)
##### calculate #####
trainer.draw_loss_acc('./runs/nin/loss_acc.png', y_lim=False)
trainer.save_best_checkpoint('./runs/nin/best_checkpoint.pth')
trainer.calculate_model()