FA:formulas and algorithm,PC:planning and control,RRT:Rapidly-exploring Random Tree
一、RRT 核心原理(从本质到数学定义)
1. 核心定义
快速探索随机树(Rapidly-exploring Random Tree,RRT)是由 Steven M. LaValle 在 1998 年提出的基于采样的无路径规划算法,核心思想是:
- 通过随机采样的方式在配置空间(C 空间)中逐步生长一棵 "随机树";
- 树的根节点为起点,每次采样一个随机点,将树向该点扩展固定步长;
- 当树扩展到目标点附近时,完成路径规划。
2. 数学基础
- 配置空间(C 空间) :描述机器人所有可能姿态的空间,2D 平面机器人的 C 空间为(x,y)(x,y)(x,y),记为C⊆R2C⊆R^2C⊆R2;
- 自由空间(CfreeC_{free}Cfree) :无碰撞的配置空间,Cfree=q∈C∣q无碰撞C_{free}={q∈C∣q 无碰撞}Cfree=q∈C∣q无碰撞;
- 随机采样 :采样点qrand∼Uniform(C)q_{rand}∼Uniform(C)qrand∼Uniform(C)(均匀分布);
- 扩展步长 :每次从最近节点qnearq_{near}qnear向qrandq_{rand}qrand扩展固定步长ddd,得到新节点qnewq_{new}qnew:qnew=qnear+d⋅qrand−qnear∥qrand−qnear∥q_{new}=q_{near}+d⋅\frac{q_{rand}−q_{near}}{∥q_{rand}−q_{near}∥}qnew=qnear+d⋅∥qrand−qnear∥qrand−qnear
3. 核心特性
- 概率完备性:只要存在可行路径,随着采样次数趋近于无穷,RRT 找到路径的概率趋近于 1;
- 快速探索性:树会优先向未探索的区域生长,适合高维空间(如机械臂)的路径规划。
二、RRT 适用场景(精准分类)
| 场景类型 | 是否适用 | 核心原因 |
|---|---|---|
| 高维空间规划(机械臂) | ✅ 核心场景 | 相比 A*/Dijkstra,RRT 无需遍历网格,高维空间计算效率远高于网格类算法 |
| 复杂障碍物环境 | ✅ 非常适合 | 随机采样能绕过不规则障碍物,无需提前建模环境拓扑 |
| 非完整约束机器人(AGV) | ✅ 适合 | 可结合运动学约束(如最小转弯半径)扩展为 RRT*、Kinodynamic RRT |
| 动态环境规划 | ❌ 不适合 | 离线采样,对动态障碍物适应性差(需结合重规划或 RRT*) |
| 最优路径要求 | ❌ 不适合 | 生成的路径是 "可行但非最优",需用 RRT*(RRT 的优化版) |
| 实时性要求极高的场景 | ❌ 慎用 | 采样过程有随机性,最坏情况下收敛慢(可优化为 Informed RRT*) |
三、RRT 操作步骤(标准流程 + 图解)
RRT 的核心流程分为初始化、迭代扩展、终止判断三步,具体如下:
步骤 1:初始化
- 定义起点qstartq_{start}qstart、终点qgoalq_{goal}qgoal、障碍物列表、采样区域、扩展步长d、最大迭代次数Nmax;
- 初始化随机树T,将根节点qstartq_{start}qstart加入树的节点集合V,边集合E为空。
步骤 2:迭代扩展(核心)
对i=1到NmaxN_{max}Nmax:
- 随机采样 :生成随机点qrandq_{rand}qrand(以小概率直接采样qgoalq_{goal}qgoal,加快收敛);
- 找最近节点 :在树中找到距离qrandq_{rand}qrand最近的节点qnearq_{near}qnear(欧氏距离);
- 扩展新节点 :从qnearq_{near}qnear向qrandq_{rand}qrand方向扩展步长d,得到新节点qnewq_{new}qnew;
- 碰撞检测 :检查qnearq_{near}qnear到qnewq_{new}qnew的路径是否与障碍物碰撞:
- 若碰撞:舍弃qnewq_{new}qnew,进入下一次迭代;
- 若无碰撞:将qnewq_{new}qnew加入V,将边(qnear,qnewq_{near},q_{new}qnear,qnew)加入E;
- 目标检测 :若qnewq_{new}qnew到qgoalq_{goal}qgoal的距离≤步长d,且qnewq_{new}qnew到qgoalq_{goal}qgoal无碰撞,直接连接qnewq_{new}qnew和qgoalq_{goal}qgoal,完成规划。
步骤 3:终止判断
- 若找到可行路径:回溯从qgoalq_{goal}qgoal到qstartq_{start}qstart的父节点,生成最终路径;
- 若迭代次数耗尽仍未找到路径:返回 "无可行路径"。
四、RRT 优缺点(对比分析)
表格
| 维度 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 空间复杂度 | 无需存储网格,仅存储树的节点和边,高维空间内存占用远低于网格算法 | 节点数量随迭代次数增加而线性增长,需设置最大迭代次数限制 |
| 时间复杂度 | 单次迭代为O(n)(n为节点数),高维空间效率远高于 A*/Dijkstra | 随机性导致收敛速度不稳定,最坏情况下需大量迭代 |
| 路径质量 | 能找到可行路径(概率完备) | 路径曲折、非最优,需后处理(如路径平滑) |
| 工程适配性 | 易扩展(可结合运动学、动力学约束) | 对窄通道场景采样效率低,容易 "卡壳" |
| 实现难度 | 逻辑简单,代码实现门槛低 | 碰撞检测的精度直接影响路径合法性,需仔细实现 |
五、RRT 与主流算法对比(关键)
表格
| 算法 | 核心特点 | 适用场景 | 路径质量 | 高维适配性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RRT | 随机采样、快速探索 | 高维 / 复杂障碍物环境 | 可行非最优 | ✅ 优秀 |
| RRT* | RRT 的优化版、渐近最优 | 高维 / 需最优路径场景 | 渐近最优 | ✅ 优秀 |
| A* | 启发式搜索、最优路径 | 低维 / 网格环境 | 最优 | ❌ 差 |
| PRM | 离线建图、在线查询 | 多次查询的静态环境 | 可行 | ✅ 较好 |
| Reeds-Shepp | 解析解、最短路径 | 两点间非完整约束规划 | 最优 | ❌ 仅低维 |
六、Python 代码示例(完整可运行)
示例一
1. 前置依赖
无需额外安装特殊库,仅需基础库:
bash
pip install numpy matplotlib2. 完整代码
bash
import math
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class RRT:
"""快速探索随机树(RRT)核心类"""
class Node:
"""树节点类:存储坐标、路径、父节点"""
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x # 节点x坐标
self.y = y # 节点y坐标
self.path_x = [] # 从父节点到当前节点的路径x坐标
self.path_y = [] # 从父节点到当前节点的路径y坐标
self.parent = None # 父节点引用
def __init__(self, start, goal, obstacle_list,
rand_area=[0, 20], expand_dis=2.0,
goal_sample_rate=5, max_iter=500, robot_radius=0.5):
"""
初始化RRT参数
:param start: 起点 [x, y]
:param goal: 终点 [x, y]
:param obstacle_list: 障碍物列表 [[x, y, size], ...](圆形障碍物)
:param rand_area: 随机采样区域 [min, max]
:param expand_dis: 扩展步长
:param goal_sample_rate: 目标点采样概率(%)
:param max_iter: 最大迭代次数
:param robot_radius: 机器人半径(碰撞检测用)
"""
self.start = self.Node(start[0], start[1]) # 根节点
self.goal = self.Node(goal[0], goal[1]) # 目标节点
self.min_rand = rand_area[0] # 采样最小值
self.max_rand = rand_area[1] # 采样最大值
self.expand_dis = expand_dis # 扩展步长
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate # 目标采样概率
self.max_iter = max_iter # 最大迭代次数
self.obstacle_list = obstacle_list # 障碍物列表
self.robot_radius = robot_radius # 机器人半径
self.node_list = [self.start] # 树的节点集合
def planning(self, animation=True):
"""
RRT路径规划主函数
:param animation: 是否显示动画
:return: 规划路径 [[x1,y1], [x2,y2], ...],无路径则返回None
"""
for i in range(self.max_iter):
# 1. 随机采样一个节点
rnd_node = self._sample_free()
# 2. 找到树中距离采样点最近的节点
nearest_ind = self._get_nearest_node_index(self.node_list, rnd_node)
nearest_node = self.node_list[nearest_ind]
# 3. 向采样点扩展,生成新节点
new_node = self._steer(nearest_node, rnd_node)
# 4. 碰撞检测:新节点路径无碰撞且在采样区域内
if self._is_collision_free(new_node):
self.node_list.append(new_node)
# 5. 检查是否到达目标点附近
if self._calc_dist_to_goal(new_node.x, new_node.y) <= self.expand_dis:
# 直接连接新节点和目标点
final_node = self._steer(new_node, self.goal)
if self._is_collision_free(final_node):
return self._generate_final_path(len(self.node_list)-1)
# 6. 动画可视化(每5次迭代更新一次)
if animation and i % 5 == 0:
self._draw_graph(rnd_node)
return None # 迭代耗尽,未找到路径
def _sample_free(self):
"""随机采样:以一定概率采样目标点,加快收敛"""
if random.randint(0, 100) > self.goal_sample_rate:
# 随机采样普通点
rnd = self.Node(
random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand),
random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand)
)
else:
# 采样目标点
rnd = self.Node(self.goal.x, self.goal.y)
return rnd
def _get_nearest_node_index(self, node_list, rnd_node):
"""找到距离采样点最近的节点索引"""
# 计算所有节点到采样点的欧氏距离平方(避免开方,提高效率)
dist_list = [(node.x - rnd_node.x)**2 + (node.y - rnd_node.y)**2
for node in node_list]
return dist_list.index(min(dist_list))
def _steer(self, from_node, to_node):
"""
从from_node向to_node扩展固定步长,生成新节点
:param from_node: 起始节点(树中最近节点)
:param to_node: 目标节点(采样点)
:return: 新节点
"""
# 计算方向角和距离
dx = to_node.x - from_node.x
dy = to_node.y - from_node.y
dist = math.hypot(dx, dy)
theta = math.atan2(dy, dx)
# 扩展固定步长
new_node = self.Node(from_node.x, from_node.y)
new_node.path_x = [new_node.x]
new_node.path_y = [new_node.y]
if dist <= self.expand_dis:
# 距离小于步长,直接到达采样点
new_x = to_node.x
new_y = to_node.y
else:
# 扩展固定步长
new_x = from_node.x + self.expand_dis * math.cos(theta)
new_y = from_node.y + self.expand_dis * math.sin(theta)
new_node.path_x.append(new_x)
new_node.path_y.append(new_y)
new_node.x = new_x
new_node.y = new_y
new_node.parent = from_node
return new_node
def _is_collision_free(self, node):
"""碰撞检测:检查节点路径是否与障碍物碰撞"""
if node is None:
return False
# 遍历路径上的所有点
for (x, y) in zip(node.path_x, node.path_y):
# 检查每个障碍物
for (ox, oy, size) in self.obstacle_list:
dx = x - ox
dy = y - oy
dist = math.hypot(dx, dy)
# 距离小于机器人半径+障碍物尺寸,判定为碰撞
if dist <= size + self.robot_radius:
return False
return True
def _calc_dist_to_goal(self, x, y):
"""计算点到目标点的距离"""
dx = x - self.goal.x
dy = y - self.goal.y
return math.hypot(dx, dy)
def _generate_final_path(self, goal_ind):
"""回溯父节点,生成最终路径"""
path = [[self.goal.x, self.goal.y]]
node = self.node_list[goal_ind]
# 从目标点回溯到起点
while node.parent is not None:
path.append([node.x, node.y])
node = node.parent
path.append([node.x, node.y])
return path
def _draw_graph(self, rnd_node=None):
"""可视化RRT生长过程"""
plt.clf()
# 绘制随机采样点
if rnd_node is not None:
plt.plot(rnd_node.x, rnd_node.y, "^k", markersize=8)
# 绘制树的所有边
for node in self.node_list:
if node.parent is not None:
plt.plot(node.path_x, node.path_y, "-g", linewidth=1)
# 绘制障碍物
for (ox, oy, size) in self.obstacle_list:
self._plot_circle(ox, oy, size, color="-r")
# 绘制起点和终点
plt.plot(self.start.x, self.start.y, "xg", markersize=12, label="Start")
plt.plot(self.goal.x, self.goal.y, "xr", markersize=12, label="Goal")
# 配置绘图参数
plt.axis("equal")
plt.xlim(self.min_rand-2, self.max_rand+2)
plt.ylim(self.min_rand-2, self.max_rand+2)
plt.grid(True)
plt.legend()
plt.pause(0.01)
@staticmethod
def _plot_circle(x, y, size, color="-b"):
"""绘制圆形障碍物"""
deg = np.linspace(0, 2*math.pi, 100)
xl = [x + size * math.cos(d) for d in deg]
yl = [y + size * math.sin(d) for d in deg]
plt.plot(xl, yl, color, linewidth=2)
# ---------------------- 测试代码 ----------------------
def main():
print("RRT Path Planning Demo")
# 1. 定义障碍物列表(圆形障碍物)
obstacle_list = [
(5, 5, 1), # (x, y, 半径)
(3, 8, 2),
(7, 6, 2),
(10, 10, 1.5),
(12, 4, 2)
]
# 2. 初始化RRT
rrt = RRT(
start=[0, 0], # 起点
goal=[15, 15], # 终点
obstacle_list=obstacle_list,
rand_area=[0, 20], # 采样区域
expand_dis=2.0, # 扩展步长
goal_sample_rate=10, # 目标采样概率10%
max_iter=800, # 最大迭代次数
robot_radius=0.5 # 机器人半径
)
# 3. 路径规划
path = rrt.planning(animation=True)
# 4. 结果展示
if path is None:
print("❌ 未找到可行路径!")
else:
print("✅ 找到可行路径!")
# 绘制最终路径
rrt._draw_graph()
plt.plot([x for (x, y) in path], [y for (x, y) in path], "-r", linewidth=2, label="Final Path")
plt.legend()
plt.title("RRT Path Planning Result")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()示例二
bash
import math
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
class RRT:
"""
Class for RRT planning
"""
class Node:
"""
创建节点
"""
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x # 节点坐标
self.y = y
self.path_x = [] # 路径,作为画图的数据
self.path_y = []
self.parent = None #父节点
class AreaBounds:
"""区域大小
"""
def __init__(self, area):
self.xmin = float(area[0])
self.xmax = float(area[1])
self.ymin = float(area[2])
self.ymax = float(area[3])
def __init__(self,
start,
goal,
obstacle_list,
rand_area,
expand_dis=3.0,
goal_sample_rate=5,
max_iter=1000, # ========== 更改点:增加迭代次数,适配复杂场景 ==========
play_area=None,
robot_radius=0.0,
):
"""
Setting Parameter
start:起点 [x,y]
goal:目标点 [x,y]
obstacleList:障碍物位置列表
圆形:[x,y,size, 'circle']
矩形:[x1,y1,x2,y2, 'rect'] (x1/y1为左下,x2/y2为右上)
rand_area: 采样区域 x,y ∈ [min,max]
play_area: 约束随机树的范围 [xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax]
robot_radius: 机器人半径
expand_dis: 扩展的步长
goal_sample_rate: 采样目标点的概率,百分制.default: 5,即表示5%的概率直接采样目标点
"""
self.start = self.Node(start[0], start[1]) # 根节点
self.end = self.Node(goal[0], goal[1])
self.min_rand = rand_area[0]
self.max_rand = rand_area[1]
if play_area is not None:
self.play_area = self.AreaBounds(play_area)
else:
self.play_area = None
self.expand_dis = expand_dis
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.obstacle_list = obstacle_list
self.node_list = []
self.robot_radius = robot_radius
def planning(self, animation=True,camera=None):
"""
rrt path planning
animation: flag for animation on or off
camera: 是否保存动图
"""
# 将起点作为根节点x_{init},加入到随机树的节点集合中。
self.node_list = [self.start]
for i in range(self.max_iter):
# 从可行区域内随机选取一个节点x_{rand}
rnd_node = self.sample_free()
# 已生成的树中利用欧氏距离判断距离x_{rand}最近的点x_{near}。
nearest_ind = self.get_nearest_node_index(self.node_list, rnd_node)
nearest_node = self.node_list[nearest_ind]
# 从x_{near}与x_{rand}的连线方向上扩展固定步长u,得到新节点 x_{new}
new_node = self.steer(nearest_node, rnd_node, self.expand_dis)
# 如果在可行区域内,且x_{near}与x_{new}之间无障碍物
if self.is_inside_play_area(new_node, self.play_area) and \
self.obstacle_free(new_node, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
self.node_list.append(new_node)
# 如果此时得到的节点x_new到目标点的距离小于扩展步长,则直接将目标点作为x_rand。
if self.calc_dist_to_goal(self.node_list[-1].x,self.node_list[-1].y) <= self.expand_dis:
final_node = self.steer(self.node_list[-1], self.end,self.expand_dis)
if self.obstacle_free(final_node, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
# 返回最终路径
return self.generate_final_course(len(self.node_list) - 1)
if animation and i % 5 ==0:
self.draw_graph(rnd_node, camera)
return None # cannot find path
def steer(self, from_node, to_node, extend_length=float("inf")):
"""连线方向扩展固定步长查找x_new
Args:
from_node (_type_): x_near
to_node (_type_): x_rand
extend_length (_type_, optional): 扩展步长u. Defaults to float("inf").
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
# 利用反正切计算角度, 然后利用角度和步长计算新坐标
d, theta = self.calc_distance_and_angle(from_node, to_node)
# 如果$x_{near}$与$x_{rand}$间的距离小于步长,则直接将$x_{rand}$作为新节点$x_{new}$
if extend_length >= d:
new_x = to_node.x
new_y = to_node.y
else:
# ========== 更改点:修复步长计算错误(原代码未乘expand_dis) ==========
new_x = from_node.x + math.cos(theta) * self.expand_dis
new_y = from_node.y + math.sin(theta) * self.expand_dis
new_node = self.Node(new_x, new_y)
new_node.path_x = [from_node.x]
new_node.path_y = [from_node.y]
new_node.path_x.append(new_x)
new_node.path_y.append(new_y)
new_node.parent = from_node
return new_node
def generate_final_course(self, goal_ind):
"""生成路径
Args:
goal_ind (_type_): 目标点索引
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
path = [[self.end.x, self.end.y]]
node = self.node_list[goal_ind]
while node.parent is not None:
path.append([node.x, node.y])
node = node.parent
path.append([node.x, node.y])
return path
def calc_dist_to_goal(self, x, y):
"""计算(x,y)离目标点的距离
"""
dx = x - self.end.x
dy = y - self.end.y
return math.hypot(dx, dy)
def sample_free(self):
# 以(100-goal_sample_rate)%的概率随机生长,(goal_sample_rate)%的概率朝向目标点生长
if random.randint(0, 100) > self.goal_sample_rate:
rnd = self.Node(
random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand),
random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand))
else: # goal point sampling
rnd = self.Node(self.end.x, self.end.y)
return rnd
def draw_graph(self, rnd=None, camera=None):
if camera==None:
plt.clf()
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
'key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
# 画随机点
if rnd is not None:
plt.plot(rnd.x, rnd.y, "^k")
if self.robot_radius > 0.0:
self.plot_circle(rnd.x, rnd.y, self.robot_radius, '-r')
# 画已生成的树
for node in self.node_list:
if node.parent:
plt.plot(node.path_x, node.path_y, "-g")
# 画障碍物
# ========== 更改点:新增矩形障碍物绘制逻辑 ==========
for obs in self.obstacle_list:
if obs[-1] == 'circle':
ox, oy, size, _ = obs
self.plot_circle(ox, oy, size)
elif obs[-1] == 'rect':
x1, y1, x2, y2, _ = obs
self.plot_rect(x1, y1, x2, y2)
# 如果约定了可行区域,则画出可行区域
if self.play_area is not None:
plt.plot([self.play_area.xmin, self.play_area.xmax,
self.play_area.xmax, self.play_area.xmin,
self.play_area.xmin],
[self.play_area.ymin, self.play_area.ymin,
self.play_area.ymax, self.play_area.ymax,
self.play_area.ymin],
"-k")
# 画出起点和目标点
plt.plot(self.start.x, self.start.y, "xr", markersize=10)
plt.plot(self.end.x, self.end.y, "xr", markersize=10)
plt.axis("equal")
plt.axis([-2, 25, -2, 25]) # ========== 更改点:扩大可视化范围 ==========
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.01)
if camera!=None:
camera.snap()
# ========== 更改点:新增矩形绘制函数 ==========
@staticmethod
def plot_rect(x1, y1, x2, y2, color="-b"):
"""绘制矩形障碍物"""
plt.plot([x1, x2, x2, x1, x1], [y1, y1, y2, y2, y1], color, linewidth=2)
@staticmethod
def plot_circle(x, y, size, color="-b"): # pragma: no cover
deg = list(range(0, 360, 5))
deg.append(0)
xl = [x + size * math.cos(np.deg2rad(d)) for d in deg]
yl = [y + size * math.sin(np.deg2rad(d)) for d in deg]
plt.plot(xl, yl, color)
@staticmethod
def get_nearest_node_index(node_list, rnd_node):
dlist = [(node.x - rnd_node.x)**2 + (node.y - rnd_node.y)**2
for node in node_list]
minind = dlist.index(min(dlist))
return minind
@staticmethod
def is_inside_play_area(node, play_area):
if play_area is None:
return True # no play_area was defined, every pos should be ok
if node.x < play_area.xmin or node.x > play_area.xmax or \
node.y < play_area.ymin or node.y > play_area.ymax:
return False # outside - bad
else:
return True # inside - ok
# ========== 更改点:重构碰撞检测,支持矩形障碍物 ==========
@staticmethod
def obstacle_free(node, obstacle_list, robot_radius):
if node is None:
return False
# 遍历所有路径点,检查是否与障碍物碰撞
for (x, y) in zip(node.path_x, node.path_y):
# 检查每个障碍物
for obs in obstacle_list:
if obs[-1] == 'circle':
# 圆形障碍物碰撞检测
ox, oy, size, _ = obs
dx = x - ox
dy = y - oy
if dx*dx + dy*dy <= (size + robot_radius)**2:
return False
elif obs[-1] == 'rect':
# 矩形障碍物碰撞检测(带机器人半径膨胀)
x1, y1, x2, y2, _ = obs
# 矩形膨胀(考虑机器人半径)
x1_exp = x1 - robot_radius
y1_exp = y1 - robot_radius
x2_exp = x2 + robot_radius
y2_exp = y2 + robot_radius
# 判断点是否在膨胀后的矩形内
if (x1_exp <= x <= x2_exp) and (y1_exp <= y <= y2_exp):
return False
return True # safe
@staticmethod
def calc_distance_and_angle(from_node, to_node):
"""计算两个节点间的距离和方位角
Args:
from_node (_type_): _description_
to_node (_type_): _description_
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
dx = to_node.x - from_node.x
dy = to_node.y - from_node.y
d = math.hypot(dx, dy)
theta = math.atan2(dy, dx)
return d, theta
def main(gx=22.0, gy=22.0): # ========== 更改点:调整终点位置 ==========
print("start " + __file__)
fig = plt.figure(1)
camera = Camera(fig) # 保存动图时使用
camera = None # 不保存动图时,camara为None
show_animation = True
# ========== 更改点:定义4个方格障碍物(矩形),方格间保留通道 ==========
# 障碍物格式:
# 矩形:[x1,y1,x2,y2, 'rect'] (x1/y1=左下,x2/y2=右上)
# 4个方格布局:
# 方格1:左上 (2,18) - (8,24)
# 方格2:右上 (12,18) - (18,24)
# 方格3:左下 (2,2) - (8,8)
# 方格4:右下 (12,2) - (18,8)
# 方格间通道:水平通道y=11(9-13),垂直通道x=10(1-25)
obstacleList = [
# 4个主方格(矩形障碍物)
(2, 18, 8, 24, 'rect'), # 方格1(左上)
(12, 18, 18, 24, 'rect'), # 方格2(右上)
(2, 2, 8, 8, 'rect'), # 方格3(左下)
(12, 2, 18, 8, 'rect'), # 方格4(右下)
# 可选:添加少量圆形障碍物增加复杂度
(10, 11, 0.5, 'circle'), # 通道中心标记
]
# Set Initial parameters
rrt = RRT(
start=[0, 0], # 起点(左下)
goal=[gx, gy], # 终点(右上)
rand_area=[-2, 25], # 采样区域扩大
obstacle_list=obstacleList,
play_area=[-2, 25, -2, 25], # 可行区域扩大
robot_radius=0.5, # 机器人半径调整
expand_dis=2.0, # 扩展步长调整(适配大场景)
goal_sample_rate=10, # 提高目标采样概率(加快收敛)
max_iter=1000 # 增加迭代次数
)
path = rrt.planning(animation=show_animation,camera=camera)
if path is None:
print("Cannot find path")
else:
print("found path!!")
# Draw final path
if show_animation:
rrt.draw_graph(camera=camera)
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.plot([x for (x, y) in path], [y for (x, y) in path], '-r', linewidth=2)
if camera!=None:
camera.snap()
animation = camera.animate()
animation.save('trajectory.gif')
plt.figure(2)
plt.axis("equal")
plt.axis([-2, 25, -2, 25])
plt.grid(True)
# 绘制障碍物(用于最终路径图)
for obs in obstacleList:
if obs[-1] == 'circle':
ox, oy, size, _ = obs
RRT.plot_circle(ox, oy, size)
elif obs[-1] == 'rect':
x1, y1, x2, y2, _ = obs
RRT.plot_rect(x1, y1, x2, y2)
# 绘制最终路径
plt.plot([x for (x, y) in path], [y for (x, y) in path], '-r', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(rrt.start.x, rrt.start.y, "xr", markersize=10, label='Start')
plt.plot(rrt.end.x, rrt.end.y, "xr", markersize=10, label='Goal')
plt.legend()
plt.title('RRT Path Planning (4 Grids Obstacle)')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()运行后效果
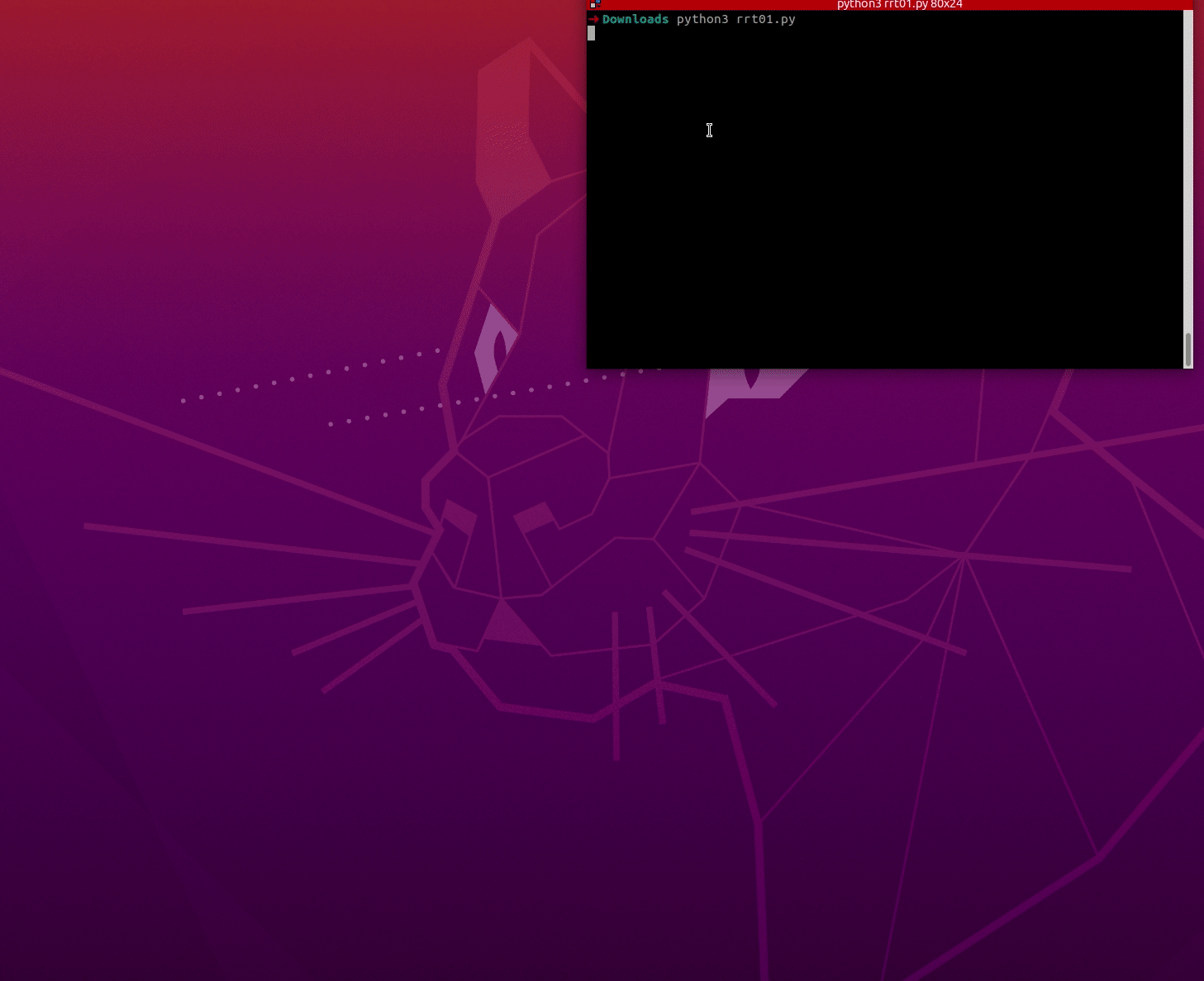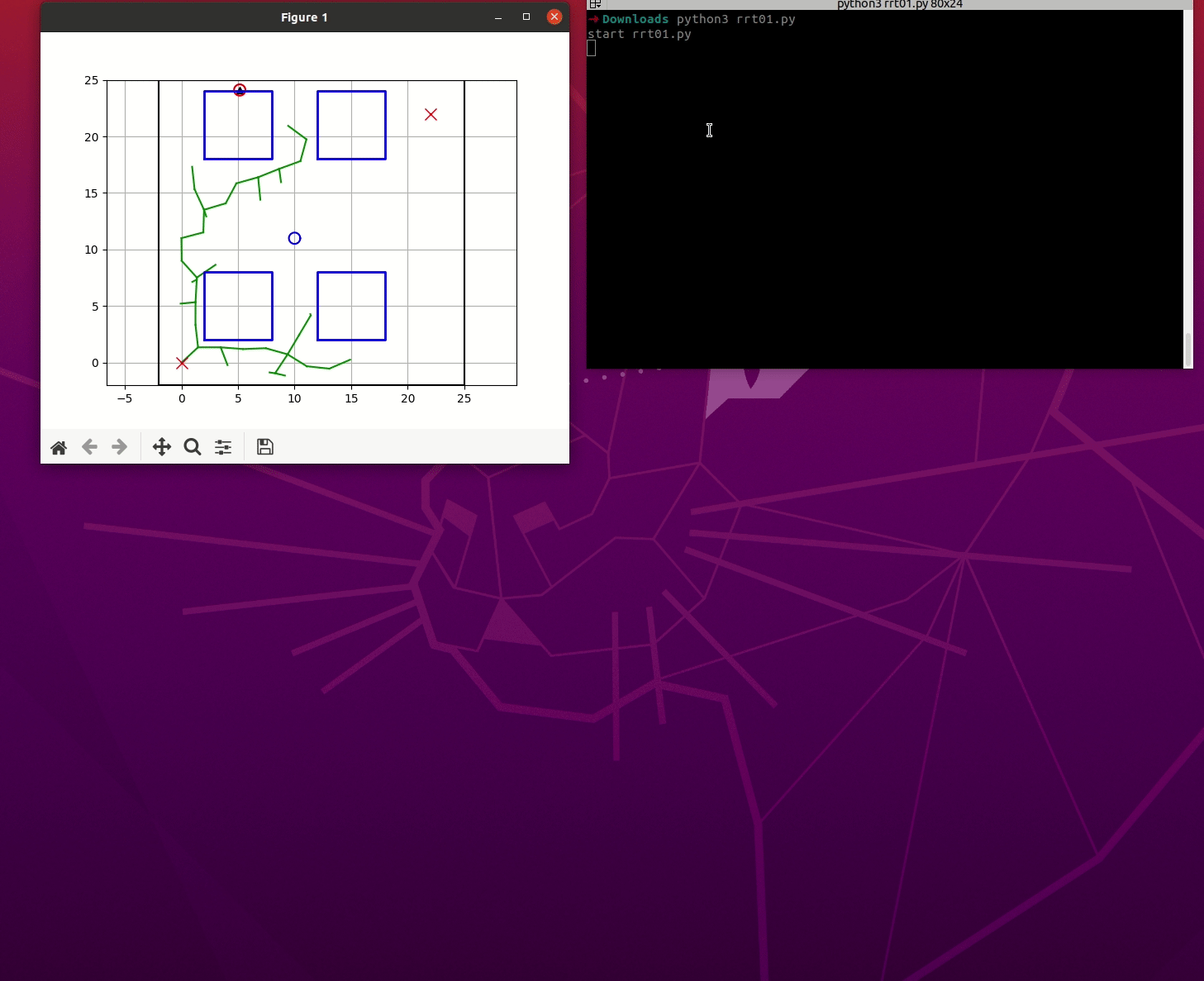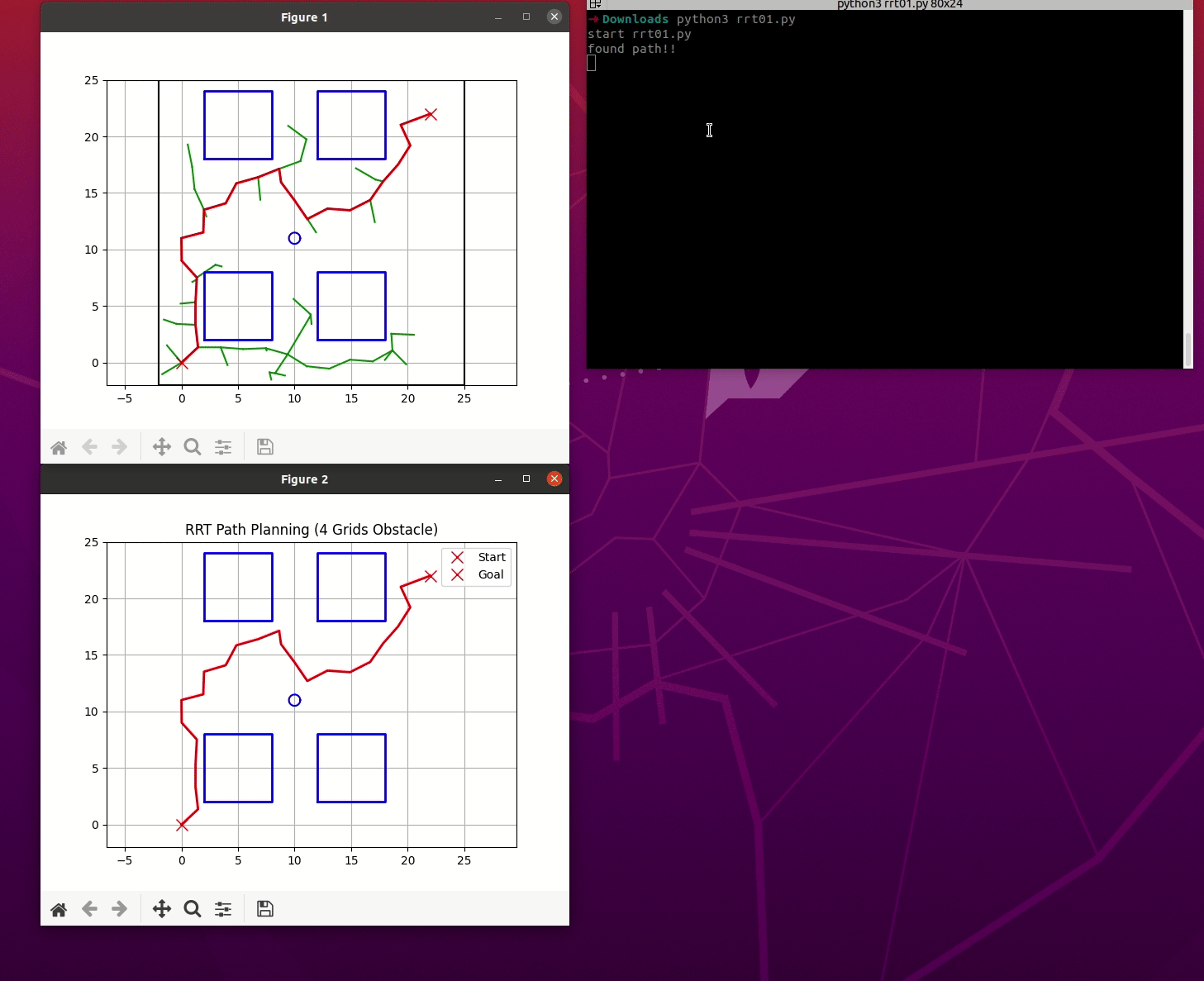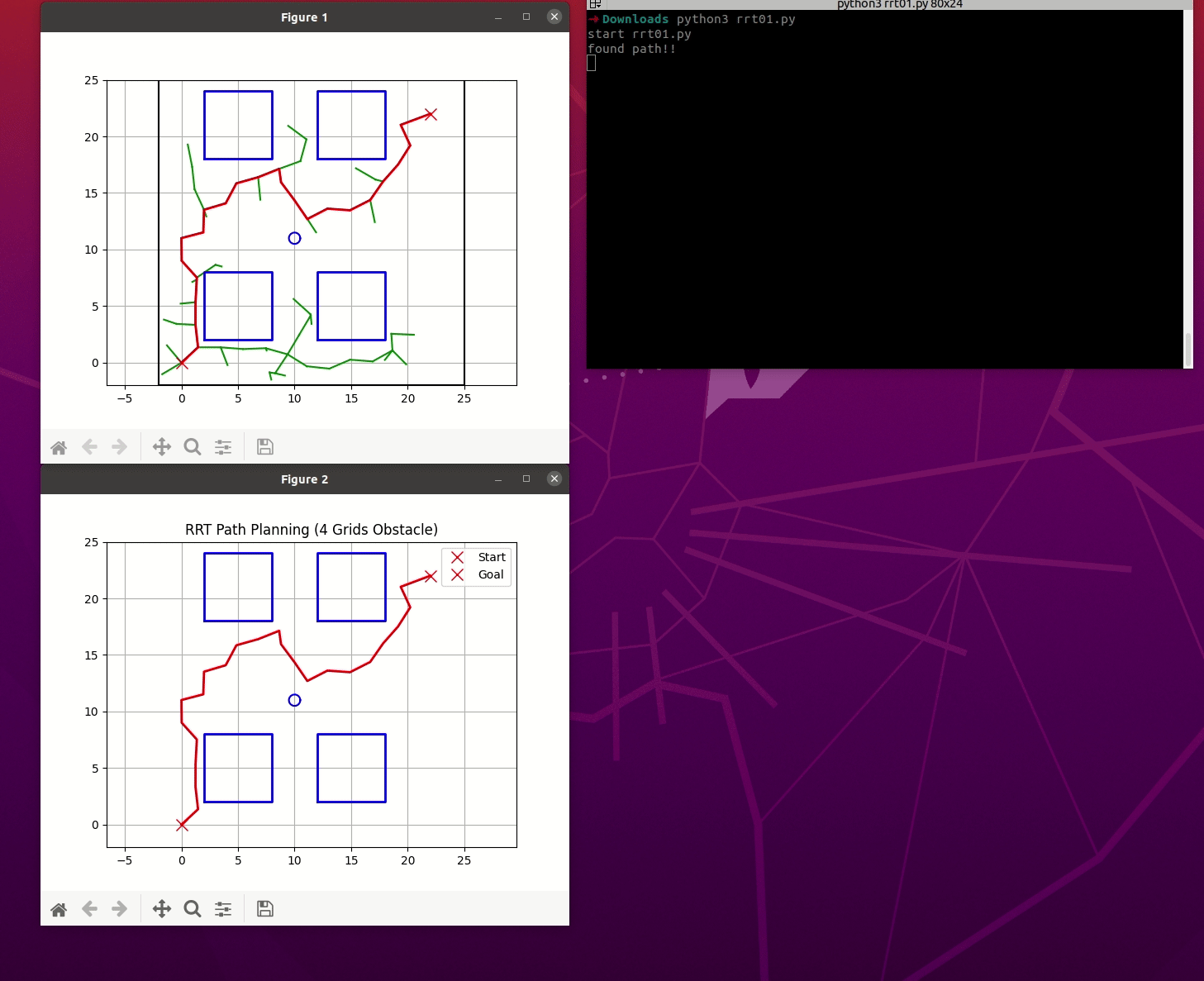
RRT及其发展示例三
bash
# rrt_planning
import math
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
class RRT:
"""
Class for RRT planning
"""
class Node:
"""
创建节点
"""
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x # 节点坐标
self.y = y
self.path_x = [] # 路径,作为画图的数据
self.path_y = []
self.parent = None #父节点
class AreaBounds:
"""区域大小
"""
def __init__(self, area):
self.xmin = float(area[0])
self.xmax = float(area[1])
self.ymin = float(area[2])
self.ymax = float(area[3])
def __init__(self,
start,
goal,
obstacle_list,
rand_area,
expand_dis=3.0,
goal_sample_rate=5,
max_iter=500,
play_area=None,
robot_radius=0.0,
):
"""
Setting Parameter
start:起点 [x,y]
goal:目标点 [x,y]
obstacleList:障碍物位置列表 [[x,y,size],...]
rand_area: 采样区域 x,y ∈ [min,max]
play_area: 约束随机树的范围 [xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax]
robot_radius: 机器人半径
expand_dis: 扩展的步长
goal_sample_rate: 采样目标点的概率,百分制.default: 5,即表示5%的概率直接采样目标点
"""
self.start = self.Node(start[0], start[1]) # 根节点
self.end = self.Node(goal[0], goal[1])
self.min_rand = rand_area[0]
self.max_rand = rand_area[1]
if play_area is not None:
self.play_area = self.AreaBounds(play_area)
else:
self.play_area = None
self.expand_dis = expand_dis
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.obstacle_list = obstacle_list
self.node_list = []
self.robot_radius = robot_radius
def planning(self, animation=True,camera=None):
"""
rrt path planning
animation: flag for animation on or off
camera: 是否保存动图
"""
# 将起点作为根节点x_{init},加入到随机树的节点集合中。
self.node_list = [self.start]
for i in range(self.max_iter):
# 从可行区域内随机选取一个节点x_{rand}
rnd_node = self.sample_free()
# 已生成的树中利用欧氏距离判断距离x_{rand}最近的点x_{near}。
nearest_ind = self.get_nearest_node_index(self.node_list, rnd_node)
nearest_node = self.node_list[nearest_ind]
# 从x_{near}与x_{rand}的连线方向上扩展固定步长u,得到新节点 x_{new}
new_node = self.steer(nearest_node, rnd_node, self.expand_dis)
# 如果在可行区域内,且x_{near}与x_{new}之间无障碍物
if self.is_inside_play_area(new_node, self.play_area) and \
self.obstacle_free(new_node, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
self.node_list.append(new_node)
# 如果此时得到的节点x_new到目标点的距离小于扩展步长,则直接将目标点作为x_rand。
if self.calc_dist_to_goal(self.node_list[-1].x,self.node_list[-1].y) <= self.expand_dis:
final_node = self.steer(self.node_list[-1], self.end,self.expand_dis)
if self.obstacle_free(final_node, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
# 返回最终路径
return self.generate_final_course(len(self.node_list) - 1)
if animation and i % 5 ==0:
self.draw_graph(rnd_node, camera)
return None # cannot find path
def steer(self, from_node, to_node, extend_length=float("inf")):
"""连线方向扩展固定步长查找x_new
Args:
from_node (_type_): x_near
to_node (_type_): x_rand
extend_length (_type_, optional): 扩展步长u. Defaults to float("inf").
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
# 利用反正切计算角度, 然后利用角度和步长计算新坐标
d, theta = self.calc_distance_and_angle(from_node, to_node)
# 如果$x_{near}$与$x_{rand}$间的距离小于步长,则直接将$x_{rand}$作为新节点$x_{new}$
if extend_length >= d:
new_x = to_node.x
new_y = to_node.y
else:
new_x = from_node.x+math.cos(theta)
new_y = from_node.y+math.sin(theta)
new_node = self.Node(new_x,new_y)
new_node.path_x = [from_node.x]
new_node.path_y = [from_node.y]
new_node.path_x.append(new_x)
new_node.path_y.append(new_y)
new_node.parent = from_node
return new_node
def generate_final_course(self, goal_ind):
"""生成路径
Args:
goal_ind (_type_): 目标点索引
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
path = [[self.end.x, self.end.y]]
node = self.node_list[goal_ind]
while node.parent is not None:
path.append([node.x, node.y])
node = node.parent
path.append([node.x, node.y])
return path
def calc_dist_to_goal(self, x, y):
"""计算(x,y)离目标点的距离
"""
dx = x - self.end.x
dy = y - self.end.y
return math.hypot(dx, dy)
def sample_free(self):
# 以(100-goal_sample_rate)%的概率随机生长,(goal_sample_rate)%的概率朝向目标点生长
if random.randint(0, 100) > self.goal_sample_rate:
rnd = self.Node(
random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand),
random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand))
else: # goal point sampling
rnd = self.Node(self.end.x, self.end.y)
return rnd
def draw_graph(self, rnd=None, camera=None):
if camera==None:
plt.clf()
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
'key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
# 画随机点
if rnd is not None:
plt.plot(rnd.x, rnd.y, "^k")
if self.robot_radius > 0.0:
self.plot_circle(rnd.x, rnd.y, self.robot_radius, '-r')
# 画已生成的树
for node in self.node_list:
if node.parent:
plt.plot(node.path_x, node.path_y, "-g")
# 画障碍物
for (ox, oy, size) in self.obstacle_list:
self.plot_circle(ox, oy, size)
# 如果约定了可行区域,则画出可行区域
if self.play_area is not None:
plt.plot([self.play_area.xmin, self.play_area.xmax,
self.play_area.xmax, self.play_area.xmin,
self.play_area.xmin],
[self.play_area.ymin, self.play_area.ymin,
self.play_area.ymax, self.play_area.ymax,
self.play_area.ymin],
"-k")
# 画出起点和目标点
plt.plot(self.start.x, self.start.y, "xr")
plt.plot(self.end.x, self.end.y, "xr")
plt.axis("equal")
plt.axis([-2, 15, -2, 15])
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.01)
if camera!=None:
camera.snap()
# 静态方法无需实例化,也可以实例化后调用,静态方法内部不能调用self.的变量
@staticmethod
def plot_circle(x, y, size, color="-b"): # pragma: no cover
deg = list(range(0, 360, 5))
deg.append(0)
xl = [x + size * math.cos(np.deg2rad(d)) for d in deg]
yl = [y + size * math.sin(np.deg2rad(d)) for d in deg]
plt.plot(xl, yl, color)
@staticmethod
def get_nearest_node_index(node_list, rnd_node):
dlist = [(node.x - rnd_node.x)**2 + (node.y - rnd_node.y)**2
for node in node_list]
minind = dlist.index(min(dlist))
return minind
@staticmethod
def is_inside_play_area(node, play_area):
if play_area is None:
return True # no play_area was defined, every pos should be ok
if node.x < play_area.xmin or node.x > play_area.xmax or \
node.y < play_area.ymin or node.y > play_area.ymax:
return False # outside - bad
else:
return True # inside - ok
@staticmethod
def obstacle_free(node, obstacleList, robot_radius):
if node is None:
return False
for (ox, oy, size) in obstacleList:
dx_list = [ox - x for x in node.path_x]
dy_list = [oy - y for y in node.path_y]
d_list = [dx * dx + dy * dy for (dx, dy) in zip(dx_list, dy_list)]
if min(d_list) <= (size+robot_radius)**2:
return False # collision
return True # safe
@staticmethod
def calc_distance_and_angle(from_node, to_node):
"""计算两个节点间的距离和方位角
Args:
from_node (_type_): _description_
to_node (_type_): _description_
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
dx = to_node.x - from_node.x
dy = to_node.y - from_node.y
d = math.hypot(dx, dy)
theta = math.atan2(dy, dx)
return d, theta
def main(gx=6.0, gy=10.0):
print("start " + __file__)
fig = plt.figure(1)
camera = Camera(fig) # 保存动图时使用
camera = None # 不保存动图时,camara为None
show_animation = True
# ====Search Path with RRT====
obstacleList = [
(5, 5, 1),
(3, 6, 2),
(3, 8, 2),
(3, 10, 2),
(7, 5, 2),
(9, 5, 2),
(8, 10, 1),
(6, 12, 1),
] # [x,y,size(radius)]
# Set Initial parameters
rrt = RRT(
start=[0, 0],
goal=[gx, gy],
rand_area=[-2, 15],
obstacle_list=obstacleList,
play_area=[-2, 12, 0, 14],
robot_radius=0.8
)
path = rrt.planning(animation=show_animation,camera=camera)
if path is None:
print("Cannot find path")
else:
print("found path!!")
# Draw final path
if show_animation:
rrt.draw_graph(camera=camera)
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.plot([x for (x, y) in path], [y for (x, y) in path], '-r')
if camera!=None:
camera.snap()
animation = camera.animate()
animation.save('trajectory.gif')
plt.figure(2)
plt.axis("equal")
plt.axis([-2, 15, -2, 15])
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot([x for (x, y) in path], [y for (x, y) in path], '-r')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
bash
# rrt-start
import math
import os
import sys
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
sys.path.append("../RRT")
try:
from rrt_planning import RRT
except ImportError:
raise
show_animation = True
class RRTStar(RRT):
"""
Class for RRT Star planning
"""
class Node(RRT.Node):
def __init__(self, x, y):
super().__init__(x, y)
self.cost = 0.0
def __init__(self,
start,
goal,
obstacle_list,
rand_area,
expand_dis=3.0,
goal_sample_rate=20,
max_iter=500,
connect_circle_dist=50.0,
search_until_max_iter=False,
robot_radius=0.0):
"""
Setting Parameter
start:Start Position [x,y]
goal:Goal Position [x,y]
obstacleList:obstacle Positions [[x,y,size],...]
randArea:Random Sampling Area [min,max]
"""
super().__init__(start, goal, obstacle_list, rand_area, expand_dis,
goal_sample_rate, max_iter,
robot_radius=robot_radius)
self.connect_circle_dist = connect_circle_dist
self.goal_node = self.Node(goal[0], goal[1])
self.search_until_max_iter = search_until_max_iter
def planning(self, animation=True, camera=None):
"""
rrt star path planning
animation: flag for animation on or off .
"""
self.node_list = [self.start]
for i in range(self.max_iter):
print("Iter:", i, ", number of nodes:", len(self.node_list))
rnd = self.sample_free()
nearest_ind = self.get_nearest_node_index(self.node_list, rnd)
new_node = self.steer(self.node_list[nearest_ind], rnd,
self.expand_dis)
near_node = self.node_list[nearest_ind]
# 计算代价,欧氏距离
new_node.cost = near_node.cost + math.hypot(new_node.x-near_node.x, new_node.y-near_node.y)
if self.obstacle_free(new_node, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
near_inds = self.find_near_nodes(new_node) # 找到x_new的邻近节点
node_with_updated_parent = self.choose_parent(new_node, near_inds) # 重新选择父节点
# 如果父节点更新了
if node_with_updated_parent:
# 重布线
self.rewire(node_with_updated_parent, near_inds)
self.node_list.append(node_with_updated_parent)
else:
self.node_list.append(new_node)
if animation and i % 5 ==0:
self.draw_graph(rnd, camera)
if ((not self.search_until_max_iter) and new_node): # if reaches goal
last_index = self.search_best_goal_node()
if last_index is not None:
return self.generate_final_course(last_index)
print("reached max iteration")
last_index = self.search_best_goal_node()
if last_index is not None:
return self.generate_final_course(last_index)
return None
def choose_parent(self, new_node, near_inds):
"""
在新产生的节点 $x_{new}$ 附近以定义的半径范围$r$内寻找所有的近邻节点 $X_{near}$,
作为替换 $x_{new}$ 原始父节点 $x_{near}$ 的备选
我们需要依次计算起点到每个近邻节点 $X_{near}$ 的路径代价 加上近邻节点 $X_{near}$ 到 $x_{new}$ 的路径代价,
取路径代价最小的近邻节点$x_{min}$作为 $x_{new}$ 新的父节点
Arguments:
--------
new_node, Node
randomly generated node with a path from its neared point
There are not coalitions between this node and th tree.
near_inds: list
Indices of indices of the nodes what are near to new_node
Returns.
------
Node, a copy of new_node
"""
if not near_inds:
return None
# search nearest cost in near_inds
costs = []
for i in near_inds:
near_node = self.node_list[i]
t_node = self.steer(near_node, new_node)
if t_node and self.obstacle_free(t_node, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
costs.append(self.calc_new_cost(near_node, new_node))
else:
costs.append(float("inf")) # the cost of collision node
min_cost = min(costs)
if min_cost == float("inf"):
print("There is no good path.(min_cost is inf)")
return None
min_ind = near_inds[costs.index(min_cost)]
new_node = self.steer(self.node_list[min_ind], new_node)
new_node.cost = min_cost
return new_node
def search_best_goal_node(self):
dist_to_goal_list = [self.calc_dist_to_goal(n.x, n.y) for n in self.node_list]
goal_inds = [
dist_to_goal_list.index(i) for i in dist_to_goal_list
if i <= self.expand_dis
]
safe_goal_inds = []
for goal_ind in goal_inds:
t_node = self.steer(self.node_list[goal_ind], self.goal_node)
if self.obstacle_free(t_node, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
safe_goal_inds.append(goal_ind)
if not safe_goal_inds:
return None
min_cost = min([self.node_list[i].cost for i in safe_goal_inds])
for i in safe_goal_inds:
if self.node_list[i].cost == min_cost:
return i
return None
def find_near_nodes(self, new_node):
"""
1) defines a ball centered on new_node
2) Returns all nodes of the three that are inside this ball
Arguments:
---------
new_node: Node
new randomly generated node, without collisions between
its nearest node
Returns:
-------
list
List with the indices of the nodes inside the ball of
radius r
"""
nnode = len(self.node_list) + 1
r = self.connect_circle_dist * math.sqrt((math.log(nnode) / nnode))
# if expand_dist exists, search vertices in a range no more than
# expand_dist
if hasattr(self, 'expand_dis'):
r = min(r, self.expand_dis)
dist_list = [(node.x - new_node.x)**2 + (node.y - new_node.y)**2
for node in self.node_list]
near_inds = [dist_list.index(i) for i in dist_list if i <= r**2]
return near_inds
def rewire(self, new_node, near_inds):
"""
For each node in near_inds, this will check if it is cheaper to
arrive to them from new_node.
In such a case, this will re-assign the parent of the nodes in
near_inds to new_node.
Parameters:
----------
new_node, Node
Node randomly added which can be joined to the tree
near_inds, list of uints
A list of indices of the self.new_node which contains
nodes within a circle of a given radius.
Remark: parent is designated in choose_parent.
"""
for i in near_inds:
near_node = self.node_list[i]
edge_node = self.steer(new_node, near_node)
if not edge_node:
continue
edge_node.cost = self.calc_new_cost(new_node, near_node)
no_collision = self.obstacle_free(
edge_node, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius)
improved_cost = near_node.cost > edge_node.cost
if no_collision and improved_cost:
near_node.x = edge_node.x
near_node.y = edge_node.y
near_node.cost = edge_node.cost
near_node.path_x = edge_node.path_x
near_node.path_y = edge_node.path_y
near_node.parent = edge_node.parent
self.propagate_cost_to_leaves(new_node)
def calc_new_cost(self, from_node, to_node):
d, _ = self.calc_distance_and_angle(from_node, to_node)
return from_node.cost + d
def propagate_cost_to_leaves(self, parent_node):
for node in self.node_list:
if node.parent == parent_node:
node.cost = self.calc_new_cost(parent_node, node)
self.propagate_cost_to_leaves(node)
def main():
print("Start " )
fig = plt.figure(1)
camera = Camera(fig) # 保存动图时使用
# camera = None # 不保存动图时,camara为None
show_animation = True
# ====Search Path with RRT====
obstacle_list = [
(5, 5, 1),
(3, 6, 2),
(3, 8, 2),
(3, 10, 2),
(7, 5, 2),
(9, 5, 2),
(8, 10, 1),
(6, 12, 1),
] # [x,y,size(radius)]
# Set Initial parameters
rrt_star = RRTStar(
start=[0, 0],
goal=[6, 10],
rand_area=[-2, 15],
obstacle_list=obstacle_list,
expand_dis=3,
robot_radius=0.8)
path = rrt_star.planning(animation=show_animation,camera=None)
if path is None:
print("Cannot find path")
else:
print("found path!!")
# Draw final path
if show_animation:
rrt_star.draw_graph(camera=None)
plt.plot([x for (x, y) in path], [y for (x, y) in path], 'r--')
plt.grid(True)
# if camera!=None:
# camera.snap()
# animation = camera.animate()
# animation.save('trajectory.gif')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()运行后结果:
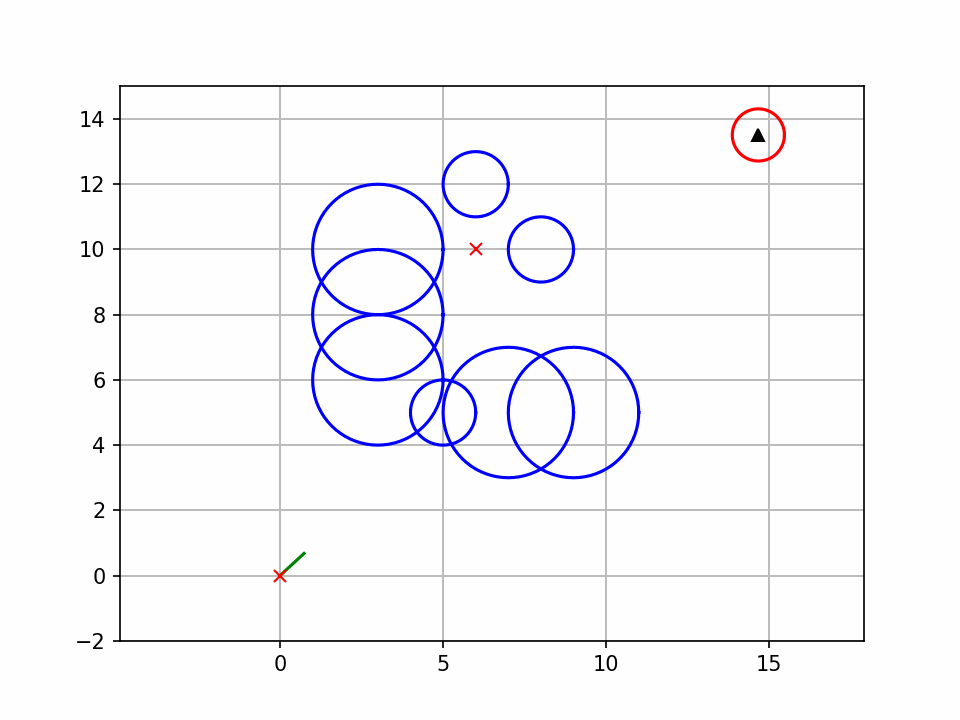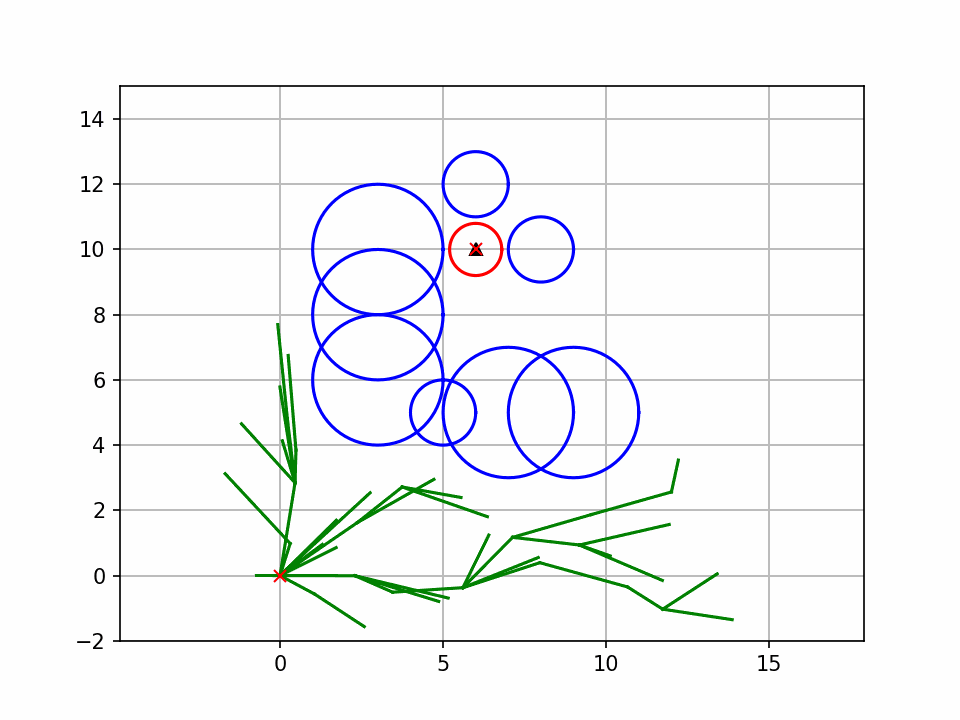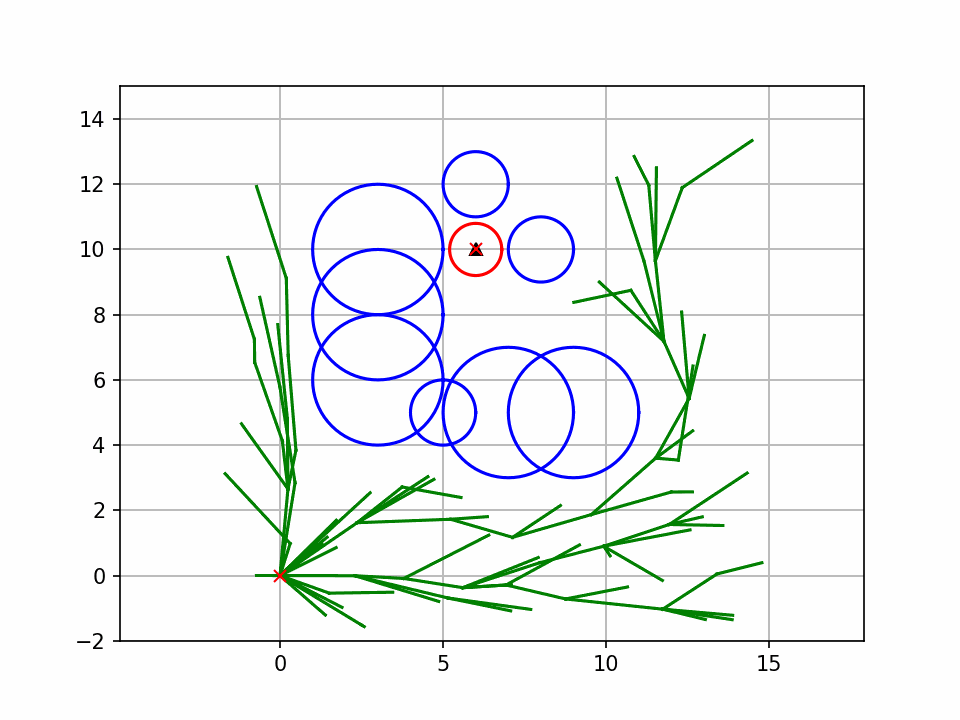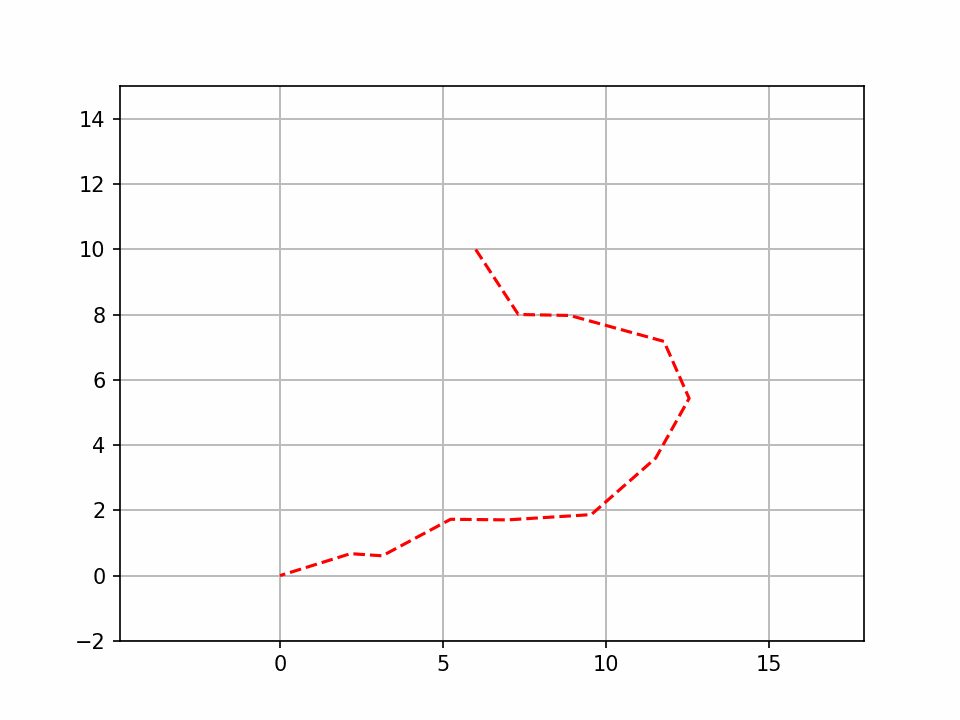
RRT规划发展示例四
bash
import math
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from celluloid import Camera # 保存动图时用,pip install celluloid
import operator
import copy
class RRT_Connect:
"""
Class for RRT_Connect planning
"""
class Node:
"""
创建节点
"""
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x # 节点坐标
self.y = y
self.path_x = [] # 路径,作为画图的数据,也可以理解成保存的边集
self.path_y = []
self.parent = None #父节点
class AreaBounds:
"""区域大小
"""
def __init__(self, area):
self.xmin = float(area[0])
self.xmax = float(area[1])
self.ymin = float(area[2])
self.ymax = float(area[3])
def __init__(self,
start,
goal,
obstacle_list,
rand_area,
expand_dis=3.0,
goal_sample_rate=5,
max_iter=1000,
play_area=None,
robot_radius=0.0,
):
"""
Setting Parameter
start:起点 [x,y]
goal:目标点 [x,y]
obstacleList:障碍物位置列表 [[x,y,size],...]
rand_area: 采样区域 x,y ∈ [min,max]
play_area: 约束随机树的范围 [xmin,xmax,ymin,ymax]
robot_radius: 机器人半径
expand_dis: 扩展的步长
goal_sample_rate: 采样目标点的概率,百分制.default: 5,即表示5%的概率直接采样目标点
"""
self.start = self.Node(start[0], start[1]) # 根节点
self.end = self.Node(goal[0], goal[1])
self.min_rand = rand_area[0]
self.max_rand = rand_area[1]
if play_area is not None:
self.play_area = self.AreaBounds(play_area)
else:
self.play_area = None
self.expand_dis = expand_dis
self.goal_sample_rate = goal_sample_rate
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.obstacle_list = obstacle_list
self.node_list_1 = []
self.node_list_2 = []
self.robot_radius = robot_radius
def planning(self, animation=True,camara=None):
"""
rrt path planning
animation: flag for animation on or off
camara: 是否保存动图
"""
# 将起点作为根节点x_{init},加入到随机树的节点集合中。
self.node_list_1 = [self.start]
self.node_list_2 = [self.end]
for i in range(self.max_iter):
# 从可行区域内随机选取一个节点q_{rand}
rnd_node = self.sample_free()
# 已生成的树中利用欧氏距离判断距离q_{rand}最近的点q_{near}。
nearest_ind_1 = self.get_nearest_node_index(self.node_list_1, rnd_node)
nearest_node_1 = self.node_list_1[nearest_ind_1]
# 从q_{near}与q_{rand}的连线方向上扩展固定步长u,得到新节点 q_{new}
new_node_1 = self.steer(nearest_node_1, rnd_node, self.expand_dis)
# 第一棵树,如果在可行区域内,且q_{near}与q_{new}之间无障碍物
if self.is_inside_play_area(new_node_1, self.play_area) and self.obstacle_free(new_node_1, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
self.node_list_1.append(new_node_1)
# 扩展完第一棵树的新节点$x_{𝑛𝑒𝑤}$后,以这个新的目标点$x_{𝑛𝑒𝑤}$作为第二棵树扩展的方向。
nearest_ind_2 = self.get_nearest_node_index(self.node_list_2, new_node_1)
nearest_node_2 = self.node_list_2[nearest_ind_2]
new_node_2 = self.steer(nearest_node_2, new_node_1, self.expand_dis)
# 第二棵树
if self.is_inside_play_area(new_node_2, self.play_area) and self.obstacle_free(new_node_2, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
self.node_list_2.append(new_node_2)
while True:
new_node_2_ = self.steer(new_node_2, new_node_1, self.expand_dis)
if self.obstacle_free(new_node_2_, self.obstacle_list, self.robot_radius):
self.node_list_2.append(new_node_2_)
new_node_2 = new_node_2_
else:
break
# print([new_node_2.x,new_node_2.y], [new_node_1.x,new_node_1.y])
# 当$𝑞′_{𝑛𝑒𝑤}=𝑞_{𝑛𝑒𝑤}$时,表示与第一棵树相连,算法结束
if operator.eq([new_node_2.x,new_node_2.y], [new_node_1.x,new_node_1.y]):
return self.generate_final_path()
# 考虑两棵树的平衡性,即两棵树的节点数的多少,交换次序选择"小"的那棵树进行扩展。
# 不过不交换的情况下好像搜索速度还更快
if len(self.node_list_1)>len(self.node_list_2):
list_tmp = copy.deepcopy(self.node_list_1)
self.node_list_1 = copy.deepcopy(self.node_list_2)
self.node_list_2 = list_tmp
if animation and i % 5 ==0:
self.draw_graph(rnd_node,new_node_1, camara)
return None # cannot find path
def steer(self, from_node, to_node, extend_length=float("inf")):
"""连线方向扩展固定步长查找x_new
Args:
from_node (_type_): x_near
to_node (_type_): x_rand
extend_length (_type_, optional): 扩展步长u. Defaults to float("inf").
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
# 利用反正切计算角度, 然后利用角度和步长计算新坐标
d, theta = self.calc_distance_and_angle(from_node, to_node)
# 如果$q_{near}$与$q_{rand}$间的距离小于步长,则直接将$q_{rand}$作为新节点$q_{new}$
if extend_length >= d:
new_x = to_node.x
new_y = to_node.y
else:
new_x = from_node.x+math.cos(theta)
new_y = from_node.y+math.sin(theta)
new_node_1 = self.Node(new_x,new_y)
new_node_1.path_x = [from_node.x] # 边集
new_node_1.path_y = [from_node.y]
new_node_1.path_x.append(new_x)
new_node_1.path_y.append(new_y)
new_node_1.parent = from_node
return new_node_1
def generate_final_path(self):
"""生成路径
Args:
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
path_1 = []
node = self.node_list_1[-1]
while node.parent is not None:
path_1.append([node.x, node.y])
node = node.parent
path_1.append([node.x, node.y])
path_2 = []
node = self.node_list_2[-1]
while node.parent is not None:
path_2.append([node.x, node.y])
node = node.parent
path_2.append([node.x, node.y])
path=[]
for i in range(len(path_1)-1,-1,-1):
path.append(path_1[i])
for i in range(len(path_2)):
path.append(path_2[i])
return path
def calc_dist(self, x1, y1,x2,y2):
"""计算距离
"""
dx = x1 - x2
dy = y1 - y2
return math.hypot(dx, dy)
def sample_free(self):
# 以(100-goal_sample_rate)%的概率随机生长,(goal_sample_rate)%的概率朝向目标点生长
if random.randint(0, 100) > self.goal_sample_rate:
rnd = self.Node(
random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand),
random.uniform(self.min_rand, self.max_rand))
else: # goal point sampling
rnd = self.Node(self.end.x, self.end.y)
return rnd
def draw_graph(self, rnd=None,rnd_2=None, camera=None):
if camera==None:
plt.clf()
# for stopping simulation with the esc key.
plt.gcf().canvas.mpl_connect(
'key_release_event',
lambda event: [exit(0) if event.key == 'escape' else None])
# 画随机点
if rnd is not None:
plt.plot(rnd.x, rnd.y, "^k")
if self.robot_radius > 0.0:
self.plot_circle(rnd.x, rnd.y, self.robot_radius, '-r')
if rnd_2 is not None:
plt.plot(rnd_2.x, rnd_2.y, "^r")
if self.robot_radius > 0.0:
self.plot_circle(rnd_2.x, rnd_2.y, self.robot_radius, '-b')
# 画已生成的树
for node in self.node_list_1:
if node.parent:
plt.plot(node.path_x, node.path_y, "-g")
for node in self.node_list_2:
if node.parent:
plt.plot(node.path_x, node.path_y, "-g")
# 画障碍物
for (ox, oy, size) in self.obstacle_list:
self.plot_circle(ox, oy, size)
# 如果约定了可行区域,则画出可行区域
if self.play_area is not None:
plt.plot([self.play_area.xmin, self.play_area.xmax,
self.play_area.xmax, self.play_area.xmin,
self.play_area.xmin],
[self.play_area.ymin, self.play_area.ymin,
self.play_area.ymax, self.play_area.ymax,
self.play_area.ymin],
"-k")
# 画出起点和目标点
plt.plot(self.start.x, self.start.y, "xr")
plt.plot(self.end.x, self.end.y, "xr")
plt.axis("equal")
plt.axis([-2, 15, -2, 15])
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.01)
if camera!=None:
camera.snap()
# 静态方法无需实例化,也可以实例化后调用,静态方法内部不能调用self.的变量
@staticmethod
def plot_circle(x, y, size, color="-b"): # pragma: no cover
deg = list(range(0, 360, 5))
deg.append(0)
xl = [x + size * math.cos(np.deg2rad(d)) for d in deg]
yl = [y + size * math.sin(np.deg2rad(d)) for d in deg]
plt.plot(xl, yl, color)
@staticmethod
def get_nearest_node_index(node_list_1, rnd_node):
dlist = [(node.x - rnd_node.x)**2 + (node.y - rnd_node.y)**2
for node in node_list_1]
minind = dlist.index(min(dlist))
return minind
@staticmethod
def is_inside_play_area(node, play_area):
if play_area is None:
return True # no play_area was defined, every pos should be ok
if node.x < play_area.xmin or node.x > play_area.xmax or \
node.y < play_area.ymin or node.y > play_area.ymax:
return False # outside - bad
else:
return True # inside - ok
@staticmethod
def obstacle_free(node, obstacleList, robot_radius):
if node is None:
return False
for (ox, oy, size) in obstacleList:
dx_list = [ox - x for x in node.path_x]
dy_list = [oy - y for y in node.path_y]
d_list = [dx * dx + dy * dy for (dx, dy) in zip(dx_list, dy_list)]
if min(d_list) <= (size+robot_radius)**2:
return False # collision
return True # safe
@staticmethod
def calc_distance_and_angle(from_node, to_node):
"""计算两个节点间的距离和方位角
Args:
from_node (_type_): _description_
to_node (_type_): _description_
Returns:
_type_: _description_
"""
dx = to_node.x - from_node.x
dy = to_node.y - from_node.y
d = math.hypot(dx, dy)
theta = math.atan2(dy, dx)
return d, theta
def main(gx=6.0, gy=10.0):
print("start " + __file__)
fig = plt.figure(1)
camera = Camera(fig) # 保存动图时使用
camera = None # 不保存动图时,camara为None
show_animation = True
# ====Search Path with RRT_Connect====
obstacleList = [
(5, 5, 1),
(3, 6, 2),
(3, 8, 2),
(3, 10, 2),
(7, 5, 2),
(9, 5, 2),
(8, 10, 1),
(6, 12, 1),
] # [x,y,size(radius)]
# Set Initial parameters
rrt = RRT_Connect(
start=[0, 0],
goal=[gx, gy],
rand_area=[-2, 15],
obstacle_list=obstacleList,
play_area=[0, 10, 0, 14],
robot_radius=0.8
)
path = rrt.planning(animation=show_animation,camara=camera)
if path is None:
print("Cannot find path")
else:
path = np.array(path)
print(path)
print("found path!!")
# Draw final path
if show_animation:
rrt.draw_graph(camera=camera)
plt.grid(True)
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.plot(path[:,0], path[:,1], '-r')
if camera!=None:
camera.snap()
animation = camera.animate()
animation.save('trajectory.gif')
plt.figure(2)
plt.axis("equal")
plt.axis([-2, 15, -2, 15])
plt.grid(True)
plt.plot(path[:,0], path[:,1], '-r')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()运行后结果如图:
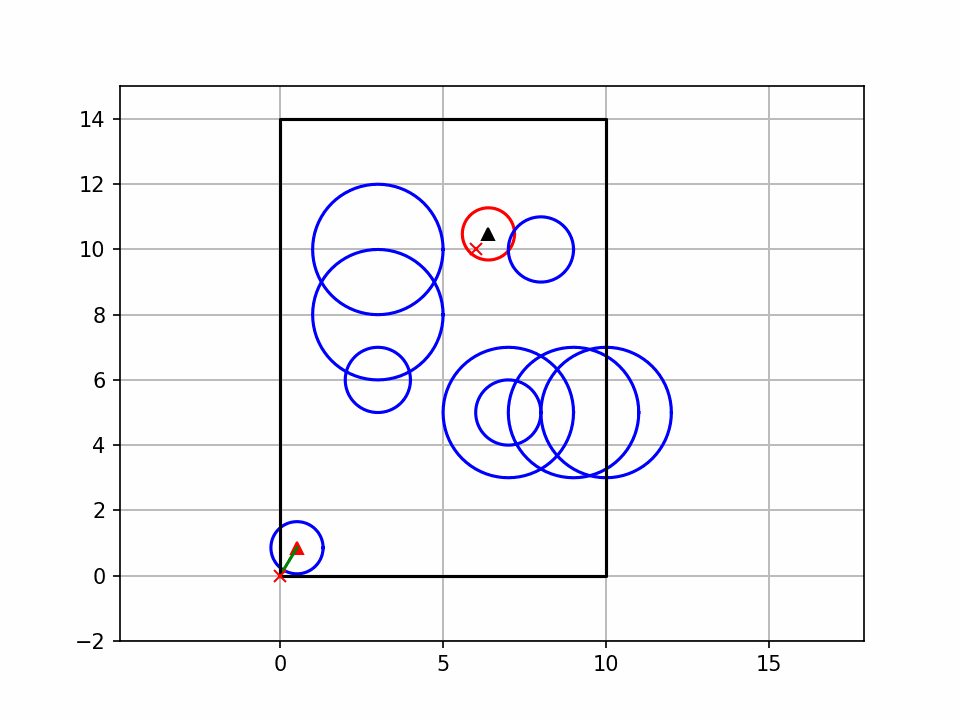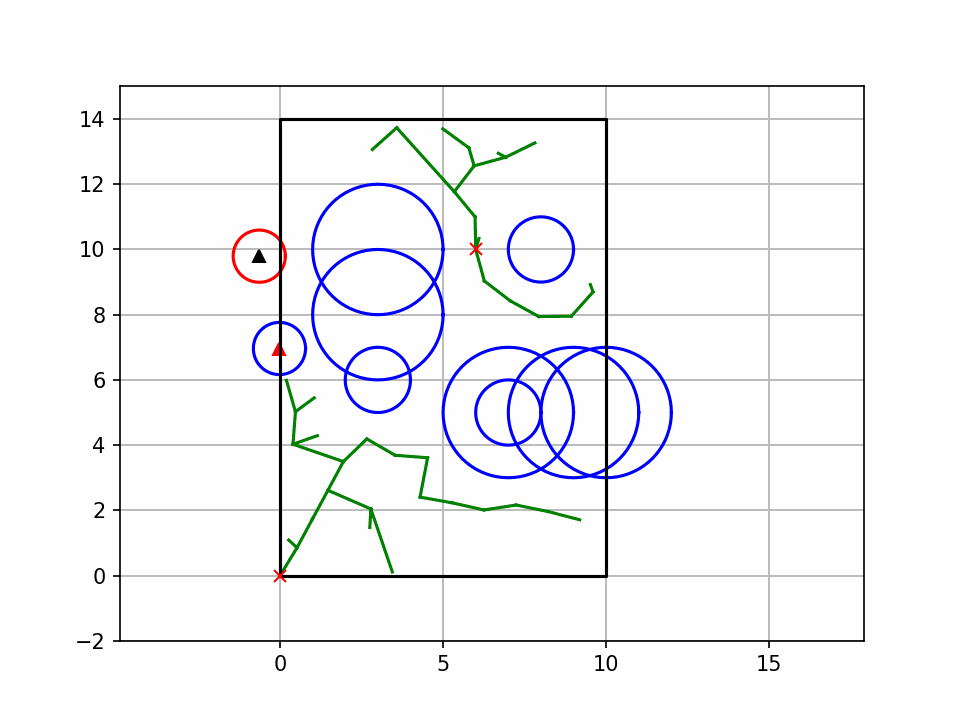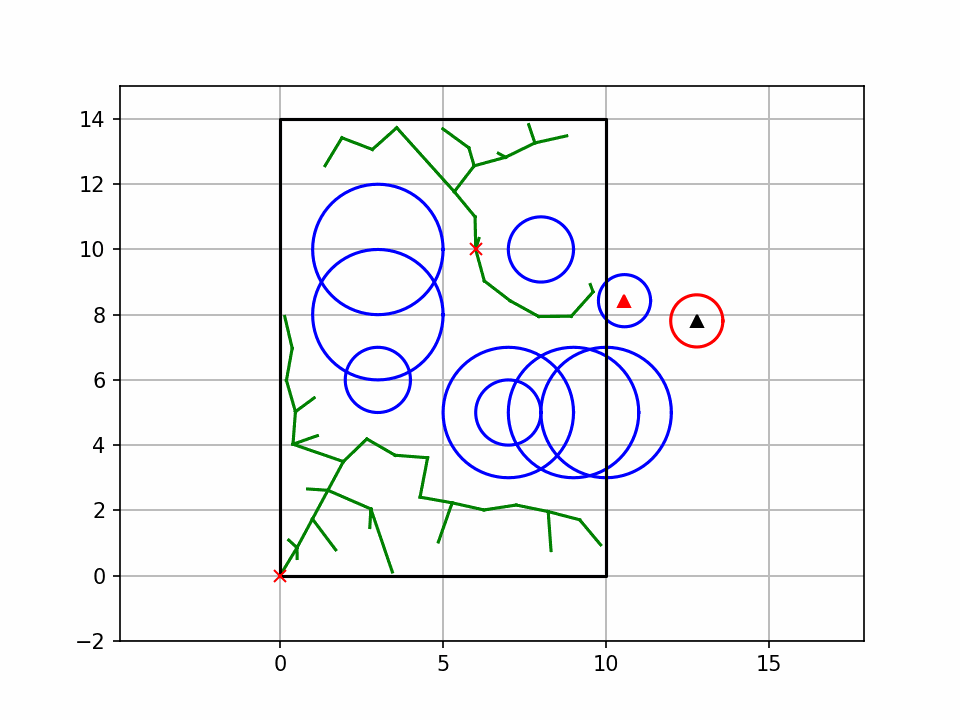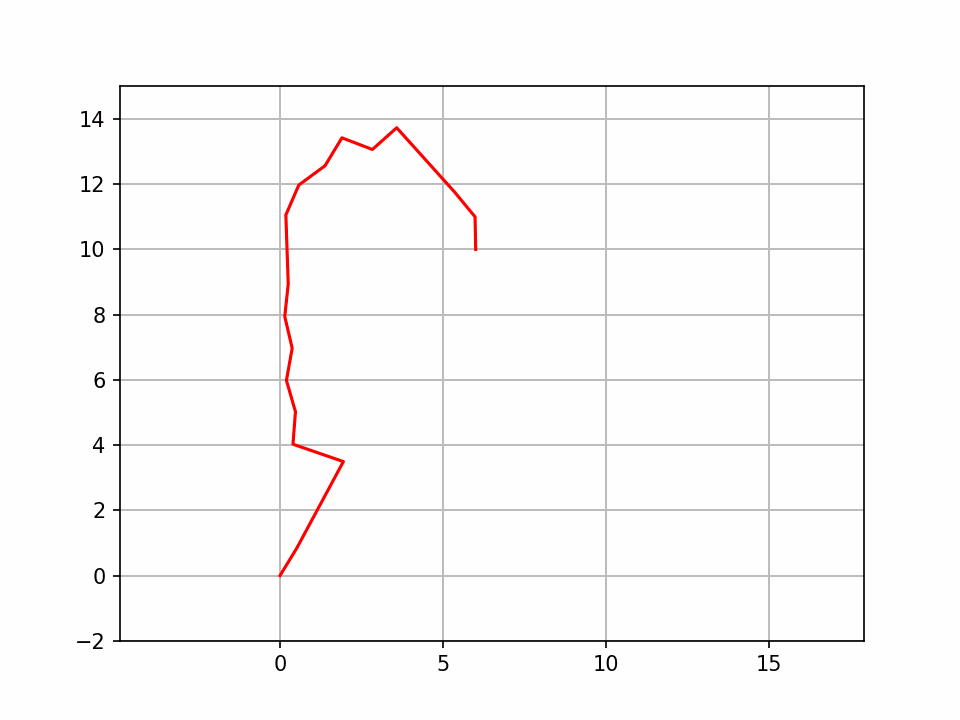
3. 代码关键解释
- Node 类:存储节点坐标、路径(用于绘图)和父节点引用,是构成随机树的基本单元;
- _sample_free 函数:核心采样逻辑,以小概率采样目标点,解决 RRT 收敛慢的问题;
- _steer 函数:实现 "固定步长扩展",是 RRT 的核心操作,确保树的生长可控;
- _is_collision_free 函数:碰撞检测核心,检查路径上的所有点是否与障碍物重叠;
- _generate_final_path 函数:回溯父节点生成最终路径,从目标点反向找到起点。
4. 运行结果说明
- 运行代码后会弹出动态窗口,绿色线条是随机树的生长过程,红色线条是最终规划路径;
- 绿色叉号是起点,红色叉号是终点,红色圆形是障碍物;
- 若路径规划成功,控制台会输出 "找到可行路径",并展示最终路径;若失败,输出 "未找到可行路径"。
七、结束语
- 核心逻辑:RRT 通过 "随机采样→找最近节点→扩展新节点→碰撞检测" 的循环生长随机树,最终连接起点和终点;
- 适用场景:高维空间、复杂障碍物环境是 RRT 的核心优势场景,低维网格环境不如 A * 高效;
- 关键参数:扩展步长(expand_dis)影响树的生长效率,目标采样概率(goal_sample_rate)影响收敛速度;
- 优化方向:RRT 的核心优化是 RRT*(渐近最优)、Informed RRT*(更快收敛到最优路径)、Kinodynamic RRT(考虑动力学约束)。