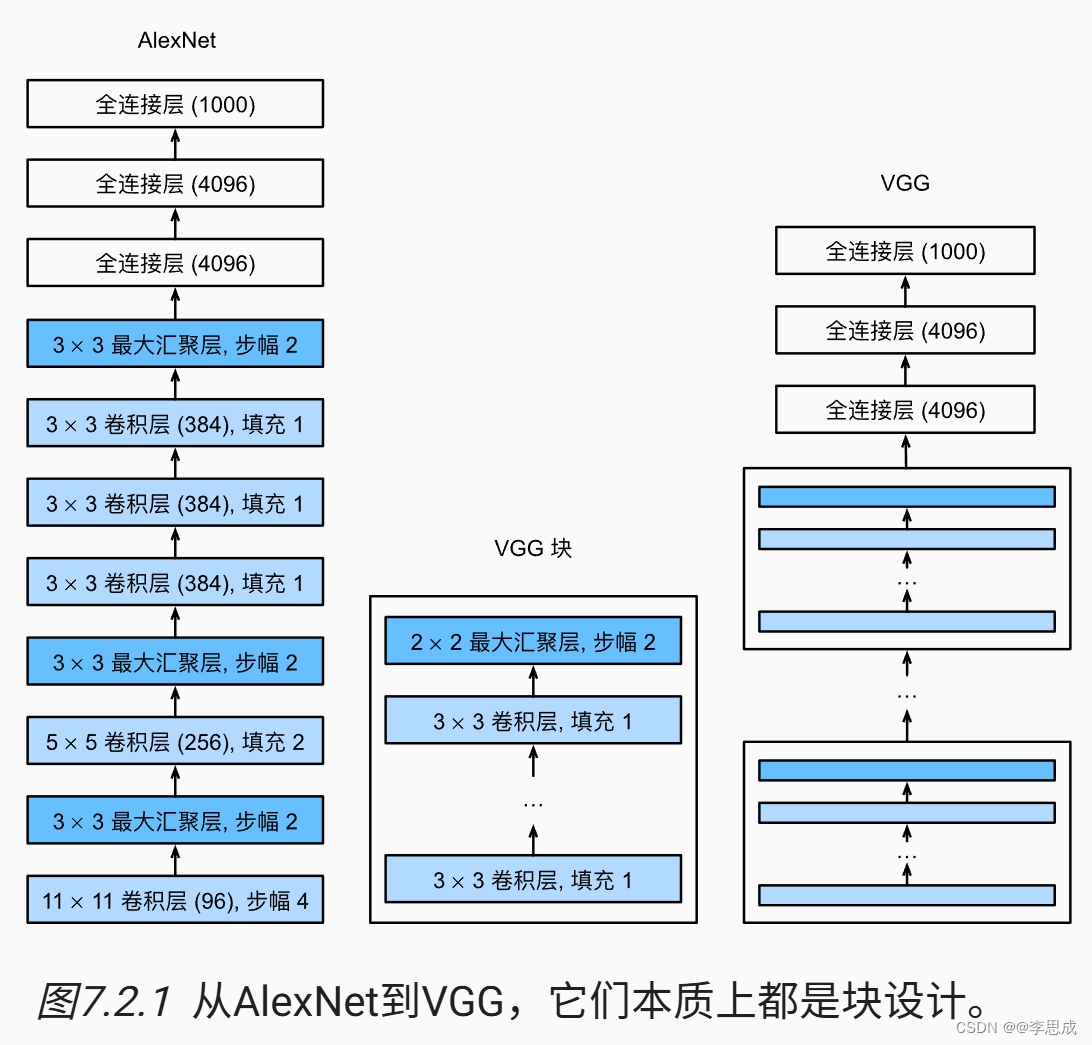
25使用块的网络VGG
python
import torch
from torch import nn
import liliPytorch as lp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义VGG块
# num_convs: 卷积层的数量
# in_channels: 输入通道的数量
# out_channels: 输出通道的数量
def vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels):
layers = []
# 添加num_convs个卷积层
for _ in range(num_convs):
layers.append(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1))
layers.append(nn.ReLU())
in_channels = out_channels # 更新输入通道为当前卷积层的输出通道
# 添加最大池化层
layers.append(nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
return nn.Sequential(*layers) # 返回包含所有层的序列
# 定义VGG架构
conv_arch = ((1, 64), (1, 128), (2, 256), (2, 512), (2, 512)) # 每个元组表示(卷积层数量, 输出通道数量)
dropout = 0.5 # 定义dropout率
def vgg(conv_arch):
conv_blks = []
in_channels = 1 # 输入通道数为1(灰度图像)
# 构建卷积层部分
for num_convs, out_channels in conv_arch:
conv_blks.append(vgg_block(num_convs, in_channels, out_channels))
in_channels = out_channels # 更新输入通道数
# 返回包含卷积层和全连接层的完整网络
return nn.Sequential(
*conv_blks,
nn.Flatten(), # 展平层,将多维输入展平成一维
nn.Linear(out_channels * 7 * 7, 4096), # 第一个全连接层
nn.Dropout(dropout), # dropout层,防止过拟合
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), # 第二个全连接层
nn.ReLU(), # ReLU激活函数
nn.Dropout(dropout), # dropout层
nn.Linear(4096, 10) # 输出层,使用的Fashion-MNIST数据集,10分类
)
net = vgg(conv_arch) # 创建VGG网络
# 测试网络结构,打印每一层的输出形状
X = torch.randn(size=(1, 1, 224, 224)) # 创建一个随机输入张量
for blk in net:
X = blk(X)
print(blk.__class__.__name__, 'output shape:\t', X.shape)
"""
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 56, 56])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 28, 28])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
Sequential output shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 7, 7])
Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 25088])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
"""
# 训练模型
# VGG-11比AlexNet计算量更大,因此我们构建了一个通道数较少的网络,足够用于训练Fashion-MNIST数据集。
ratio = 8 # 缩小通道数的比例
small_conv_arch = [(pair[0], pair[1] // ratio) for pair in conv_arch] # 缩小后的卷积层结构
net = vgg(small_conv_arch) # 创建缩小后的VGG网络
# 定义训练参数
lr, num_epochs, batch_size = 0.01, 10, 128 # 学习率、训练轮数和批量大小
train_iter, test_iter = lp.loda_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224) # 加载训练和测试数据
lp.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, lp.try_gpu()) # 训练模型
plt.show() # 显示绘图
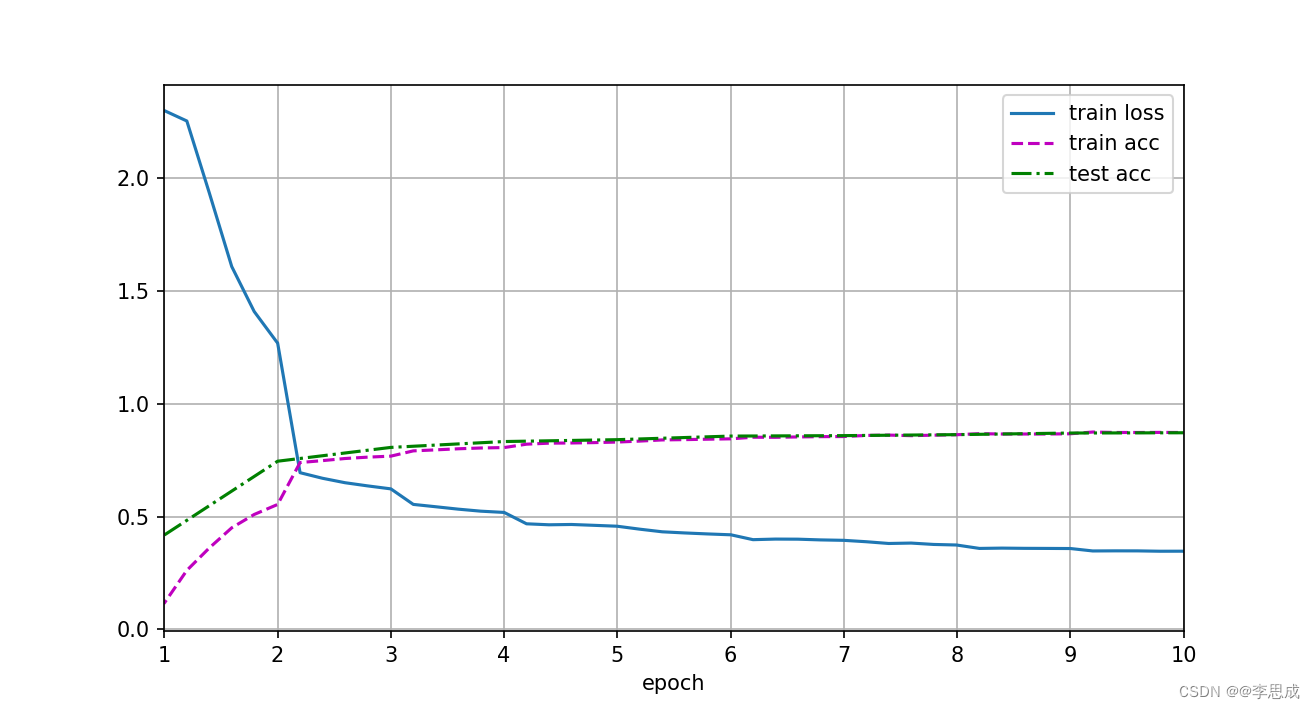
# loss 0.346, train acc 0.873, test acc 0.872
# 1733.7 examples/sec on cuda:0运行结果: