模块出处
[link] [code] [ACM MM 23] Frequency Perception Network for Camouflaged Object Detection
模块名称
Frequency-Perception Module (FPM)
模块作用
获取频域信息,更好识别伪装对象
模块结构
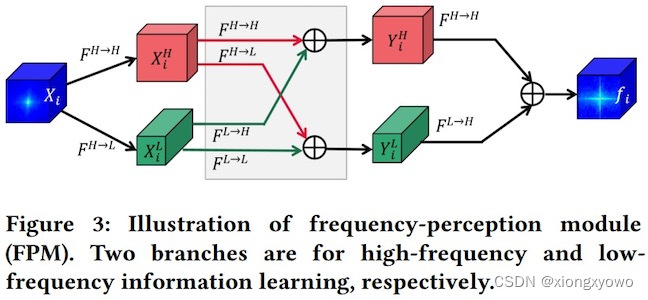
模块代码
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class FirstOctaveConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, alpha=0.5, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1,
groups=1, bias=False):
super(FirstOctaveConv, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
kernel_size = kernel_size[0]
self.h2g_pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=2)
self.h2l = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, int(alpha * in_channels),
kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
self.h2h = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels - int(alpha * in_channels),
kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
def forward(self, x):
if self.stride ==2:
x = self.h2g_pool(x)
X_h2l = self.h2g_pool(x)
X_h = x
X_h = self.h2h(X_h)
X_l = self.h2l(X_h2l)
return X_h, X_l
class OctaveConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, alpha=0.5, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1,
groups=1, bias=False):
super(OctaveConv, self).__init__()
kernel_size = kernel_size[0]
self.h2g_pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=2)
self.upsample = torch.nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
self.stride = stride
self.l2l = torch.nn.Conv2d(int(alpha * in_channels), int(alpha * out_channels),
kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
self.l2h = torch.nn.Conv2d(int(alpha * in_channels), out_channels - int(alpha * out_channels),
kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
self.h2l = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels - int(alpha * in_channels), int(alpha * out_channels),
kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
self.h2h = torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels - int(alpha * in_channels),
out_channels - int(alpha * out_channels),
kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
def forward(self, x):
X_h, X_l = x
if self.stride == 2:
X_h, X_l = self.h2g_pool(X_h), self.h2g_pool(X_l)
X_h2l = self.h2g_pool(X_h)
X_h2h = self.h2h(X_h)
X_l2h = self.l2h(X_l)
X_l2l = self.l2l(X_l)
X_h2l = self.h2l(X_h2l)
X_l2h = F.interpolate(X_l2h, (int(X_h2h.size()[2]),int(X_h2h.size()[3])), mode='bilinear')
X_h = X_l2h + X_h2h
X_l = X_h2l + X_l2l
return X_h, X_l
class LastOctaveConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, alpha=0.5, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1,
groups=1, bias=False):
super(LastOctaveConv, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
kernel_size = kernel_size[0]
self.h2g_pool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=2)
self.l2h = torch.nn.Conv2d(int(alpha * out_channels), out_channels,
kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
self.h2h = torch.nn.Conv2d(out_channels - int(alpha * out_channels),
out_channels,
kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups, bias)
self.upsample = torch.nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
def forward(self, x):
X_h, X_l = x
if self.stride == 2:
X_h, X_l = self.h2g_pool(X_h), self.h2g_pool(X_l)
X_h2h = self.h2h(X_h)
X_l2h = self.l2h(X_l)
X_l2h = F.interpolate(X_l2h, (int(X_h2h.size()[2]), int(X_h2h.size()[3])), mode='bilinear')
X_h = X_h2h + X_l2h
return X_h
class FPM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=(3, 3)):
super(FPM, self).__init__()
self.fir = FirstOctaveConv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size)
self.mid1 = OctaveConv(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size)
self.mid2 = OctaveConv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size)
self.lst = LastOctaveConv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size)
def forward(self, x):
x_h, x_l = self.fir(x)
x_h_1, x_l_1 = self.mid1((x_h, x_l))
x_h_2, x_l_2 = self.mid1((x_h_1, x_l_1))
x_h_5, x_l_5 = self.mid2((x_h_2, x_l_2))
x_ret = self.lst((x_h_5, x_l_5))
return x_ret
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = torch.randn([3, 256, 16, 16])
fpm = FPM(in_channels=256, out_channels=64)
out = fpm(x)
print(out.shape) # 3, 64, 16, 16原文表述
具体来说,我们采用八度卷积以端到端的方式自动感知高频和低频信息,从而实现伪装物体检测的在线学习。八度卷积可以有效避免DCT 引起的块状效应,并利用GPU的计算速度优势。此外,它可以轻松插入任意网络。