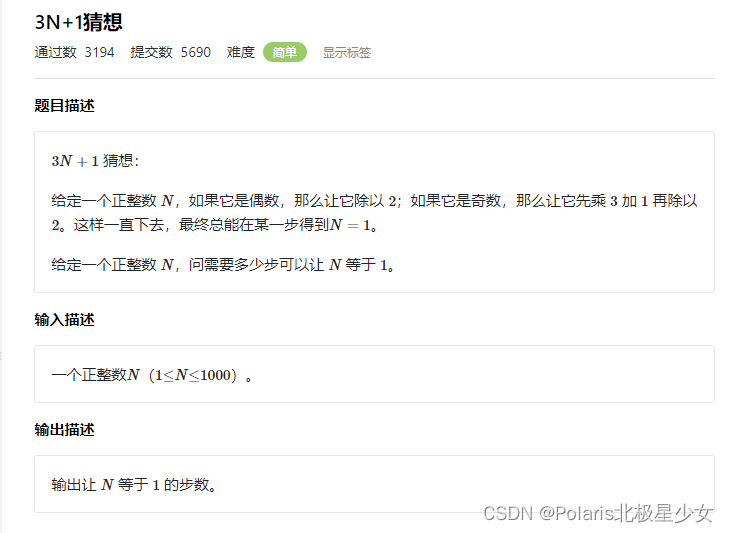
3.1简单模拟

自己写的题解
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int N;
int num=0;
scanf("%d",&N);
while(N!=1)
{
if(N%2==0)
{
N=N/2;
}
else
{
N=(3*N+1)/2;
}
num++;
}
printf("%d",num);
system("pause"); // 防止运行后自动退出,需头文件stdlib.h
return 0;
}标答
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int n,step=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n!=1)
{
if(n%2==0)n=n/2;
else n=(3*n+1)/2;
step++;
}
printf("%d\n",step);
system("pause"); // 防止运行后自动退出,需头文件stdlib.h
return 0;
}3.2查找元素


自己写的题解
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int n;
int f=0;
int a[100000];
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
scanf("%d",&f);
int find=-1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(a[i]==f)
{
find=i+1;
}
}
if(find!=-1)
printf("%d\n",find);
else
printf("NO");
system("pause"); // 防止运行后自动退出,需头文件stdlib.h
return 0;
}标答
cpp
#include <cstdio>
const int MAXN = 20;
int a[MAXN];
int main() {
int n, x;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
int position = -1; // 待查找元素的下标,-1表示找不到
scanf("%d", &x);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 遍历序列
if (a[i] == x) { // 如果当前元素就是待查找的元素
position = i + 1; // 记录下标,注意要加1
break; // 不需要继续查找了,退出循环
}
}
if (position == -1) { // 如果找不到
printf("NO"); // 输出NO
} else { // 如果能找到
printf("%d", position); // 输出对应的下标
}
return 0;
}3.3图形输出


自己写的题解
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int row=0;
scanf("%d",&row);
int col=row;
for(int i=0;i<row-1;i++)
{
printf("*");
for(int j=0;j<i+1;j++)
{
if(i==j&&j!=0)
{
printf("*");
}
else if(j!=0)
printf(" ");
}
printf("\n");
}
for(int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
printf("*");
}
system("pause"); // 防止运行后自动退出,需头文件stdlib.h
return 0;
}标答1
cpp
#include <cstdio>
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("*\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n - 2; i++) {
printf("*");
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
printf(" ");
}
printf("*\n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("*");
}
return 0;
}标答2
cpp
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
const int MAXN = 100;
char s[MAXN][MAXN + 1];
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
memset(s, ' ', sizeof(s));
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
s[i][0] = s[i][i] = '*';
s[i][i + 1] = '\0';
printf("%s\n", s[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("*");
}
return 0;
}3.4日期处理


标答
cpp
#include <cstdio>
bool isLeapYear(int year) {
return year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0);
}
int main() {
int year;
scanf("%d", &year);
printf(isLeapYear(year) ? "YES" : "NO");
return 0;
}

标答
cpp
#include <cstdio>
// 每个月的天数
int dayOfMonth[2][13] = {
{0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31},
{0, 31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}
};
// 是否是闰年
bool isLeapYear(int year) {
return year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0);
}
// 给当前日期加1天(注意参数都用了引用&,这样对参数的修改可以同步到函数外)
void addOneDay(int &year, int &month, int &day) {
day++; // 让day加1
if (day > dayOfMonth[isLeapYear(year)][month]) { // 如果超过当前月的天数
month++; // 让month加1
day = 1; // 重置day为1号
}
if (month > 12) { // 如果月份大于12
year++; // 让year加1
month = 1; // 重置month为1月
}
}
int main() {
int year, month, day, n;
scanf("%d-%d-%d", &year, &month, &day); // 按格式输入年月日
scanf("%d", &n); // 输入需要增加的天数
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 遍历n次,每次加1天
addOneDay(year, month, day);
}
printf("%04d-%02d-%02d", year, month, day); // 按格式输出年月日
return 0;
}3.5进制转换


自己写的题解
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int y=0;
scanf("%d",&y);
int z[40],num=0;
do{
z[num++]=y%2;
y=y/2;
}while(y!=0);
for(int i=num-1;i>=0;i--)
{
printf("%d",z[i]);
}
system("pause"); // 防止运行后自动退出,需头文件stdlib.h
return 0;
}公式:将十进制数y转换为Q进制数z
cpp
int z[40],num=0;
do{
z[num++]=y%Q;
y=y/Q;
}while(y!=0);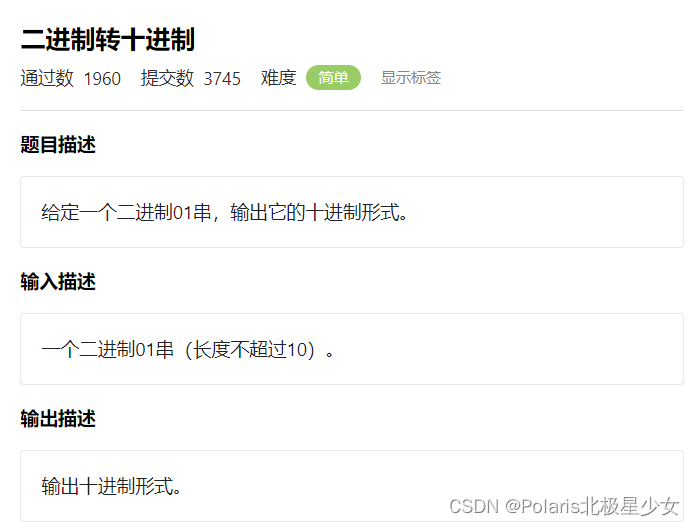

自己写的题解
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
int y=0,product=1;
int x=0;
scanf("%d",&x);
while(x!=0){
y=y+(x%10)*product;
x=x/10;
product=product*2;
}
printf("%d",y);
system("pause"); // 防止运行后自动退出,需头文件stdlib.h
return 0;
}公式:将P进制数x转换为十进制数y
cpp
int y=0,product=1;
while(x!=0){
y=y+(x%10)*product;
x=x/10;
product=product*P;
}3.6字符串处理


标答
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
const int maxn=50;
int judge(char str[]){
int len=strlen(str);
for(int i=0;i<len/2;i++){
if(str[i]!=str[len-1-i]){
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
int main() {
char str[maxn];
while(scanf("%s",str)!=EOF)
{
int flag=judge(str);
if(flag==1){
printf("YES\n");
}else{
printf("NO\n");
}
}
system("pause"); // 防止运行后自动退出,需头文件stdlib.h
return 0;
}

标答
cpp
#include <cstdio>
const int MAXN = 500;
const int MAXL = 11;
char str[MAXN][MAXL], num = 0;
int main() {
while (scanf("%s", str[num]) != EOF) {
num++;
}
for (int i = num - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
printf("%s", str[i]);
if (i > 0) {
printf(" ");
}
}
return 0;
}