秋招面试专栏推荐 :深度学习算法工程师面试问题总结【百面算法工程师】------点击即可跳转
💡💡💡 本专栏所有程序均经过测试,可成功执行💡💡💡
专栏目录 :《YOLOv8改进有效涨点》专栏介绍 & 专栏目录 | 目前已有50+篇内容,内含各种Head检测头、损失函数Loss、Backbone、Neck、NMS等创新点改进------点击即可跳转
在目标检测任务中,多尺度特征对于编码具有尺度变化的对象非常重要。常用的多尺度特征提取策略是采用经典的由上至下和由下至上的特征金字塔网络。然而,这些方法存在特征信息丢失或降级的问题,影响了非相邻层次之间的融合效果。本文提出了一个渐进特征金字塔网络(AFPN)来支持非相邻层次之间的直接交互。AFPN从融合两个相邻的低层特征开始,并逐渐将更高层的特征融入融合过程中。这样,可以避免非相邻层次之间较大的语义差距。考虑到在每个空间位置的特征融合过程中可能出现的多对象信息冲突,进一步利用自适应空间融合操作来减轻这些不一致性。文章在介绍主要的原理后,将手把手教学如何进行模块的代码添加和修改,并将修改后的完整代码放在文章的最后,方便大家一键运行,小白也可轻松上手实践。以帮助您更好地学习深度学习目标检测YOLO系列的挑战。
目录
[1. 原理](#1. 原理)
[2. 将AFPN添加到YOLOv8中](#2. 将AFPN添加到YOLOv8中)
[2.1 AFPN的代码实现](#2.1 AFPN的代码实现)
[2.2 更改init.py文件](#2.2 更改init.py文件)
[2.3 添加yaml文件](#2.3 添加yaml文件)
[2.4 在task.py中进行注册](#2.4 在task.py中进行注册)
[2.5 执行程序](#2.5 执行程序)
[3. 完整代码分享](#3. 完整代码分享)
[4. GFLOPs](#4. GFLOPs)
[5. 进阶](#5. 进阶)
[6. 总结](#6. 总结)
1. 原理

论文地址: AFPN: Asymptotic Feature Pyramid Network for Object Detection------点击即可跳转
官方代码: 官方代码仓库------点击即可跳转
AFPN(渐近特征金字塔网络)旨在通过解决传统特征金字塔网络(FPN)中特征信息丢失或退化的问题来增强对象检测。以下是 AFPN 背后的关键原则的总结:
AFPN 的关键原则
渐近特征融合:
-
AFPN 从融合两个相邻的低级特征开始,并逐步合并高级特征。这种方法避免了非相邻级别之间的较大语义差距导致融合结果不佳。
-
该过程从最低级特征的融合开始,然后在后续阶段添加高级特征,最后集成最顶层特征。
自适应空间融合:
-
在融合过程中,自适应空间融合用于解决每个空间位置上多对象信息中的潜在冲突。
-
此操作有助于在特征融合期间过滤和保留有用信息,同时抑制矛盾信息。
自下而上和自上而下的路径:
-
AFPN 结合了自下而上和自上而下的路径,以确保有效利用来自低级特征的详细信息和来自高级特征的语义信息。
-
这种双路径方法有助于在整个网络中保持详细和语义信息的完整性。
效率和性能:
-
与其他特征金字塔网络相比,AFPN 旨在以更少的参数和计算复杂度实现具有竞争力的结果。
-
实验结果表明,AFPN 在保持计算效率的同时提高了物体检测任务的性能。
架构概述
-
多级特征提取:
-
从骨干网络中提取不同级别的特征,通常表示为 {C2、C3、C4、C5}。
-
首先融合低级特征(C2 和 C3),然后融合高级特征(C4 和 C5)。
-
特征融合过程:
-
融合过程是渐进的,先合并较低级别的特征,然后再合并较高级别的特征。
-
这种渐近融合有助于减少语义差距并增强融合效果。
-
维度处理:
-
1×1 卷积和双线性插值用于对特征进行上采样以对齐维度。
-
根据需要应用不同的卷积核和步幅进行下采样。
评估和结果
-
它在 MS COCO 2017 等数据集上的平均精度 (AP) 等性能指标方面表现出显着改进。
-
与其他最先进的特征金字塔网络相比,该网络在保持适中的参数数量和 GFLOP 的同时实现了更好的结果。
结论
AFPN 代表了一种创新的特征金字塔网络方法,它专注于非相邻层之间的直接交互和自适应空间融合以处理多对象信息冲突。其架构确保了高效、有效的特征融合,从而提高了对象检测性能。
2. 将AFPN添加到YOLOv8中
2.1 AFPN的代码实现
关键步骤一: 将下面代码粘贴到在/ultralytics/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py中,并在该文件的__all__中添加"Detect_AFPN4"
python
import math
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from ultralytics.nn.modules import DFL
from ultralytics.nn.modules.conv import Conv
from ultralytics.utils.tal import dist2bbox, make_anchors
__all__ = ['Detect_AFPN4']
def BasicConv(filter_in, filter_out, kernel_size, stride=1, pad=None):
if not pad:
pad = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 if kernel_size else 0
else:
pad = pad
return nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
("conv", nn.Conv2d(filter_in, filter_out, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=pad, bias=False)),
("bn", nn.BatchNorm2d(filter_out)),
("relu", nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
]))
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, filter_in, filter_out):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(filter_in, filter_out, 3, padding=1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(filter_out, momentum=0.1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(filter_out, filter_out, 3, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(filter_out, momentum=0.1)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Upsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, scale_factor=2):
super(Upsample, self).__init__()
self.upsample = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 1),
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=scale_factor, mode='bilinear')
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.upsample(x)
return x
class Downsample_x2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Downsample_x2, self).__init__()
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 2, 2, 0)
)
def forward(self, x, ):
x = self.downsample(x)
return x
class Downsample_x4(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Downsample_x4, self).__init__()
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 4, 4, 0)
)
def forward(self, x, ):
x = self.downsample(x)
return x
class Downsample_x8(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(Downsample_x8, self).__init__()
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_channels, out_channels, 8, 8, 0)
)
def forward(self, x, ):
x = self.downsample(x)
return x
class ASFF_2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inter_dim=512):
super(ASFF_2, self).__init__()
self.inter_dim = inter_dim
compress_c = 8
self.weight_level_1 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_level_2 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_levels = nn.Conv2d(compress_c * 2, 2, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, self.inter_dim, 3, 1)
def forward(self, input1, input2):
level_1_weight_v = self.weight_level_1(input1)
level_2_weight_v = self.weight_level_2(input2)
levels_weight_v = torch.cat((level_1_weight_v, level_2_weight_v), 1)
levels_weight = self.weight_levels(levels_weight_v)
levels_weight = F.softmax(levels_weight, dim=1)
fused_out_reduced = input1 * levels_weight[:, 0:1, :, :] + \
input2 * levels_weight[:, 1:2, :, :]
out = self.conv(fused_out_reduced)
return out
class ASFF_3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inter_dim=512):
super(ASFF_3, self).__init__()
self.inter_dim = inter_dim
compress_c = 8
self.weight_level_1 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_level_2 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_level_3 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_levels = nn.Conv2d(compress_c * 3, 3, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, self.inter_dim, 3, 1)
def forward(self, input1, input2, input3):
level_1_weight_v = self.weight_level_1(input1)
level_2_weight_v = self.weight_level_2(input2)
level_3_weight_v = self.weight_level_3(input3)
levels_weight_v = torch.cat((level_1_weight_v, level_2_weight_v, level_3_weight_v), 1)
levels_weight = self.weight_levels(levels_weight_v)
levels_weight = F.softmax(levels_weight, dim=1)
fused_out_reduced = input1 * levels_weight[:, 0:1, :, :] + \
input2 * levels_weight[:, 1:2, :, :] + \
input3 * levels_weight[:, 2:, :, :]
out = self.conv(fused_out_reduced)
return out
class ASFF_4(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inter_dim=512):
super(ASFF_4, self).__init__()
self.inter_dim = inter_dim
compress_c = 8
self.weight_level_0 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_level_1 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_level_2 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_level_3 = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, compress_c, 1, 1)
self.weight_levels = nn.Conv2d(compress_c * 4, 4, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv = BasicConv(self.inter_dim, self.inter_dim, 3, 1)
def forward(self, input0, input1, input2, input3):
level_0_weight_v = self.weight_level_0(input0)
level_1_weight_v = self.weight_level_1(input1)
level_2_weight_v = self.weight_level_2(input2)
level_3_weight_v = self.weight_level_3(input3)
levels_weight_v = torch.cat((level_0_weight_v, level_1_weight_v, level_2_weight_v, level_3_weight_v), 1)
levels_weight = self.weight_levels(levels_weight_v)
levels_weight = F.softmax(levels_weight, dim=1)
fused_out_reduced = input0 * levels_weight[:, 0:1, :, :] + \
input1 * levels_weight[:, 1:2, :, :] + \
input2 * levels_weight[:, 2:3, :, :] + \
input3 * levels_weight[:, 3:, :, :]
out = self.conv(fused_out_reduced)
return out
class BlockBody(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels=[64, 128, 256, 512]):
super(BlockBody, self).__init__()
self.blocks_scalezero1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(channels[0], channels[0], 1),
)
self.blocks_scaleone1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(channels[1], channels[1], 1),
)
self.blocks_scaletwo1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(channels[2], channels[2], 1),
)
self.blocks_scalethree1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(channels[3], channels[3], 1),
)
self.downsample_scalezero1_2 = Downsample_x2(channels[0], channels[1])
self.upsample_scaleone1_2 = Upsample(channels[1], channels[0], scale_factor=2)
self.asff_scalezero1 = ASFF_2(inter_dim=channels[0])
self.asff_scaleone1 = ASFF_2(inter_dim=channels[1])
self.blocks_scalezero2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
)
self.blocks_scaleone2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
)
self.downsample_scalezero2_2 = Downsample_x2(channels[0], channels[1])
self.downsample_scalezero2_4 = Downsample_x4(channels[0], channels[2])
self.downsample_scaleone2_2 = Downsample_x2(channels[1], channels[2])
self.upsample_scaleone2_2 = Upsample(channels[1], channels[0], scale_factor=2)
self.upsample_scaletwo2_2 = Upsample(channels[2], channels[1], scale_factor=2)
self.upsample_scaletwo2_4 = Upsample(channels[2], channels[0], scale_factor=4)
self.asff_scalezero2 = ASFF_3(inter_dim=channels[0])
self.asff_scaleone2 = ASFF_3(inter_dim=channels[1])
self.asff_scaletwo2 = ASFF_3(inter_dim=channels[2])
self.blocks_scalezero3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
)
self.blocks_scaleone3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
)
self.blocks_scaletwo3 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[2], channels[2]),
BasicBlock(channels[2], channels[2]),
BasicBlock(channels[2], channels[2]),
BasicBlock(channels[2], channels[2]),
)
self.downsample_scalezero3_2 = Downsample_x2(channels[0], channels[1])
self.downsample_scalezero3_4 = Downsample_x4(channels[0], channels[2])
self.downsample_scalezero3_8 = Downsample_x8(channels[0], channels[3])
self.upsample_scaleone3_2 = Upsample(channels[1], channels[0], scale_factor=2)
self.downsample_scaleone3_2 = Downsample_x2(channels[1], channels[2])
self.downsample_scaleone3_4 = Downsample_x4(channels[1], channels[3])
self.upsample_scaletwo3_4 = Upsample(channels[2], channels[0], scale_factor=4)
self.upsample_scaletwo3_2 = Upsample(channels[2], channels[1], scale_factor=2)
self.downsample_scaletwo3_2 = Downsample_x2(channels[2], channels[3])
self.upsample_scalethree3_8 = Upsample(channels[3], channels[0], scale_factor=8)
self.upsample_scalethree3_4 = Upsample(channels[3], channels[1], scale_factor=4)
self.upsample_scalethree3_2 = Upsample(channels[3], channels[2], scale_factor=2)
self.asff_scalezero3 = ASFF_4(inter_dim=channels[0])
self.asff_scaleone3 = ASFF_4(inter_dim=channels[1])
self.asff_scaletwo3 = ASFF_4(inter_dim=channels[2])
self.asff_scalethree3 = ASFF_4(inter_dim=channels[3])
self.blocks_scalezero4 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
BasicBlock(channels[0], channels[0]),
)
self.blocks_scaleone4 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
BasicBlock(channels[1], channels[1]),
)
self.blocks_scaletwo4 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[2], channels[2]),
BasicBlock(channels[2], channels[2]),
BasicBlock(channels[2], channels[2]),
BasicBlock(channels[2], channels[2]),
)
self.blocks_scalethree4 = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(channels[3], channels[3]),
BasicBlock(channels[3], channels[3]),
BasicBlock(channels[3], channels[3]),
BasicBlock(channels[3], channels[3]),
)
def forward(self, x):
x0, x1, x2, x3 = x
x0 = self.blocks_scalezero1(x0)
x1 = self.blocks_scaleone1(x1)
x2 = self.blocks_scaletwo1(x2)
x3 = self.blocks_scalethree1(x3)
scalezero = self.asff_scalezero1(x0, self.upsample_scaleone1_2(x1))
scaleone = self.asff_scaleone1(self.downsample_scalezero1_2(x0), x1)
x0 = self.blocks_scalezero2(scalezero)
x1 = self.blocks_scaleone2(scaleone)
scalezero = self.asff_scalezero2(x0, self.upsample_scaleone2_2(x1), self.upsample_scaletwo2_4(x2))
scaleone = self.asff_scaleone2(self.downsample_scalezero2_2(x0), x1, self.upsample_scaletwo2_2(x2))
scaletwo = self.asff_scaletwo2(self.downsample_scalezero2_4(x0), self.downsample_scaleone2_2(x1), x2)
x0 = self.blocks_scalezero3(scalezero)
x1 = self.blocks_scaleone3(scaleone)
x2 = self.blocks_scaletwo3(scaletwo)
scalezero = self.asff_scalezero3(x0, self.upsample_scaleone3_2(x1), self.upsample_scaletwo3_4(x2),
self.upsample_scalethree3_8(x3))
scaleone = self.asff_scaleone3(self.downsample_scalezero3_2(x0), x1, self.upsample_scaletwo3_2(x2),
self.upsample_scalethree3_4(x3))
scaletwo = self.asff_scaletwo3(self.downsample_scalezero3_4(x0), self.downsample_scaleone3_2(x1), x2,
self.upsample_scalethree3_2(x3))
scalethree = self.asff_scalethree3(self.downsample_scalezero3_8(x0), self.downsample_scaleone3_4(x1),
self.downsample_scaletwo3_2(x2), x3)
scalezero = self.blocks_scalezero4(scalezero)
scaleone = self.blocks_scaleone4(scaleone)
scaletwo = self.blocks_scaletwo4(scaletwo)
scalethree = self.blocks_scalethree4(scalethree)
return scalezero, scaleone, scaletwo, scalethree
class AFPN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024, 2048],
out_channels=128):
super(AFPN, self).__init__()
self.fp16_enabled = False
self.conv0 = BasicConv(in_channels[0], in_channels[0] // 8, 1)
self.conv1 = BasicConv(in_channels[1], in_channels[1] // 8, 1)
self.conv2 = BasicConv(in_channels[2], in_channels[2] // 8, 1)
self.conv3 = BasicConv(in_channels[3], in_channels[3] // 8, 1)
self.body = nn.Sequential(
BlockBody([in_channels[0] // 8, in_channels[1] // 8, in_channels[2] // 8, in_channels[3] // 8])
)
self.conv00 = BasicConv(in_channels[0] // 8, out_channels, 1)
self.conv11 = BasicConv(in_channels[1] // 8, out_channels, 1)
self.conv22 = BasicConv(in_channels[2] // 8, out_channels, 1)
self.conv33 = BasicConv(in_channels[3] // 8, out_channels, 1)
self.conv44 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=1, stride=2)
# init weight
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.xavier_normal_(m.weight, gain=0.02)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
torch.nn.init.normal_(m.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
torch.nn.init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
def forward(self, x):
x0, x1, x2, x3 = x
x0 = self.conv0(x0)
x1 = self.conv1(x1)
x2 = self.conv2(x2)
x3 = self.conv3(x3)
out0, out1, out2, out3 = self.body([x0, x1, x2, x3])
out0 = self.conv00(out0)
out1 = self.conv11(out1)
out2 = self.conv22(out2)
out3 = self.conv33(out3)
return out0, out1, out2, out3
class Detect_AFPN4(nn.Module):
"""YOLOv8 Detect head for detection models."""
dynamic = False # force grid reconstruction
export = False # export mode
shape = None
anchors = torch.empty(0) # init
strides = torch.empty(0) # init
def __init__(self, nc=80, channel=128, ch=()):
"""Initializes the YOLOv8 detection layer with specified number of classes and channels."""
super().__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.nl = len(ch) # number of detection layers
self.reg_max = 16 # DFL channels (ch[0] // 16 to scale 4/8/12/16/20 for n/s/m/l/x)
self.no = nc + self.reg_max * 4 # number of outputs per anchor
self.stride = torch.zeros(self.nl) # strides computed during build
c2, c3 = max((16, ch[0] // 4, self.reg_max * 4)), max(ch[0], min(self.nc, 100)) # channels
self.cv2 = nn.ModuleList(
nn.Sequential(Conv(channel, c2, 3), Conv(c2, c2, 3), nn.Conv2d(c2, 4 * self.reg_max, 1)) for x in ch)
self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(
nn.Sequential(Conv(channel, c3, 3), Conv(c3, c3, 3), nn.Conv2d(c3, self.nc, 1)) for x in ch)
self.dfl = DFL(self.reg_max) if self.reg_max > 1 else nn.Identity()
self.AFPN = AFPN(ch)
def forward(self, x):
"""Concatenates and returns predicted bounding boxes and class probabilities."""
x = list(self.AFPN(x))
shape = x[0].shape # BCHW
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = torch.cat((self.cv2[i](x[i]), self.cv3[i](x[i])), 1)
if self.training:
return x
elif self.dynamic or self.shape != shape:
self.anchors, self.strides = (x.transpose(0, 1) for x in make_anchors(x, self.stride, 0.5))
self.shape = shape
x_cat = torch.cat([xi.view(shape[0], self.no, -1) for xi in x], 2)
if self.export and self.format in ('saved_model', 'pb', 'tflite', 'edgetpu', 'tfjs'): # avoid TF FlexSplitV ops
box = x_cat[:, :self.reg_max * 4]
cls = x_cat[:, self.reg_max * 4:]
else:
box, cls = x_cat.split((self.reg_max * 4, self.nc), 1)
dbox = dist2bbox(self.dfl(box), self.anchors.unsqueeze(0), xywh=True, dim=1) * self.strides
if self.export and self.format in ('tflite', 'edgetpu'):
# Normalize xywh with image size to mitigate quantization error of TFLite integer models as done in YOLOv5:
# https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/blob/0c8de3fca4a702f8ff5c435e67f378d1fce70243/models/tf.py#L307-L309
# See this PR for details: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/pull/1695
img_h = shape[2] * self.stride[0]
img_w = shape[3] * self.stride[0]
img_size = torch.tensor([img_w, img_h, img_w, img_h], device=dbox.device).reshape(1, 4, 1)
dbox /= img_size
y = torch.cat((dbox, cls.sigmoid()), 1)
return y if self.export else (y, x)
def bias_init(self):
"""Initialize Detect() biases, WARNING: requires stride availability."""
m = self # self.model[-1] # Detect() module
# cf = torch.bincount(torch.tensor(np.concatenate(dataset.labels, 0)[:, 0]).long(), minlength=nc) + 1
# ncf = math.log(0.6 / (m.nc - 0.999999)) if cf is None else torch.log(cf / cf.sum()) # nominal class frequency
for a, b, s in zip(m.cv2, m.cv3, m.stride): # from
a[-1].bias.data[:] = 1.0 # box
b[-1].bias.data[:m.nc] = math.log(5 / m.nc / (640 / s) ** 2) # cls (.01 objects, 80 classes, 640 img)AFPN(Asymptotic Feature Pyramid Network)的主要原理和图像处理流程如下:
主要原理
-
多尺度特征提取:AFPN在物体检测任务中利用多尺度特征编码来处理对象的尺度变化。传统的特征金字塔网络(如FPN)通常采用自顶向下和自底向上的方式进行多尺度特征提取。然而,这些方法在融合非相邻层的特征时会导致信息损失或退化。
-
渐近融合:AFPN采用渐近融合的方法,从融合两个相邻的低层特征开始,逐步将更高层的特征引入融合过程中。这种方式避免了非相邻层之间较大的语义差距,保留了更多有用的信息。
-
自适应空间融合:在每个空间位置的特征融合过程中,可能会出现多对象信息冲突的问题。AFPN采用自适应空间融合操作来缓解这些不一致性,确保融合过程中保留有用的信息。
图像处理流程
-
特征提取:从主干网络(如ResNet-50或ResNet-101)的每一层提取最后的特征,得到不同尺度的特征集{C2, C3, C4, C5}。对于YOLO架构,只输入{C3, C4, C5}到特征金字塔网络,生成输出{P3, P4, P5}。
-
低层特征融合:首先将低层特征C2和C3输入到特征金字塔网络进行融合。通过1×1卷积和双线性插值的方法对特征进行上采样,确保特征尺寸一致。
-
高层特征渐近融合:在低层特征融合之后,逐步将更高层的特征(如C4和C5)引入融合过程中。利用不同卷积核和步幅进行下采样,确保特征尺寸的一致性。
-
自适应空间融合:在特征融合过程中,使用自适应空间融合操作过滤多层特征,以解决不同对象在同一位置的信息冲突问题。
-
生成多尺度特征:完成融合后,生成多尺度特征集{P2, P3, P4, P5, P6}(对于YOLO架构为{P3, P4, P5}),这些特征用于后续的物体检测。
优势
-
直接特征交互:避免了非相邻层特征的直接交互引起的信息损失或退化。
-
高效的特征融合:通过渐近融合和自适应空间融合,有效保留了多层次的详细和语义信息。
-
提升检测性能:实验结果表明,AFPN在MS COCO数据集上相比其他特征金字塔网络取得了更具竞争力的结果,同时保持了较低的计算成本。
AFPN在物体检测任务中显示出了显著的优势,尤其是在处理尺度变化和复杂场景下的信息融合方面。

2.2 更改init.py文件
**关键步骤二:**修改modules文件夹下的__init__.py文件,先导入函数

然后在下面的__all__中声明函数

2.3 添加yaml文件
**关键步骤三:**在/ultralytics/ultralytics/cfg/models/v8下面新建文件yolov8_detect_AFPN4.yaml文件,粘贴下面的内容
python
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [[2, 4, 6, 9], 1, Detect_AFPN4, [nc, 128]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)温馨提示:因为本文只是对yolov8基础上添加模块,如果要对yolov8n/l/m/x进行添加则只需要指定对应的depth_multiple 和 width_multiple。
python
# YOLOv8n
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.25 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 1024 # max_channels
# YOLOv8s
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 1024 # max_channels
# YOLOv8l
depth_multiple: 1.0 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.0 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 512 # max_channels
# YOLOv8m
depth_multiple: 0.67 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.75 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 768 # max_channels
# YOLOv8x
depth_multiple: 1.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 1.25 # layer channel multiple
max_channels: 512 # max_channels2.4 在task.py中进行注册
**关键步骤四:**在task.py的中进行注册,
- 在BaseModel的类下 _apply的函数下添加Detect_AFPN4,如下图

- 在DetectionModel类下的__init__函数中,添加Detect_AFPN3,如下图所示

- 在parse_model函数中,在elif语句添加Detect_AFPN3,如下图所示,

- 在guess_model_task的函数中添加Detect_AFPN3,如下图所示

2.5 执行程序
关键步骤五:在ultralytics文件中新建train.py,将model的参数路径设置为yolov8_detect_AFPN4.yaml的路径即可
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
# model = YOLO('yolov8n.yaml') # build a new model from YAML
# model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
model = YOLO(r'/projects/ultralytics/ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8_detect_AFPN4.yaml') # build from YAML and transfer weights
# Train the model
model.train(batch=16)🚀运行程序,如果出现下面的内容则说明添加成功🚀
python
from n params module arguments
0 -1 1 464 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [3, 16, 3, 2]
1 -1 1 4672 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [16, 32, 3, 2]
2 -1 1 7360 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [32, 32, 1, True]
3 -1 1 18560 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [32, 64, 3, 2]
4 -1 2 49664 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [64, 64, 2, True]
5 -1 1 73984 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [64, 128, 3, 2]
6 -1 2 197632 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [128, 128, 2, True]
7 -1 1 295424 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [128, 256, 3, 2]
8 -1 1 460288 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [256, 256, 1, True]
9 -1 1 164608 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.SPPF [256, 256, 5]
10 [2, 4, 6, 9] 1 836385 ultralytics.nn.Addmodules.AFPNHead4.Detect_AFPN4[1, 128, [32, 64, 128, 256]]
YOLOv8_AFPN4 summary: 750 layers, 2,109,041 parameters, 2,109,025 gradients, 15.1 GFLOPs3. 完整代码分享
python
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1O8zSD69Ottdyr09_CaAymA?pwd=5a7r提取码:5a7r
4. GFLOPs
关于GFLOPs的计算方式可以查看:百面算法工程师 | 卷积基础知识------Convolution
未改进的YOLOv8n GFLOPs
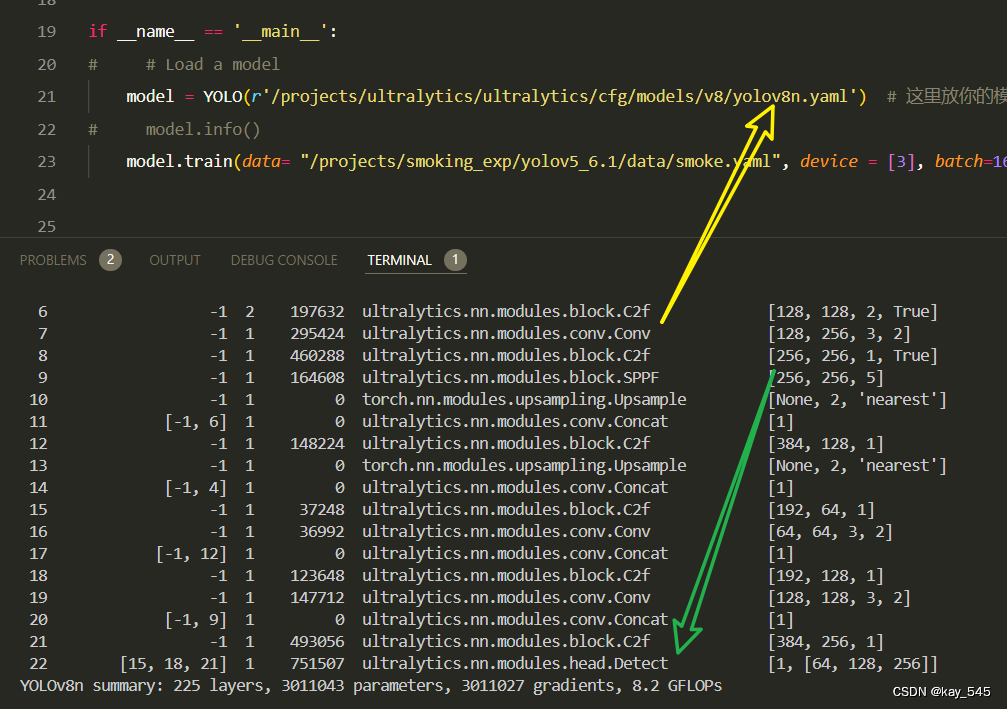
改进后的GFLOPs

5. 进阶
可以结合损失函数或者卷积模块进行多重改进
6. 总结
渐近特征金字塔网络 (AFPN) 是一种先进的架构,旨在通过解决传统特征金字塔网络中常见的特征信息丢失问题来改进对象检测。它通过渐近特征融合过程实现这一目标,该过程从融合相邻的低级特征开始,然后逐步合并高级特征。这种逐步融合减少了非相邻级别之间的语义差距,从而增强了融合结果。采用自适应空间融合来处理每个空间位置上的多对象信息冲突,过滤和保留有用信息,同时抑制矛盾数据。AFPN 同时使用自下而上和自上而下的路径来有效利用详细的低级和语义高级信息,从而保持整个网络中特征的完整性。这种双路径方法与用于维度对齐的高效卷积运算相结合,可显著提高对象检测性能,同时保持较低的计算复杂度。AFPN 的创新方法确保以更少的参数和更高的效率获得具有竞争力的结果。