理论基础以后加入。
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
import time
import numpy as np
import torch
import scipy
import scipy.optimize as opt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pywph as pw
import os
cwd = os.getcwd()
import sys
sys.path.append(cwd)
from comp_sep_functions import create_batch, compute_bias_std, compute_mask, compute_loss_BR, compute_loss_JMD
from tools import plot, plot_PS, plot_wphData loading
s = np.load('dust_simulation.npy').astype(np.float64)
plot(s)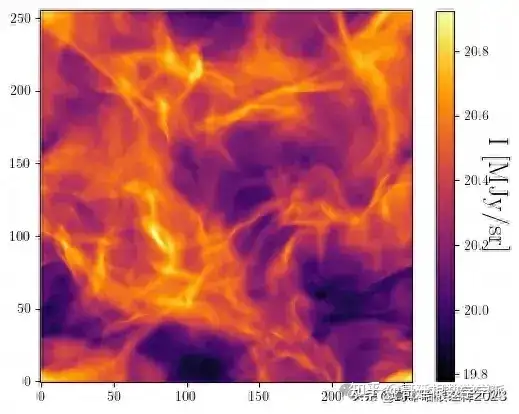
Mock data generation
SNR = 2
n = np.random.normal(0,np.std(s)/SNR,size=np.shape(s)).astype(np.float64)
d = s + n
plot(d)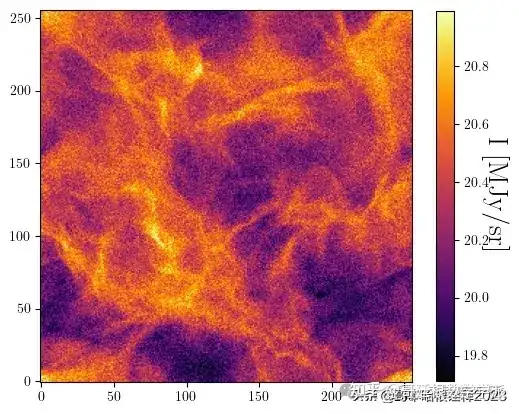
plot_PS(np.array([d,s,n]),labels=['d','s','n'])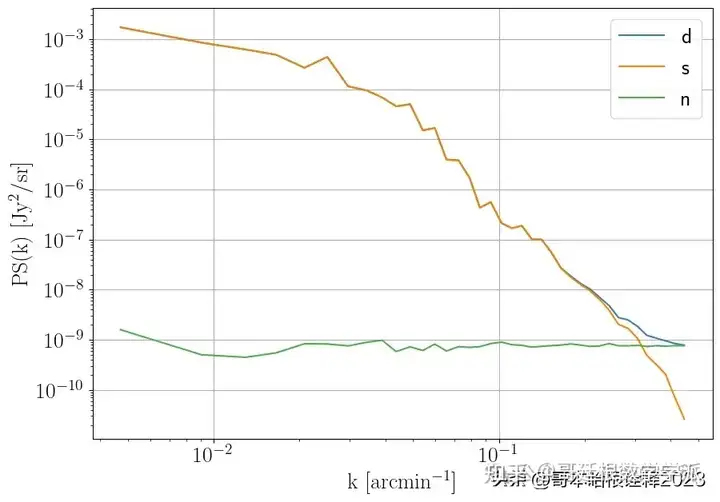
Mn = 20
noise = np.random.normal(0,np.std(s)/SNR,size=(Mn,np.shape(s)[0],np.shape(s)[0])).astype(np.float64)Parameters setting
N, N = np.shape(s) # map size
J = int(np.log2(N))-2 # number of scales
L = 4 # number of angles
pbc = True # periodic boundary conditions
dn = 5 # number of translations
wph_model = ["S11","S00","S01","Cphase","C01","C00","L"] # list of WPH coefficients
style = 'JMD'
method = 'L-BFGS-B'
n_epoch = 5
n_iter = 50
device = "cpu"
batch_size = 5Initialization
batch_number = int(Mn/batch_size)
n_batch = create_batch(noise, device, batch_number, batch_size, N)
wph_op = pw.WPHOp(N, N, J, L=L, dn=dn, device=device)Objective function
def objective(x):
"""
Computes the loss and the corresponding gradient.
Parameters
----------
x : torch 1D tensor
Flattened running map.
Returns
-------
float
Loss value.
torch 1D tensor
Gradient of the loss.
"""
global eval_cnt
global loss_list
start_time = time.time()
u = x.reshape((N, N)) # Reshape x
u = torch.from_numpy(u).to(device).requires_grad_(True) # Track operations on u
if style == 'BR':
L = compute_loss_BR(u, coeffs_target, std, mask, device, Mn, wph_op, noise, pbc) # Compute the loss 'à la Bruno'
if style == 'JMD':
L = compute_loss_JMD(u, coeffs_target, std, mask, device, wph_op, pbc) # Compute the loss 'à la Jean-Marc'
u_grad = u.grad.cpu().numpy().astype(x.dtype) # Compute the gradient
if eval_cnt % 5 == 0:
print(f"Evaluation: {eval_cnt}")
print("L = "+str(round(L.item(),5)))
print("(computed in "+str(round(time.time() - start_time,3))+"s)")
print("")
eval_cnt += 1
loss_list.append(L.item())
return L.item(), u_grad.ravel()Beginning of the optimization
# Initialization of evaluation count.
eval_cnt = 0
# Initialization of the running map s_tilde0.
s_tilde0 = d
# Creation of the loss list.
loss_list = []
# WPH model loading (only the power-spectrum-like coefficients in the first step).
wph_op.load_model(["S11"])
# Loop of the epochs.
for i in range(n_epoch):
print("Starting epoch "+str(i+1)+"...")
# Bring s_tilde0 from array to tensor.
s_tilde0 = torch.from_numpy(s_tilde0).to(device)
print('Computing loss arguments...')
# Computation of the noise-induced bias and std on the s_tilde0 map.
# The bias is only used for style='JMD', but is computed
# in both cases (no significant additional calculations).
bias, std = compute_bias_std(s_tilde0, n_batch, wph_op, pbc, Mn, batch_number, batch_size, device)
# Computation of the WPH statistics of "d".
coeffs = wph_op.apply(torch.from_numpy(d).to(device), norm=None, pbc=pbc)
if style == 'BR':
# In BR's formalism, the target WPH coefficients are the ones of "d".
# They are split into real and imaginary parts.
coeffs_target = torch.cat((torch.unsqueeze(torch.real(coeffs),dim=0),
torch.unsqueeze(torch.imag(coeffs),dim=0)))
if style == 'JMD':
# In JMD's formalism, the target WPH coefficients are computed as
# the ones of "d" corrected from the bias estimated before.
# They are here also split into real and imaginary parts.
coeffs_target = torch.cat((torch.unsqueeze(torch.real(coeffs)-bias[0],dim=0),
torch.unsqueeze(torch.imag(coeffs)-bias[1],dim=0)))
# Computation of the mask for the WPH statistics threshold.
mask = compute_mask(1, s_tilde0, std, wph_op, wph_model, pbc, device)
print('Loss arguments computed !')
print('Beginning optimization...')
# Beginning of the optimization.
result = opt.minimize(objective, s_tilde0.cpu().ravel(), method=method, jac=True, tol=None,
options={"maxiter": n_iter, "gtol": 1e-14, "ftol": 1e-14, "maxcor": 20})
final_loss, s_tilde0, niter, msg = result['fun'], result['x'], result['nit'], result['message']
# Reshaping of the running map s_tilde0.
s_tilde0 = s_tilde0.reshape((N, N)).astype(np.float64)
print("Epoch "+str(i+1)+" done !")
# Plot of the running map.
plot(s_tilde0)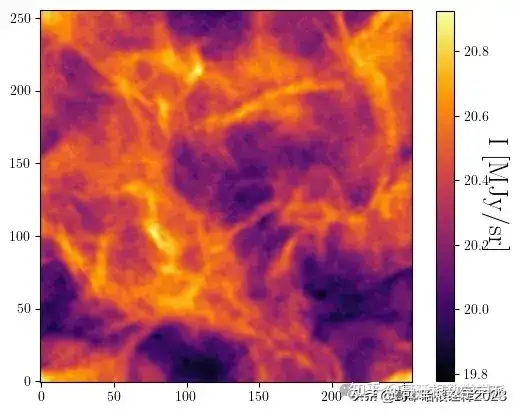
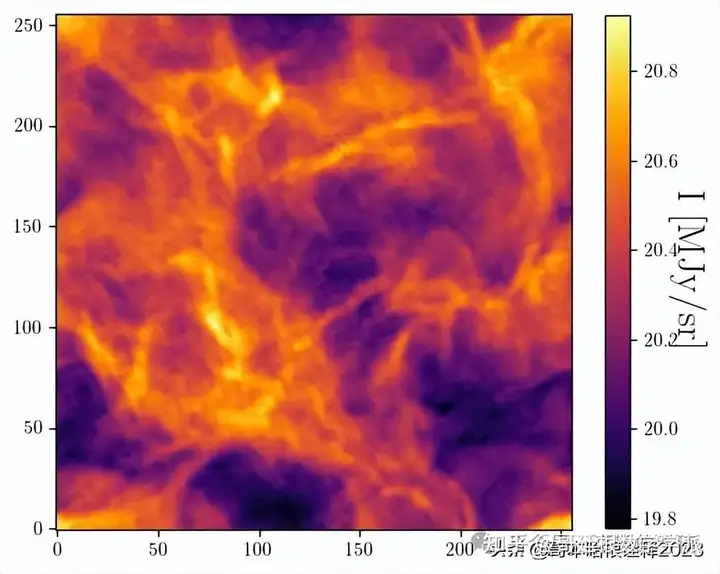
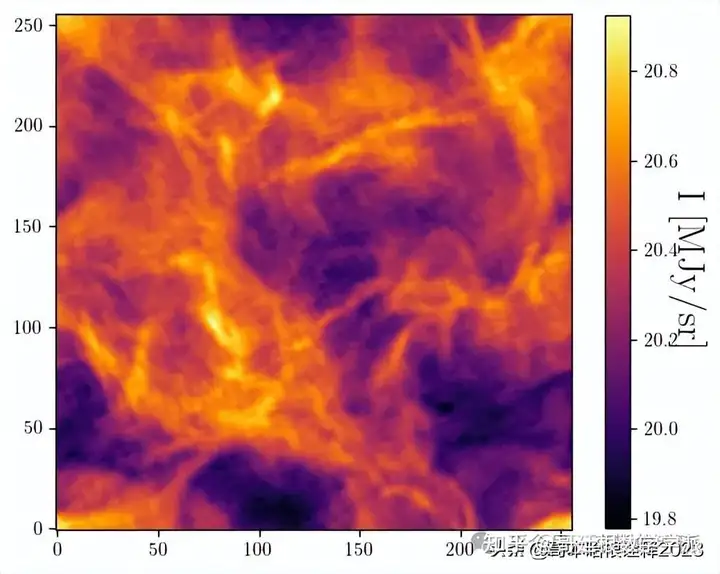
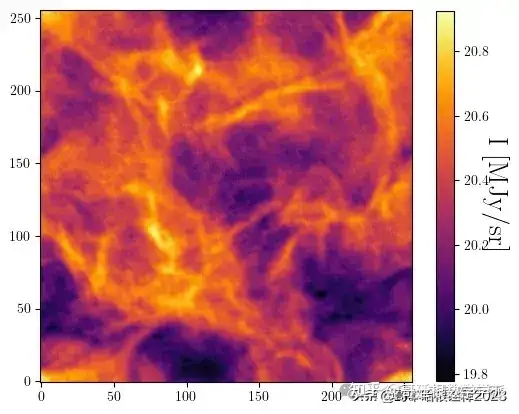
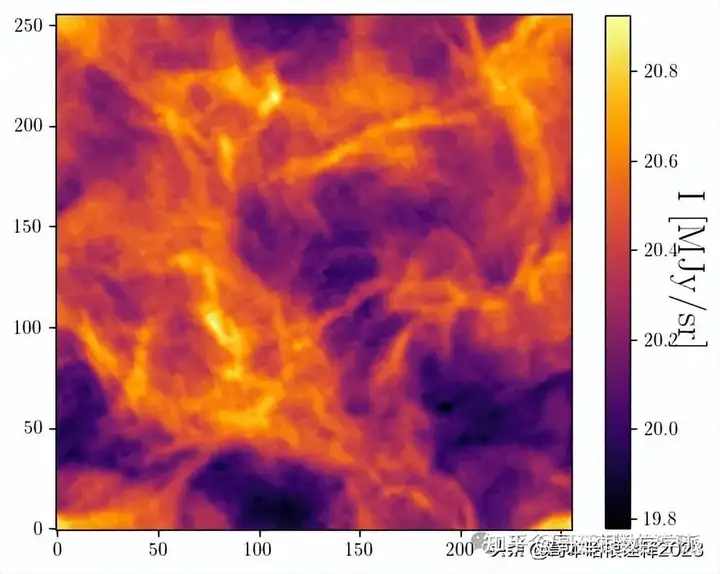
plt.figure()
plt.plot(loss_list)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.show()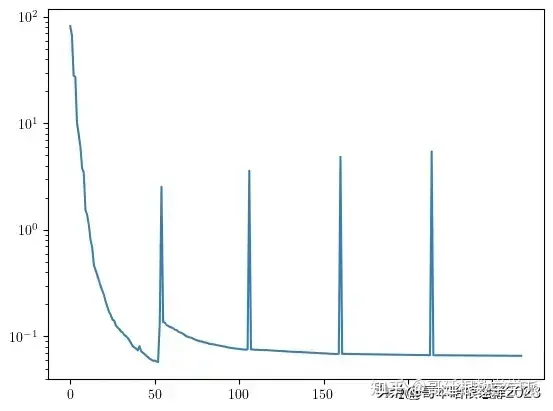
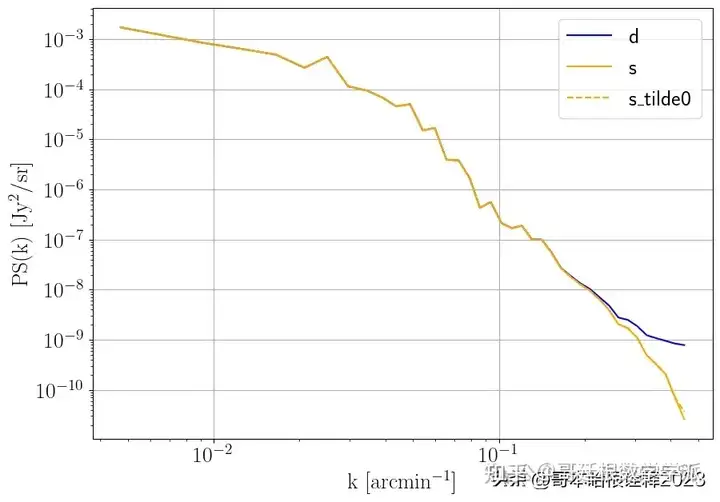
plot_PS(
np.array([d,s,s_tilde0]),
labels=['d','s','s_tilde0'],
colors=['blue','orange','orange'],
styles=['-','-','--']
)
# Initialization of evaluation count.
eval_cnt = 0
# Initialization of the running map s_tilde.
s_tilde = s_tilde0
# Creation of the loss list.
loss_list = []
# WPH model loading (all the WPH coefficients in the second step).
wph_op.load_model(wph_model)
# Loop of the epochs.
for i in range(n_epoch):
print("Starting epoch "+str(i+1)+"...")
# Bring s_tilde from array to tensor.
s_tilde = torch.from_numpy(s_tilde).to(device)
print('Computing loss arguments...')
# Computation of the noise-induced bias and std on the s_tilde map.
# The bias is only used for style='JMD', but is computed
# in both cases (no significant additional calculations).
bias, std = compute_bias_std(s_tilde, n_batch, wph_op, pbc, Mn, batch_number, batch_size, device)
# Computation of the WPH statistics of "d".
coeffs = wph_op.apply(torch.from_numpy(d).to(device), norm=None, pbc=pbc)
if style == 'BR':
# In BR's formalism, the target WPH coefficients are the ones of "d".
# They are split into real and imaginary parts.
coeffs_target = torch.cat((torch.unsqueeze(torch.real(coeffs),dim=0),
torch.unsqueeze(torch.imag(coeffs),dim=0)))
if style == 'JMD':
# In JMD's formalism, the target WPH coefficients are computed as
# the ones of "d" corrected from the bias estimated before.
# They are here also split into real and imaginary parts.
coeffs_target = torch.cat((torch.unsqueeze(torch.real(coeffs)-bias[0],dim=0),
torch.unsqueeze(torch.imag(coeffs)-bias[1],dim=0)))
# Computation of the mask for the WPH statistics threshold.
mask = compute_mask(2, s_tilde, std, wph_op, wph_model, pbc, device)
print('Loss arguments computed !')
print('Beginning optimization...')
# Beginning of the optimization.
result = opt.minimize(objective, s_tilde.cpu().ravel(), method=method, jac=True, tol=None,
options={"maxiter": n_iter, "gtol": 1e-14, "ftol": 1e-14, "maxcor": 20})
final_loss, s_tilde, niter, msg = result['fun'], result['x'], result['nit'], result['message']
# Reshaping of the running map s_tilde.
s_tilde = s_tilde.reshape((N, N)).astype(np.float64)
print("Epoch "+str(i+1)+" done !")
# Plot of the running map.
plot(s_tilde)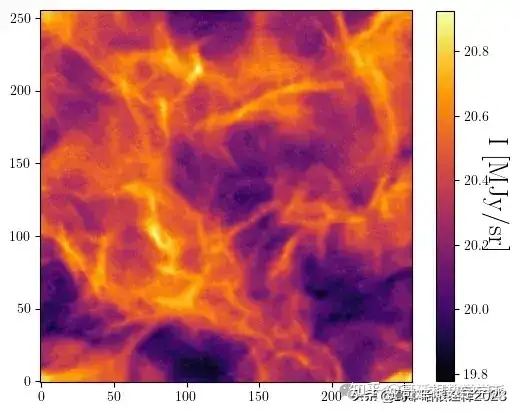
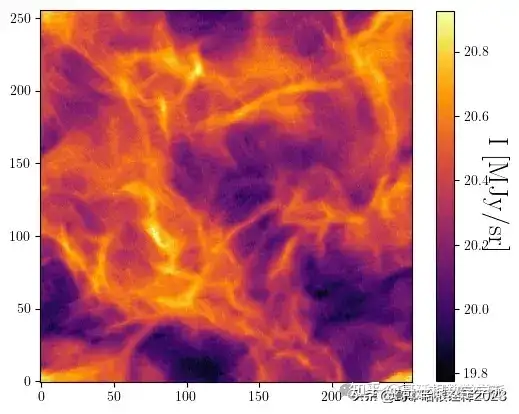
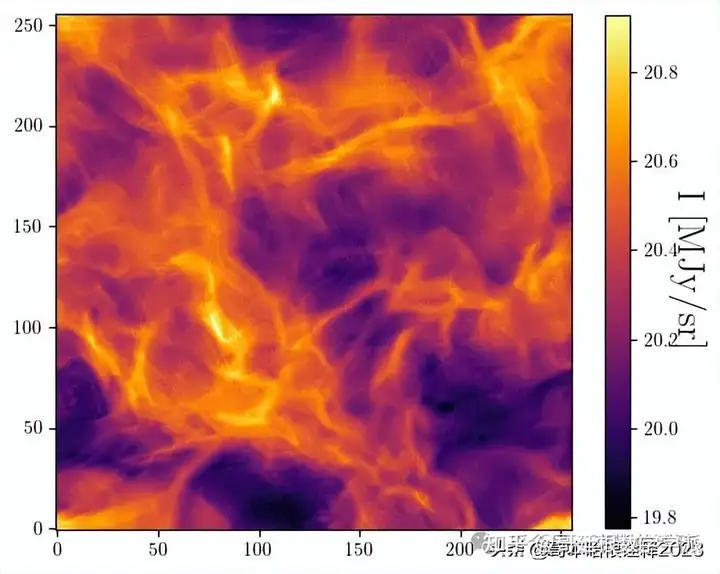
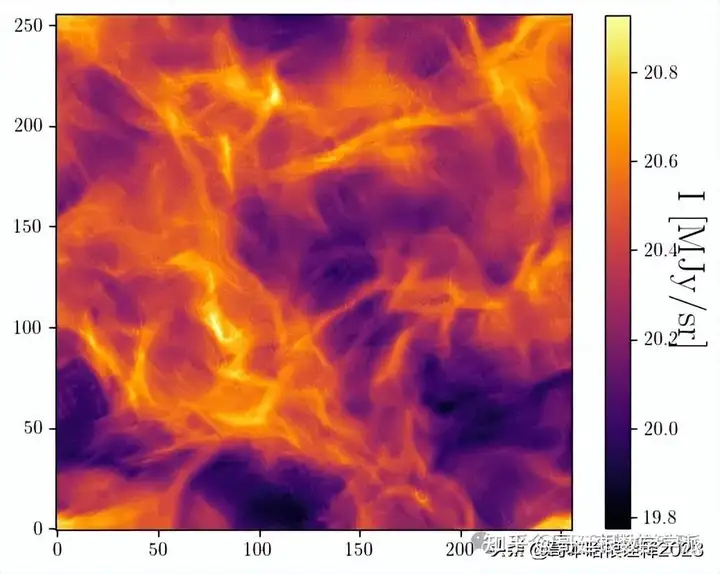
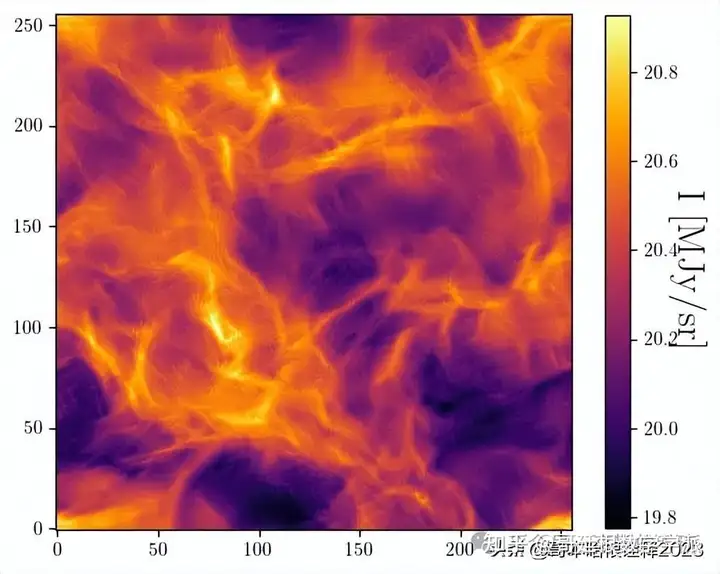
plt.figure()
plt.plot(loss_list)
plt.yscale('log')
plt.show()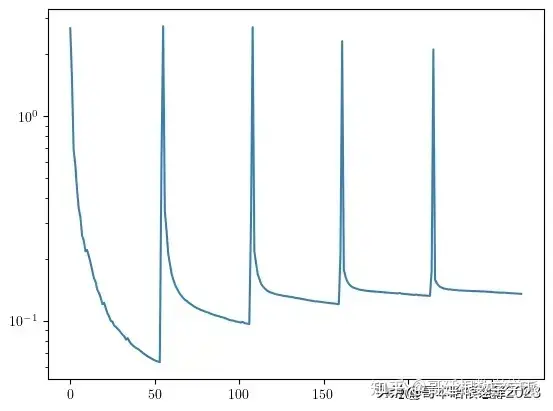
plot(s_tilde)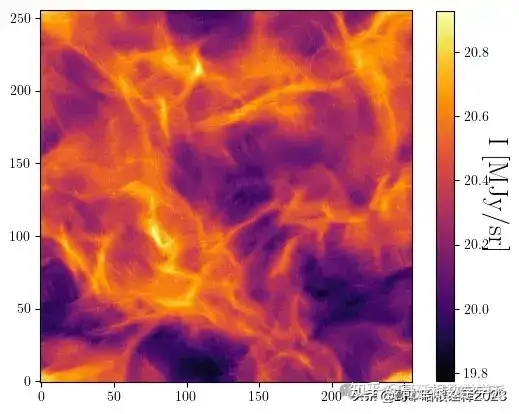
工学博士,担任《Mechanical System and Signal Processing》审稿专家,担任《中国电机工程学报》优秀审稿专家,《控制与决策》,《系统工程与电子技术》,《电力系统保护与控制》,《宇航学报》等EI期刊审稿专家,擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。
知乎学术咨询:https://www.zhihu.com/consult/people/792359672131756032?isMe=1
工学博士,担任《Mechanical System and Signal Processing》审稿专家,担任《中国电机工程学报》优秀审稿专家,《控制与决策》,《系统工程与电子技术》,《电力系统保护与控制》,《宇航学报》等EI期刊审稿专家,擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。