Interesting thing!
About Bert you just need to know that it is like gpt, but focus on pre-training Encoder instead of decoder. It has a mask method which enhances its precision remarkbably. (judge not only the word before the blank but the later one )
model : BertForSequenceClassfication constructs the model and load the config and set the sentiment classification to 3 kinds
python
model = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('bert-base-chinese', num_labels = 3)
model = auto_mixed_precision(model, '01')
optimizer = nn.Adam(model.trainable_params(), learning_rate = 2e-5)
metric = Accuracy()
ckpoint_cb = CheckpointCallback(save_path = 'checkpoint', ckpt_name = 'bert_emotect', epochs = 1, keep_checkpoint_max = 2)
best_model_cb = BestModelCallback(save_path = 'checkpoint', ckpt_name = 'bert_emotect_best', auto_load = True)
trainer = Trainer(network = model, train_dataset = dataset_train,
eval_dataset=dataset_val, metrics = metric,
epochs = 5, optimizer = optimizer, callback = [ckpoint_cb, best_model_cb])
trainer.run(tgt_columns = 'labels')the model validation and prediction are the same mostly like Sentiment by any model:
python
evaluator = Evaluator(network = model, eval_dataset = dataset_test, metrics= metric)
evaluator.run(tgt_columns='labels')
dataset_infer = SentimentDataset('data/infer.tsv')
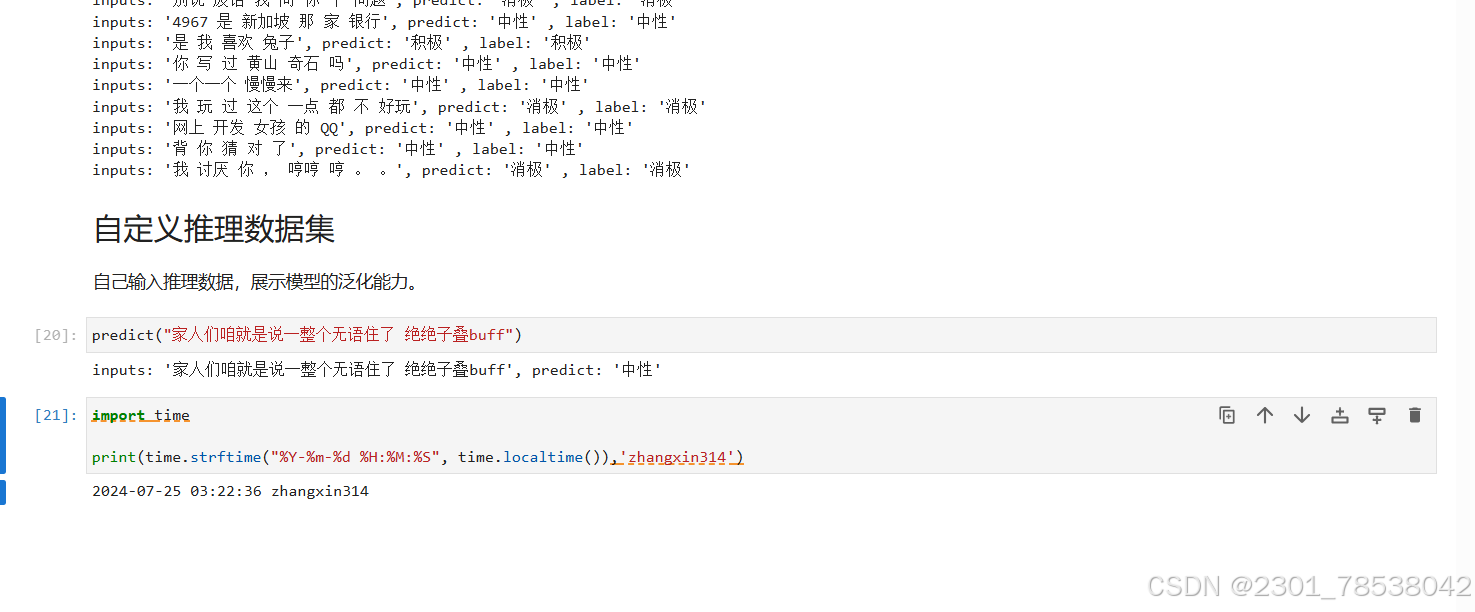
def predict(text, label = None):
label_map = {0:'消极', 1:'中性', 2:'积极'}
text_tokenized = Tensor([tokenizer(text).input_ids])
logits = model(text_tokenized)
predict_label = logits[0].asnumpy().argmax()
info = f"inputs:'{text}',predict:
'{label_map[predict_label]}'"
if label is not None:
info += f", label:'{label_map[label]}'"
print(info)