hello,又见面了!

目录
[1. 栈的概念与结构](#1. 栈的概念与结构)
正文开始------
1. 栈的概念与结构
**栈:**一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守先进后出的原则。
**压栈:**栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
**出栈:**栈的删除操作叫出栈,出数据也在栈顶。
【图解】
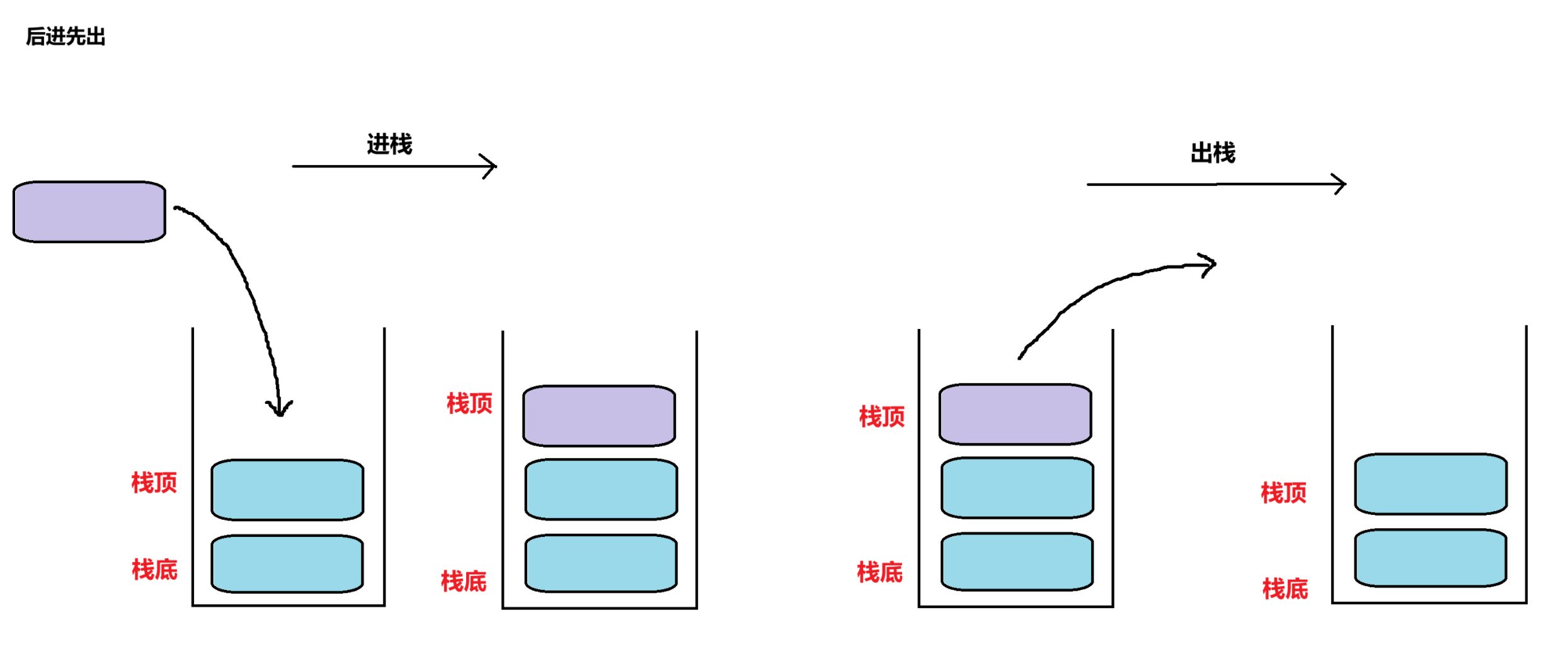
栈的底层结构
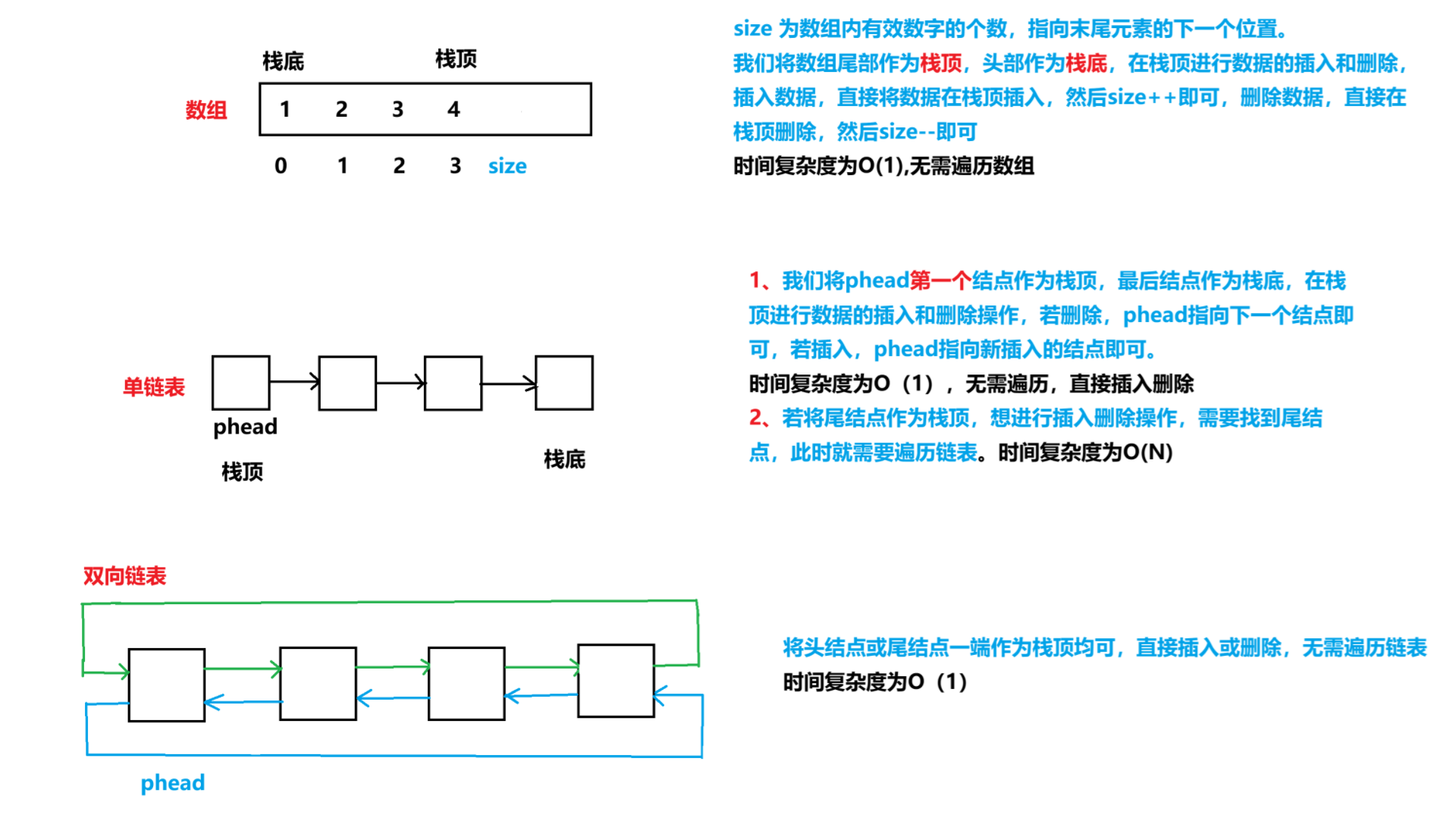
**内存比较:**双向链表比单链表多了一种指针,内存占用就相对多一些;数组和单链表,数组每次都以2倍大小增容,正因如此,无需多次增容,而单链表每次增加数据都要申请空间,删除数据要释放空间,较为繁琐。
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更好一些,因为数组在尾插数据时代价更小。
2、栈的实现
栈里的数据不能被遍历,不能被随机访问。每次取数据只能取栈顶数据
Stack.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//定义栈的结构
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* arr;
int capacity; //栈的容量
int top; //栈顶
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps);
//入数据
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//出数据
void StackPop(ST* st);
//取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
//判空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
//获取栈中有效的数据个数
int STsize(ST* ps);Stack.c
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Stack.h"
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0; //此时栈为空,栈顶=栈底
}
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->arr)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//入数据
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//判断空间是否足够
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
//申请空间
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc file!");
exit(1);
}
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//空间足够
ps->arr[ps->top++] = x;
}
//出数据
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
//判空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
//取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}
//获取栈中有效的数据个数
int STsize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}test.c
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Stack.h"
void STTest()
{
ST st;
STInit(&st);
StackPush(&st,1);
StackPush(&st,2);
StackPush(&st,3);
StackPush(&st,4);
StackPush(&st,5);
printf("size:%d\n", STsize(&st));
/*StackPop(&st);*/
//循环出栈,直到栈为空
while (!StackEmpty(&st))
{
STDataType data = StackTop(&st);
printf("%d ", data);
//出栈
StackPop(&st);
}
printf("size:%d\n", STsize(&st));
STDestroy(&st);
}
int main()
{
STTest();
return 0;
}3、习题

【思路】

cpp
//定义栈的结构
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* arr;
int capacity; //栈的容量
int top; //栈顶
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0; //此时栈为空,栈顶=栈底
}
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->arr)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//入数据
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//判断空间是否足够
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
//申请空间
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc file!");
exit(1);
}
ps->arr = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//空间足够
ps->arr[ps->top++] = x;
}
//判空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
//出数据
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
//取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}
bool isValid(char* s) {
ST st;
STInit(&st);
char* ps=s;
while(*ps!='\0')
{
//左括号,入栈
if(*ps=='('||*ps=='['||*ps=='{')
{
StackPush(&st,*ps);
}
else //右括号,与栈顶元素判断是否匹配,匹配,出栈,不匹配,返回false
{
if(StackEmpty(&st))
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
char ch=StackTop(&st);
if(*ps==')'&&ch=='('||*ps=='}'&&ch=='{'||*ps==']'&&ch=='[')
{
StackPop(&st);
}
else
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
}
ps++;
}
bool ret=StackEmpty(&st)==true;
STDestroy(&st);
return ret;
}至此,栈,结束------
完------

至此结束------
我是云边有个稻草人
期待与你的下一次相遇 !