非机动车及驾驶人佩戴安全帽检测任务的意义主要包括以下几点:
保障行车安全:非机动车包括自行车、电动车等,佩戴安全帽能够有效保护骑车人头部,减少因交通事故造成的头部伤害风险,提高行车安全系数。
符合交通法规:许多国家和地区的交通法规要求骑车人员在骑行时佩戴安全帽,因此进行安全帽检测任务可以确保遵守相关法规,避免因未佩戴安全帽而受到处罚。
促进交通安全宣传:通过开展安全帽检测任务,可以增强公众对交通安全的认识和重视程度,提升骑车人员自我保护意识,倡导大众积极参与交通安全宣传活动。
减少交通事故伤亡:头部是人体最脆弱的部位之一,遭受外伤后很容易导致严重后果。通过佩戴安全帽,可以有效降低头部受伤的风险,减少交通事故造成的伤亡人数。
非机动车及驾驶人佩戴安全帽检测任务的意义在于提高行车安全性、符合法规要求、促进交通安全宣传和减少交通事故伤亡。
本文以YOLOv8 为基础(可以换成YOLOv11/YOLOv12),设计研究了基于YOLOv8的非机动车及驾驶人是否佩戴安全帽检测识别任务,包含完整数据介绍、训练过程和测试结果全流程。
若需要完整数据集和源代码可以私信。
目录
🌷🌷1.数据集介绍
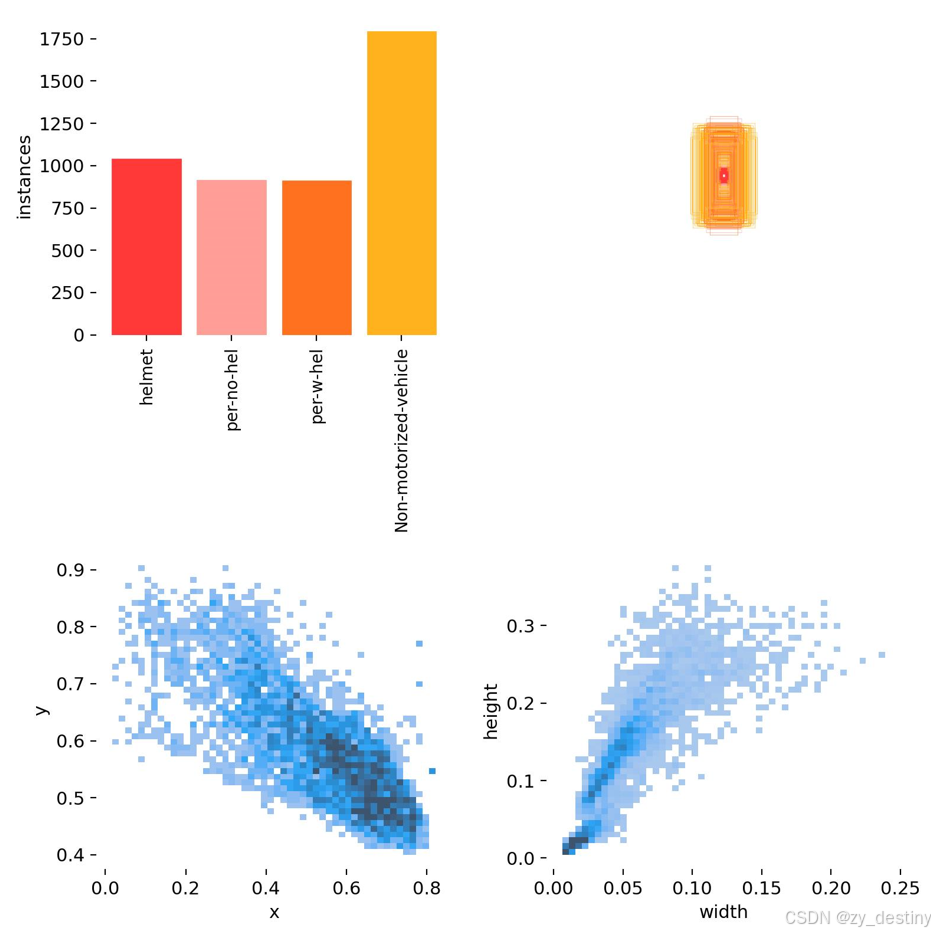
非机动车及驾驶人是否佩戴安全帽数据集为摄像头视角拍摄到的实际影像,主要包含4类数据:
bash
0:安全帽
1: 驾驶人未戴安全帽
2:驾驶人戴安全帽
3:非机动车部分影像展示如下:
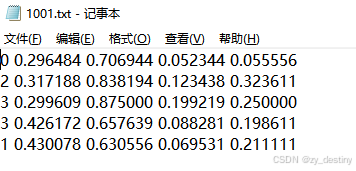
label为txt格式的yolo目标检测格式,示例txt文件内容为:
训练验证比例可以自行调整,这里不赘述。
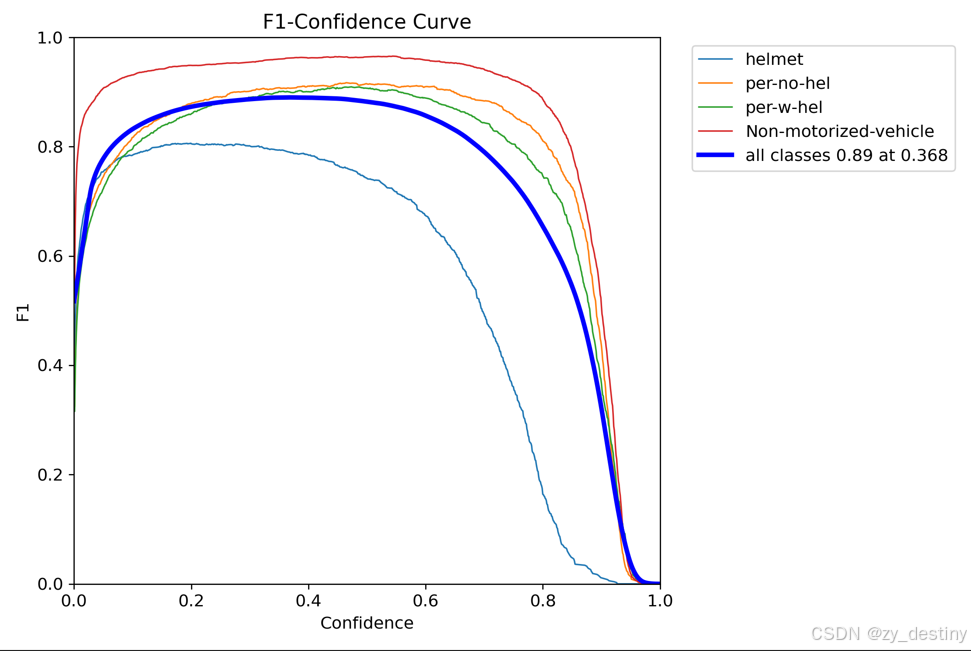
👍👍2.识别检测实现效果


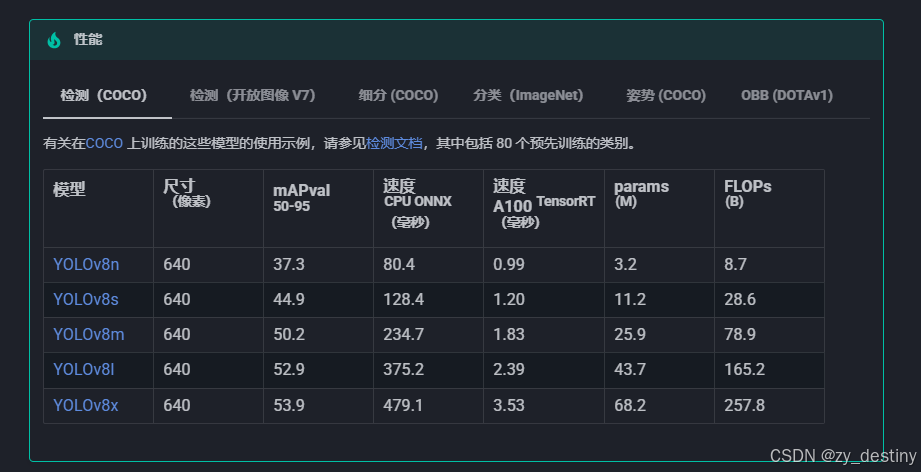
🍎🍎3.YOLOv8识别非机动车及安全帽算法步骤
通过目标检测方法进行非机动车及安全帽识别的方法不限,本文以YOLOv8为例进行说明。
🍋3.1数据准备
数据组织:
----非机动车_dataset
----images
----train
----val
----labels
----train
----val
image/train文件夹下内容如下:
labels/train文件夹下内容如下:
模型训练label部分采用的是YOLO格式的txt文件,所以如果自己的数据集是xml格式或者json格式需要进行转换哦,转换可移步这里。
具体txt格式内容如1.数据集介绍中所示。
🍋3.2模型选择
以YOLOv8为例,模型选择代码如下:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.yaml') # build a new model from YAML
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
model = YOLO('yolov8n.yaml').load('yolov8n.pt') # build from YAML and transfer weights其中yolov8n.yaml为./ultralytics/cfg/models/v8yolov8n.yaml,可根据自己的数据进行模型调整,打开yolov8n.yaml显示内容如下:
python
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 4 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 12
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 15 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 12], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 18 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 9], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 21 (P5/32-large)
- [[15, 18, 21], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)打印的网络结构如下:
bash
from n params module arguments
0 -1 1 464 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [3, 16, 3, 2]
1 -1 1 4672 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [16, 32, 3, 2]
2 -1 1 7360 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [32, 32, 1, True]
3 -1 1 18560 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [32, 64, 3, 2]
4 -1 2 49664 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [64, 64, 2, True]
5 -1 1 73984 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [64, 128, 3, 2]
6 -1 2 197632 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [128, 128, 2, True]
7 -1 1 295424 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [128, 256, 3, 2]
8 -1 1 460288 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [256, 256, 1, True]
9 -1 1 164608 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.SPPF [256, 256, 5]
10 -1 1 0 torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample [None, 2, 'nearest']
11 [-1, 6] 1 0 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Concat [1]
12 -1 1 148224 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [384, 128, 1]
13 -1 1 0 torch.nn.modules.upsampling.Upsample [None, 2, 'nearest']
14 [-1, 4] 1 0 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Concat [1]
15 -1 1 37248 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [192, 64, 1]
16 -1 1 36992 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [64, 64, 3, 2]
17 [-1, 12] 1 0 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Concat [1]
18 -1 1 123648 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [192, 128, 1]
19 -1 1 147712 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Conv [128, 128, 3, 2]
20 [-1, 9] 1 0 ultralytics.nn.modules.conv.Concat [1]
21 -1 1 493056 ultralytics.nn.modules.block.C2f [384, 256, 1]
22 [15, 18, 21] 1 752092 ultralytics.nn.modules.head.Detect [4, [64, 128, 256]]
YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3011628 parameters, 3011612 gradients, 8.2 GFLOPs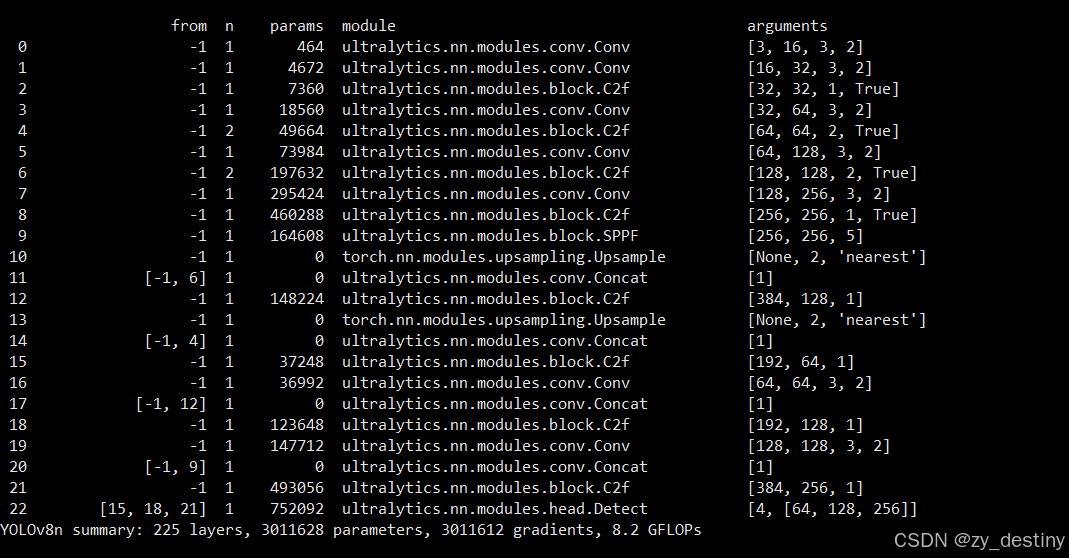
主要需要修改的地方为nc,也就是num_class,此处数据集类别为4类,所以nc=4。
如果其他的模型参数不变的话,就默认保持原版yolov12,需要改造模型结构的大佬请绕行。
🍋3.3加载预训练模型
加载预训练模型yolov8n.pt,可以在第一次运行时自动下载,如果受到下载速度限制,也可以自行下载好(下载链接),放在对应目录下即可。
🍋3.4输入数据组织
yolov8还是以yolo格式的数据为例,./ultralytics/cfg/datasets/data.yaml的内容示例如下:
bash
# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
path: ../datasets/coco8 # dataset root dir
train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 4 images
val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 4 images
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes (80 COCO classes)
names:
0: person
1: bicycle
2: car
# ...
77: teddy bear
78: hair drier
79: toothbrush这个是官方的标准coco数据集,需要换成自己的数据集格式,此处建议根据自己的数据集设置新建一个feijidongche_detect_coco128.yaml文件,放在./ultralytics/cfg/datasets/目录下,最后数据集设置就可以直接用自己的feijidongche_detect_coco128.yaml文件了。以我的feijidongche_detect_coco128.yaml文件为例:
bash
path: /home/datasets/feijidongche# dataset root dir
train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 4 images
val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 4 images
test: images/test # test images (optional)
names:
0: helmet
1: per-no-hel
2: per-w-hel
3:Non-motorized-vehicle🍭🍭4.目标检测训练代码
准备好数据和模型之后,就可以开始训练了,train.py的内容显示为:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
#model = YOLO('yolov12n.yaml') # build a new model from YAML
#model = YOLO('yolov12n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
model = YOLO('yolov12n.yaml').load('yolov12n.pt') # build from YAML and transfer weights
# Train the model
results = model.train(data='yinliao_detect_coco128.yaml', epochs=200, imgsz=640)通常我会选择在基础YOLO模型上进行transfer微调,不会从头开始训练,如果想自己从头开始,可以自行选择第一种方式。这里建议选择第三种。
⭐4.1训练过程
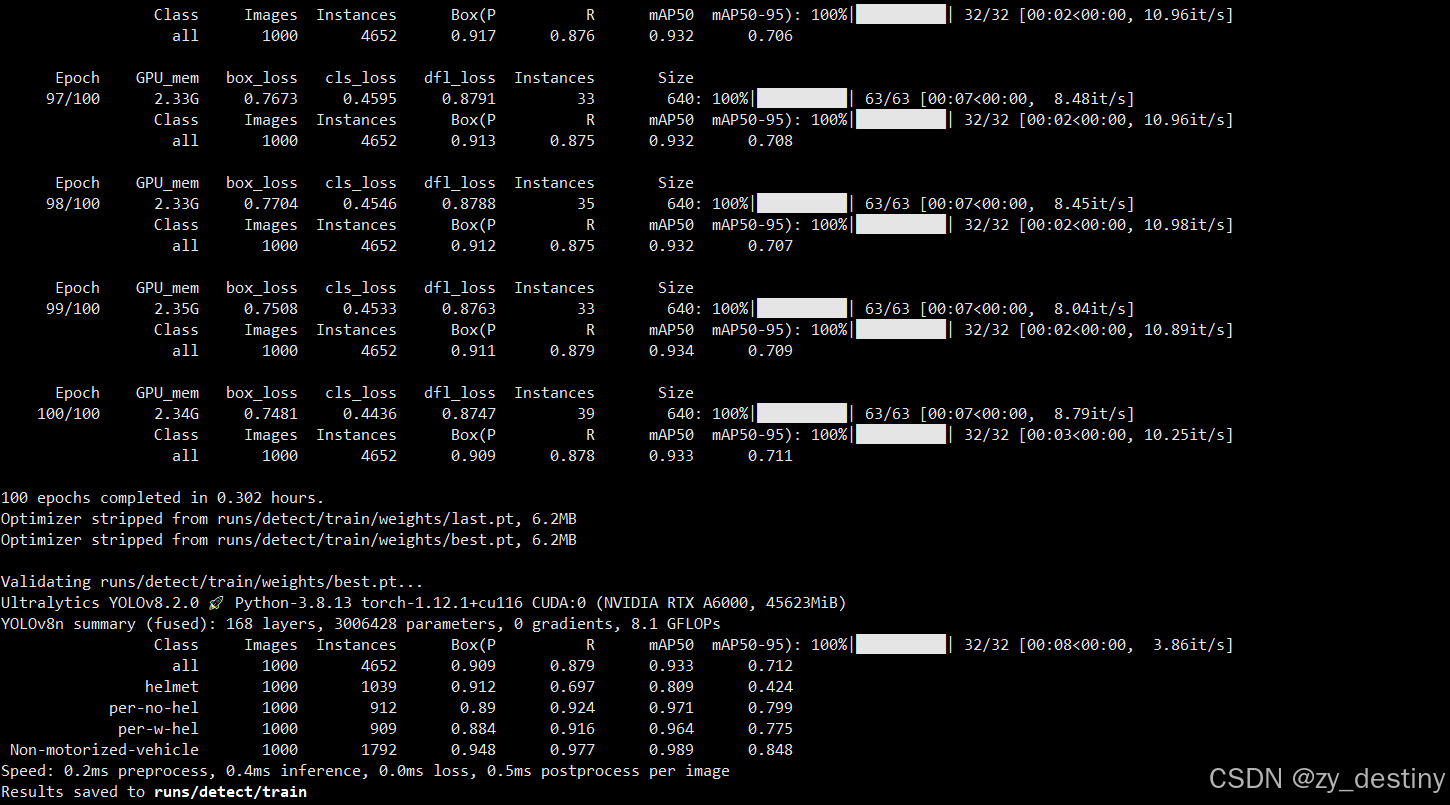
开始训练之后就会开始打印log文件了。如下图所示:
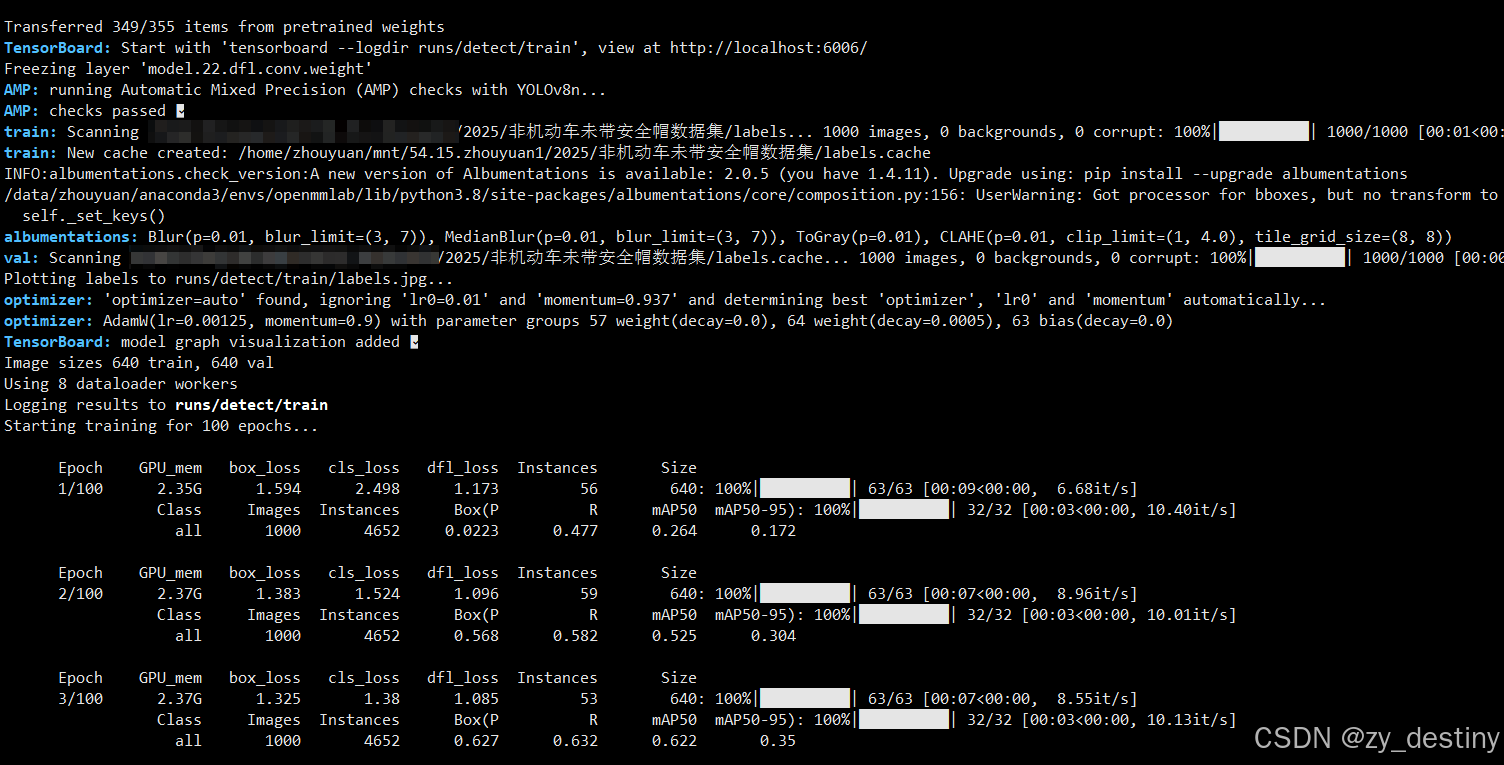
训练完成后会在/run/detect/目录下生成train或者train+数字的文件夹,存放你的训练结果。
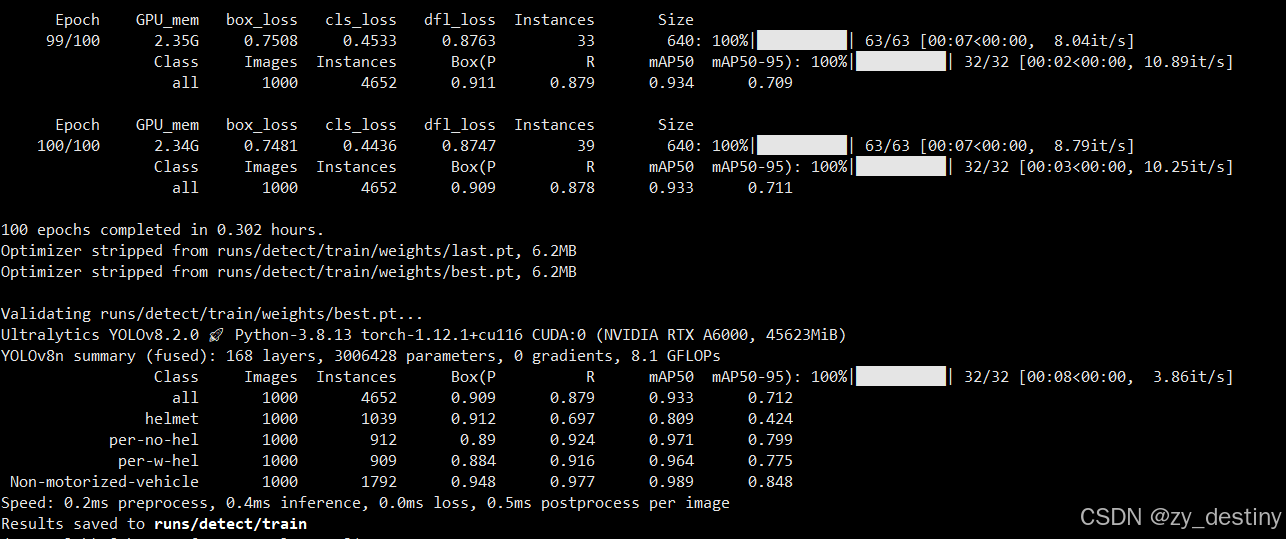
训练完成后的结果如下:
其中weights文件夹内会包含2个模型,一个best.pth,一个last.pth。
至此就可以使用best.pth进行推理检测非机动车及佩戴安全帽了。
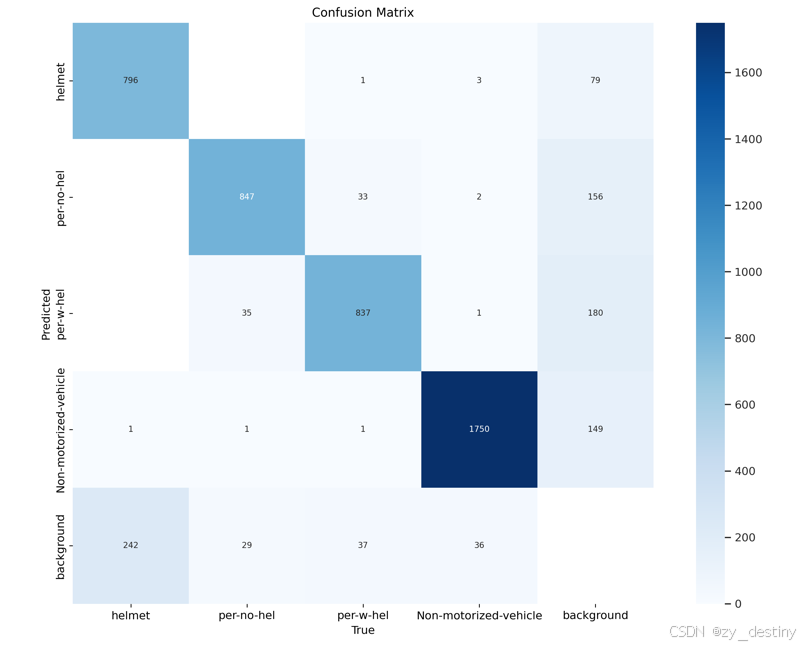
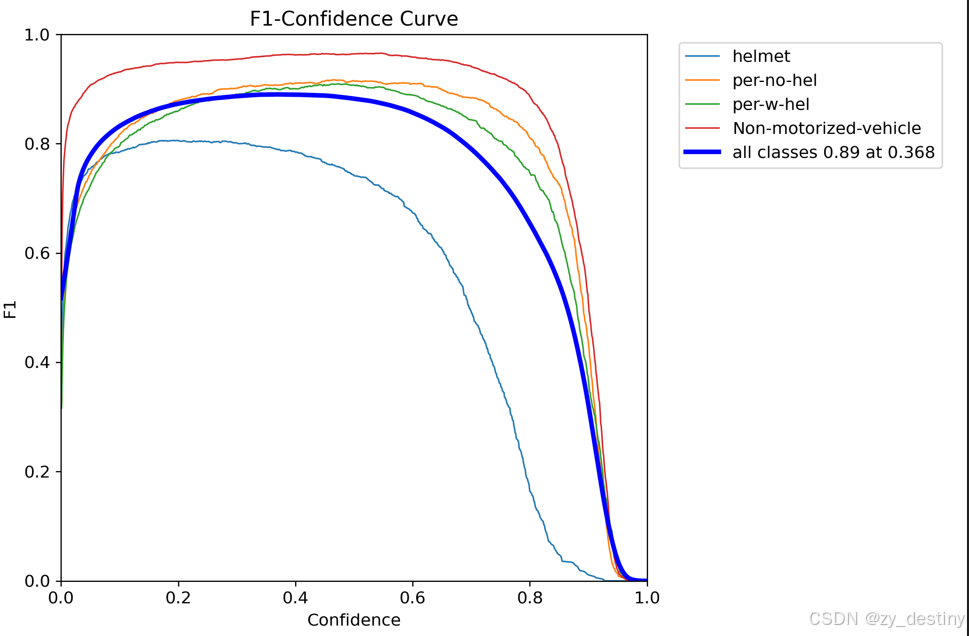
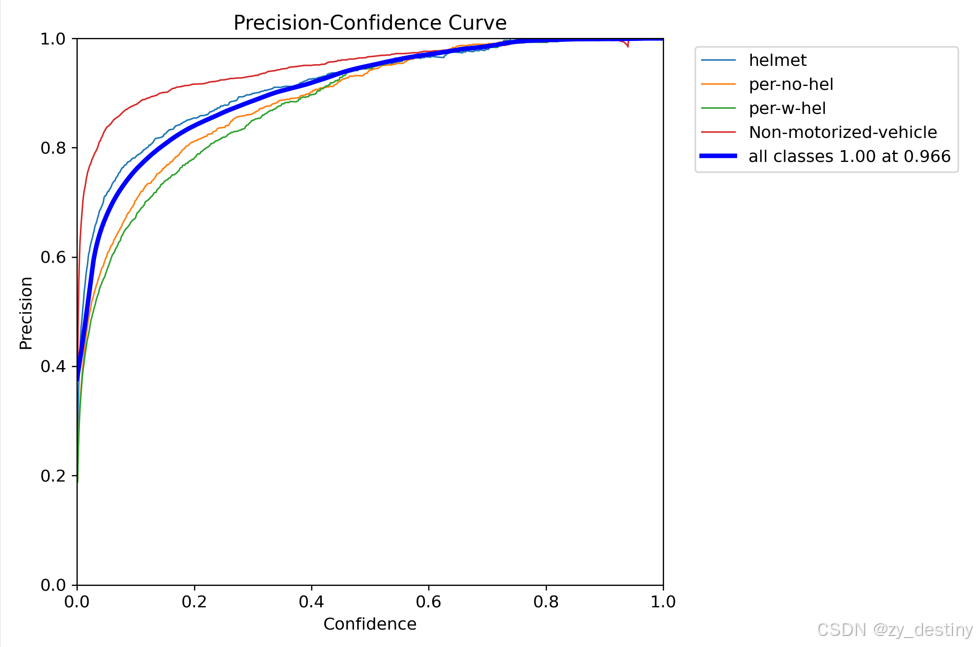
训练精度展示:
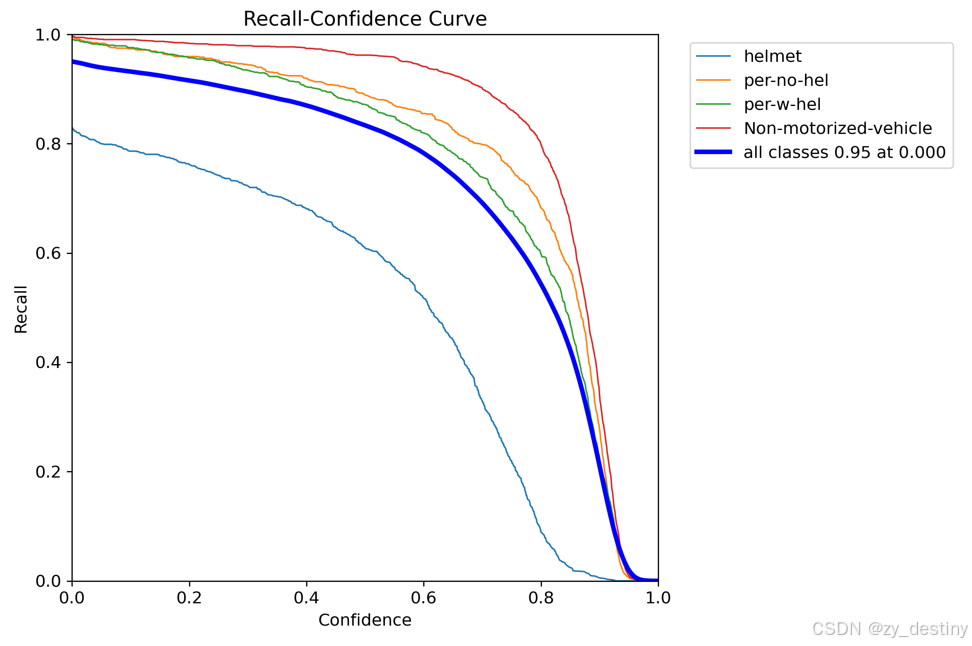
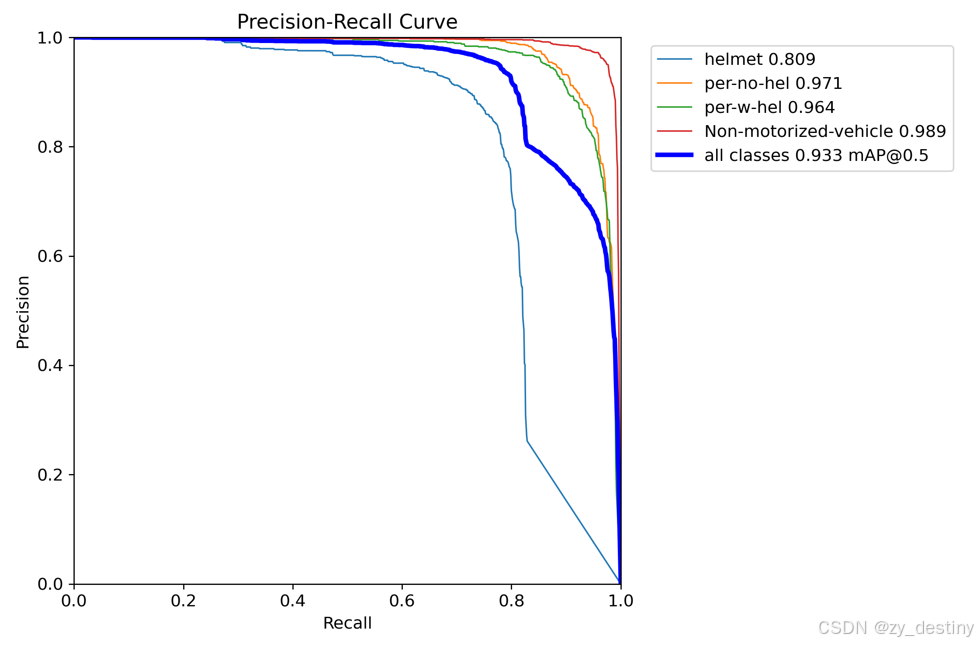
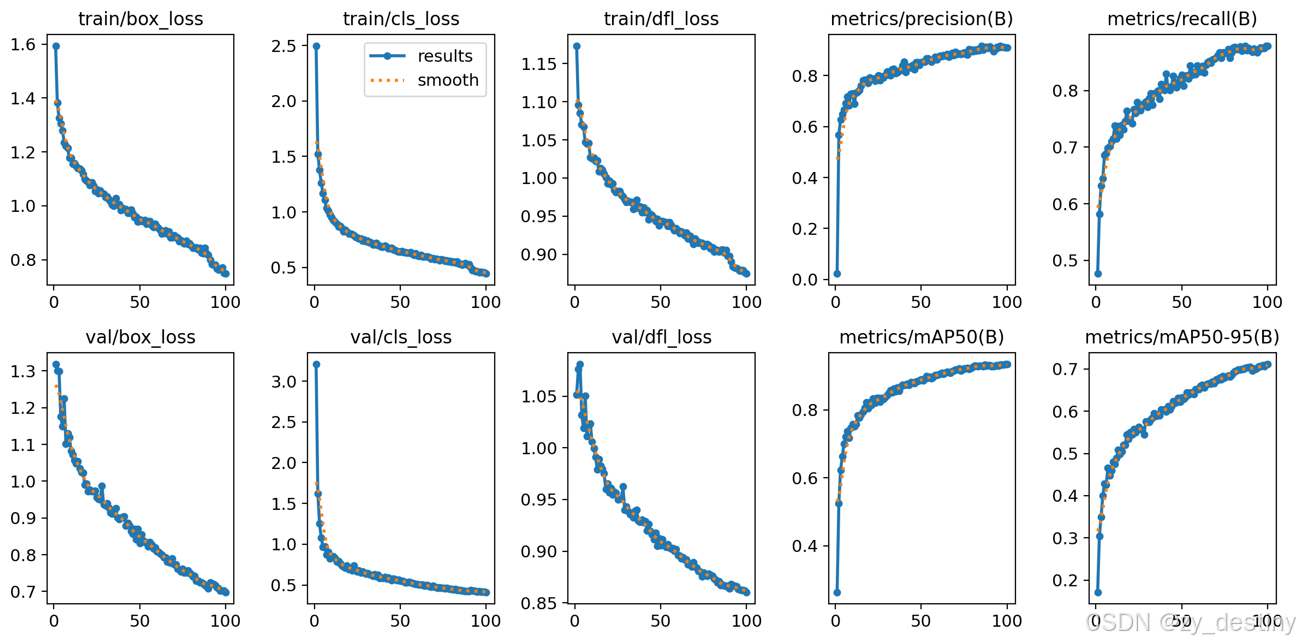
可视化效果:

🏆🏆5.目标检测推理代码
批量推理python代码如下:
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
from PIL import Image
import cv2
import os
model = YOLO('/yolov8/runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt') # load a custom model
path = '/home/dataset/feijidongche/images/test/' #test_image_path_dir
img_list = os.listdir(path)
for img_path in img_list:
### =============detect=====================
im1 = Image.open(os.path.join(path,img_path))
results = model.predict(source=im1, save=True,save_txt=True)若需要完整数据集和源代码可以私信。
整理不易,欢迎一键三连!!!
送你们一条美丽的--分割线--
🌷🌷🍀🍀🌾🌾🍓🍓🍂🍂🙋🙋🐸🐸🙋🙋💖💖🍌🍌🔔🔔🍉🍉🍭🍭🍋🍋🍇🍇🏆🏆📸📸⛵⛵⭐⭐🍎🍎👍👍🌷🌷