遗传算法是一种受达尔文生物进化论和孟德尔遗传学说启发的启发式优化算法,通过模拟生物进化过程,在复杂搜索空间中寻找最优解或近似最优解。遗传算法的核心是将问题的解编码为染色体,每个染色体代表一个候选解,通过模拟生物进化中的选择、交叉、变异等操作,将适应度高的染色体保留并繁殖,同时引入新的基因多样性,逐代优化种群,最终逼近最优解。
算法流程

集合覆盖问题
集合覆盖问题还可以通过遗传算法解决,给定一个全集U和若干子集S1, S2, ..., Sn,找到最少数量的子集,使得它们的并集等于U。例如:
- 全集 U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5},子集 S1 = {1, 3}, S2 = {2, 3}, S3 = {3, 4}, S4 = {1, 4, 5}
- 最优解:[S2, S4] 最少需要2个子集才能覆盖所有元素。
遗传算法代码
java
public class GASetCover {
// 定义全集和子集
static Set<Integer> universe = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
static List<Set<Integer>> subsets = Arrays.asList(
new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(1, 3)),
new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(2, 3)),
new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(3, 4)),
new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(1, 4, 5))
);
static int numSubsets = subsets.size();
// 遗传算法参数
static int populationSize = 100; // 种群大小
static int maxGenerations = 1000; // 最大迭代次数
static double crossoverRate = 0.8; // 交叉概率
static double mutationRate = 0.01; // 变异概率
static int tournamentSize = 5; // 锦标赛选择大小
static List<List<Integer>> population; // 种群
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化种群
population = initializePopulation();
List<Integer> bestSolution = null;
int bestFitness = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int gen = 0; gen < maxGenerations; gen++) {
// 计算适应度并更新最优解
for (List<Integer> individual : population) {
int fitness = calculateFitness(individual);
if (fitness != -1 && (bestSolution == null || fitness < bestFitness)) {
bestFitness = fitness;
bestSolution = new ArrayList<>(individual);
}
}
// 生成下一代种群
List<List<Integer>> newPopulation = new ArrayList<>();
// 精英策略:保留当前代最优个体
if (bestSolution != null) {
newPopulation.add(new ArrayList<>(bestSolution));
}
// 生成剩余个体
while (newPopulation.size() < populationSize) {
//选择
List<Integer> parent1 = tournamentSelection();
List<Integer> parent2 = tournamentSelection();
//交叉
List<Integer> child = crossover(parent1, parent2);
//变异
child = mutate(child);
newPopulation.add(child);
}
population = newPopulation;
}
// 最优解
if (bestSolution != null) {
List<Integer> selectedIndices = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < numSubsets; i++) {
if (bestSolution.get(i) == 1) {
selectedIndices.add(i);
}
}
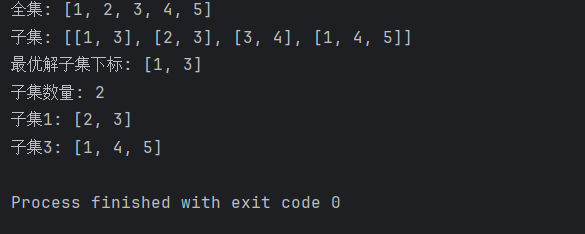
System.out.println("全集: " + universe);
System.out.println("子集: " + subsets);
System.out.println("最优解子集下标: " + selectedIndices);
System.out.println("子集数量: " + selectedIndices.size());
for (int i : selectedIndices) {
System.out.println("子集" + i + ": " + subsets.get(i));
}
} else {
System.out.println("未找到有效解");
}
}
// 初始化种群,生成随机二进制个体,1/0表示是否选择子集
private static List<List<Integer>> initializePopulation() {
List<List<Integer>> pop = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < populationSize; i++) {
List<Integer> individual = new ArrayList<>();
for (int j = 0; j < numSubsets; j++) {
individual.add(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(2));
}
pop.add(individual);
}
return pop;
}
// 计算适应度,返回子集数量
private static int calculateFitness(List<Integer> individual) {
Set<Integer> covered = new HashSet<>();
int selectedCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numSubsets; i++) {
if (individual.get(i) == 1) {
selectedCount++;
covered.addAll(subsets.get(i));
}
}
return covered.equals(universe) ? selectedCount : -1; // 有效解返回子集数量,否则返回-1
}
// 锦标赛选择,从种群中选择最优个体
private static List<Integer> tournamentSelection() {
List<List<Integer>> candidates = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < tournamentSize; i++) {
candidates.add(population.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(populationSize)));
}
// 选择适应度最高的个体
return candidates.stream()
.min(Comparator.comparingInt(GeneticAlgorithmSetCover::calculateFitness))
.orElse(population.get(0));
}
// 单点交叉操作
private static List<Integer> crossover(List<Integer> parent1, List<Integer> parent2) {
List<Integer> child = new ArrayList<>();
if (ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() < crossoverRate) {
// 随机交叉点
int crossPoint = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1, numSubsets);
// 前半段来自父代1,后半段来自父代2
child.addAll(parent1.subList(0, crossPoint));
child.addAll(parent2.subList(crossPoint, numSubsets));
} else {
// 不交叉时直接复制父代1
child.addAll(parent1);
}
return child;
}
// 变异操作,翻转基因位
private static List<Integer> mutate(List<Integer> individual) {
List<Integer> mutated = new ArrayList<>(individual);
for (int i = 0; i < numSubsets; i++) {
if (ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() < mutationRate) {
// 翻转基因
mutated.set(i, 1 - mutated.get(i));
}
}
return mutated;
}
}
遗传算法与蚁群算法区别
- 遗传算法:通过自然选择和交叉、变异等操作进化种群,适合处理离散型组合优化问题,结果依赖参数调优。
- 蚁群算法:基于信息素正反馈机制,适用于通过路径构建问题,收敛速度可能更快但结果依赖信息素参数。