本系列为笔者的 Leetcode 刷题记录,顺序为 Hot 100 题官方顺序,根据标签命名,记录笔者总结的做题思路,附部分代码解释和疑问解答,01~07为C++语言,08及以后为Java语言。
01 合并两个有序链表
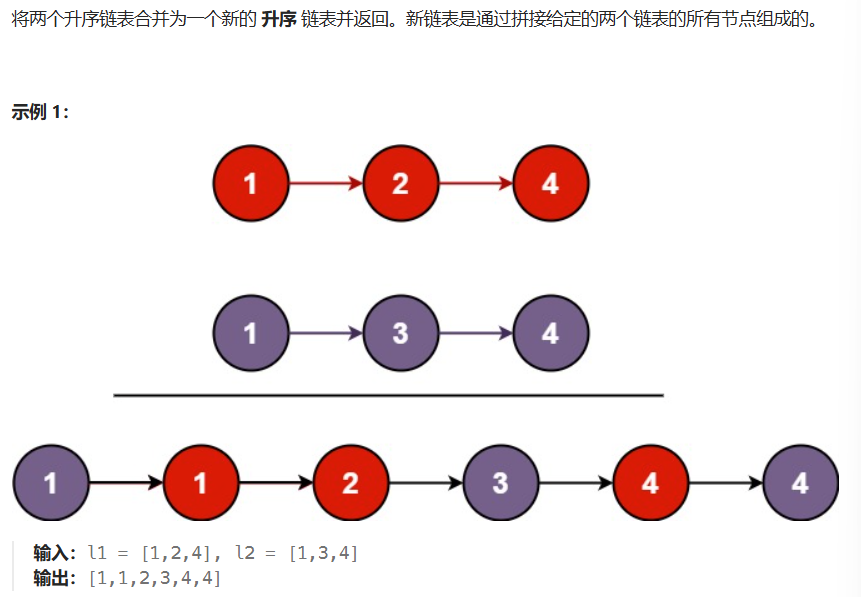
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
}
}方法一:递归
java
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}else if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}else if(list1.val < list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
}else{
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}方法二:遍历
java
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode list3 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode flag = list3; //论标记的重要性
while(list1 != null && list2 != null){
if(list1.val < list2.val){
list3.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}else{
list3.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
list3 = list3.next;
}
if(list1 != null){
list3.next = list1;
}else{
list3.next = list2;
}
return flag.next; //返回头结点指针
}
}02 两数相加

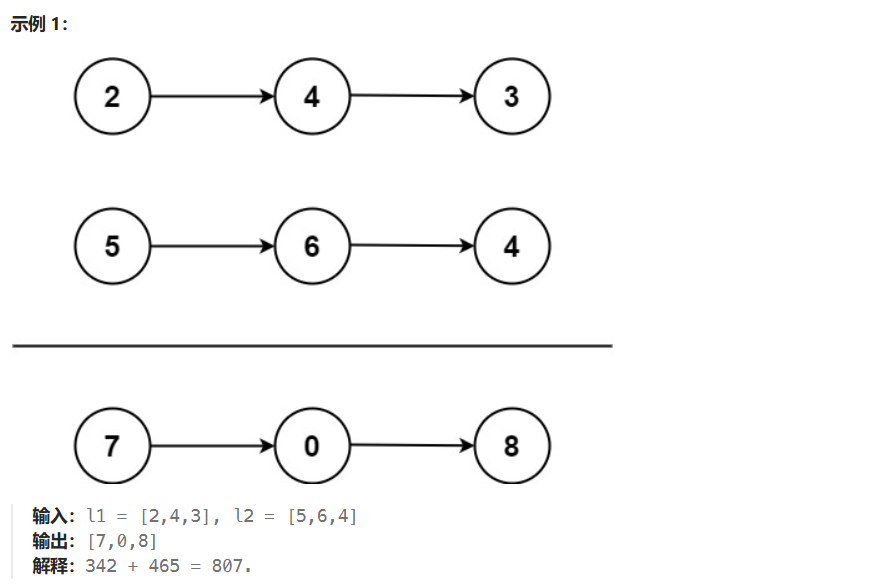
方法一:设新链表、进位值,不断创建新节点
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode start = null, end = null;
int flag = 0;
while(l1 != null || l2 != null){
//1. 计算单位加和
int n1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
int n2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
int sum = n1 + n2 + flag;
//2. 添加新链表结点,计算进位
if(start == null){
start = end = new ListNode(sum % 10);
}else{
end.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
end = end.next;
}
flag = sum / 10;
//3. 移动结点
if(l1 != null){
l1 = l1.next;
}
if(l2 != null){
l2 = l2.next;
}
}
//4. 特殊情况:高位进一
if(flag > 0){
end.next = new ListNode(flag);
}
return start;
}
}03 删除链表的倒数第N个结点
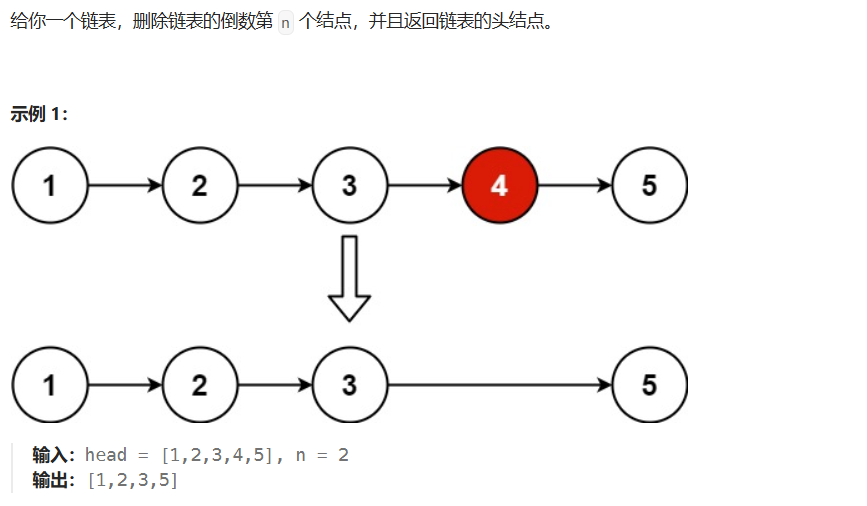

java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = dummy; //可移动结点
//1. first移动n位
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i){
first = first.next;
}
//2. first、second同时移动,first=null为止
while(first != null){
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
//3. 删除结点,释放空间
second.next = second.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}① dummy.next不是head吗,那么ListNode ans = dummy.next; return ans;存在的意义是什么?
如果 n 等于链表的长度,即需要删除头节点时,单独使用 head 会导致很复杂的边界条件处理,在这种情况下,dummy 提供一个可靠的起始节点,方便统一处理删除节点的逻辑。
② 为什么要新建一个链表ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);,而不是在原有链表上操作?
dummy节点简化了边界条件的处理,所有节点,无论是否是头节点,都可以以一致的方式处理,最终可以直接返回dummy.next作为结果,这样不会影响原始链表的头节点指向。
04 两两交换链表中的节点
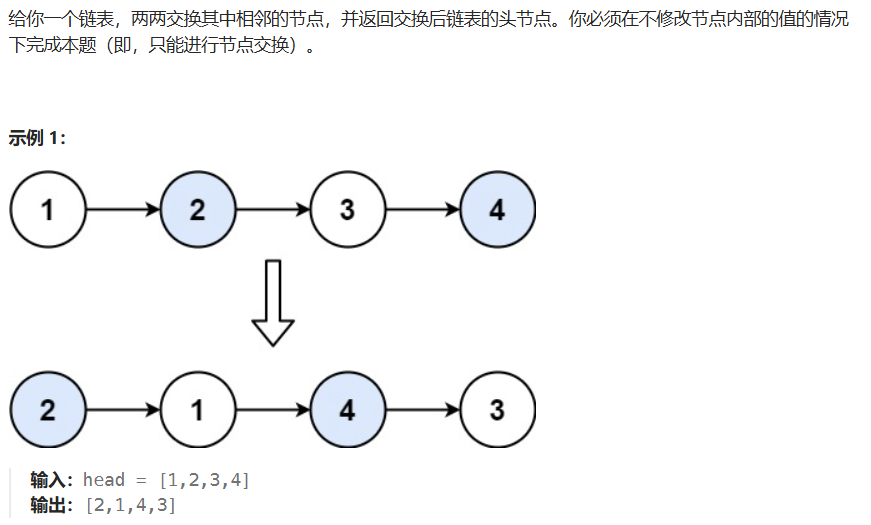

java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode flag = dummy; //可移动结点
while(flag.next != null && flag.next.next != null){
//1. 顺次两个节点
ListNode a = flag.next;
ListNode b = flag.next.next;
//2. 交换
flag.next = b;
a.next = b.next;
b.next = a;
flag = a;
}
return dummy.next; //万金油
}
}05 K个一组翻转链表
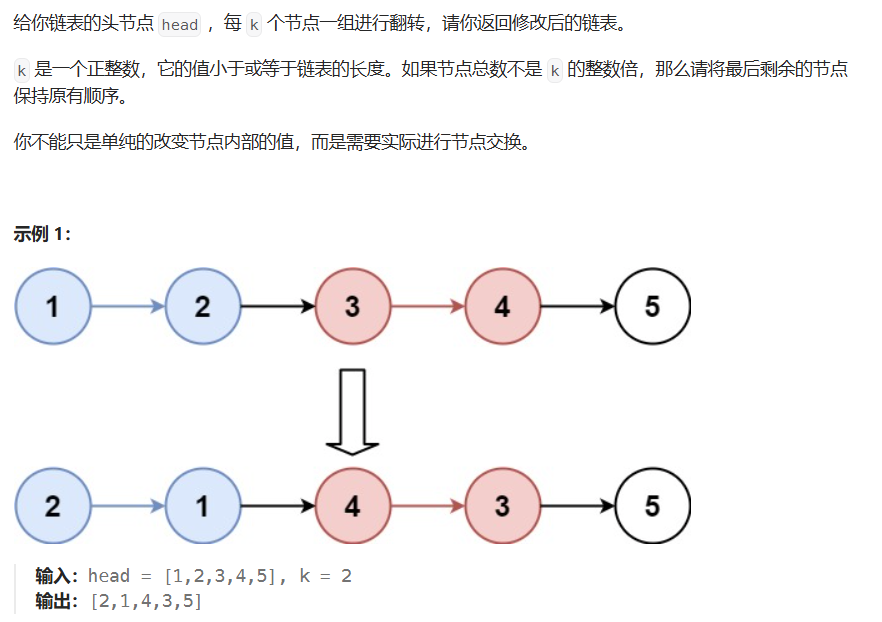
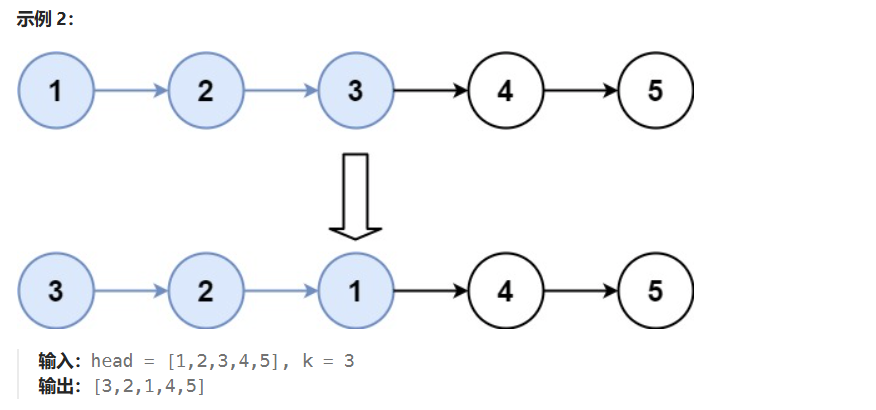
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//需要pre,head,tail,nex四个指针
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
//1.创建dummy链表,返回dummy.next
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
//2.寻找(head,tail),调用myReverse方法
while(head != null){
ListNode tail = pre;
for(int i=0; i<k; ++i){
tail = tail.next;
if(tail == null){
return dummy.next;
}
}
ListNode nex = tail.next;
ListNode[] reverse = myReverse(head, tail);
head = reverse[0];
tail = reverse[1];
//3.连接断裂链表
pre.next = head;
tail.next = nex;
pre = tail;
head = nex;
}
return dummy.next;
}
//需要a,b,c三个指针
public ListNode[] myReverse(ListNode start, ListNode end){
//1.寻找a,b,c
//2.核心操作:a->c
//3.临界条件:end==c
ListNode a = start;
ListNode c = end.next;
while(end != c){
ListNode b = a.next;
a.next = c;
c = a;
a = b;
}
return new ListNode[]{end, start};
}
}06 随机链表的复制
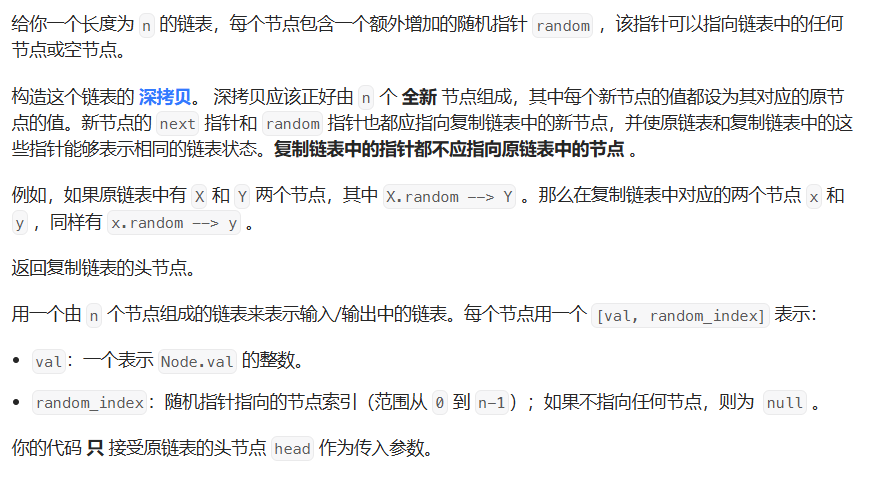
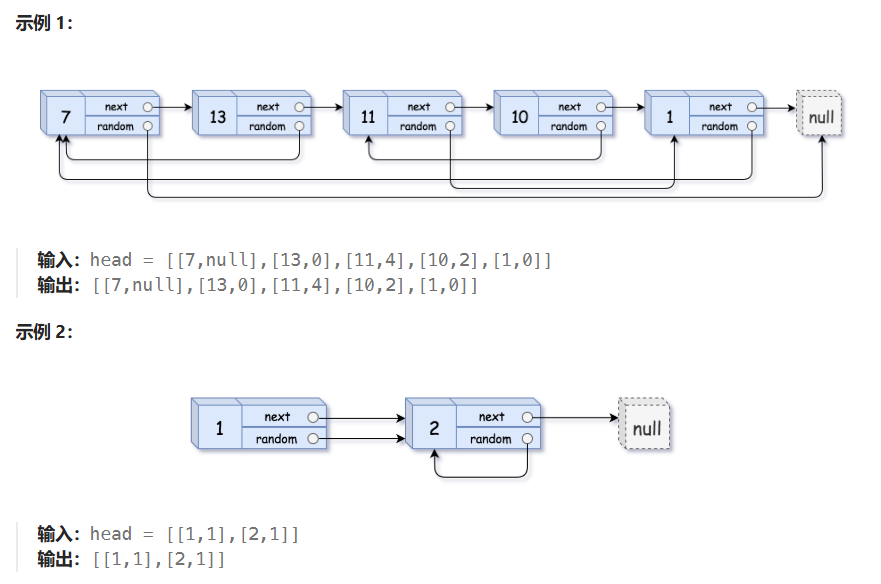
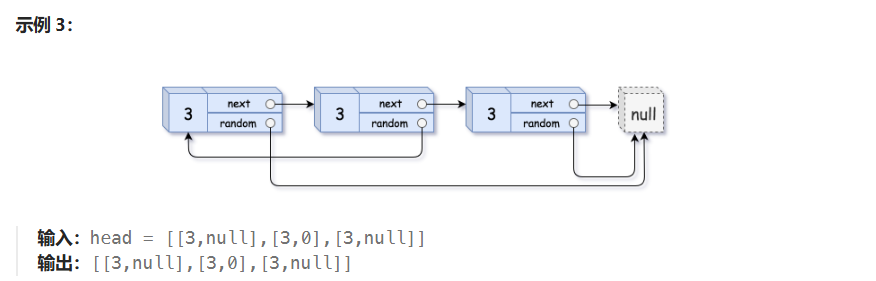
失败代码
java
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
//1.创建dummy链表,返回dummy.next
Node dummy = new Node(0);
dummy.next = head;
//2.第一次遍历,复制结点值和next指针
Node end = dummy;
Node start = head;
while(start != null){
end.next = new Node(start.val); //复制结点值
end = end.next;
end.next = start.next; //复制next指针
start = start.next;
}
//3.第二次遍历,复制random指针
Node end2 = dummy;
Node start2 = head;
while(start2 != null){
end2 = end2.next;
end2.random = start2.random; //复制random指针
start2 = start2.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}问题:当前复制的 random 指针仍然指向原链表中的节点,而不是新复制链表中的节点。
方法一:递归
java
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
//1.创建映射
Map<Node, Node> cachedNode = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
//2.创建新节点,拷贝val
if(!cachedNode.containsKey(head)){
Node headNew = new Node(head.val);
cachedNode.put(head, headNew);
//3.递归,拷贝next,random
headNew.next = copyRandomList(head.next);
headNew.random = copyRandomList(head.random);
}
return cachedNode.get(head);
}
}方法二:结点拆分
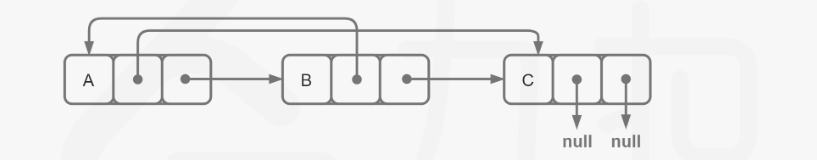
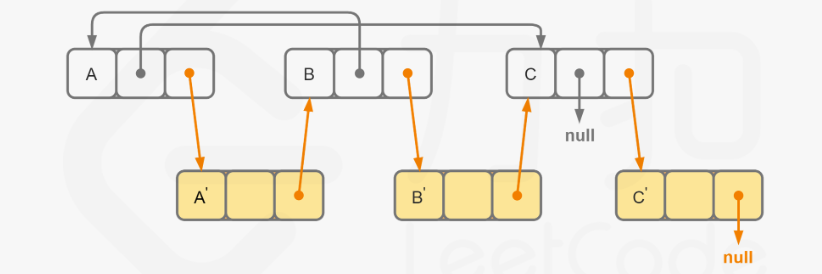
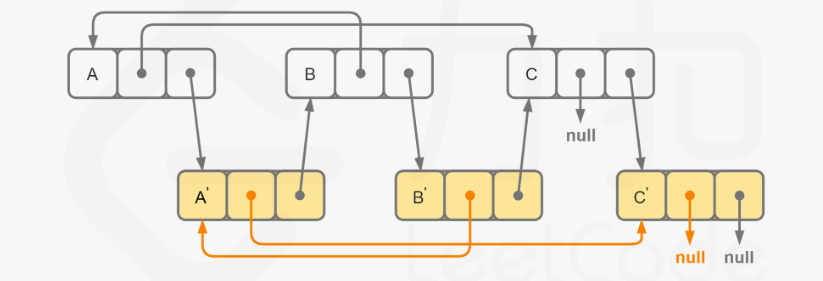
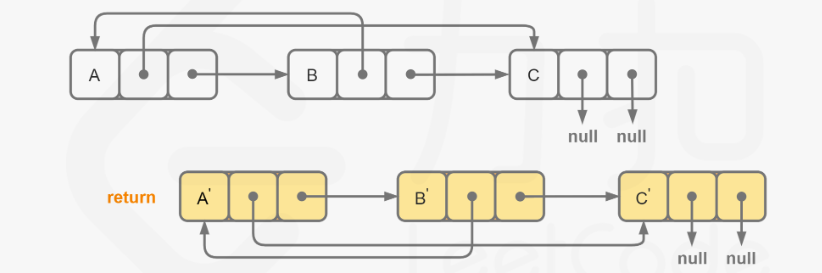
java
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
//1. 一次遍历:节点插入,拷贝val
for(Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next){
Node nodeNew = new Node(node.val);
nodeNew.next = node.next;
node.next = nodeNew;
}
//2. 二次遍历:拷贝random
for(Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next.next){
Node nodeNew = node.next;
nodeNew.random = (node.random != null) ? node.random.next : null;
}
//3. 三次遍历:拷贝next
Node headNew = head.next;
for(Node node = head; node != null; node = node.next){
Node nodeNew = node.next;
node.next = node.next.next;
nodeNew.next = (node.next != null) ? nodeNew.next.next : null;
}
return headNew;
}
}07 排序链表
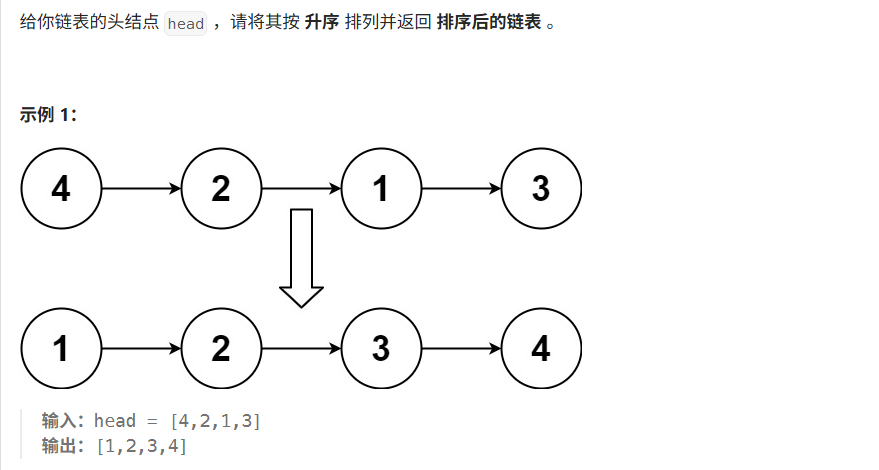
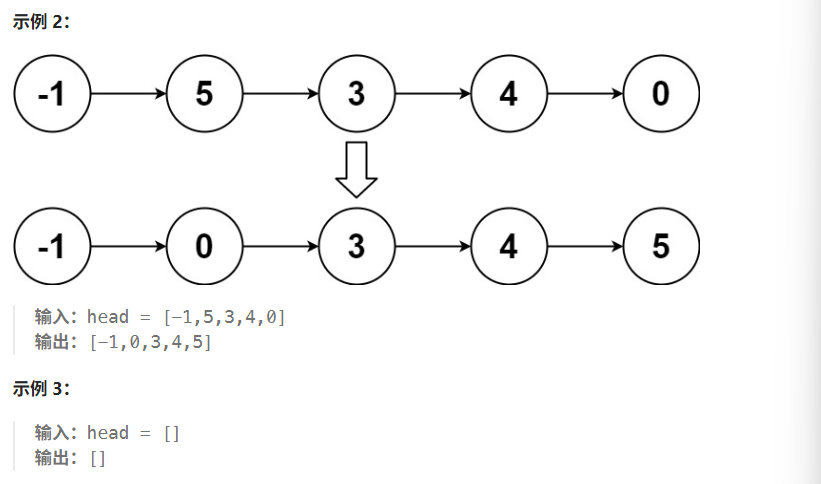
方法一:快慢指针归并排序 + 合并有序链表
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return sortList(head, null); //没说区间,默认右端点为null
}
//1.伪二分(快慢指针)
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head, ListNode tail){
// if(head == null || head.next == tail){ //特殊情况判断
// return head;
// }
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
if (head.next == tail) {
head.next = null;
return head;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != tail){
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast != tail){
fast = fast.next;
}
}
//2.归并排序(head,tail)
ListNode mid = slow;
ListNode list1 = sortList(head, mid);
ListNode list2 = sortList(mid, tail);
ListNode sorted = mergeList(list1, list2);
return sorted;
}
//3.合并两个有序链表
public ListNode mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2){
ListNode l3 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode flag = l3; //return flag.next;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val < l2.val){
l3.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
l3.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
l3 = l3.next;
}
if(l1 != null){
l3.next = l1;
}
if(l2 != null){
l3.next = l2;
}
return flag.next;
}
}方法二:倍增长度 + 合并两个有序链表
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){ //特殊情况判断
return head;
}
//1.获取链表长度length
int length = 0;
ListNode node = head;
while(node != null){
length++;
node = node.next;
}
//2.倍增长度subLength
//a.四指针 pre/head1/head2/nex
//b.两断链
//c.一接骨
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for(int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1){
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode curr = dummy.next;
while(curr != null){
ListNode head1 = curr;
for(int i=1; i<length && curr.next != null; i++){
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode head2 = curr;
curr.next = null;
curr = head2;
for(int i=1; i<length && curr.next != null && curr != null; i++){
curr = curr.next;
}
ListNode nex = null;
if(curr.next != null){
nex = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
}
ListNode merged = mergeList(head1, head2);
pre.next = merged;
pre = curr;
curr = nex;
}
}
//3.合并方法
return dummy.next;
}
//合并两个有序链表
public ListNode mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2){
ListNode l3 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode flag = l3; //return flag.next;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val < l2.val){
l3.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
l3.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
l3 = l3.next;
}
if(l1 != null){
l3.next = l1;
}
if(l2 != null){
l3.next = l2;
}
return flag.next;
}
}.next;
}
//合并两个有序链表
public ListNode mergeList(ListNode l1, ListNode l2){
ListNode l3 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode flag = l3; //return flag.next;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val < l2.val){
l3.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
l3.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
l3 = l3.next;
}
if(l1 != null){
l3.next = l1;
}
if(l2 != null){
l3.next = l2;
}
return flag.next;
}}