1. 分布式训练核心概念
1.1 并行策略对比
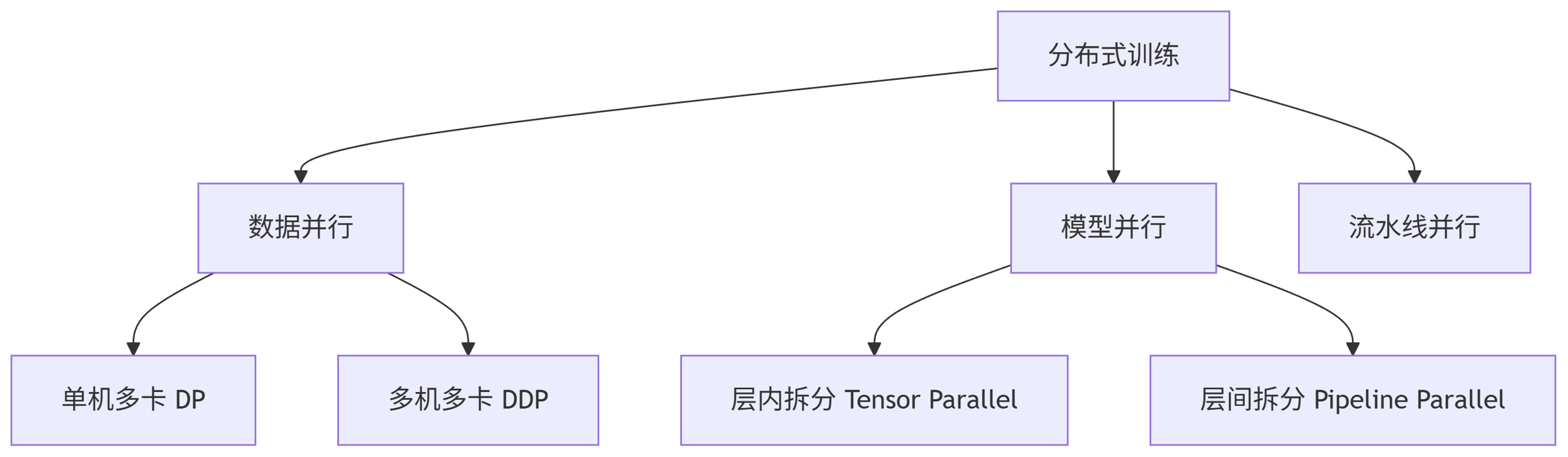
graph TD
A[分布式训练] --> B[数据并行]
A --> C[模型并行]
A --> D[流水线并行]
B --> B1[单机多卡 DP]
B --> B2[多机多卡 DDP]
C --> C1[层内拆分 Tensor Parallel]
C --> C2[层间拆分 Pipeline Parallel]
1.2 关键组件
| 组件 | 功能 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
torch.distributed |
分布式通信后端 | NCCL, Gloo, MPI |
DistributedDataParallel |
数据并行实现 | DDP |
RPC |
远程过程调用 | 模型并行 |
DataLoader |
分布式数据采样 | DistributedSampler |
2. 数据并行实践
2.1 DP vs DDP 架构
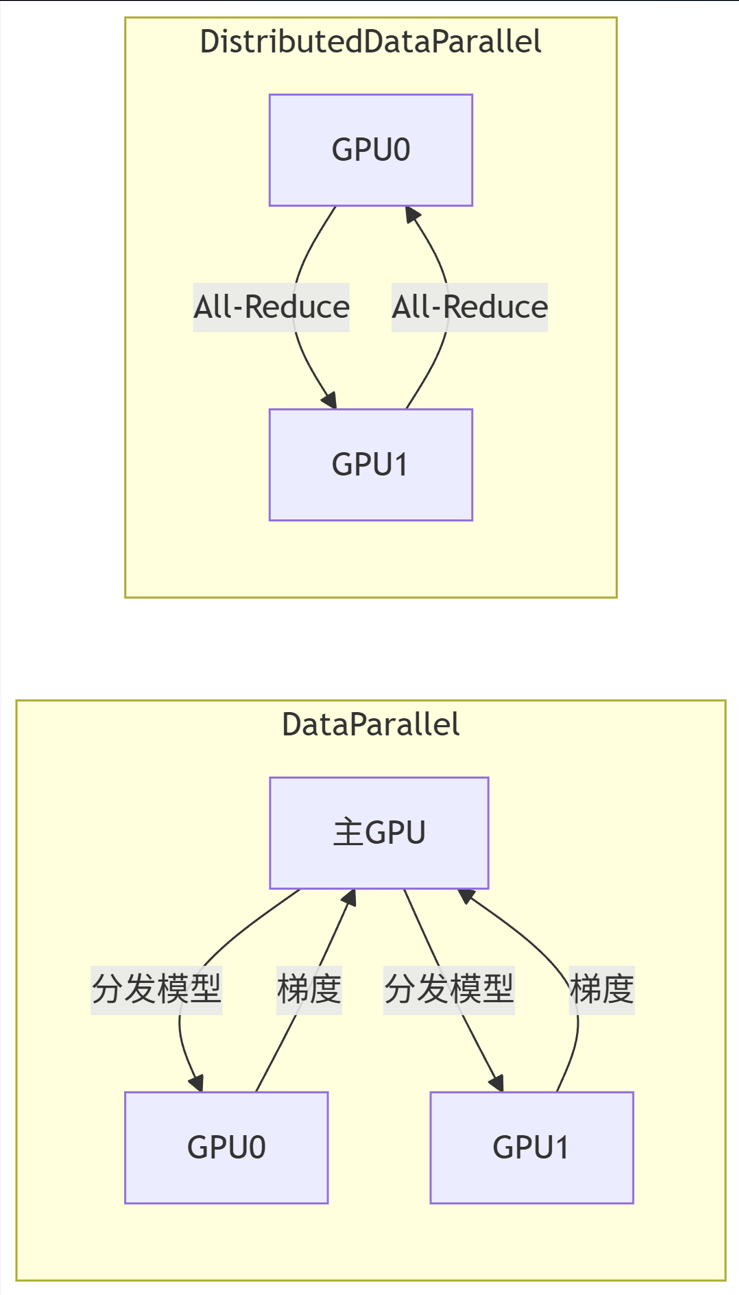
graph LR
subgraph DP[DataParallel]
Master[主GPU] -->|分发模型| Worker1[GPU0]
Master -->|分发模型| Worker2[GPU1]
Worker1 -->|梯度| Master
Worker2 -->|梯度| Master
end
subgraph DDP[DistributedDataParallel]
WorkerA[GPU0] -->|All-Reduce| WorkerB[GPU1]
WorkerB -->|All-Reduce| WorkerA
end
2.2 DDP 训练代码
python
import torch
import torch.distributed as dist
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel as DDP
def setup(rank, world_size):
dist.init_process_group("nccl", rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
torch.cuda.set_device(rank)
def cleanup():
dist.destroy_process_group()
def train(rank, world_size):
setup(rank, world_size)
# 1. 准备模型
model = ResNet50().to(rank)
ddp_model = DDP(model, device_ids=[rank])
# 2. 分布式数据加载器
dataset = ImageDataset(...)
sampler = DistributedSampler(dataset, num_replicas=world_size, rank=rank)
loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64, sampler=sampler)
# 3. 训练循环
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(ddp_model.parameters())
for epoch in range(10):
sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
for x, y in loader:
x, y = x.to(rank), y.to(rank)
loss = ddp_model(x, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
cleanup()
# 启动脚本: torchrun --nproc_per_node=4 --nnodes=2 train.py3. 混合精度训练
3.1 AMP 工作流程
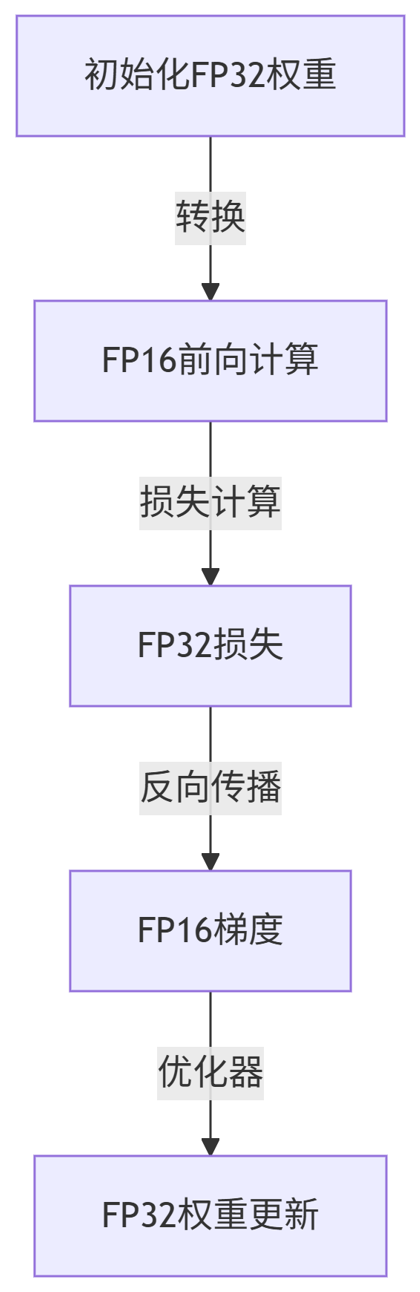
flowchart TB
FP32[初始化FP32权重] -->|转换| FP16[FP16前向计算]
FP16 -->|损失计算| Loss[FP32损失]
Loss -->|反向传播| Grad[FP16梯度]
Grad -->|优化器| Update[FP32权重更新]
3.2 AMP 代码实现
python
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast, GradScaler
scaler = GradScaler()
for x, y in loader:
optimizer.zero_grad()
with autocast():
outputs = model(x)
loss = criterion(outputs, y)
# 缩放梯度避免下溢
scaler.scale(loss).backward()
# 梯度裁剪
scaler.unscale_(optimizer)
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), 1.0)
# 更新参数
scaler.step(optimizer)
scaler.update()4. 模型并行技术
4.1 模型拆分策略
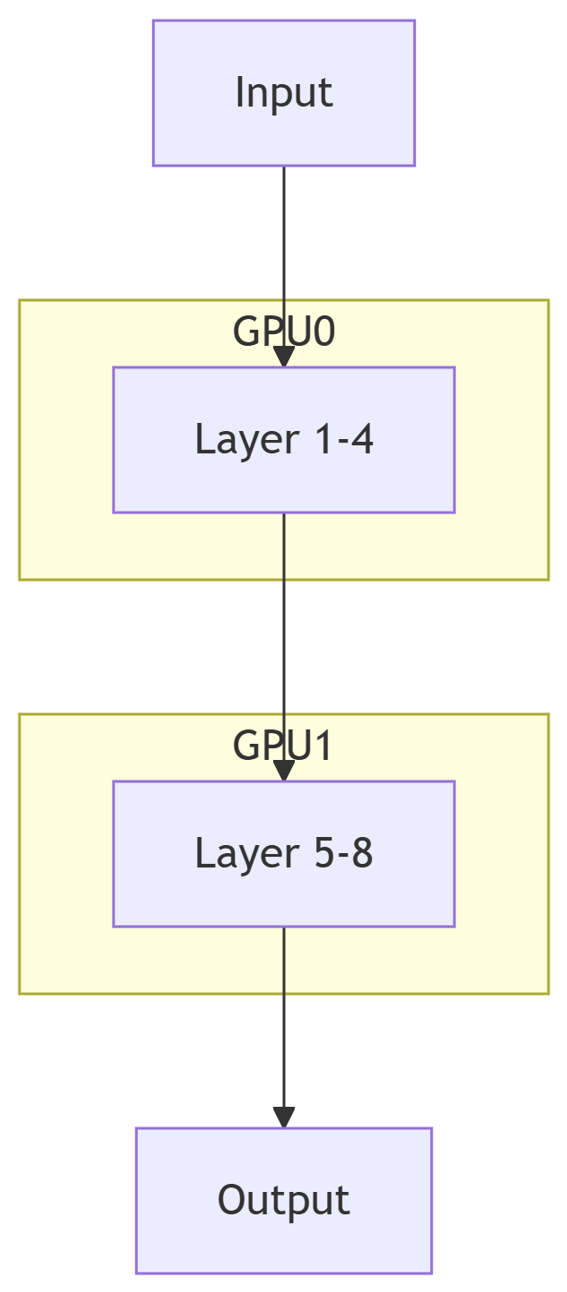
graph TB
Input --> Layer1
subgraph GPU0
Layer1[Layer 1-4]
end
Layer1 --> Layer2
subgraph GPU1
Layer2[Layer 5-8]
end
Layer2 --> Output
4.2 使用 PiPPy 实现流水线并行
python
from torch.distributed.pipeline.sync import Pipe
# 1. 模型拆分
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1024, 2048).to('cuda:0'),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(2048, 4096).to('cuda:1'),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(4096, 10).to('cuda:2')
)
# 2. 创建流水线
pipe_model = Pipe(model, chunks=8) # 拆分微批次
# 3. 训练
output = pipe_model(input)
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()5. 性能优化技巧
5.1 通信优化策略
| 技术 | 原理 | 提升效果 |
|---|---|---|
| 梯度累积 | 多次迭代后更新 | 减少通信频率 |
| Bucketing | 梯度分组聚合 | 减少通信次数 |
| Overlap | 计算通信重叠 | 隐藏延迟 |
python
# Bucketing 示例 (DDP)
ddp_model = DDP(model,
device_ids=[rank],
bucket_cap_mb=25, # 25MB桶大小
find_unused_parameters=False)5.2 计算性能分析
gantt
title 训练时间分布 (4x A100)
dateFormat s
section GPU0
数据加载 :a1, 0, 2s
前向计算 :a2, after a1, 4s
反向传播 :a3, after a2, 5s
section GPU1
通信等待 :b1, 0, 3s
梯度聚合 :b2, after b1, 2s
6. 弹性训练与容错
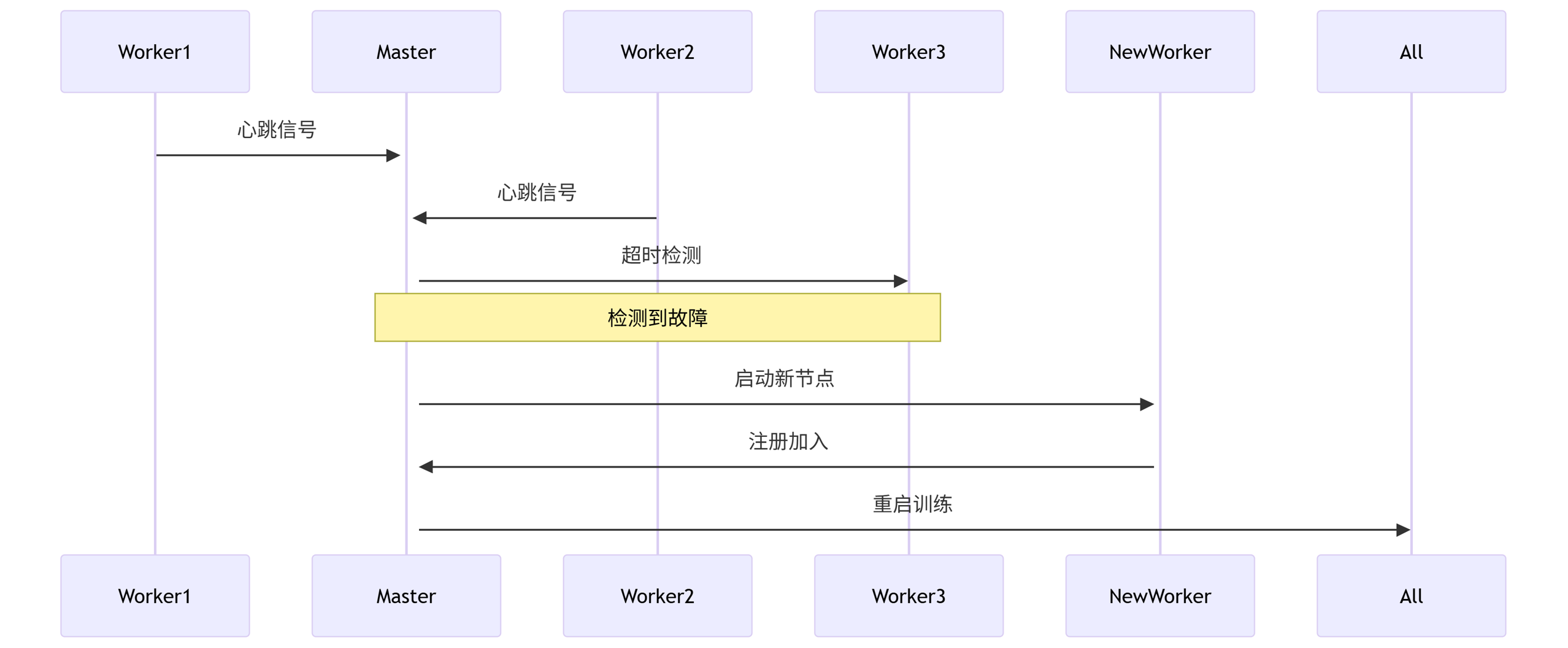
6.1 弹性训练架构
sequenceDiagram
Worker1->>+Master: 心跳信号
Worker2->>+Master: 心跳信号
Master->>Worker3: 超时检测
Note over Master,Worker3: 检测到故障
Master->>+NewWorker: 启动新节点
NewWorker->>Master: 注册加入
Master->>All: 重启训练
6.2 使用 TorchElastic
python
from torch.distributed.elastic.agent.api import ElasticAgent
def train_fn(args):
# 训练逻辑
agent = ElasticAgent(
local_world_size=8,
entrypoint=train_fn,
max_restarts=3
)
agent.run()7. 实战案例:分布式训练ResNet-152
7.1 集群配置
| 组件 | 规格 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|
| GPU | NVIDIA A100 80GB | 16 |
| 网络 | InfiniBand HDR 200Gb/s | 1 |
| CPU | AMD EPYC 7763 | 4 |
7.2 性能对比
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
gpus = [1, 2, 4, 8, 16]
speedup = [1.0, 1.8, 3.5, 6.2, 11.0] # 实际加速比
ideal = gpus # 理想加速比
plt.plot(gpus, speedup, 'o-', label='实际加速')
plt.plot(gpus, ideal, '--', label='理想加速')
plt.xlabel('GPU数量')
plt.ylabel('加速比')
plt.title('ResNet-152分布式训练扩展性')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig('scaling.png')8. 调试与性能分析
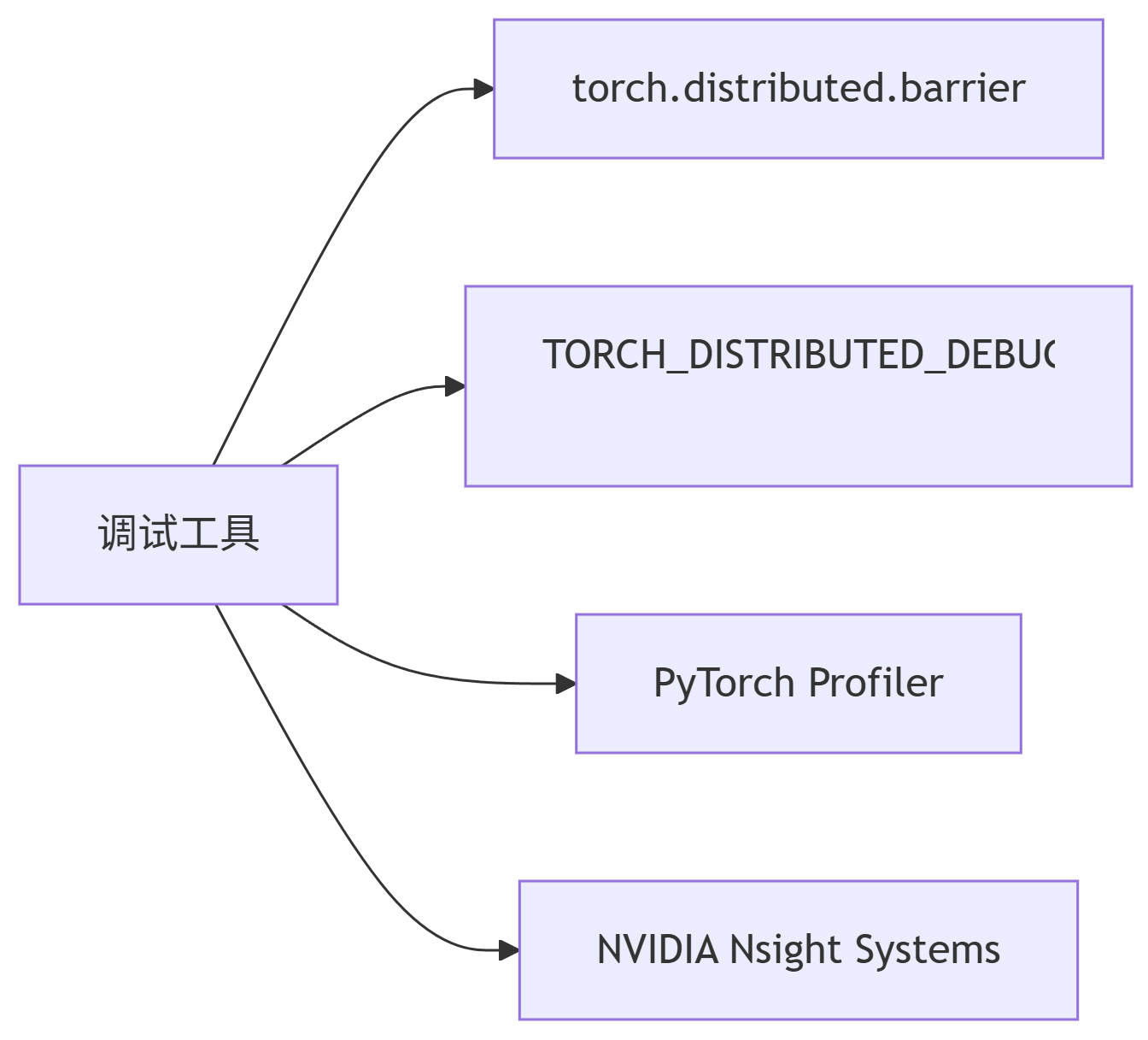
8.1 常用工具
graph LR
A[调试工具] --> B[torch.distributed.barrier]
A --> C[TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_DEBUG=DETAIL]
A --> D[PyTorch Profiler]
A --> E[NVIDIA Nsight Systems]
8.2 Profiler 使用
python
with torch.profiler.profile(
activities=[torch.profiler.ProfilerActivity.CPU,
torch.profiler.ProfilerActivity.CUDA],
schedule=torch.profiler.schedule(wait=1, warmup=1, active=3),
on_trace_ready=torch.profiler.tensorboard_trace_handler('./log'),
record_shapes=True
) as prof:
for step, data in enumerate(loader):
if step >= 5: break
train_step(data)
prof.step()9. 前沿技术扩展
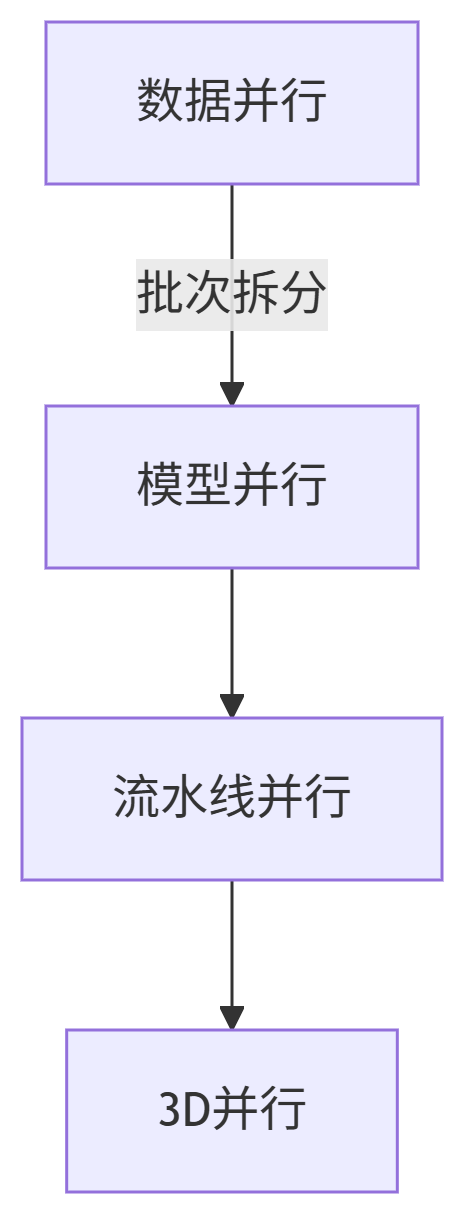
9.1 3D并行整合
graph TD
Data[数据并行] -->|批次拆分| Model[模型并行]
Model --> Pipeline[流水线并行]
Pipeline --> Full[3D并行]
9.2 DeepSpeed 集成
python
# DeepSpeed 配置文件 ds_config.json
{
"train_batch_size": 4096,
"fp16": {"enabled": true},
"zero_optimization": {
"stage": 3,
"offload_optimizer": {"device": "cpu"}
}
}
# 初始化
model, optimizer, _, _ = deepspeed.initialize(
model=model,
model_parameters=params,
config_params="ds_config.json"
)10. 性能优化最佳实践
-
通信优化:
python
# 设置环境变量提升NCCL性能 os.environ["NCCL_ALGO"] = "Tree" os.environ["NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME"] = "ib0" -
计算优化:
python
# Kernel融合 torch.jit.script_module = torch.jit.script(model) -
内存优化:
python
# 激活检查点 model = checkpoint_sequential(model, segments=4)
总结:分布式训练路线图
journey
title PyTorch分布式训练演进
section 基础阶段
单机DP: 2020: DataParallel
多机DDP: 2021: DistributedDataParallel
section 进阶阶段
混合精度: 2022: AMP/Apex
模型并行: 2023: PiPPy/FSDP
section 前沿阶段
3D并行: 2024: DeepSpeed集成
弹性训练: 2025: TorchElastic
最佳实践建议:
8卡以下使用DDP+AMP
超大模型使用ZeRO-3+流水线并行
定期用Profiler分析性能瓶颈
完整代码库 :
https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/main/distributed
通过本指南,您已掌握PyTorch分布式训练的核心技术和实践方法,能够高效利用GPU集群训练大规模深度学习模型。