73. 矩阵置零
给定一个 m x n 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 0 ,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 0 。请使用 原地 算法。
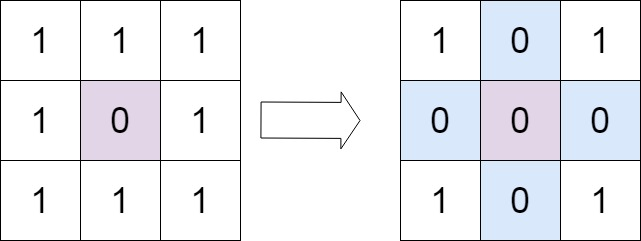
示例 1:
输入:matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
输出:[[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
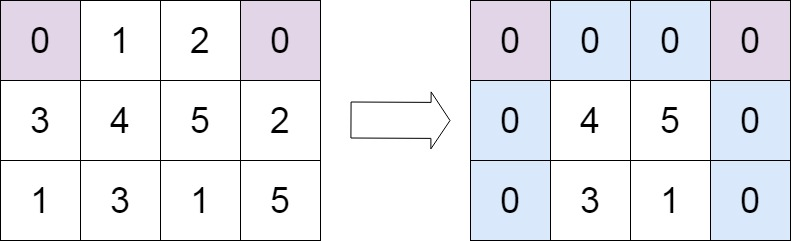
示例 2:
输入:matrix = [[0,1,2,0],[3,4,5,2],[1,3,1,5]]
输出:[[0,0,0,0],[0,4,5,0],[0,3,1,0]]
一、用额外空间(不符题意)
- 遍历矩阵,记录哪些行和列包含0
- 再次遍历,将对应行列置零
python
def setZeroes_v1(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
if not matrix or not matrix[0]: # []和[[]]情况(题目说m,n>=1,可以不写,但要没说就一定要写这里)
return
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
zero_rows = set()
zero_cols = set()
# 第一次遍历,记录包含0的行和列
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if matrix[i][j] == 0:
zero_rows.add(i)
zero_cols.add(j)
# 第二次遍历,将对应行列置零
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if i in zero_rows or j in zero_cols:
matrix[i][j] = 0- 时间复杂度 O(m * n)
- 空间复杂度 O(m + n)
二、原地方法【推荐】
- 【思路】用第一行记录列、用第一列记录行
- 利用矩阵的第一行和第一列来记录哪些行列需要置零
- 需要特殊处理第一行和第一列本身是否包含0的情况
- 【步骤】
- 检查第一行和第一列是否本身包含0,用两个标志位记录
- 遍历矩阵其余部分,如果发现0,则在对应的第一行(记列 信息)和第一列(记行信息)位置标记
- 根据第一行和第一列的标记,将对应行列置零
- 最后根据标志位处理第一行和第一列
python
def setZeroes_v1(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
if not matrix or not matrix[0]: # []和[[]](虽然题目说m,n>=1,可以不写,但要没说就一定要写这里)
return
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0]) # m行,n列
# 检查第一行和第一列是否包含0
first_row_zero = any(matrix[0][j] == 0 for j in range(n)) # 【注意】检查行要遍历列
first_col_zero = any(matrix[i][0] == 0 for i in range(m)) # 【注意】检查列要遍历行
# 遍历矩阵其余部分,使用第一行和第一列作为标记
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
if matrix[i][j] == 0:
matrix[i][0] = 0 # 标记该行需要置零
matrix[0][j] = 0 # 标记该列需要置零
# 根据标记将对应行列置零
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
if matrix[i][0] == 0 or matrix[0][j] == 0:
matrix[i][j] = 0
# 处理第一行
if first_row_zero:
for j in range(n):
matrix[0][j] = 0
# 处理第一列
if first_col_zero:
for i in range(m):
matrix[i][0] = 054. 螺旋矩阵
给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
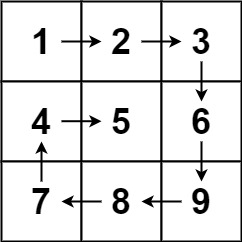
示例 1:
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
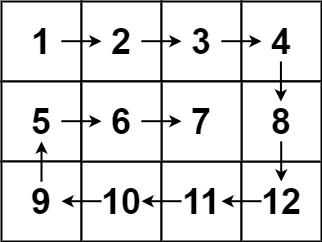
示例 2:
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
一、四个边界指针【最推荐】
- 【思路】
- 维护四个边界:
top,bottom,left,right - 每遍历完一条边,对应边界向内收缩
- 注意处理单行或单列的情况
- 维护四个边界:
- 【步骤】
- 初始化四个边界指针
- 按照右→下→左→上的顺序遍历上/右/下/左边界
- 每遍历完一条边,先 收缩对应边界,再开始下一条边的遍历
- 当边界重叠时结束遍历
while top <= bottom and left <= right:(注意top小哦)
python
def spiralOrder_v1(matrix):
if not matrix or not matrix[0]:
return []
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
res = []
# 四个边界指针
top, bottom = 0, m - 1
left, right = 0, n - 1
while top <= bottom and left <= right: # 一定记得要加=号啊!不然最中心的遍历不到!!
# 1. 向右遍历上边界
for j in range(left, right + 1):
res.append(matrix[top][j])
top += 1
# 2. 向下遍历右边界
for i in range(top, bottom + 1):
res.append(matrix[i][right])
right -= 1
# 3. 向左遍历下边界(需要检查是否还有行)
if top <= bottom: # 就算在本轮迭代中,上面已经top++过,所以要再检查!!!
for j in range(right, left - 1, -1):
res.append(matrix[bottom][j])
bottom -= 1
# 4. 向上遍历左边界(需要检查是否还有列)
if left <= right: # 就算在本轮迭代中,上面已经right--过,所以要再检查!!!
for i in range(bottom, top - 1, -1):
res.append(matrix[i][left])
left += 1
return res- 时间复杂度 O(m*n)
- 空间复杂度 O(1):不算结果数组的话
- 【注意】因为循环条件
while top <= bottom and left <= right:中有等于号,所以循环中遍历bottom和left前一定要检查if top <= bottom:和if left <= right:!!不然最后一轮循环中(开头就重叠,上面两条边再+/-)还会额外添加一个值进去!!! - ------>记忆: "遍历bottom前检查top,遍历left前检查right"!!!
二、方向数组
- 使用方向数组表示四个方向的移动
- 遇到边界或已访问元素时改变方向
- 使用visited数组标记已访问元素
python
def spiralOrder_v2(matrix):
if not matrix or not matrix[0]:
return []
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
result = []
visited = [[False] * n for _ in range(m)]
# 方向数组:右、下、左、上
directions = [(0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -1), (-1, 0)]
direction_idx = 0
row, col = 0, 0
for _ in range(m * n):
result.append(matrix[row][col])
visited[row][col] = True
# 计算下一个位置
next_row = row + directions[direction_idx][0]
next_col = col + directions[direction_idx][1]
# 检查是否需要转向
if (next_row < 0 or next_row >= m or
next_col < 0 or next_col >= n or
visited[next_row][next_col]):
# 转向
direction_idx = (direction_idx + 1) % 4
next_row = row + directions[direction_idx][0]
next_col = col + directions[direction_idx][1]
row, col = next_row, next_col
return result- 时间复杂度 O(m*n)
- 空间复杂度 O(m*n)
三、递归分治
- 递归处理外圈和内圈
- 每次递归处理当前矩形的一圈
python
def spiralOrder_v3(matrix):
if not matrix or not matrix[0]:
return []
def spiral_helper(matrix, start_row, end_row, start_col, end_col):
if start_row > end_row or start_col > end_col:
return []
result = []
# 只有一行
if start_row == end_row:
for j in range(start_col, end_col + 1):
result.append(matrix[start_row][j])
return result
# 只有一列
if start_col == end_col:
for i in range(start_row, end_row + 1):
result.append(matrix[i][start_col])
return result
# 遍历外圈
# 上边界
for j in range(start_col, end_col):
result.append(matrix[start_row][j])
# 右边界
for i in range(start_row, end_row):
result.append(matrix[i][end_col])
# 下边界
for j in range(end_col, start_col, -1):
result.append(matrix[end_row][j])
# 左边界
for i in range(end_row, start_row, -1):
result.append(matrix[i][start_col])
# 递归处理内圈
result.extend(spiral_helper(matrix, start_row + 1, end_row - 1,
start_col + 1, end_col - 1))
return result
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
return spiral_helper(matrix, 0, m - 1, 0, n - 1)- 时间复杂度 O(m*n)
- 空间复杂度 O(min(m,n)):递归栈深度
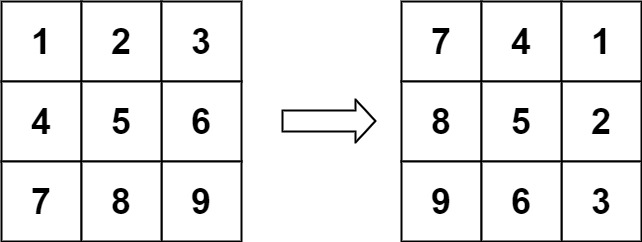
48. 旋转图像
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
你必须在原地 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
示例 1:
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]]
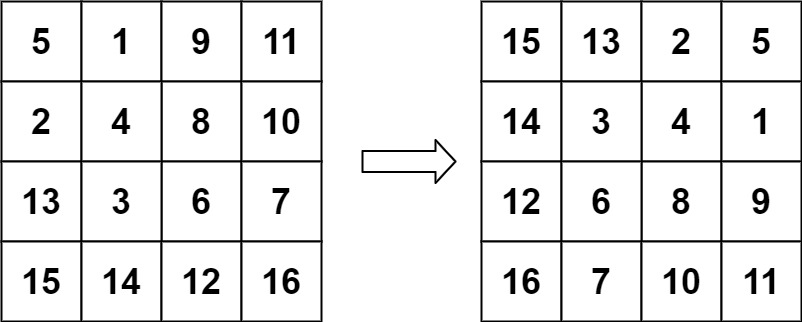
示例 2:
输入:matrix = [[5,1,9,11],[2,4,8,10],[13,3,6,7],[15,14,12,16]]
输出:[[15,13,2,5],[14,3,4,1],[12,6,8,9],[16,7,10,11]]
一、转置 + 水平翻转 = 顺时针90°旋转 【推荐】
-
【原理】旋转90°的数学本质:
(i,j) → (j, n-1-i) -
【思路】先转置,再沿中轴线水平翻转
matrix[i][j] → matrix[j][i] → matrix[j][n-1-i]原矩阵 转置后 水平翻转后 [1,2,3] [1,4,7] [7,4,1] [4,5,6] → [2,5,8] → [8,5,2] [7,8,9] [3,6,9] [9,6,3] -
【算法步骤】
- 转置矩阵:
matrix[i][j]与matrix[j][i]交换 - 水平翻转:每行沿中轴线左右对称交换(是镜像,也是
reverse())
- 转置矩阵:
python
def rotate(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
n = len(matrix)
# 第一步:转置矩阵(沿主对角线翻折)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i, n): # 只处理上三角,避免重复交换
matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i] = matrix[j][i], matrix[i][j]
# 第二步:水平翻转(每行左右对称交换)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n // 2):
matrix[i][j], matrix[i][n - 1 - j] = matrix[i][n - 1 - j], matrix[i][j]
# 或者直接reverse每一行:
'''
for i in range(n):
matrix[i].reverse()
'''- 时间复杂度 O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度 O(1)
二、四元素循环法
- 【思路】每次处理四个位置的元素循环移动:
(i,j) → (j,n-1-i) → (n-1-i,n-1-j) → (n-1-j,i) → (i,j)
python
def rotate(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
n = len(matrix)
# 处理每一层(环)
for layer in range(n // 2):
first = layer
last = n - 1 - layer
# 处理当前层的每个元素
for i in range(first, last):
offset = i - first
# 保存top元素
top = matrix[first][i]
# left → top
matrix[first][i] = matrix[last - offset][first]
# bottom → left
matrix[last - offset][first] = matrix[last][last - offset]
# right → bottom
matrix[last][last - offset] = matrix[i][last]
# top → right
matrix[i][last] = top
######---------------- 优化写法 ----------------######
def rotate(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
n = len(matrix)
for i in range(n // 2):
for j in range(n - n // 2):
# 四个位置同时交换,使用Python的多重赋值
(matrix[i][j],
matrix[~j][i],
matrix[~i][~j],
matrix[j][~i]) = (matrix[~j][i],
matrix[~i][~j],
matrix[j][~i],
matrix[i][j])
# 注意:~i 等价于 n-1-i- 时间复杂度 O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度 O(1)
关键技巧:
- 转置时只处理上三角:避免重复交换导致还原
- 边界处理:注意n//2的使用,确保正确的循环边界
- Python多重赋值:可以优雅地实现多元素交换
拓展
逆时针90° = 垂直翻转 + 转置
旋转180° = 水平翻转 + 垂直翻转
旋转270° = 旋转90°三次,或者逆时针90°
240. 搜索二维矩阵 II
编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target 。该矩阵具有以下特性:
- 每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
- 每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
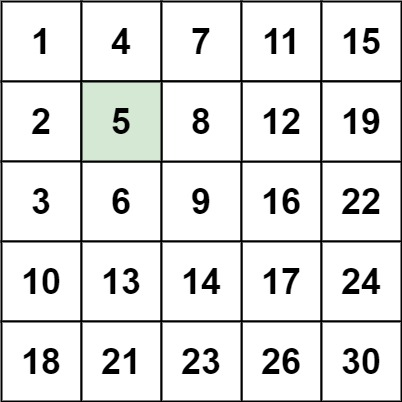
示例 1:
输入:matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5
输出:true
示例 2:
输入:matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 20
输出:false
一、暴力解法
python
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
if not matrix or not matrix[0]:
return False
for row in matrix:
for val in row:
if val == target:
return True
return False- 时间复杂度 O(m * n)
- 空间复杂度 O(1)
二、角落搜索法【推荐】
- 【思路】 右上角元素的特性:
- 是当前行的最大值
- 是当前列的最小值
- 这个性质使得我们可以明确移动方向
- 【步骤】
- 从右上角
(0, n-1)开始 - 如果当前值等于target,返回True
- 如果当前值大于target,左移(排除当前列)
- 如果当前值小于target,下移(排除当前行)
- 重复直到找到目标或越界
- 从右上角
- 【举例】:
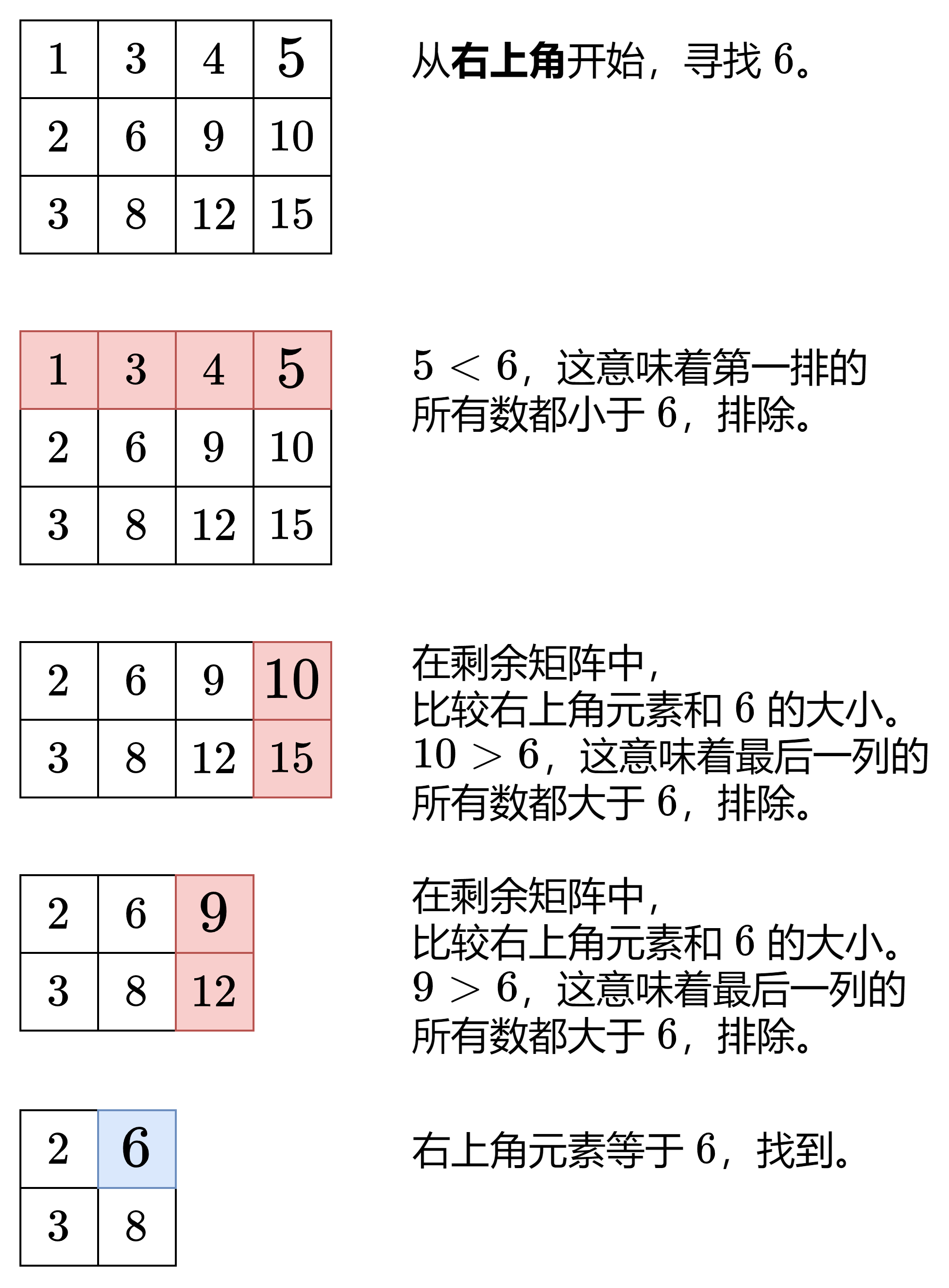
python
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
i, j = 0, n - 1 # 从右上角开始
while i <= m - 1 and j >= 0: # 或者i < m and j >= 0都可以,只是确保还有剩余元素
if matrix[i][j] == target:
return True
if matrix[i][j] < target: # 该行max都小于target, 整行排除,i下移
i += 1
else: # 该列min都大于target, 整列排除,j上移
j -= 1
return False- 时间复杂度 O(m + n) :每次循环排除掉一行或者一列,一共
m+n行列,最坏情况下需要排除m+n−1行列才能找到答案。 - 空间复杂度 O(1)
- 【另外】还可以用左下角搜索(是该行的最小值,也是该列的最大值),思路类似。
三、逐行二分查找
- 【思路】对每一行进行二分查找
python
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
def binary_search_row(row):
"""在指定行进行二分查找"""
left, right = 0, len(row) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if row[mid] == target:
return True
elif row[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return False
for row in matrix:
# 优化:如果target小于行首或大于行尾,跳过该行
if target < row[0] or target > row[-1]:
continue
if binary_search_row(row):
return True
return False- 时间复杂度 O(m * log n)
- 空间复杂度 O(1)