一 交叉验证
1 保留交叉验证HoldOut
holdOut Cross-validation(Train-Test Split)
在这种交叉验证技术中,整个技术集被随机划分为训练集和验证集。
根据经验法则,++整个数据集的近70%被用作训练集,其余30%被用作验证集++,也就是最常使用的直接划分数据集的方法。
1.1 缺点
1、不适用不平衡的数据集
假设有不平衡的数据集,有0类和1类。其中80%属于0类,20%属于1类。也就是说,训练集的大小为80%,测试数据的大小为数据集的20%。可能发生的情况是,所有80%的0类数据都在训练集中,所有1类数据都在测试集中。那么模型不能很好地概括测试数据,原因也很简单,就是在训练的时候就没见过1类数据,自然也识别不出来。
2、一大块数据被剥夺了训练模型的机会
在小数据集的情况下,有一部分数据被保留下来用于测试模型,这些数据可能具有重要的特征,模型可能因为没有在被保留测试的数据上进行训练而错过。
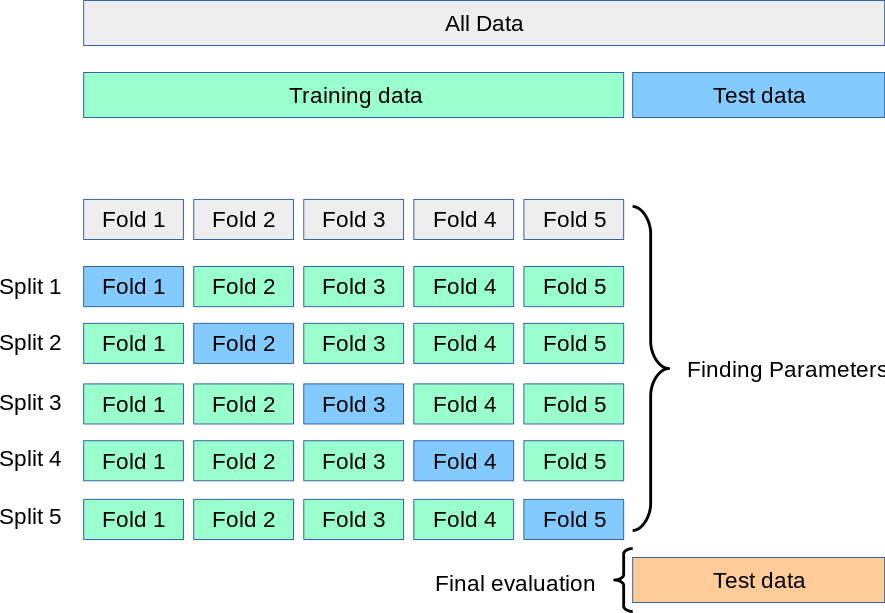
2 K-折交叉验证(K-fold)
K-fold Cross Validation,记为K-CV或K-fold
K-Fold交叉验证技术中,整个数据集被划分为++K个大小相同的部分++ 。每个分区被称为 一个"Fold"。所以我们有K个部分,我们称之为K-Fold。++一个Fold被用作验证集,其余的K-1个Fold被用作训练集。++
该技术重复K次,直到每个Fold都被用作验证集,其余的作为训练集。
模型的最终准确度是通过取k个模型验证数据的平均准确度来计算的。
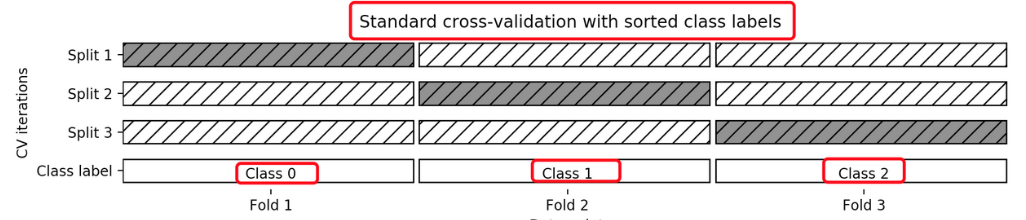
3 分层k-折交叉验证Stratified k-fold
Stratified k-fold cross validation,
K-折交叉验证的变种
分层是说在++每一折中都保持着原始数据中各个类别的比例关系。++
比如说:原始数据有3类,比例为1:2:1,采用3折分层交叉验证,那么划分的3折中,每一折中的数据类别保持着1:2:1的比例,这样的验证结果更加可信。
补充:去除p交叉验证、留一交叉验证、蒙特卡罗交叉验证、时间序列交叉验证
4 API
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold普通K折交叉验证和分层K折交叉验证的使用是一样的,只是引入的类不同
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold使用时只是KFold这个类名不一样其他代码完全一样
strat_k_fold=sklearn.model_selection.StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=42)n_splits划分为几个折叠 shuffle是否在拆分之前被打乱(随机化),False则按照顺序拆分
random_state随机因子
indexs=strat_k_fold.split(X,y)返回一个可迭代对象,一共有5个折叠,每个折叠对应的是训练集和测试集的下标
for train_index, test_index in indexs:
X[train_index] y[train_index] X[test_index ] y[test_index ]用for循环取出每一个折叠对应的X和y下标来访问到对应的测试数据集和训练数据集 以及测试目标集和训练目标集
5 代码实例
'''使用StratifiedKFold来创建5个折叠,每个折叠中鸢尾花数据集的类别分布与整体数据集的分布一致。然后我们对每个折叠进行了训练和测试,计算了分类器的准确性。'''
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris#加载鸢尾花数据集
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold#分层K折交叉验证,确保每折中各类别比例相同
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier#K近邻分类器
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler#书标准化处理器
'''加载鸢尾花数据集
提取特征和标签:
x:特征数据,150*4矩阵,包含4个特征
y:目标标签,150*1向量,包含012三个类别'''
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
'''初始化分层k-折交叉验证器
#n_splits划分为几个折叠 ,5个,80%训练,20测试
shuffle是否在拆分之前被打乱(随机化),True打乱顺序,避免顺序偏差,False则按照顺序拆分
random_state随机因子,确保结果可重现'''
strat_k_fold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
'''创建一个K近邻分类器实例,使用7个最近邻'''
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=7)
'''初始化准确率列表,用于存储每次交叉验证的准确率得分'''
accuracies = []
'''开始交叉验证循环
strat_k_fold.split(X,y)生成5对训练集和测试机索引
每次循环得到一对索引train_index(训练样本索引)和test_index(测试样本索引)'''
for train_index, test_index in strat_k_fold.split(X, y):
print(train_index, test_index)#显示每次折叠的训练集和测试集样本索引
'''划分训练集和测试集,根据索引从完整数据中提取对应的特征和标签'''
X_train, X_test = X[train_index], X[test_index]
y_train, y_test = y[train_index], y[test_index]
'''数据预处理(标准化)
StandardScaler(): 创建标准化处理器(均值为0,标准差为1)
fit_transform(X_train): 计算训练集的均值和标准差,并转换训练集
transform(X_test): 使用训练集的参数来转换测试集(避免数据泄露)'''
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
'''使用标准化的训练数据来训练K近邻分类器'''
knn.fit(X_train_scaled, y_train)
'''计算在测试机的准确率,因为测试数据也需要标准化'''
score = knn.score(X_test_scaled,y_test)
print(score)
'''把每次折叠的准确率并添加到列表中'''
accuracies.append(score)
'''输出5次交叉验证的平均准确率'''
print(sum(accuracies)/len(accuracies))结果:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 12 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 26 27 28 30 31 32 34 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 46 47 48 49 50 51 53 54 55 56 57 58 60 61 62 63 64 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 79 80 81 82 83 84 86 88 89 90 91 93 95 96 98 101 103 104 105 106 108 109 110 111 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 125 126 127 128 129 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 140 141 142 143 145 146 147 149\] \[ 11 13 14 15 20 25 29 33 35 45 52 59 65 78 85 87 92 94 97 99 100 102 107 112 124 130 138 139 144 148
0.9666666666666667
1 2 3 5 6 7 8 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 41 43 44 45 46 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 59 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 69 70 71 72 73 76 77 78 79 81 83 84 85 86 87 88 91 92 93 94 95 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 107 112 113 115 116 117 118 119 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148\] \[ 0 4 9 10 19 21 31 40 42 47 58 60 68 74 75 80 82 89 90 96 106 108 109 110 111 114 120 121 136 149
0.9666666666666667
0 1 2 3 4 5 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 23 24 25 26 28 29 31 32 33 35 36 37 39 40 42 43 45 46 47 49 51 52 53 54 55 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 65 67 68 69 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 96 97 99 100 101 102 103 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 117 119 120 121 122 124 125 128 129 130 131 134 135 136 137 138 139 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149\] \[ 6 7 22 27 30 34 38 41 44 48 50 56 64 66 70 71 72 83 95 98 104 105 116 118 123 126 127 132 133 140
0.9
0 3 4 5 6 7 9 10 11 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 25 26 27 29 30 31 33 34 35 36 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 50 52 53 54 56 57 58 59 60 62 64 65 66 68 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 80 81 82 83 85 86 87 89 90 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 116 118 119 120 121 123 124 126 127 130 131 132 133 134 136 137 138 139 140 141 143 144 146 148 149\] \[ 1 2 8 12 23 24 28 32 37 49 51 55 61 63 67 69 79 84 88 91 115 117 122 125 128 129 135 142 145 147
1.0
0 1 2 4 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 37 38 40 41 42 44 45 47 48 49 50 51 52 55 56 58 59 60 61 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 74 75 78 79 80 82 83 84 85 87 88 89 90 91 92 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 102 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 114 115 116 117 118 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 132 133 135 136 138 139 140 142 144 145 147 148 149\] \[ 3 5 16 17 18 26 36 39 43 46 53 54 57 62 73 76 77 81 86 93 101 103 113 119 131 134 137 141 143 146
0.9666666666666667
0.96
二 超参数搜索
超参数搜索也叫网格搜索(Grid Search)
例如,在KNN算法中,K是一个可以人为设置的参数,所以就是一个超参数。网格搜索能够自动帮助我们找到最好的超参数值。
三 Sklearn API
同时进行交叉验证(cv)、网络搜索(GridSearch)
GridSearchCV实际上也是一个估计器(estimator),它有几个重要属性:
估计器(estimator),同时它有几个重要属性:
best_params_ 最佳参数
best_score_ 在训练集中的准确率
best_estimator_ 最佳估计器
cv_results_ 交叉验证过程描述
best_index_最佳k在列表中的下标
class sklearn.model_selection.GridSearchCV(estimator, param_grid)参数:
estimator:scikit-learn估计器实例;
param_grid:以参数名称(str)作为键,将参数设置列表尝试作为值的字典;
示例:
{"n_neighbors": [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11]}
cv: 确定交叉验证切分策略,值为:
(1)None 默认5折
(2)integer 设置多少折
如果估计器是分类器,使用"分层k-折交叉验证(StratifiedKFold)"。在所有其他情况下,使用KFold。
四 代码实例
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
def knn_iris_gscv():
# 1)获取数据
iris = load_iris()
# 2)划分数据集
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, random_state=22)
# 3)特征工程:标准化
transfer = StandardScaler()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.transform(x_test)
# 4)KNN算法预估器, 这里就不传参数n_neighbors了,交给GridSearchCV来传递
estimator = KNeighborsClassifier()
# 加入网格搜索与交叉验证, GridSearchCV会让k分别等于1,2,5,7,9,11进行网格搜索偿试。cv=10表示进行10次交叉验证
estimator = GridSearchCV(estimator, param_grid={"n_neighbors": [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11]}, cv=10)
estimator.fit(x_train, y_train)
# 5)模型评估
# 方法1:直接比对真实值和预测值
y_predict = estimator.predict(x_test)
print("y_predict:\n", y_predict)
print("直接比对真实值和预测值:\n", y_test == y_predict)
# 方法2:计算准确率
score = estimator.score(x_test, y_test)
print("在测试集中的准确率为:\n", score) #0.9736842105263158
# 最佳参数:best_params_
print("最佳参数:\n", estimator.best_params_) #{'n_neighbors': 3}, 说明k=3时最好
# 最佳结果:best_score_
print("在训练集中的准确率:\n", estimator.best_score_) #0.9553030303030303
# 最佳估计器:best_estimator_
print("最佳估计器:\n", estimator.best_estimator_) # KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
# 交叉验证结果:cv_results_
print("交叉验证过程描述:\n", estimator.cv_results_)
#最佳参数组合的索引:最佳k在列表中的下标
print("最佳参数组合的索引:\n",estimator.best_index_)
#通常情况下,直接使用best_params_更为方便
return None
knn_iris_gscv()五 补充
20 新闻KNN,加GridSearchCV