一、为什么是灰度图
相较于 RGB 三通道图像,灰度图仅保留亮度信息(Y 分量),数据量减少 2/3,相比于常用的 NV12 图像,数据量减少 1/3,内存占用与计算负载显著降低。对于下游网络结构而言,单通道网络计算量/参数量也会更少,这对边缘设备的实时处理至关重要。
灰度图部署有一个问题:如何将视频流中的 NV12 数据高效转换为模型所需的灰度输入,并在工具链中实现标准化前处理流程。
视频通路传输的原始数据通常采用 NV12 格式,这是一种适用于 YUV 色彩空间的半平面格式:
- 数据结构:NV12 包含一个平面的 Y 分量(亮度信息)和一个平面的 UV 分量(色度信息),其中 Y 分量分辨率为 W×H,UV 分量分辨率为 W×H/2。
- 灰度图提取:对于灰度图部署,仅需使用 NV12 中的 Y 分量。以 1920×1080 分辨率为例,若 NV12 中 Y 与 UV 分量连续存储,Y 分量占据前 1920×1080 字节,后续部分为 UV 分量,可直接忽略或舍弃,若分开存储,使用起来更简单。
二、灰度图部署数据链路
视频通路过来的数据不能直接是灰度图,而是 nv12 数据,对于灰度图部署,可以只使用其中的 y 分量。
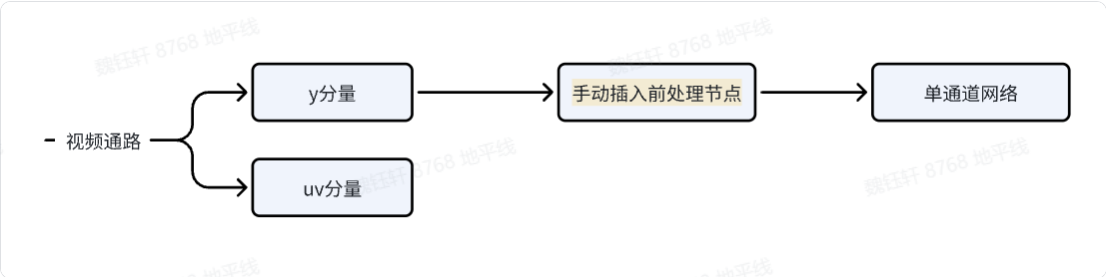
2.1 手动插入前处理节点
在工具链提供的绝大部分材料中,前处理节点多是对于 3 通道网络、nv12 输入进行的,查看工具链用户手册《进阶内容->HBDK Tool API Reference》中几处 api 介绍,可以发现也是支持 gray 灰度图的,具体内容如下:
- insert_image_convert(self, mode str = "nv12")
Plain
Insert image_convert op. Change input parameter type.
Args:
* mode (str): Specify conversion mode, optional values are "nv12"(default) and "gray".
Returns:
List of newly inserted function arguments which is also the inputs of inserted image convert op
Raises:
ValueError when this argument is no longer valid
Note:
To avoid the new insertion operator not running in some conversion passes, it is recommended to call the insert_xxx api before the convert stage
Example:
module = load("model.bc")
func = module[0]
res = func.inputs[0].insert_image_convert("nv12")对于 batch 输入,均值、标准化、归一化等操作,可以在 insert_image_preprocess 中实现:
- insert_image_preprocess( self, mode str, divisor int, mean List[float], std List[float], is_signed bool = True)
Plain
Insert image_convert op. Change input parameter type.
Args:
* mode (str): Specify conversion mode, optional values are "skip"(default, same as None), "yuvbt601full2rgb", "yuvbt601full2bgr", "yuvbt601video2rgb" and "yuvbt601video2bgr".
Returns:
List of newly inserted function arguments which is also the inputs of inserted image preprocess op
Raises:
ValueError when this argument is no longer valid
Note:
To avoid the new insertion operator not running in some conversion passes, it is recommended to call the insert_xxx api before the convert stage
Example:
module = load("model.bc")
func = module[0]
res = func.inputs[0].insert_image_preprocess("yuvbt601full2rgb", 255, [0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225], True)手动插入前处理节点可参考:
Plain
mean = [0.485]
std = [0.229]
func = qat_bc[0]
for input in func.flatten_inputs[::-1]:
split_inputs = input.insert_split(dim=0)
for split_input in reversed(split_inputs):
node = split_input.insert_transpose([0, 3, 1, 2])
node = node.insert_image_preprocess(mode="skip",
divisor=255,
mean=mean,
std=std,
is_signed=True)
node.insert_image_convert(mode="gray")- mean = [0.485] 和 std = [0.229]:定义图像归一化时使用的均值和标准差
- func = qat_bc[0]:获取量化感知训练 (QAT) 模型中的第一个函数 / 模块作为处理入口。
- for input in func.flatten_inputs[::-1]:逆序遍历模型的所有扁平化输入节点。
- split_inputs = input.insert_split(dim=0):将输入数据按批次维度 (dim=0) 分割,这是处理 batch 输入必须要做的。
- node = split_input.insert_transpose([0, 3, 1, 2]):将数据维度从[B, H, W, C](NHWC 格式) 转换为[B, C, H, W](NCHW 格式),也是必须要做的。
- node.insert_image_preprocess(...):执行图像预处理
- node.insert_image_convert(mode="gray"):插入单通道灰度图
三、全流程示例代码
Plain
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from horizon_plugin_pytorch import set_march, March
set_march(March.NASH_M)
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization import prepare, set_fake_quantize, FakeQuantState
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization import QuantStub
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.hbdk4 import export
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.qconfig_template import calibration_8bit_weight_16bit_act_qconfig_setter, default_calibration_qconfig_setter
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.qconfig import get_qconfig, MSEObserver, MinMaxObserver
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.dtype import qint8, qint16
from torch.quantization import DeQuantStub
from hbdk4.compiler import statistics, save, load,visualize,compile,convert, hbm_perf
class SimpleConvNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimpleConvNet, self).__init__()
# 第一个节点:输入通道 1,输出通道 16,卷积核 3x3
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
# 后续添加一个池化层和一个全连接层
self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
self.fc = nn.Linear(16 * 14 * 14, 10) # 假设输入图像为 28x28
self.quant = QuantStub()
self.dequant = DeQuantStub()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.quant(x)
x = self.conv1(x) # 卷积层
x = F.relu(x) # 激活
x = self.pool(x) # 池化
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # Flatten
x = self.fc(x) # 全连接层输出
x = self.dequant(x)
return x
# 构造模型
model = SimpleConvNet()
# 构造一个假输入:batch_size=4,单通道,28x28 图像
example_input = torch.randn(4, 1, 28, 28)
output = model(example_input)
print("输出 shape:", output.shape) # torch.Size([4, 10])
calib_model = prepare(model.eval(), example_input,
qconfig_setter=(
default_calibration_qconfig_setter,
),
)
calib_model.eval()
set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.CALIBRATION)
calib_model(example_input)
calib_model.eval()
set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.VALIDATION)
calib_out = calib_model(example_input)
print("calib输出数据:", calib_out)
qat_bc = export(calib_model, example_input)
mean = [0.485]
std = [0.229]
func = qat_bc[0]
for input in func.flatten_inputs[::-1]:
split_inputs = input.insert_split(dim=0)
for split_input in reversed(split_inputs):
node = split_input.insert_transpose([0, 3, 1, 2])
node = node.insert_image_preprocess(mode="skip",
divisor=255,
mean=mean,
std=std,
is_signed=True)
node.insert_image_convert(mode="gray")
quantized_bc = convert(qat_bc, "nash-m")
hbir_func = quantized_bc.functions[0]
hbir_func.remove_io_op(op_types = ["Dequantize","Quantize"])
visualize(quantized_bc, "model_result/quantized_batch4.onnx")
statistics(quantized_bc)
params = {'jobs': 64, 'balance': 100, 'progress_bar': True,
'opt': 2,'debug': True, "advice": 0.0}
hbm_path="model_result/batch4-gray.hbm"
print("start to compile")
compile(quantized_bc, march="nash-m", path=hbm_path, **params)
print("end to compile")
ebug': True, "advice": 0.0}
hbm_path="model_result/batch4-gray.hbm"
print("start to compile")
compile(quantized_bc, march="nash-m", path=hbm_path, **params)
print("end to compile")