文章目录
- [一. 力扣 [1046. 最后一块石头的重量](https://leetcode.cn/problems/last-stone-weight/description/)](#一. 力扣 1046. 最后一块石头的重量)
-
- [1. 题目](#1. 题目)
- [2. 算法原理](#2. 算法原理)
- [3. 代码](#3. 代码)
- [二. 力扣 [703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素](https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-largest-element-in-a-stream/description/)](#二. 力扣 703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素)
-
- [1. 题目](#1. 题目)
- [2. 算法原理](#2. 算法原理)
- [3. 代码](#3. 代码)
- [三. 力扣 [692. 前K个高频单词](https://leetcode.cn/problems/top-k-frequent-words/description/)](#三. 力扣 692. 前K个高频单词)
-
- [1. 题目](#1. 题目)
- [2. 算法原理](#2. 算法原理)
- [3. 代码](#3. 代码)
- [四. 力扣 [295. 数据流的中位数](https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-median-from-data-stream/description/)](#四. 力扣 295. 数据流的中位数)
-
- [1. 题目](#1. 题目)
- [2. 算法原理](#2. 算法原理)
- [3. 代码](#3. 代码)
一. 力扣 1046. 最后一块石头的重量
1. 题目
2. 算法原理
这道题的算法原理十分简单, 直接建立大根堆即可, 这里简单梳理下
3. 代码
java
public int lastStoneWeight(int[] stones) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b) -> b - a);
for (int x : stones) {
queue.offer(x);
}
while (queue.size() > 1) {
int max1 = queue.poll();
int max2 = queue.poll();
if (max1 > max2) {
queue.offer(max1 - max2);
}
}
if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
return queue.poll();
}else {
return 0;
}
}二. 力扣 703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素
1. 题目
题目意思简单易懂, 这里不过多赘述, 直接看图即可
2. 算法原理
这道题有点绕口, 这里我们在初始化类的时候先求出来topk, 然后在后台调用add方法的时候, 只需要重复求topk流程即可, 下面图片解析的是求topk问题时,应该建立哪种类型的堆, 为什么要建这种堆?
3. 代码
java
PriorityQueue<Integer> q;
int t_k;
public KthLargest(int k, int[] nums) {
q = new PriorityQueue<>();
t_k = k;
for (int x : nums) {
q.offer(x);
if (q.size() > t_k) {
q.poll();
}
}
}
public int add(int val) {
q.offer(val);
if (q.size() > t_k) {
q.poll();
}
return q.peek();
}三. 力扣 692. 前K个高频单词
1. 题目
2. 算法原理
这道题原理不难, 难的是如何将代码实现, 注意掌握Pair的特性
3. 代码
java
public List<String> topKFrequent(String[] words, int k) {
Map<String, Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();
for (String s : words) {
hash.put(s, hash.getOrDefault(s, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<Pair<String, Integer>> q = new PriorityQueue<>(
(a, b) -> {
if (a.getValue().equals(b.getValue())) {
return b.getKey().compareTo(a.getKey());
}else {
return a.getValue() - b.getValue();
}
}
);
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : hash.entrySet()) {
q.offer(new Pair<>(e.getKey(), e.getValue()));
if (q.size() > k) {
q.poll();
}
}
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
ret.add(q.poll().getKey());
}
Collections.reverse(ret);
return ret;
}四. 力扣 295. 数据流的中位数
1. 题目
题目就是让求中位数, 最后结果需要注意是double类型
2. 算法原理
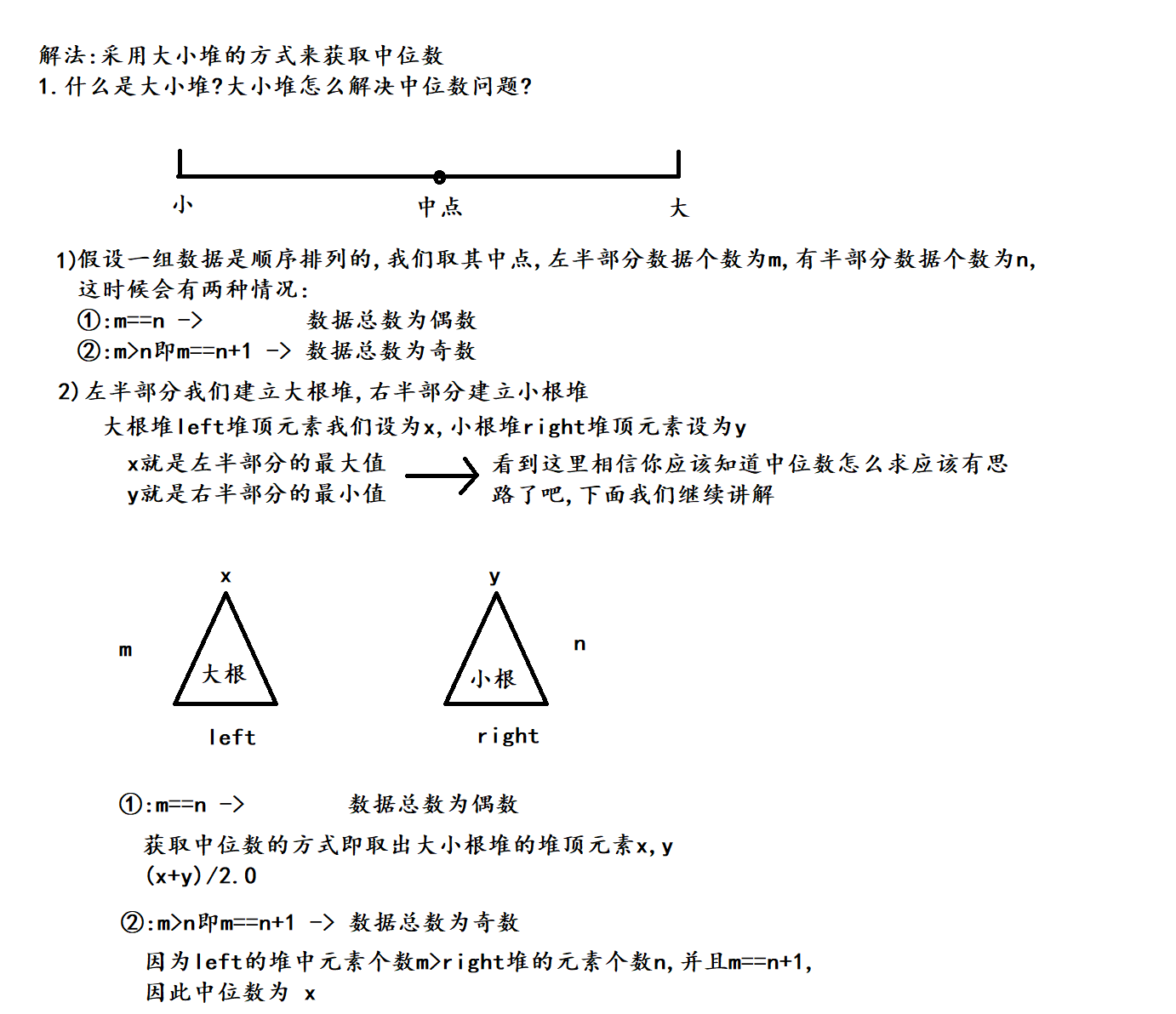
(1) 我们这里采用大小堆的解法, 下面我们来解释什么是大小堆
(2)一些细节问题, 例如如何入堆?如何维护顺序排列的数据流?
3. 代码
java
PriorityQueue<Integer> left;
PriorityQueue<Integer> right;
public MedianFinder() {
left = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);
right = new PriorityQueue<>();
}
public void addNum(int num) {
int m = left.size();
int n = right.size();
Integer x = left.peek();
if (m == n) {
if (x == null) {
left.offer(num);
} else if (num <= x) {
left.offer(num);
} else {
right.offer(num);
left.offer(right.poll());
}
} else {
if (num <= x) {
left.offer(num);
x = left.poll();
right.offer(x);
}else {
right.offer(num);
}
}
}
public double findMedian() {
if (left.size() == right.size()) {
return (left.peek() + right.peek()) / 2.0;
}else {
return left.peek();
}
}