
🔥个人主页:Cx330🌸
❄️个人专栏:《C语言》《LeetCode刷题集》《数据结构-初阶》《C++知识分享》《优选算法指南-必刷经典100题》
🌟心向往之行必能至
🎥Cx330🌸的简介:
目录
[2.1 简单了解string类](#2.1 简单了解string类)
[2.2 auto关键词和范围for](#2.2 auto关键词和范围for)
[2.2.1 auto关键字](#2.2.1 auto关键字)
[2.2.2 范围for](#2.2.2 范围for)
[3.1 string对象的常见构造](#3.1 string对象的常见构造)
[3.2 迭代器](#3.2 迭代器)
[3.2.1 迭代器的特点](#3.2.1 迭代器的特点)
[3.2.2 伟大的设计](#3.2.2 伟大的设计)
[3.2.3 const迭代器](#3.2.3 const迭代器)
[3.2.4 rbegin() && rend()](#3.2.4 rbegin() && rend())
[3.3 string类对象的容量操作](#3.3 string类对象的容量操作)
[3.4 string类对象的访问及遍历操作](#3.4 string类对象的访问及遍历操作)
[3.4.1 operator](#3.4.1 operator)
[3.5 string类对象的修改操作(Modifiers)](#3.5 string类对象的修改操作(Modifiers))
[3.5.1 push_back && append](#3.5.1 push_back && append)
[3.5.2 insert && erase](#3.5.2 insert && erase)
[3.5.3 replace](#3.5.3 replace)
[3.6 string类非成员函数](#3.6 string类非成员函数)
C++参考文档:cplusplus
前言:在之前C语言的学习中,我们深刻体会到了字符串函数的折磨,大家可以看下博主之前的博客:【C语言】:字符串函数超详解(10个最重要函数),在这里我就直接给大家放张图片,给大家体会一下,总结来说就是及其的难用:

一、学习string类的好处
C语言中str库函数难用
C语言中,字符串是以'\0'结尾的一些字符的集合,为了操作方便,C标准库中提供了一些str系列
的库函数,但是这些库函数与字符串是分离开的,不太符合OOP的思想,而且**底层空间需要用户
自己管理,**可谓及其难用
二、STL标准库中的string类
2.1 简单了解string类
我们学习到这一个阶段就要养成自己看文档的习惯了,文档才是原汁原味的、最直接的资料,这里我就不做过多介绍,以后我们进入到公司,熟悉业务的时候公司也是直接甩给你一份文档,让你自己研究去,导师,也就是你的领导也是一样,只会给一些指导,还是要靠自己的能力,好了扯远了,上半年C++网站的官方中文版下线了,如果看不懂文档没关系,我们可以借助工具,比如翻译软件、浏览器插件,都是可行的
这里我们就不作介绍,直接带大家来看一下string的文档:string类的文档介绍
注意:
在使用string类时,必须包含**#include<string>以及using namespacestd;**命名空间
2.2 auto关键词和范围for
这两个都是C++11支持的语法,方便我们后面的学习
2.2.1 auto关键字
- 在早期C/C++中auto的含义是:使用auto修饰的变量,是具有自动存储器的局部变量,后来这个不重要了。C++11中,标准委员会变废为宝赋予了auto全新的含义即:auto不再是一个存储类型指示符,而是作为一个新的类型指示符来指示编译器,auto声明的变量必须由编译器在编译时期推导而得。
- 用auto声明指针类型时,用auto和auto*没有任何区别,但用auto声明引用类型时则必须加&
- 当在同一行声明多个变量时,这些变量必须是相同的类型,否则编译器将会报错,因为编译器实际只对第一个类型进行推导,然后用推导出来的类型定义其他变量。
- auto不能作为函数的参数,可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用,auto用太多会降低代码的可读性,你熟悉这段代码、知道这些是什么类型倒还好,换个人过来做你的工作,一定会骂街,也就是说,auto好用但别auto满天飞,长类型可以用auto。
- auto不能直接用来声明数组
代码示例:
cpp
int i = 0;
//通过初始化表达式值类型自动给推荐对象类型
auto j = i;
auto k = 10;
auto p1 = &i;
//指定一定是指针
auto* p2 = &i;
cout << p1 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
cout << "-----------------" << endl;
//引用
int& r1 = i;
//r2不是引用
auto r2 = r1;
//r3是int&引用
auto& r3 = r1;
cout << &r1 << endl;
cout << &i << endl;
cout << &r2 << endl;
cout << &r3 << endl;2.2.2 范围for
- 对于一个有范围的集合而言,由程序员来说明循环的范围是多余的,有时候还会容易犯错误。因此C++11中引|入了基于范围的for循环。for循环后的括号由冒号":"分为两部分:第一部分是范围内用于迭代的变量,第二部分则表示被迭代的范围,自动迭代,自动取数据,自动判断结束
- 范围for可以作用到数组和容器对象上进行遍历
- 范围for的底层很简单,容器遍历实际就是替换为迭代器,这个从汇编层也可以看到
代码示例:
cpp
//C++11
//范围for
//自动取容器数据赋值,自动迭代++,自动判断结束
//for (char ch : s1)
//语法糖
for (auto ch : s1)//ch自己取的名字
{
cout << ch << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
//引用才可以修改
for (auto& ch : s1)//char&都可以
{
ch -= 1;
}
cout << endl;
for (const auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : lt)//e自己取的名字
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
//支持迭代器的容器都可以用范围for
//数组也支持
int a[] = { 1,2,3 };
for (auto e : a)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}范围for很好使,也是由C++11提供的。
自动取容器数据赋值,自动迭代++、自动判断结束------被形象地称为**"语法糖"**。
范围for不是必须适配auto关键字使用的,例如:

三、string类的常见接口介绍说明
3.1 string对象的常见构造
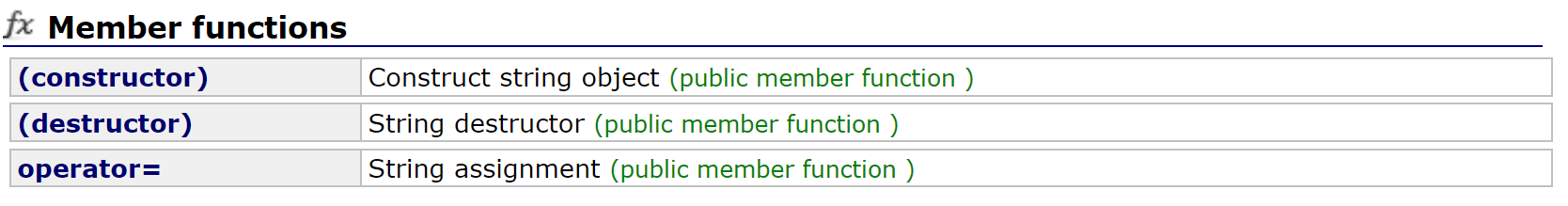
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------|
| (constructor)函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| string()(重点) | 构造空的string类对象,即空字符串 |
| string(const char* s)(重点) | 用C-string来构造string类对象 |
| string(size_t n, char c) | string类对象中包含n个字符c |
| string(const string&s)(重点) | 拷贝构造函数 |
代码示例:
cpp
void Test_string1()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello world");
string s3(s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
string s4(s2, 0, 5);
cout << s4 << endl;
string s5(s2, 6, 15);//不会报错
cout << s5 << endl;
//npos
string s6(s2, 6);//会自动复制到结尾
cout << s6 << endl;
string s7("hello world", 6);
cout << s7 << endl;
string s8(10, '*');
cout << s8 << endl;
s7 = "xxxx";
cout << s7 << endl;
}3.2 迭代器
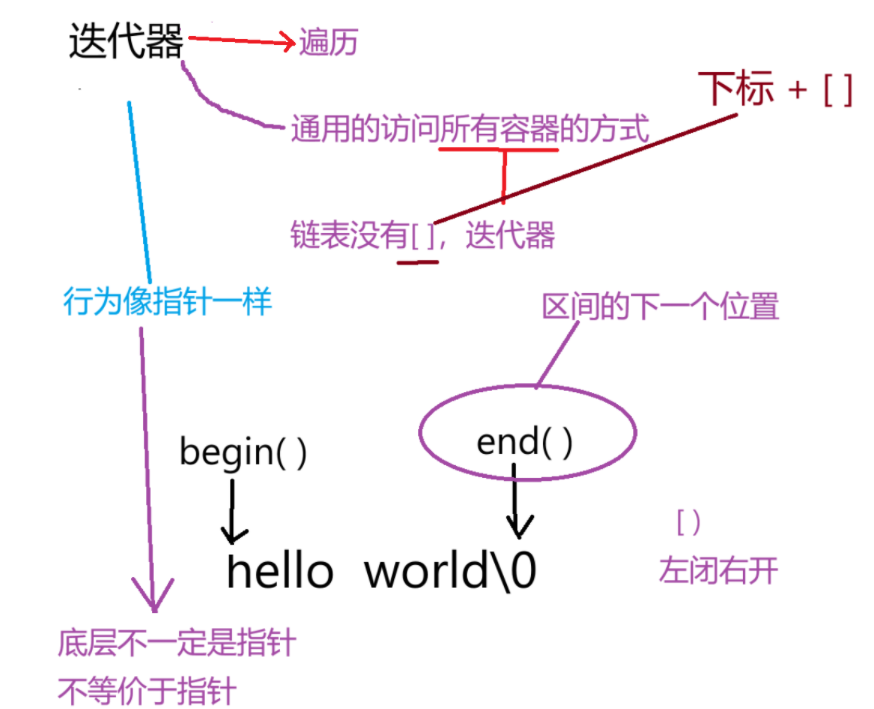
3.2.1 迭代器的特点
1、提供统一的方式遍历容器
2、算法可以泛型化,算法借助迭代器处理容器的数据
3.2.2 伟大的设计

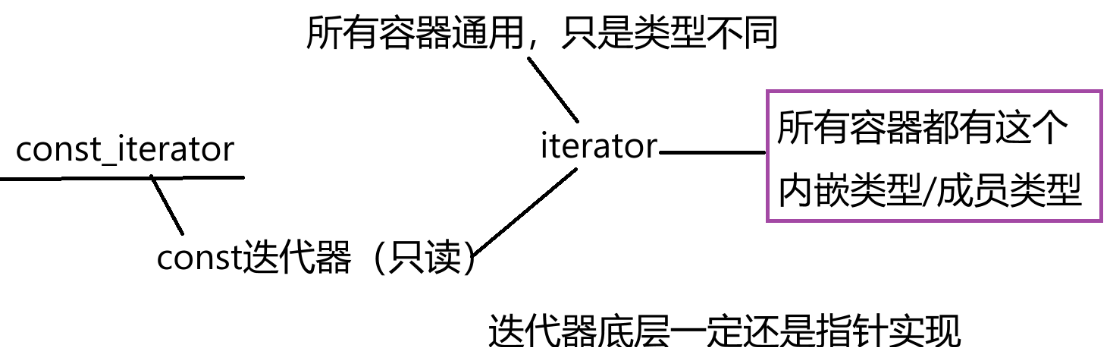
3.2.3 const迭代器
3.2.4 rbegin() && rend()
3.3 string类对象的容量操作
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------|
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| size(重点) | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| length | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| resize(重点) | (改变数据,影响size)将有效字符的个数该成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充 |
| capacity | 返回空间总大小 |
| clear(重点) | 清空有效字符 |
| reserve(重点) | 为字符串预留空间,请求扩容到n,给小了可能会缩容,VS不会缩,g++(Linux下)会缩容,缩容不会小于内容量 |
| empty(重点) | 检测字符串释放为空串,是返回true,否则返回false |
| shrink_to_fit | 缩容接口,浪费太多空间的时候用这个才有意义 |

- size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size()
- clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小
- resize(size_tn)与resize(size_tn,charc)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字符个数增多时:resize(n)用o来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_tn,char c)用字符c来填充多出的元素空间。注意:resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变
- reserve(size_tres_arg=0):为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小

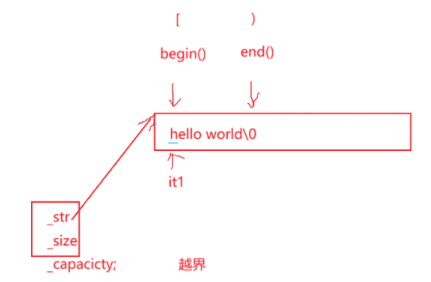
3.4 string类对象的访问及遍历操作
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------|
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| operator[ ](重点) | 返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用 |
| begin+end | begin获取一个字符的迭代器 + end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin+rend | begin获取一个字符的迭代器 + end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器(rbegin(),反向迭代器) |
| 范围for | C++11支持更简洁的范围for的新遍历方式 |
3.4.1 operator
cpp
class string {
public:
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
return _str[pos];
}
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
};3.5 string类对象的修改操作(Modifiers)
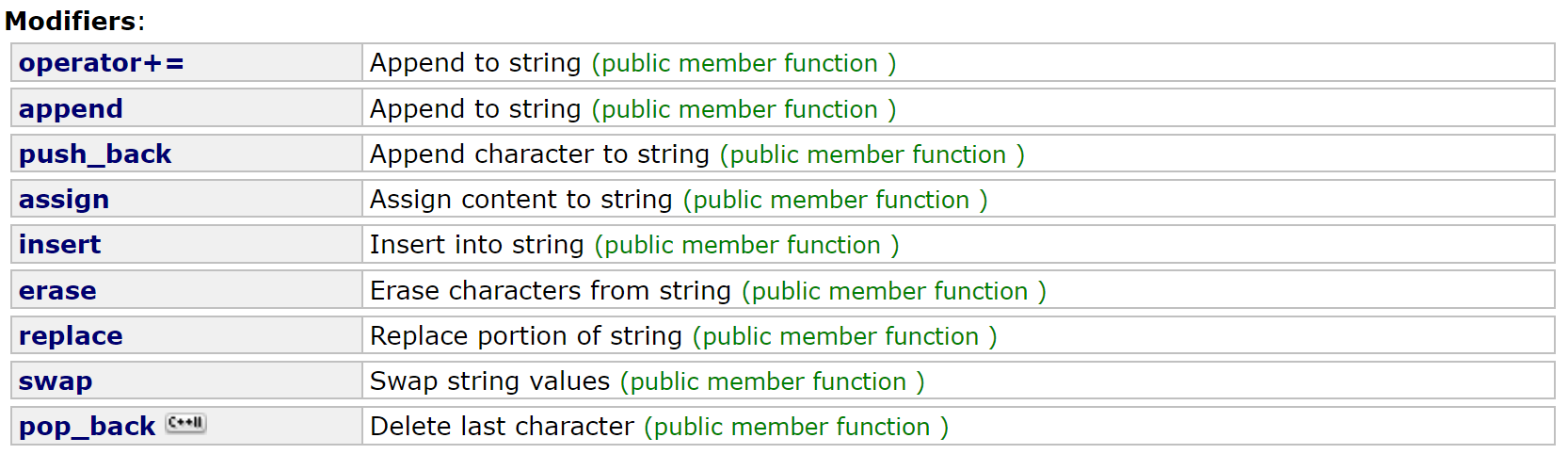
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------|
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| push_back | 在字符串后尾插字符c |
| append | 在字符串后追加一个字符串 |
| operator+=(重点) | 在字符串后追加字符串str |
| c_str(重点) | 返回C格式字符串 |
| find+npos(重点) | 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| rfind | 从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| substr | 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回 |
- 在string尾部追加字符时,**s.push_back(c) / s.append(1,c) / s+='c'**三种的实现方式差不多,一般情况下string类的+=操作用的比较多,+=操作不仅可以连接单个字符,还可以连接字符串
- 对string操作时,如果能够大概预估到放多少字符,可以先通过reserve把空间预留好
3.5.1 push_back && append
3.5.2 insert && erase
cpp
void Test_string5()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(0, "xxx");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(0, 1, '#');
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(5, 1, '#');
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(s1.begin(), 1, '$');
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(s2.begin());//头删
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(0, 1);//头删
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(5, 2);//第五个开始删除2个字符
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(5);//全删
cout << s2 << endl << endl;
}3.5.3 replace

1、所有的空格替换"%%%"
cpp
//s所有空格替换成%%
string s4("hello world hello bit");
size_t pos = s4.find(' ');
while (pos != string::npos)
{
s4.replace(pos, 1, "%%");
//找下一个空格
pos = s4.find(' ', pos + 2);
}
cout << s4 << endl;我们用前面介绍过的reserve、范围for来实现
cpp
string s5("hello world hello bit");
cout << s5 << endl;
string s6;
s6.reserve(s5.size());//提前扩容
for (auto ch : s5)
{
if (ch != ' ')
{
s6 += ch;
}
else
{
s6 += "%%";
}
}
cout << s6 << endl;3.6 string类非成员函数
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------|
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
| operator+ | 尽量少用,因为传值返回,导致深拷贝效率低 |
| operator>>(重点) | 输入运算符重载 |
| operator<<(重点) | 输出运算符重载 |
| getline(重点) | 获取一行字符串 |
| relational operators(重点) | 大小比较 |
上面表格里的的这几个接口大家先了解一下,OJ题目中会有一些体现它们的使用。string类中还有
一些其他的操作,这里不再一一列举,大家在需要用到时不明白了查文档即可。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin, s);//相当于getline(cin,s,' ')可读进空格,也可以自定义
//getline(cin, s,'#')读到#就自动结束
int pos = s.rfind(' ');
if (pos != s.size())
{
cout << s.size() - pos - 1 << endl;
}
else
{
cout << s.size() << endl;
}
}四、完整代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<list>
#include<algorithm>//算法
using namespace std;
//int main()
//{
// char buff1[] = "abcA";
// buff1[0]++;
//
// char buff2[] = "比特abc";
// cout << sizeof(buff2) << endl;//两个字节表示一个汉字
//
// buff2[1]++;
// cout << buff2 << endl;
//
// buff2[1]++;
// cout << buff2 << endl;
//
// buff2[3]++;
// cout << buff2 << endl;
//
// buff2[3]++;
// cout << buff2 << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
void Test_string1()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello world");
string s3(s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
string s4(s2, 0, 5);
cout << s4 << endl;
string s5(s2, 6, 15);//不会报错
cout << s5 << endl;
//npos
string s6(s2, 6);//会自动复制到结尾
cout << s6 << endl;
string s7("hello world", 6);
cout << s7 << endl;
string s8(10, '*');
cout << s8 << endl;
s7 = "xxxx";
cout << s7 << endl;
}
//class string {
//public:
// char& operator[](size_t pos)
// {
// return _str[pos];
// }
//private:
// char* _str;
// size_t _size;
// size_t _capacity;
//
//};
void Print(const string& s)
{
//const修饰迭代器本身
//const string::iterator it1 = s.begin();
string::const_iterator it1 = s.begin();
while (it1 != s.end())
{
//*it='x';//不能修改
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
//反向迭代器
string::const_reverse_iterator it2 = s.rbegin();
while (it2 != s.rend())
{
//*it='x';//不能修改
cout << *it2 << ' ';
it2++;
}
cout << endl;
}
void Test_string2()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1[0] = 'x';
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s1[0] << endl;
//越界有严格断言检查
//s1[15];//断言
//s1.at(15);//抛异常
cout << s1.size() << endl;//推荐
cout << s1.length() << endl;
//下标+[]
//遍历 or 修改
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
s1[i]++;
}
cout << s1 << endl;
//行为像指针一样的东西
string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();
while (it1 != s1.end())
{
//(*it1)--;//可修改
cout << *it1 << ' ';
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
list<int>::iterator lit1 = lt.begin();
while (lit1 != lt.end())
{
//(*it1)--;//可修改
cout << *lit1 << ' ';
lit1++;
}
cout << endl;
Print(s1);
string::iterator ret1 = find(s1.begin(), s1.end(), 'x');
//auto ret1 = find(s1.begin(), s1.end(), 'x');
if (ret1 != s1.end())
{
cout << "找到了x" << endl;
}
list<int>::iterator ret2 = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 2);
//auto ret2 = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), 2);
if (ret2 != lt.end())
{
cout << "找到了2" << endl;
}
int i = 0;
//通过初始化表达式值类型自动给推荐对象类型
auto j = i;
auto k = 10;
auto p1 = &i;
//指定一定是指针
auto* p2 = &i;
cout << p1 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
cout << "-----------------" << endl;
//引用
int& r1 = i;
//r2不是引用
auto r2 = r1;
//r3是int&引用
auto& r3 = r1;
cout << &r1 << endl;
cout << &i << endl;
cout << &r2 << endl;
cout << &r3 << endl;
//C++11
//范围for
//自动取容器数据赋值,自动迭代++,自动判断结束
//语法糖
for (char ch : s1)
//for (auto ch : s1)//ch自己取的名字
{
cout << ch << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
//引用才可以修改
for (auto& ch : s1)//char&都可以
{
ch -= 1;
}
cout << endl;
for (const auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : lt)//e自己取的名字
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
//支持迭代器的容器都可以用范围for
//数组也支持
int a[] = { 1,2,3 };
for (auto e : a)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
void TestCapacity()
{
string s1;
s1.reserve(200);//确定要插入多少数据,提前扩容
size_t old = s1.capacity();
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < 200; i++)
{
s1.push_back('x');
if (s1.capacity() != old)
{
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
old = s1.capacity();
}
}
cout << endl << endl;
}
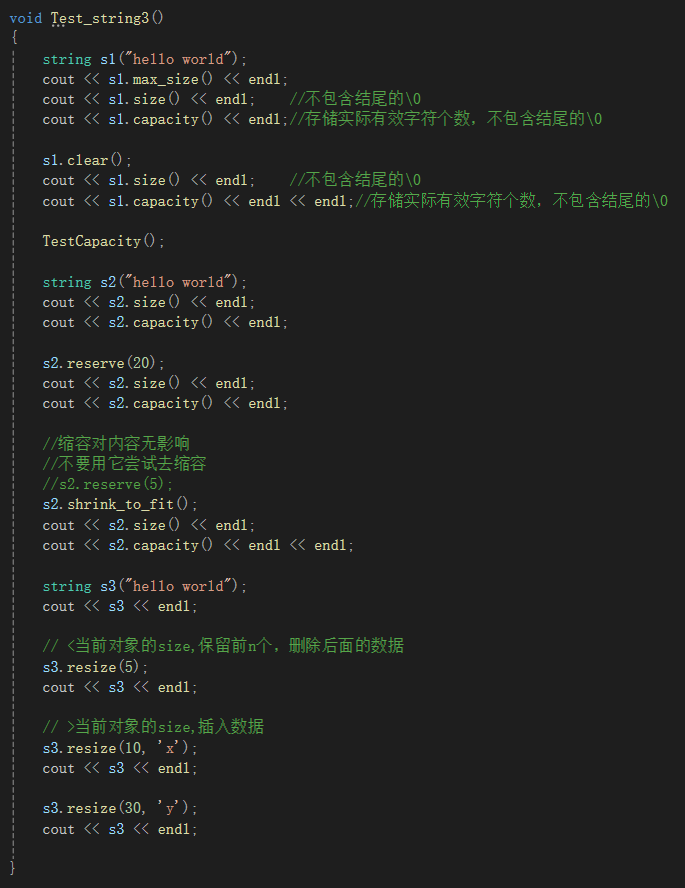
void Test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1.max_size() << endl;
cout << s1.size() << endl; //不包含结尾的\0
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//存储实际有效字符个数,不包含结尾的\0
s1.clear();
cout << s1.size() << endl; //不包含结尾的\0
cout << s1.capacity() << endl << endl;//存储实际有效字符个数,不包含结尾的\0
TestCapacity();
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
s2.reserve(20);
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
//缩容对内容无影响
//不要用它尝试去缩容
//s2.reserve(5);
s2.shrink_to_fit();
cout << s2.size() << endl;
cout << s2.capacity() << endl << endl;
string s3("hello world");
cout << s3 << endl;
// <当前对象的size,保留前n个,删除后面的数据
s3.resize(5);
cout << s3 << endl;
// >当前对象的size,插入数据
s3.resize(10, 'x');
cout << s3 << endl;
s3.resize(30, 'y');
cout << s3 << endl;
}
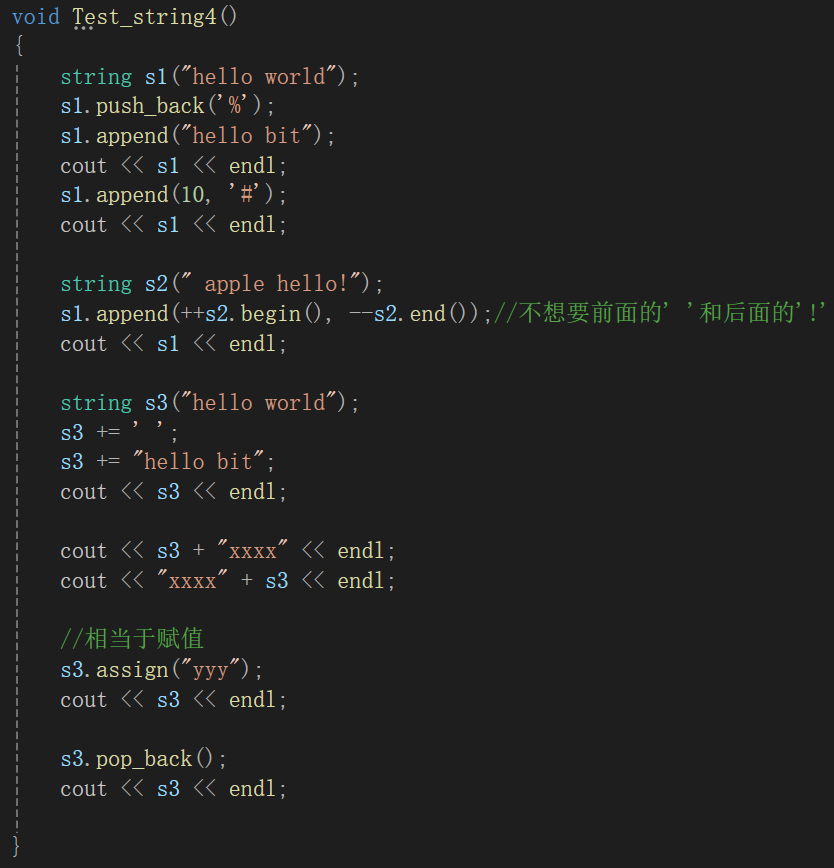
void Test_string4()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.push_back('%');
s1.append("hello bit");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.append(10, '#');
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2(" apple hello!");
s1.append(++s2.begin(), --s2.end());//不想要前面的' '和后面的'!'
cout << s1 << endl;
string s3("hello world");
s3 += ' ';
s3 += "hello bit";
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s3 + "xxxx" << endl;
cout << "xxxx" + s3 << endl;
//相当于赋值
s3.assign("yyy");
cout << s3 << endl;
s3.pop_back();
cout << s3 << endl;
}
void Test_string5()
{
string s1("hello world");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(0, "xxx");
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(0, 1, '#');
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(5, 1, '#');
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.insert(s1.begin(), 1, '$');
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2("hello world");
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(s2.begin());//头删
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(0, 1);//头删
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(5, 2);//第五个开始删除2个字符
cout << s2 << endl;
s2.erase(5);//全删
cout << s2 << endl << endl;
string s3("hello world");
cout << s3 << endl;
//本质是插入
s3.replace(5, 1, "%%%");//5:第五个字符,1:替换1个字符,"%%%":要替换的字符
cout << s3 << endl;
s3.replace(5, 3, "*");
cout << s3 << endl;
//s所有空格替换成%%
string s4("hello world hello bit");
size_t pos = s4.find(' ');
while (pos != string::npos)
{
s4.replace(pos, 1, "%%");
//找下一个空格
pos = s4.find(' ', pos + 2);
}
cout << s4 << endl;
string s5("hello world hello bit");
cout << s5 << endl;
string s6;
s6.reserve(s5.size());//提前扩容
for (auto ch : s5)
{
if (ch != ' ')
{
s6 += ch;
}
else
{
s6 += "%%";
}
}
cout << s6 << endl;
}
int main()
{
try {
Test_string5();
}
catch (const exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}结尾:
完整代码源:****【CPP知识学习仓库】 - Gitee.com
往期回顾:
结语:本篇博客系统讲解了C++string类的知识以及补充,如果文章对你有帮助的话,欢迎评论,点赞,收藏加关注,感谢大家的支持