文章目录
- [109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树](#109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树)
109. 有序链表转换二叉搜索树
题目描述
给定一个单链表的头节点 head ,其中的元素 按升序排序 ,将其转换为 平衡 二叉搜索树。
示例 1:
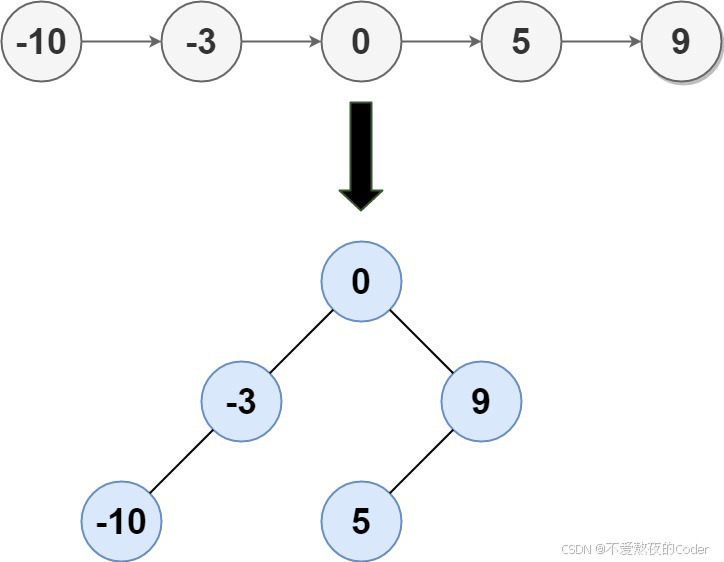
输入: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
解释: 一个可能的答案是[0,-3,9,-10,null,5],它表示所示的高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
示例 2:
输入: head = []
输出: []
提示:
- head 中的节点数在[0, 2 * 104] 范围内
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
解题思路
问题分析
这道题是 LeetCode 108 的升级版,核心差异:
| 维度 | 108题 | 109题 |
|---|---|---|
| 数据结构 | 有序数组 | 有序链表 |
| 访问方式 | O(1)随机访问 | O(n)顺序访问 |
| 找中点 | 直接计算索引 | 需要遍历/快慢指针 |
| 难度提升 | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
关键挑战:链表无法像数组那样 O(1) 访问中间元素!
方法一:快慢指针 + 递归(最优解)
核心思想 :使用快慢指针找链表中点,然后递归构建
graph TD
A[输入: -10→-3→0→5→9] --> B[快慢指针找中点]
B --> C[slow指向0, 断开链表]
C --> D[左半: -10→-3]
C --> E[中点: 0]
C --> F[右半: 5→9]
E --> G[创建根节点 val=0]
D --> H[递归处理左半链表]
F --> I[递归处理右半链表]
H --> J[左子树: -3为根]
I --> K[右子树: 5为根]
style A fill:#e1f5ff
style E fill:#bbdefb
style G fill:#90caf9
style J fill:#c8e6c9
style K fill:#c8e6c9
快慢指针找中点技巧:
否 是 输入: head链表 slow = head
fast = head
prev = nil fast != nil &&
fast.Next != nil? 找到中点: slow prev = slow
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next 断开链表
prev.Next = nil 返回: 左半链表, 中点, 右半链表
算法步骤:
- 边界处理:链表为空或只有一个节点
- 找中点:快指针走2步,慢指针走1步
- 断开链表:将链表分为左半和右半
- 递归构建 :
- 创建根节点(中点值)
- 递归处理左半链表 → 左子树
- 递归处理右半链表 → 右子树
代码实现:
go
func sortedListToBST(head *ListNode) *TreeNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if head.Next == nil {
return &TreeNode{Val: head.Val}
}
// 快慢指针找中点
slow, fast, prev := head, head, (*ListNode)(nil)
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
prev = slow
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
// 断开链表
prev.Next = nil
// 构建树
root := &TreeNode{Val: slow.Val}
root.Left = sortedListToBST(head) // 左半链表
root.Right = sortedListToBST(slow.Next) // 右半链表
return root
}时间复杂度:O(n log n)
- 每层递归需要 O(n) 时间找中点
- 递归深度 O(log n)
空间复杂度:O(log n) - 递归栈
方法二:转换为数组
核心思想:先将链表转为数组,然后用108题的方法
flowchart LR
A[链表: -10→-3→0→5→9] --> B[遍历转数组]
B --> C[数组: -10,-3,0,5,9]
C --> D[108题方法构建BST]
D --> E[返回根节点]
style A fill:#e1f5ff
style C fill:#bbdefb
style E fill:#c5cae9
优缺点分析:
| 维度 | 评价 |
|---|---|
| 实现难度 | ⭐ 简单,复用108题代码 |
| 时间复杂度 | O(n) 遍历 + O(n) 构建 = O(n) ✅ |
| 空间复杂度 | O(n) 数组存储 ❌ |
| 适用场景 | 空间充足、追求简洁 |
方法三:中序遍历模拟(最巧妙)
核心洞察 :BST的中序遍历恰好是有序序列!
算法思路:
- 先统计链表长度 n
- 按中序遍历顺序构建树(左-根-右)
- 用全局指针记录当前链表节点
统计链表长度 n=5 中序构建 0, n-1 递归左子树 0, 1 创建节点 val=链表当前值 指针后移 递归右子树 3, 4
为什么有效?
链表: -10 → -3 → 0 → 5 → 9
↑
中序遍历顺序构建树时,依次消费链表节点时间复杂度 :O(n) - 每个节点访问一次 ✅
空间复杂度:O(log n) - 递归栈
方法四:递归 + 计算长度
优化思路:避免每次都找中点
- 先遍历一次计算链表总长度
- 递归时传递子链表的起始位置和长度
- 根据长度计算中点位置
复杂度对比
| 方法 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 快慢指针 | O(n log n) | O(log n) | 直观易懂 | 重复遍历 |
| 转数组 | O(n) | O(n) | 简单快速 | 额外空间 |
| 中序遍历 | O(n) | O(log n) | 最优解 | 较难理解 |
| 计算长度 | O(n) | O(log n) | 避免重复 | 需要预处理 |
关键技巧总结
-
快慢指针找中点:
goslow, fast := head, head for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil { slow = slow.Next fast = fast.Next.Next } // slow 指向中点 -
断开链表:需要记录 prev 指针
-
中序遍历技巧:全局指针顺序消费链表节点
-
长度计算优化:避免重复遍历
与108题对比
| 维度 | 108题(数组) | 109题(链表) |
|---|---|---|
| 找中点 | O(1)计算索引 | O(n)快慢指针 |
| 分割 | O(1)传递索引 | O(1)断开链表 |
| 总复杂度 | O(n) | O(n log n) 或 O(n) |
| 实现难度 | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ |
扩展问题
- 如果链表是循环链表怎么办?
- 如何在O(n)时间、O(1)空间完成?(不计递归栈)
- 如果要求构建完全二叉搜索树?
- 如何处理链表中有重复元素的情况?
相关题目
- LeetCode 108:有序数组转BST(前置题)
- LeetCode 110:平衡二叉树
- LeetCode 876:链表的中间结点
- LeetCode 1382:将BST变平衡
完整题解代码
go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
// ListNode 链表节点定义
type ListNode struct {
Val int
Next *ListNode
}
// TreeNode 二叉树节点定义
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
// ==================== 方法一:快慢指针 + 递归 ====================
// 时间复杂度:O(n log n),每层递归O(n)找中点,深度O(log n)
// 空间复杂度:O(log n),递归栈深度
func sortedListToBST(head *ListNode) *TreeNode {
// 边界条件
if head == nil {
return nil
}
if head.Next == nil {
return &TreeNode{Val: head.Val}
}
// 使用快慢指针找中点
slow, fast := head, head
var prev *ListNode
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
prev = slow
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
// 断开链表:prev.Next = nil
if prev != nil {
prev.Next = nil
}
// 创建根节点(中点)
root := &TreeNode{Val: slow.Val}
// 递归构建左右子树
root.Left = sortedListToBST(head) // 左半链表
root.Right = sortedListToBST(slow.Next) // 右半链表
return root
}
// ==================== 方法二:转换为数组 ====================
// 时间复杂度:O(n),遍历一次链表 + 构建树
// 空间复杂度:O(n),数组存储
func sortedListToBST2(head *ListNode) *TreeNode {
// 链表转数组
nums := []int{}
curr := head
for curr != nil {
nums = append(nums, curr.Val)
curr = curr.Next
}
// 使用108题的方法构建BST
return arrayToBST(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
}
func arrayToBST(nums []int, left, right int) *TreeNode {
if left > right {
return nil
}
mid := left + (right-left)/2
root := &TreeNode{Val: nums[mid]}
root.Left = arrayToBST(nums, left, mid-1)
root.Right = arrayToBST(nums, mid+1, right)
return root
}
// ==================== 方法三:中序遍历模拟(最优解)====================
// 时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点访问一次
// 空间复杂度:O(log n),递归栈
func sortedListToBST3(head *ListNode) *TreeNode {
// 计算链表长度
length := 0
curr := head
for curr != nil {
length++
curr = curr.Next
}
// 使用全局指针,按中序遍历顺序消费链表节点
return inorderBuild(&head, 0, length-1)
}
func inorderBuild(head **ListNode, left, right int) *TreeNode {
if left > right {
return nil
}
mid := left + (right-left)/2
// 先构建左子树(中序遍历:左-根-右)
leftTree := inorderBuild(head, left, mid-1)
// 创建根节点,消费当前链表节点
root := &TreeNode{Val: (*head).Val}
*head = (*head).Next // 指针后移
// 再构建右子树
root.Left = leftTree
root.Right = inorderBuild(head, mid+1, right)
return root
}
// ==================== 方法四:递归 + 计算长度优化 ====================
// 时间复杂度:O(n)
// 空间复杂度:O(log n)
func sortedListToBST4(head *ListNode) *TreeNode {
// 计算链表长度
length := getLength(head)
return buildWithLength(head, length)
}
func getLength(head *ListNode) int {
length := 0
for head != nil {
length++
head = head.Next
}
return length
}
func buildWithLength(head *ListNode, length int) *TreeNode {
if length == 0 {
return nil
}
if length == 1 {
return &TreeNode{Val: head.Val}
}
// 找到中点位置
mid := length / 2
// 移动到中点
curr := head
for i := 0; i < mid; i++ {
curr = curr.Next
}
// 创建根节点
root := &TreeNode{Val: curr.Val}
// 递归构建左右子树
root.Left = buildWithLength(head, mid)
root.Right = buildWithLength(curr.Next, length-mid-1)
return root
}
// ==================== 辅助函数 ====================
// 创建链表
func createList(nums []int) *ListNode {
if len(nums) == 0 {
return nil
}
head := &ListNode{Val: nums[0]}
curr := head
for i := 1; i < len(nums); i++ {
curr.Next = &ListNode{Val: nums[i]}
curr = curr.Next
}
return head
}
// 打印链表
func printList(head *ListNode) {
fmt.Print("[")
for head != nil {
fmt.Print(head.Val)
if head.Next != nil {
fmt.Print(" -> ")
}
head = head.Next
}
fmt.Print("]")
}
// 中序遍历验证BST
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
result := []int{}
result = append(result, inorderTraversal(root.Left)...)
result = append(result, root.Val)
result = append(result, inorderTraversal(root.Right)...)
return result
}
// 层序遍历
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) []interface{} {
if root == nil {
return []interface{}{}
}
result := []interface{}{}
queue := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(queue) > 0 {
node := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if node == nil {
result = append(result, nil)
} else {
result = append(result, node.Val)
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
}
}
// 移除末尾的 nil
for len(result) > 0 && result[len(result)-1] == nil {
result = result[:len(result)-1]
}
return result
}
// 检查是否为平衡二叉树
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
return checkHeight(root) != -1
}
func checkHeight(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
leftHeight := checkHeight(root.Left)
if leftHeight == -1 {
return -1
}
rightHeight := checkHeight(root.Right)
if rightHeight == -1 {
return -1
}
if abs(leftHeight-rightHeight) > 1 {
return -1
}
return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1
}
// 检查是否为BST
func isValidBST(root *TreeNode) bool {
return validateBST(root, math.MinInt64, math.MaxInt64)
}
func validateBST(root *TreeNode, min, max int) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
if root.Val <= min || root.Val >= max {
return false
}
return validateBST(root.Left, min, root.Val) && validateBST(root.Right, root.Val, max)
}
// 获取树的高度
func getHeight(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return max(getHeight(root.Left), getHeight(root.Right)) + 1
}
// 树形打印
func printTree(root *TreeNode, prefix string, isLeft bool) {
if root == nil {
return
}
fmt.Print(prefix)
if isLeft {
fmt.Print("├── ")
} else {
fmt.Print("└── ")
}
fmt.Println(root.Val)
if root.Left != nil || root.Right != nil {
if root.Left != nil {
printTree(root.Left, prefix+getTreePrefix(isLeft, true), true)
} else {
fmt.Println(prefix + getTreePrefix(isLeft, true) + "├── nil")
}
if root.Right != nil {
printTree(root.Right, prefix+getTreePrefix(isLeft, false), false)
} else {
fmt.Println(prefix + getTreePrefix(isLeft, false) + "└── nil")
}
}
}
func getTreePrefix(isLeft, hasNext bool) string {
if isLeft {
return "│ "
}
return " "
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
// ==================== 测试函数 ====================
func testCase(name string, nums []int) {
fmt.Printf("\n========== %s ==========\n", name)
fmt.Print("输入链表: ")
head := createList(nums)
printList(head)
fmt.Println()
// 方法一:快慢指针
head1 := createList(nums)
root1 := sortedListToBST(head1)
fmt.Println("\n方法一(快慢指针):")
fmt.Printf("层序遍历: %v\n", levelOrder(root1))
fmt.Printf("中序遍历: %v\n", inorderTraversal(root1))
fmt.Printf("是否平衡: %v\n", isBalanced(root1))
fmt.Printf("是否BST: %v\n", isValidBST(root1))
fmt.Printf("树高度: %d\n", getHeight(root1))
fmt.Println("树结构:")
printTree(root1, "", false)
// 方法二:转数组
head2 := createList(nums)
root2 := sortedListToBST2(head2)
fmt.Println("\n方法二(转数组):")
fmt.Printf("层序遍历: %v\n", levelOrder(root2))
fmt.Printf("中序遍历: %v\n", inorderTraversal(root2))
fmt.Printf("是否平衡: %v\n", isBalanced(root2))
// 方法三:中序遍历(最优解)
head3 := createList(nums)
root3 := sortedListToBST3(head3)
fmt.Println("\n方法三(中序遍历-最优解):")
fmt.Printf("层序遍历: %v\n", levelOrder(root3))
fmt.Printf("中序遍历: %v\n", inorderTraversal(root3))
fmt.Printf("是否平衡: %v\n", isBalanced(root3))
// 方法四:计算长度优化
head4 := createList(nums)
root4 := sortedListToBST4(head4)
fmt.Println("\n方法四(计算长度优化):")
fmt.Printf("层序遍历: %v\n", levelOrder(root4))
fmt.Printf("中序遍历: %v\n", inorderTraversal(root4))
fmt.Printf("是否平衡: %v\n", isBalanced(root4))
}
// ==================== 扩展功能 ====================
// 比较108题和109题的性能差异
func compareWithArray() {
fmt.Println("\n========== 108题 vs 109题性能对比 ==========")
sizes := []int{100, 1000, 5000}
for _, size := range sizes {
// 生成数据
nums := make([]int, size)
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
nums[i] = i
}
fmt.Printf("\n数据规模: %d\n", size)
// 108题:数组方式(理论最优)
root1 := arrayToBST(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
fmt.Printf("108题(数组): 树高度=%d, 理论高度=%d\n",
getHeight(root1), int(math.Ceil(math.Log2(float64(size+1)))))
// 109题方法一:快慢指针
head := createList(nums)
root2 := sortedListToBST(head)
fmt.Printf("109题(快慢指针): 树高度=%d\n", getHeight(root2))
// 109题方法三:中序遍历
head = createList(nums)
root3 := sortedListToBST3(head)
fmt.Printf("109题(中序遍历): 树高度=%d\n", getHeight(root3))
}
}
// 链表中点查找演示
func demonstrateFindMiddle() {
fmt.Println("\n========== 快慢指针找中点演示 ==========")
testCases := [][]int{
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, // 奇数个
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, // 偶数个
{1}, // 单个
{1, 2}, // 两个
}
for _, nums := range testCases {
head := createList(nums)
fmt.Print("\n链表: ")
printList(head)
fmt.Println()
// 找中点
slow, fast := head, head
var prev *ListNode
for fast != nil && fast.Next != nil {
prev = slow
slow = slow.Next
fast = fast.Next.Next
}
fmt.Printf("中点: %d\n", slow.Val)
if prev != nil {
fmt.Printf("中点前一个: %d\n", prev.Val)
}
}
}
// 验证所有方法生成的树是否等价
func verifyAllMethods() {
fmt.Println("\n========== 验证所有方法的等价性 ==========")
nums := []int{-10, -3, 0, 5, 9}
head := createList(nums)
methods := []struct {
name string
fn func(*ListNode) *TreeNode
}{
{"快慢指针", sortedListToBST},
{"转数组", sortedListToBST2},
{"中序遍历", sortedListToBST3},
{"计算长度", sortedListToBST4},
}
fmt.Print("输入: ")
printList(head)
fmt.Println()
for _, method := range methods {
h := createList(nums)
root := method.fn(h)
inorder := inorderTraversal(root)
fmt.Printf("\n%s:\n", method.name)
fmt.Printf(" 中序遍历: %v\n", inorder)
fmt.Printf(" 是否平衡: %v\n", isBalanced(root))
fmt.Printf(" 是否BST: %v\n", isValidBST(root))
fmt.Printf(" 树高度: %d\n", getHeight(root))
}
}
func main() {
// 测试用例1:示例1
testCase("测试用例1:基本情况", []int{-10, -3, 0, 5, 9})
// 测试用例2:空链表
testCase("测试用例2:空链表", []int{})
// 测试用例3:单个元素
testCase("测试用例3:单个元素", []int{1})
// 测试用例4:两个元素
testCase("测试用例4:两个元素", []int{1, 3})
// 测试用例5:奇数个元素
testCase("测试用例5:奇数个元素", []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7})
// 测试用例6:偶数个元素
testCase("测试用例6:偶数个元素", []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6})
// 测试用例7:连续数字
testCase("测试用例7:连续数字", []int{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9})
// 扩展功能测试
compareWithArray()
demonstrateFindMiddle()
verifyAllMethods()
}