大家好,我是java1234_小锋老师,最近写了一套基于Python深度学习的车辆车牌识别系统(PyTorch2卷积神经网络CNN+OpenCV4实现)视频教程,持续更新中,计划月底更新完,感谢支持。
视频在线地址:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1BdUnBLE6N/
课程简介:
本课程采用主流的Python技术栈实现,分两套系统讲解,一套是专门讲PyTorch2卷积神经网络CNN训练模型,识别车牌,当然实现过程中还用到OpenCV实现图像格式转换,裁剪,大小缩放等。另外一套是基于前面Django+Vue通用权限系统基础上,加了车辆识别业务模型,Mysql8数据库,Django后端,Vue前端,后端集成训练好的模型,实现车牌识别。
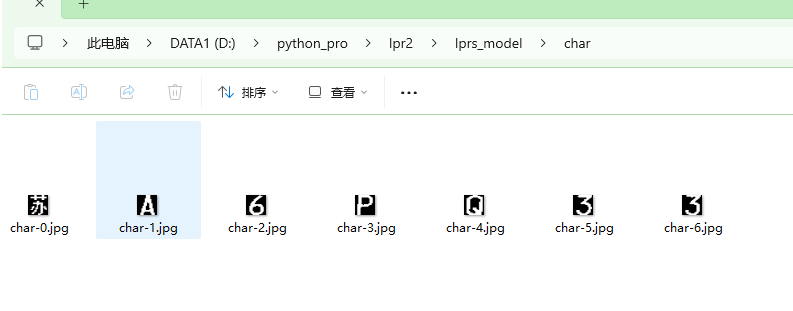
基于Python深度学习的车辆车牌识别系统(PyTorch2卷积神经网络CNN+OpenCV4实现)视频教程 - 切割车牌矩阵获取车牌字符
前面代码我们从图像中截取了车牌矩阵,现在我们来切割车牌字符。
# 左右切割
def horizontal_cut_chars(plate):
"""
该函数用于对车牌图像进行水平切割,提取字符区域。主要步骤包括:
1. 计算每列像素点总和;
2. 根据阈值判断字符区域起止位置;
3. 限制字符宽度范围以过滤无效区域;
4. 返回符合条件的字符区域坐标列表。
"""
char_addr_list = []
area_left, area_right, char_left, char_right = 0, 0, 0, 0
img_w = plate.shape[1]
# 获取车牌每列边缘像素点个数
def getColSum(img, col):
sum = 0
for i in range(img.shape[0]):
sum += round(img[i, col] / 255)
return sum;
sum = 0
for col in range(img_w):
sum += getColSum(plate, col)
# 每列边缘像素点必须超过均值的60%才能判断属于字符区域
col_limit = 0 # round(0.6*sum/img_w)
# 每个字符宽度也进行限制
charWid_limit = [round(img_w / 12), round(img_w / 5)]
is_char_flag = False
for i in range(img_w):
colValue = getColSum(plate, i)
if colValue > col_limit:
if is_char_flag == False:
area_right = round((i + char_right) / 2)
area_width = area_right - area_left
char_width = char_right - char_left
if (area_width > charWid_limit[0]) and (area_width < charWid_limit[1]):
char_addr_list.append((area_left, area_right, char_width))
char_left = i
area_left = round((char_left + char_right) / 2)
is_char_flag = True
else:
if is_char_flag == True:
char_right = i - 1
is_char_flag = False
# 手动结束最后未完成的字符分割
if area_right < char_left:
area_right, char_right = img_w, img_w
area_width = area_right - area_left
char_width = char_right - char_left
if (area_width > charWid_limit[0]) and (area_width < charWid_limit[1]):
char_addr_list.append((area_left, area_right, char_width))
return char_addr_list
# 获取字符
def get_chars(car_plate):
img_h, img_w = car_plate.shape[:2]
h_proj_list = [] # 水平投影长度列表
h_temp_len, v_temp_len = 0, 0
h_startIndex, h_end_index = 0, 0 # 水平投影记索引
h_proj_limit = [0.2, 0.8] # 车牌在水平方向得轮廓长度少于20%或多余80%过滤掉
char_imgs = []
"""
这段代码用于对二值化车牌图像进行水平投影分析。
它统计每一行的白色像素数量,记录连续有效投影段,并根据比例过滤掉过短或过长的投影区域,
最终提取出最可能包含字符的水平区域。
"""
# 将二值化的车牌水平投影到Y轴,计算投影后的连续长度,连续投影长度可能不止一段
h_count = [0 for i in range(img_h)]
for row in range(img_h):
temp_cnt = 0
for col in range(img_w):
if car_plate[row, col] == 255:
temp_cnt += 1
h_count[row] = temp_cnt
if temp_cnt / img_w < h_proj_limit[0] or temp_cnt / img_w > h_proj_limit[1]:
if h_temp_len != 0:
h_end_index = row - 1
h_proj_list.append((h_startIndex, h_end_index))
h_temp_len = 0
continue
if temp_cnt > 0:
if h_temp_len == 0:
h_startIndex = row
h_temp_len = 1
else:
h_temp_len += 1
else:
if h_temp_len > 0:
h_end_index = row - 1
h_proj_list.append((h_startIndex, h_end_index))
h_temp_len = 0
# 手动结束最后得水平投影长度累加
if h_temp_len != 0:
h_end_index = img_h - 1
h_proj_list.append((h_startIndex, h_end_index))
"""
这段代码的功能是:
1. 遍历水平投影列表,找出最长的有效投影段(即字符区域)。
2. 若该投影段高度不足图像总高度的50%,则认为未检测到有效车牌字符,直接返回空结果。
3. 否则,截取该区域作为车牌主体部分,并调用[horizontal_cut_chars]函数进一步横向切割出每个字符的边界。
4. 根据字符边界从原图中提取每个字符图像,缩放到统一尺寸后加入结果列表返回。
"""
h_maxIndex, h_maxHeight = 0, 0
for i, (start, end) in enumerate(h_proj_list):
if h_maxHeight < (end - start):
h_maxHeight = (end - start)
h_maxIndex = i
if h_maxHeight / img_h < 0.5:
return char_imgs
chars_top, chars_bottom = h_proj_list[h_maxIndex][0], h_proj_list[h_maxIndex][1]
plates = car_plate[chars_top:chars_bottom + 1, :]
cv2.imwrite('process_img/plate.jpg', plates)
char_addr_list = horizontal_cut_chars(plates)
for i, addr in enumerate(char_addr_list):
char_img = car_plate[chars_top:chars_bottom + 1, addr[0]:addr[1]]
char_img = cv2.resize(char_img, (char_w, char_h))
char_imgs.append(char_img)
return char_imgs
def extract_char(car_plate):
gray_plate = cv2.cvtColor(car_plate, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转为灰度图
ret, binary_plate = cv2.threshold(gray_plate, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU) # 二值化
cv2.imwrite('process_img/binary_plate.jpg', gray_plate)
print(binary_plate)
return get_chars(binary_plate)
if __name__ == '__main__':
car_plate_w, car_plate_h = 136, 36 # 车牌宽高
char_w, char_h = 20, 20 # 字符宽高
char_model_path = "char.pth"
test_images_root = 'images/test/' # 测试图片路径
files = list_all_files(test_images_root)
files.sort()
for file in files:
img = cv2.imread(file) # 读取图片
pred_img = pre_process(img) # 预处理图片
car_plate_list = locate_carPlate(img, pred_img) # 车牌定位
if len(car_plate_list) == 0:
continue
else:
car_plate = car_plate_list[0] # 获取车牌
char_img_list = extract_char(car_plate) # 获取车牌字符
for id in range(len(char_img_list)):
img_name = 'char/char-' + str(id) + '.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(img_name, char_img_list[id])运行后,能得到切割后的字符