
文章目录
- 一、电话号码数字组合
- 二、括号生成
- 三、组合
- 四、二叉树的最大宽度
-
- [1. 广度优先搜索(BFS)解法](#1. 广度优先搜索(BFS)解法)
- [2. 深度优先搜索(DFS)解法](#2. 深度优先搜索(DFS)解法)
- 五、目标和
- 六、组合总和
-
- [1. 数字选择法](#1. 数字选择法)
- [2. 数字选择次数法](#2. 数字选择次数法)
- 七、字母大小写全排列
- 八、优美的排列
- 九、N皇后------Hard
- 十、有效的数独
- 十一、解数独
-
- [1. 函数有返回值的写法](#1. 函数有返回值的写法)
- [2. 函数无返回值写法](#2. 函数无返回值写法)
- 十二、单词搜索
- 十三、黄金矿工
- 十四、不同路径III
- 十五、找出所有子集异或总和再求和
- 十六、全排列II
一、电话号码数字组合
这一题我们说白了就是对题目中给的数字进行解析,我们画一个决策树就好
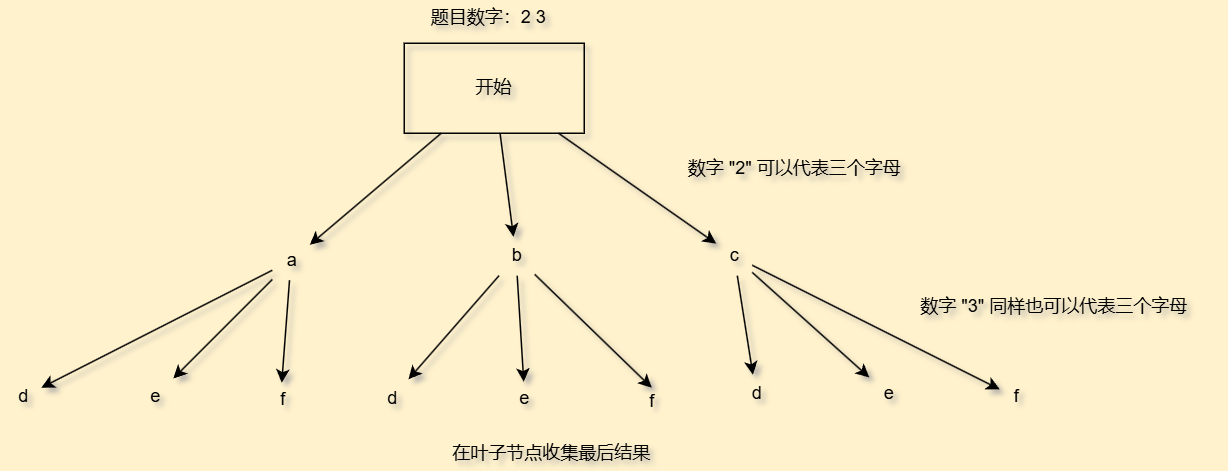
有了这个决策树,我们就知道函数怎么设计了
- 既然要映射关系,那我们就要搞一个字符串数组,下标对应不同数字映射的字母
- 肯定也要有一个
path变量去叶子节点记录结果 - 参数就是题目给的数字字符串,以及我们提取这个数字字符串的位置
java
class Solution {
String [] letter = {"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
List<String> list;
StringBuilder path;
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
path = new StringBuilder();
if(digits.equals("")){
return list;
}
dfs(digits,0);
return list;
}
private void dfs(String digits,int pos){
if(pos == digits.length()){
//说明到头了,进行添加结果
list.add(path.toString());
return;
}
//获取当前数字映射的字母
String current = letter[digits.charAt(pos)-'0'];
//开始递归
for(int i = 0;i < current.length();i++){
path.append(current.charAt(i));
dfs(digits,pos+1);
//回溯现场
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
}
}
}二、括号生成
首先我们来明确一下什么是有效的括号,那么整体上左括号数量=右括号数量,这不是废话吗!!
还有,我们要保证从头开始的子串中左括号数量必须 >= 右括号数量
比如(()))这个就是一个非法括号,而((())这个是合法的括号(前提是没有到最后位置)
因此,我们还是通过画决策树明确剪枝关系
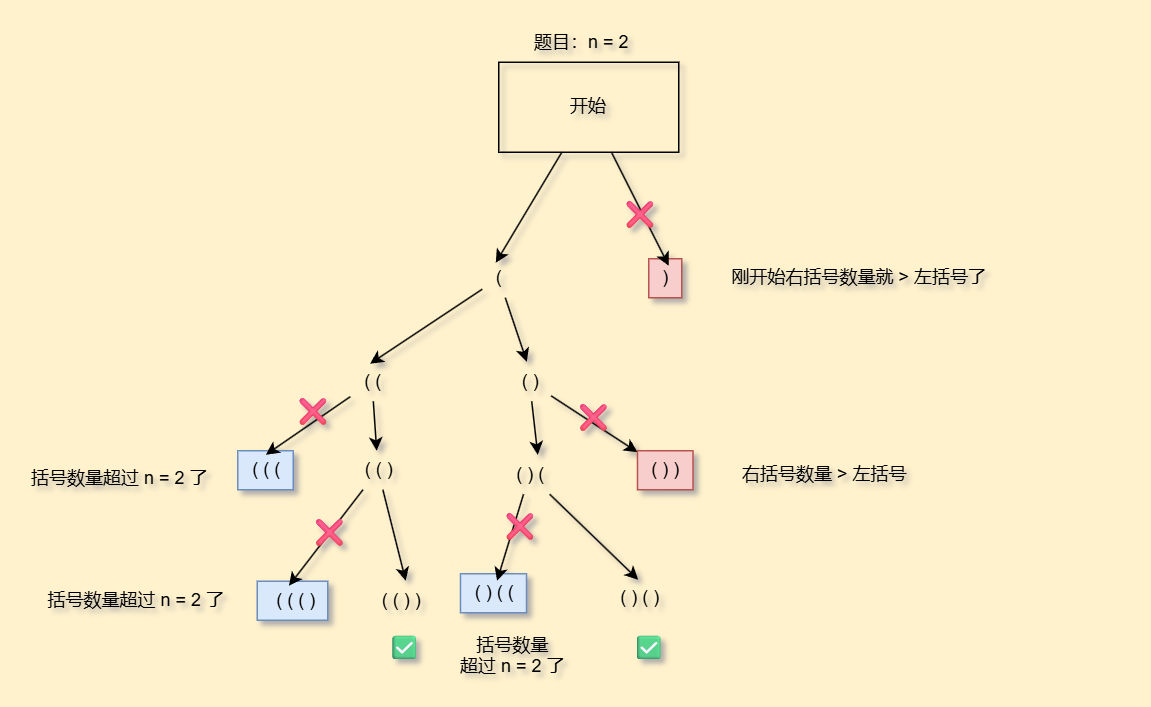
因此,我们也需要一个path变量记录路径,并且在回溯的时候要恢复现场,还原,并且根据决策树我们还涉及到一些剪枝操作
java
class Solution {
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
int left;
int right;
int count;
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
count = n;
dfs();
return list;
}
private void dfs(){
if(right == count){
list.add(path.toString());
return;
}
if(left < count){
path.append("(");
left++;
dfs();
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
left--;
}
if(right < left){
path.append(")");
right++;
dfs();
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
right--;
}
}
}三、组合
这一题不能枚举重复结果,即2,4和4,2是同一种情况
我们同样画一个决策树
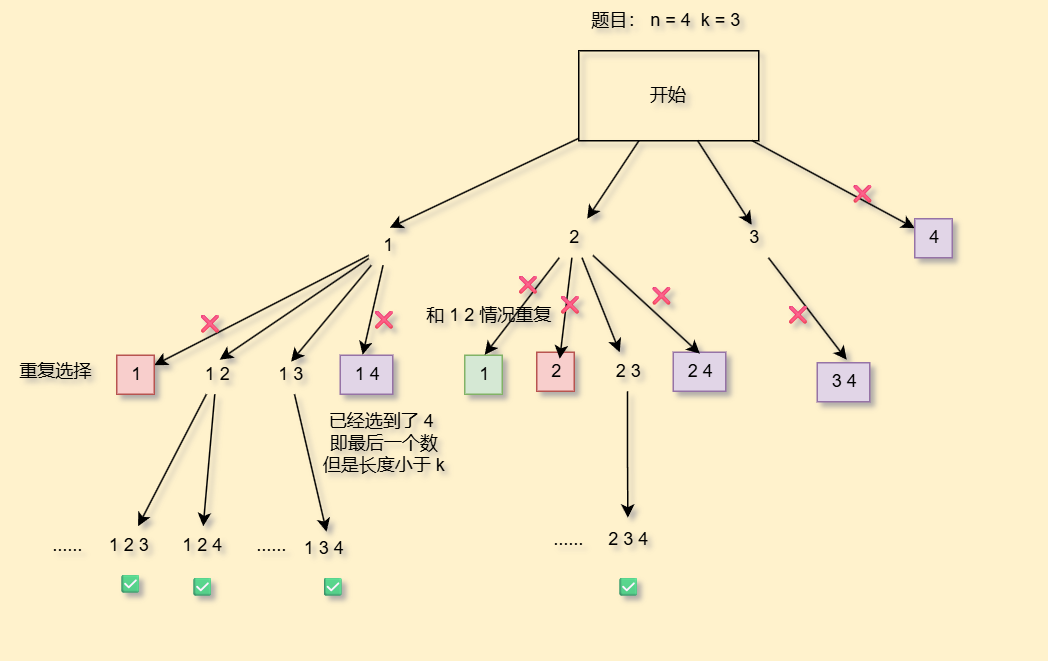
那要怎么保证不能重复呢,诶,我们可以每次枚举的时候,从上一次递归的下一个位置开始枚举
java
class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
int num;
int knum;
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
if(n <= 0){
return list;
}
num = n;
knum = k;
dfs(1);
return list;
}
private void dfs(int pos){
if(path.size() == knum){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = pos;i <= num;i++){
path.add(i);
dfs(i+1);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}四、二叉树的最大宽度
这道题如果你直接硬来的话,它可能会给你1500个单分支树的节点,因此我们可以利用堆的思想,给每个节点编号,这样我们求宽度的时候,就可以拿当前层最右侧的节点编号 - 当前层最左侧的节点编号
如果我们根节点编号从0开始,左孩子编号就是2x+1,右孩子编号就是2x+2
如果我们根节点编号从1开始,左孩子编号就是2x,右孩子就是2x+1
虽然我们编号下标可能会溢出,但是我们做的差是不可能溢出的
同时,我们使用数组去模拟队列,避免头部删除的时候增加时间复杂度
1. 广度优先搜索(BFS)解法
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
//数组模拟队列
List<Pair<TreeNode,Integer>> queue = new ArrayList<>();
//根节点从1开始
queue.add(new Pair<TreeNode,Integer>(root,1));
//记录结果
int ret = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Pair<TreeNode,Integer> cur1 = queue.get(0);
Pair<TreeNode,Integer> cur2 = queue.get(queue.size()-1);
ret = Math.max(ret,cur2.getValue()-cur1.getValue()+1);
//开始为下一层进队
//使用临时队列存储,后续直接赋值,避免头部删除增加时间复杂度
List<Pair<TreeNode,Integer>> tmps = new ArrayList<>();
for(Pair<TreeNode,Integer> tmp : queue){
TreeNode node = tmp.getKey();
int index = tmp.getValue();
if(node.left != null){
tmps.add(new Pair<TreeNode,Integer>(node.left,index*2));
}
if(node.right != null){
tmps.add(new Pair<TreeNode,Integer>(node.right,index*2+1));
}
}
//更新到下一层
queue = tmps;
}
return ret;
}
}2. 深度优先搜索(DFS)解法
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
//哈希表记录每一层最左侧节点的下标
HashMap<Integer,Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();
int maxWide;
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root,0,1);
return maxWide;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root,int depth,int index){
if(root == null){
return;
}
hash.putIfAbsent(depth,(int)index);
//计算宽度
maxWide = Math.max(maxWide,(int)(index-hash.get(depth)+1));
//递归左右子树
dfs(root.left,depth+1,index*2);
dfs(root.right,depth+1,index*2+1);
}
}五、目标和
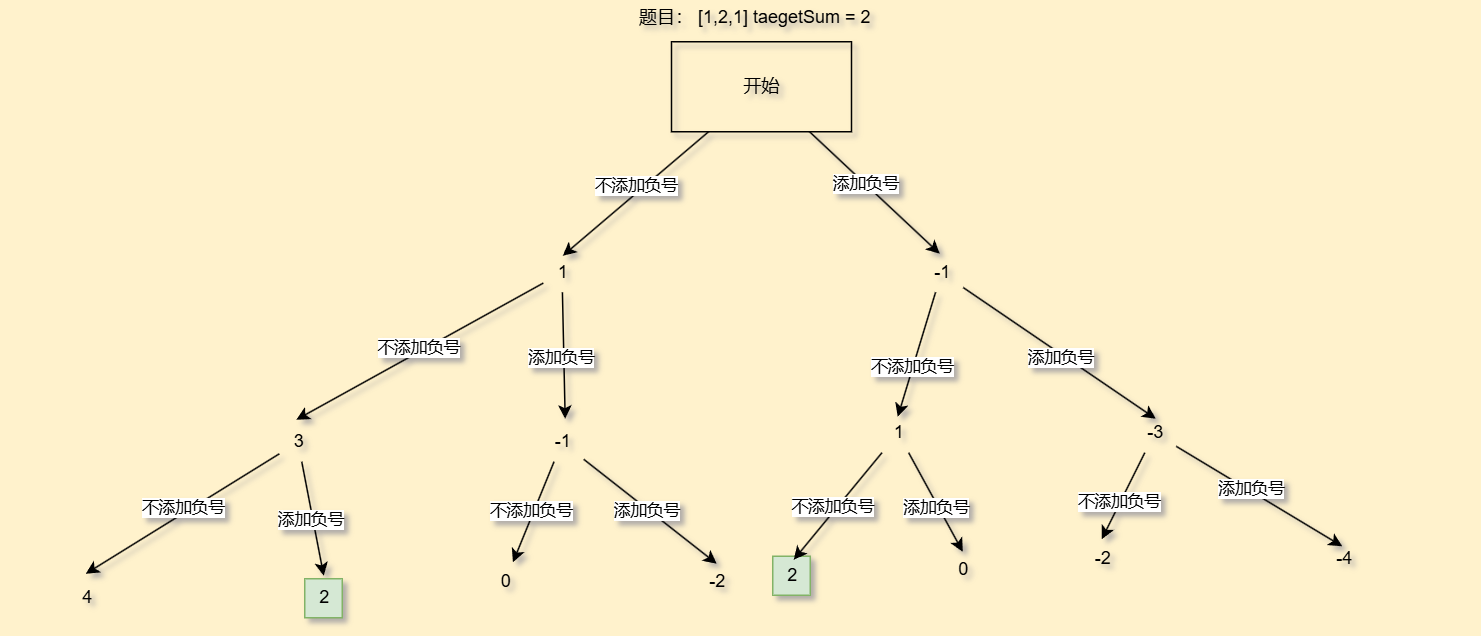
这一题我们采用暴力搜索策略
这里顺便提一嘴,如果我们的path变量是诸如int类型,就使用参数传递
如果我们的path变量是诸如List类型,就使用全局变量传递
当然具体哪种还是看个人习惯
我们还是一样画一个决策树
java
class Solution {
int path;
int targets;
int count;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
//path作为全局变量传递
targets = target;
dfs(nums,0);
return count;
}
private void dfs(int [] array,int pos){
if(pos == array.length){
if(path == targets){
count++;
}
return;
}
//加法
path += array[pos];
dfs(array,pos+1);
path -= array[pos];//恢复现场
//减法
path -= array[pos];
dfs(array,pos+1);
path += array[pos];//恢复现场
}
}六、组合总和
1. 数字选择法
这道题关键就是在于可以选择重复元素,并且2 2 3和3 2 2视为同一种情况
我们还是来画决策树
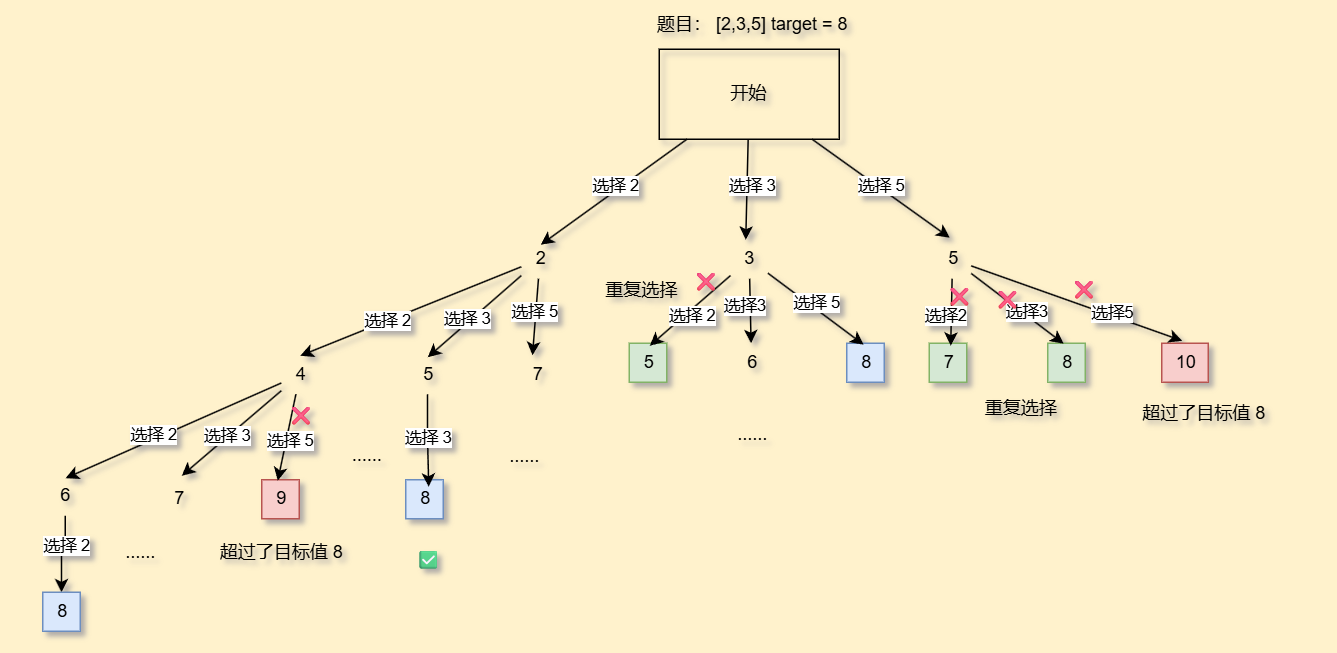
java
class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
int targets;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
targets = target;
dfs(candidates,0,0);
return list;
}
private void dfs(int [] array,int pathSum,int pos){
//递归出口一:到达数组最后一个元素
if(pathSum == targets){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
//递归出口二:路径和提前超过了目标值
if(pathSum > targets || pos == array.length){
return;
}
for(int i = pos;i < array.length;i++){
path.add(array[i]);
dfs(array,pathSum+array[i],i);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}2. 数字选择次数法
其实我们还有另外一种解法,就是考虑每个数字选择几次
我们再来画一个决策树
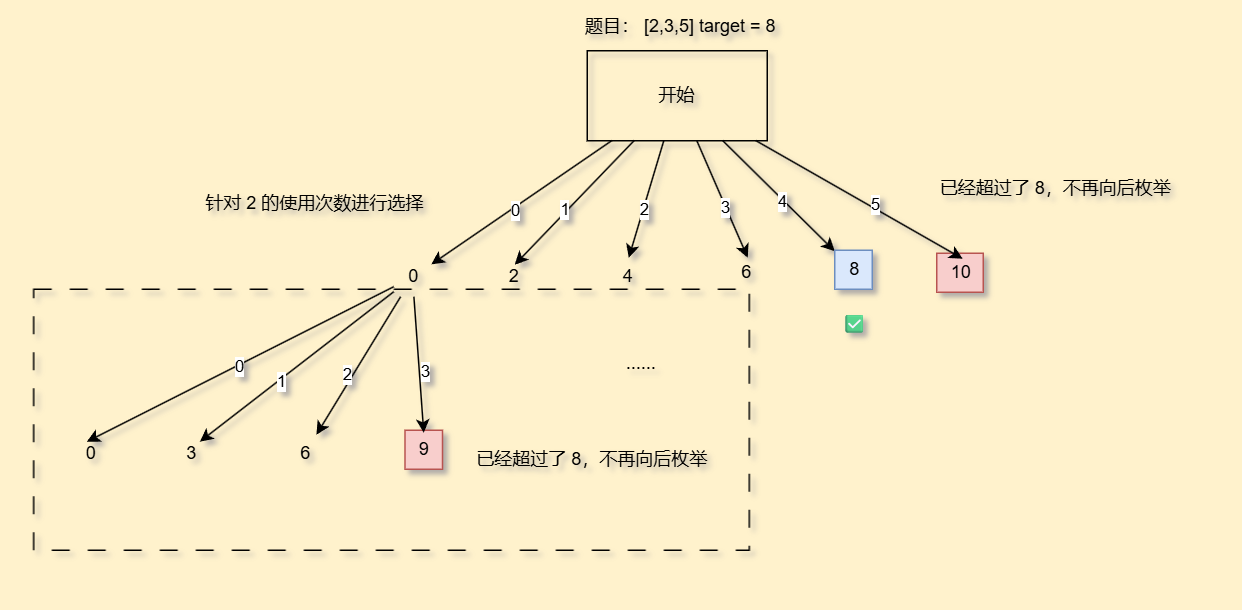
请注意,每次我们回溯现场的时候,一定要等当前数字使用次数全部枚举完毕后,再进行恢复现场
具体怎么恢复,我们递归的时候是怎么加的数字,我们回溯的时候就相反地怎么减去数字
java
class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
int targets;
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
targets = target;
dfs(candidates,0,0);
return list;
}
private void dfs(int [] array,int pathSum,int pos){
if(pathSum == targets){
list.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
if(pathSum > targets || pos == array.length){
return;
}
//枚举几个当前pos位置的数字
for(int i = 0;i*array[pos] <= targets;i++){
if(i != 0){
//只有i不为0才去添加值
//因为i为0添加值也没用
path.add(array[pos]);
}
dfs(array,pathSum+i*array[pos],pos+1);
}
//恢复现场,要把我们当前这一层添加的所有元素都删除,好让其他层保持上一层递归状态
for(int i = 1;i*array[pos] <= targets;i++){
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}七、字母大小写全排列
这题我们直接画一个决策树
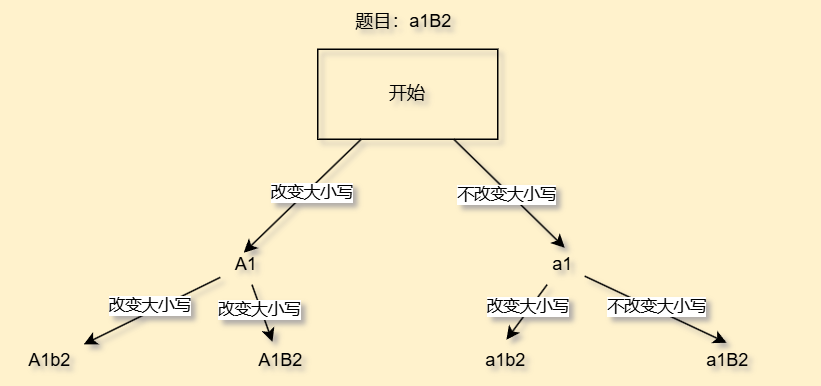
java
class Solution {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s) {
char [] ss = s.toCharArray();
dfs(ss,0);
return list;
}
private void dfs(char [] ss,int pos){
if(pos == ss.length){
list.add(path.toString());
return;
}
//不改变大小写
path.append(ss[pos]);
dfs(ss,pos+1);
//恢复现场
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
//改变大小写,并且是字母才改变
if(Character.isLetter(ss[pos])){
//判断此时字母是大写还是小写
if(Character.isLowerCase(ss[pos])){
path.append(Character.toUpperCase(ss[pos]));
}else{
path.append(Character.toLowerCase(ss[pos]));
}
dfs(ss,pos+1);
//恢复现场
path.deleteCharAt(path.length()-1);
}
}
}八、优美的排列
这题就在于不能选择重复元素,因此我们可以使用一个boolean类型数组,标记当前数字有没有被使用过
直接看代码吧
java
class Solution {
boolean[] isUse;
int count;
public int countArrangement(int n) {
isUse = new boolean[n+1];
dfs(1,n);
return count;
}
private void dfs(int pos,int num){
if(pos > num){
//说明之前都是优美排列
count++;
return;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= num;i++){
if(!isUse[i] && (i % pos == 0 || pos % i == 0)){
isUse[i] = true;
dfs(pos+1,num);
//恢复现场
isUse[i] = false;
}
}
}
}九、N皇后------Hard
我们首先来明确皇后攻击其他皇后的规则
首先,当前行和列不能有其他皇后,并且主对角线和副对角线也不能有皇后
我们先来画决策树
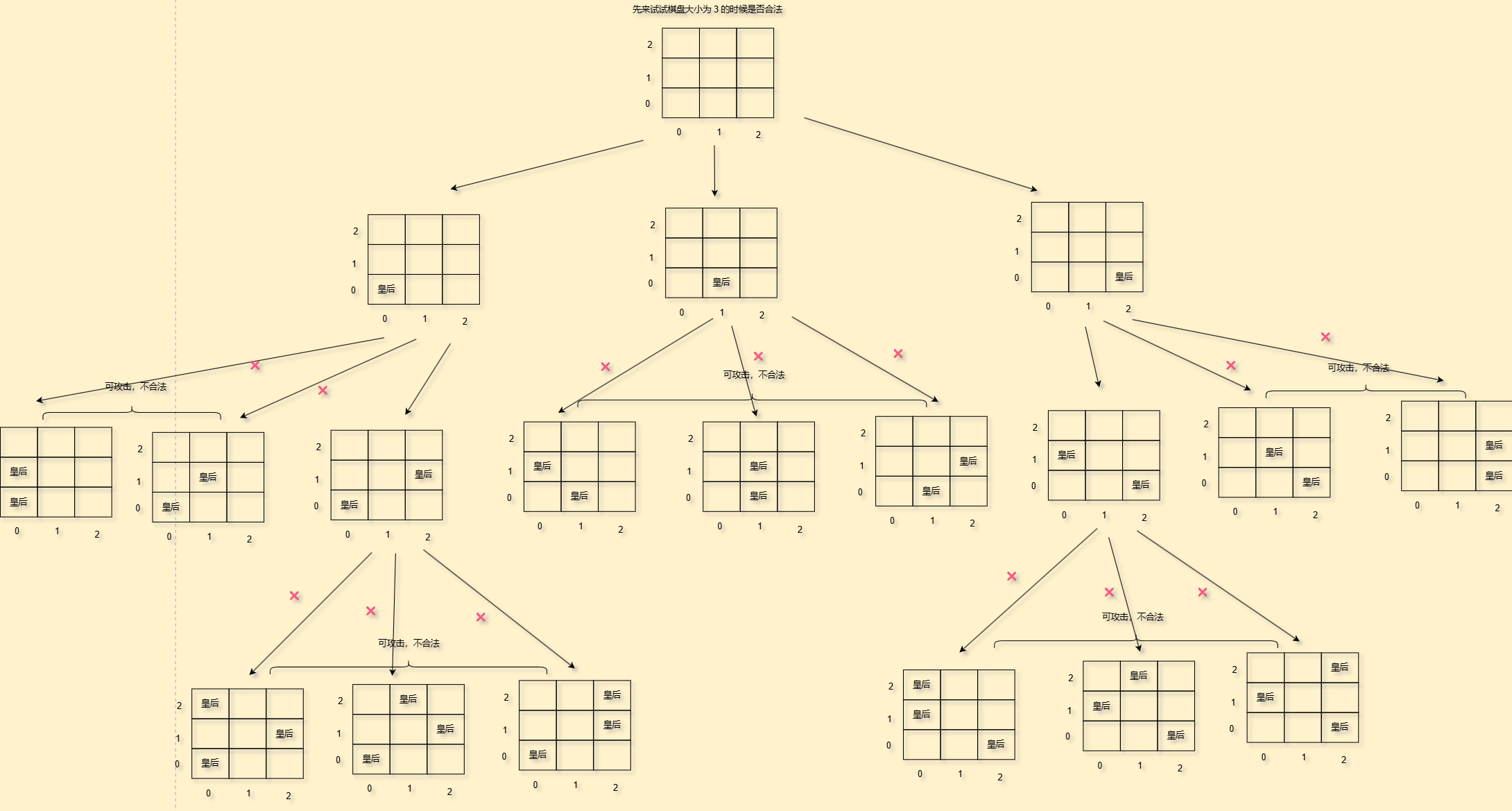
因此棋盘大小是3是不可以的,其实我们决策树里边就可以看出来我们的具体函数设计
即我们每行每行的去考虑皇后放在哪个位置,检查行列对角线,一直枚举到超出棋盘范围终止
但是如果我们直接循环四次查看行列对角线符合要求,这世界复杂度也太高了,因此我们可以类似哈希表,搞三个boolean数组
一个数组表示当前列是否存在皇后(我们是逐行递归的,行不用看)
另一个数组是主对角线数组,这个利用到我们数学原理
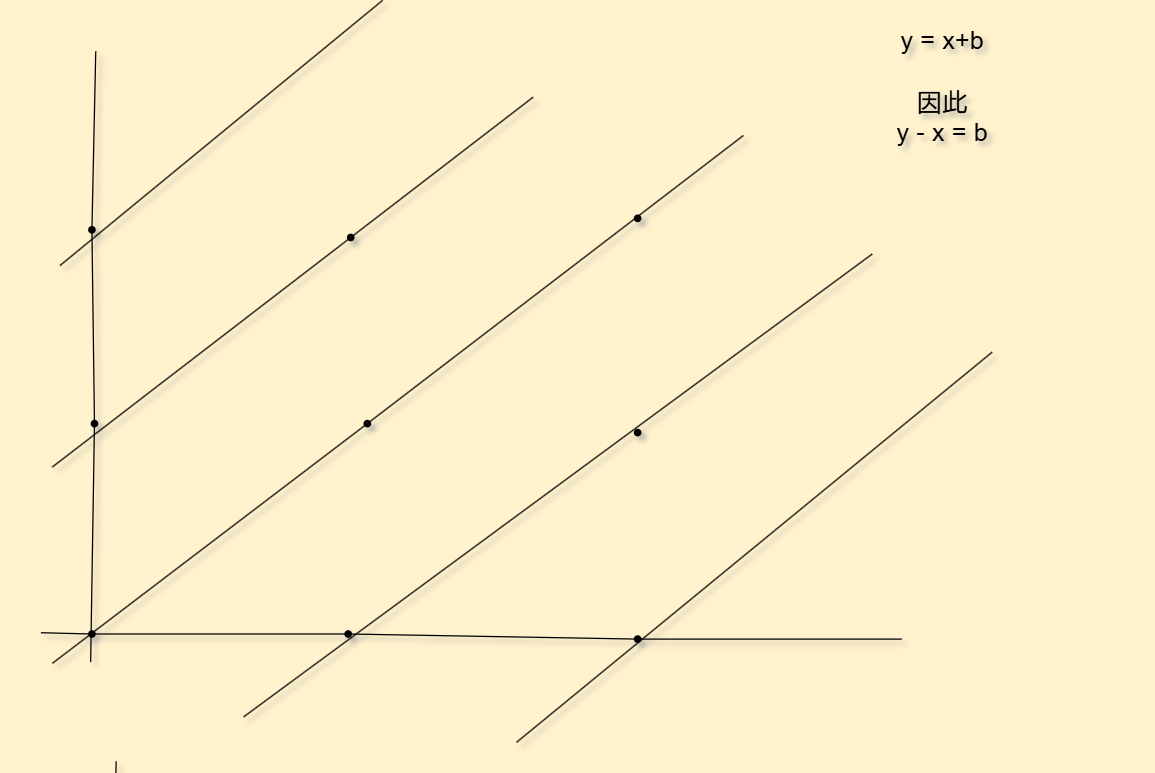
因此只要我们y-x=b,这个b值相同,就说明我们在同一条线上
但是,如果y-x < 0怎么办呢,我们可以加上偏移量,让其结果永远是正数
即y - x + 棋盘大小 = b
同理副对角线也是这样搞法,只不过不用担心负值
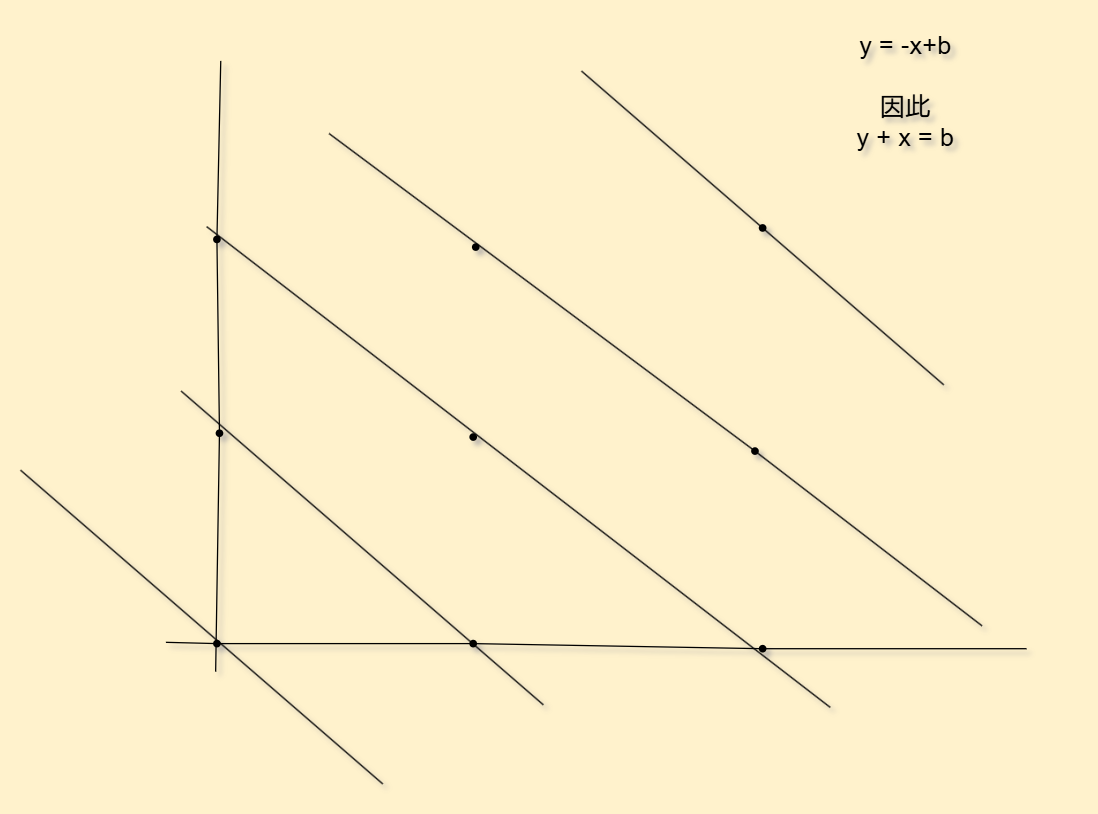
即y + x = b
同时,我们对角线数组大小必须是2倍棋盘大小,不然的话可能会越界
java
class Solution {
//列数组,标识每一列的皇后出现情况
boolean [] cols;
//主对角线数组,表示每一个主对角线皇后出现情况
boolean [] dig1;
//副对角线,表示每一个副对角线皇后出现情况
boolean [] dig2;
//统计结果
List<List<String>> list = new ArrayList<>();
//表示当前棋盘大小
int size;
//需要一个全局变量路径去记录结果
char [][] path;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
cols = new boolean[n];
//使用y-x=b这一特性判断,因此需要两倍n的大小
dig1 = new boolean[2*n];
//使用y+x=b这一特性判断,因此需要两倍n的大小
dig2 = new boolean[2*n];
//初始化路径
path = new char[n][n];
//初始化棋盘大小
size = n;
//初始棋盘
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){
path[i][j] = '.';
}
}
//因此需要一个坐标
dfs(0);
return list;
}
private void dfs(int row){
//当我们枚举到最后一行的下一行(即越界时候)停止枚举
if(row == size){
//能到达这里,说明是一种合法情况
//遍历path结果集
List<String> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
tmp.add(new String(path[i]));
}
list.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}
//开始逐行枚举,现在针对当前行的每一列进行枚举
for(int i = 0;i < size;i++){
if(!cols[i] && !dig1[row-i+size] && !dig2[row+i]){
//说明是一个合法位置
path[row][i] = 'Q';
//设置数组
cols[i] = dig1[row-i+size] = dig2[row+i] = true;
dfs(row+1);
//恢复现场
path[row][i] = '.';
cols[i] = dig1[row-i+size] = dig2[row+i] = false;
}
}
}
}十、有效的数独
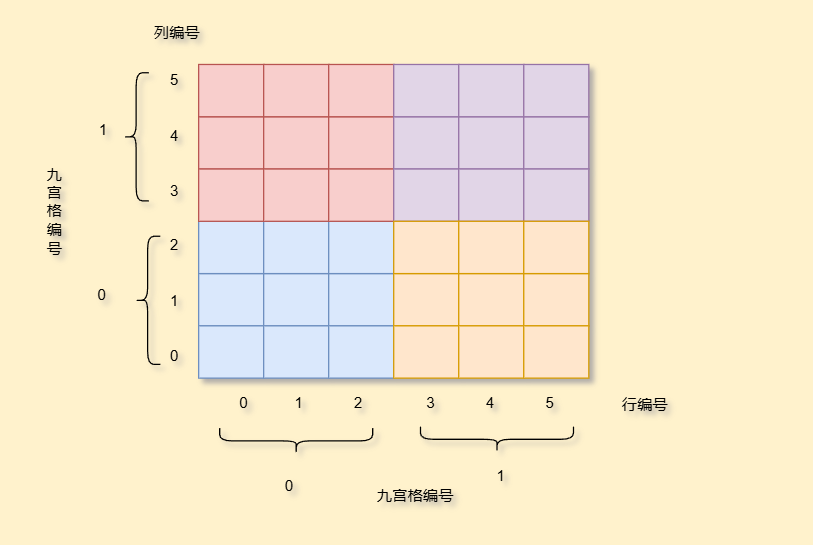
我们可以定义一个row的二维数组,row[i][j]表示第i行是否出现j这个数字
同时我们可以定义一个col的二维数组,col[i][j]表示第i列是否出现j这个数字
再者我们可以定义一个grid的三维数组,grid[i][j][num]表示第i行且第j列个九宫格内是否出现num这个数字
那我们要如何确定自己在哪个九宫格之中呢,我们仅需把当前坐标比如是(4,2)除以3,即第1行第0列的九宫格,即可找到位置
java
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
int size = 9;
// 记录每行数字出现情况
boolean[][] row = new boolean[size][size + 1];
// 记录每列数字出现情况
boolean[][] col = new boolean[size][size + 1];
// 记录每个3x3宫格数字出现情况
boolean[][][] grid = new boolean[3][3][size + 1];
// 遍历整个数独板
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
char c = board[i][j];
// 跳过空白格
if (c == '.') {
continue;
}
// 字符数字转整型数字
int num = c - '0'; // 或者使用 Character.getNumericValue(c)
// 检查当前数字是否在行、列、宫格中重复出现
if (row[i][num] || col[j][num] || grid[i / 3][j / 3][num]) {
return false; // 发现重复,立即返回false
}
// 标记数字已出现
row[i][num] = true;
col[j][num] = true;
grid[i / 3][j / 3][num] = true;
}
}
return true; // 所有检查通过
}
}十一、解数独
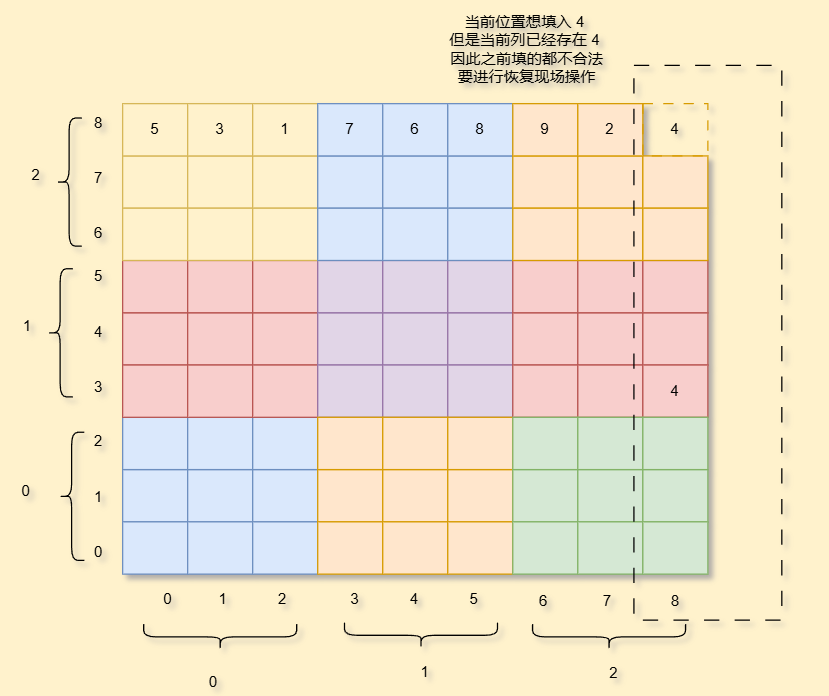
这题难点就在于我们要对每行每列(即每个单元格都要判断),并且跟上一题一样,也是使用三个数组标记
但是如果我们填入某个合法数字,后续也可能会导致数字无法填入,就要进行回溯操作
那我们要怎么知道我们填的是否正确呢,我们可以使用一个返回值,如果到了最后整个棋盘都填成功了,我们就一直向上返回true,反之就返回false,以便进行恢复现场操作
1. 函数有返回值的写法
java
class Solution {
boolean [][] row;
boolean [][] col;
boolean [][][] grid;
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
row = new boolean[9][10];
col = new boolean[9][10];
grid = new boolean[3][3][10];
//初始化原本就存在数独表中的数字
for(int i = 0;i < 9;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < 9;j++){
if(board[i][j] != '.'){
int num = board[i][j] - '0';
row[i][num] = true;
col[j][num] = true;
grid[i/3][j/3][num] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(board);
}
private boolean dfs(char[][] board){
//遍历每一个单元格
for(int rows = 0;rows < 9;rows++){
for(int cols = 0;cols < 9;cols++){
if(board[rows][cols] == '.'){
//不是数字才开始填入
for(int num = 1;num <= 9;num++){
//开始尝试1-9数字
if(!row[rows][num] && !col[cols][num] && !grid[rows/3][cols/3][num]){
//先尝试放入数字
board[rows][cols] = (char)('0' + num);
//设置状态
row[rows][num] = true;
col[cols][num] = true;
grid[rows/3][cols/3][num] = true;
//递归,自动会找到后续的单元格,尝试填入数字
//如果我们最后发现整个数独表填满了,直接向上返回
if(dfs(board)){
return true;
}
//此时如果我们填入的数字不合法,我们就进行恢复现场操作
board[rows][cols] = '.';
//同时不要忘了去设置状态
row[rows][num] = false;
col[cols][num] = false;
grid[rows/3][cols/3][num] = false;
}
}
//说明我们填入的1-9数字不合法,就要给上一层返回false
return false;
}
}
}
//说明整个棋盘每个空格我们都填完了,因此直接返回true
return true;
}
}2. 函数无返回值写法
java
class Solution {
//表示棋盘大小
int size;
//全局变量棋盘
char[][] boards;
//检查行是否存在相同的数字
boolean[][] row;
//检查列是否有存在相同的数字
boolean[][] col;
//检查九宫格内是否存在相同的数字
boolean[][][] grid;
//标记是否找到解
boolean isFound = false;
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
boards = board;
size = 9; // 数独固定为9×9
row = new boolean[size][10]; //数字1-9,所以需要10个位置
col = new boolean[size][10];
grid = new boolean[3][3][10]; //九宫格是3×3的
//初始化已有数字
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < size; j++){
char ch = board[i][j];
if(ch != '.'){
int num = ch - '0';
row[i][num] = true;
col[j][num] = true;
grid[i/3][j/3][num] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(0,0);
}
private void dfs(int posx, int posy){
if(isFound){
//整个表求解完毕
return;
}
if(posx == size){
//找到了解
isFound = true;
return;
}
if(posy == size){
//说明当前行找完了
dfs(posx+1,0);
return;
}
if(boards[posx][posy] != '.'){
//当前位置已经有数字了
dfs(posx,posy+1);
return;
}
//每个单元格看,前提要是非数字才去判断
for(int i = 1; i <= 9; i++){
//遍历1-9数字
if(!row[posx][i] && !col[posy][i] && !grid[posx/3][posy/3][i]){
boards[posx][posy] = (char)('0' + i);
row[posx][i] = true;
col[posy][i] = true;
grid[posx/3][posy/3][i] = true;
//去当前行的下一列看看
dfs(posx,posy+1);
if(isFound){
//找到了解直接向上返回
return;
}
/*
1.递归到达某个单元格,所有1-9的数字都违反规则
2.循环结束,该层递归返回false
3.返回到上一层递归,执行回溯代码
4.我们有理由认为这个数字的填入导致后续单元格数字无法填入
*/
//回溯现场
boards[posx][posy] = '.';
row[posx][i] = false;
col[posy][i] = false;
grid[posx/3][posy/3][i] = false;
}
}
}
}十二、单词搜索
这题我们可以针对性的一行行扫描,具体看图
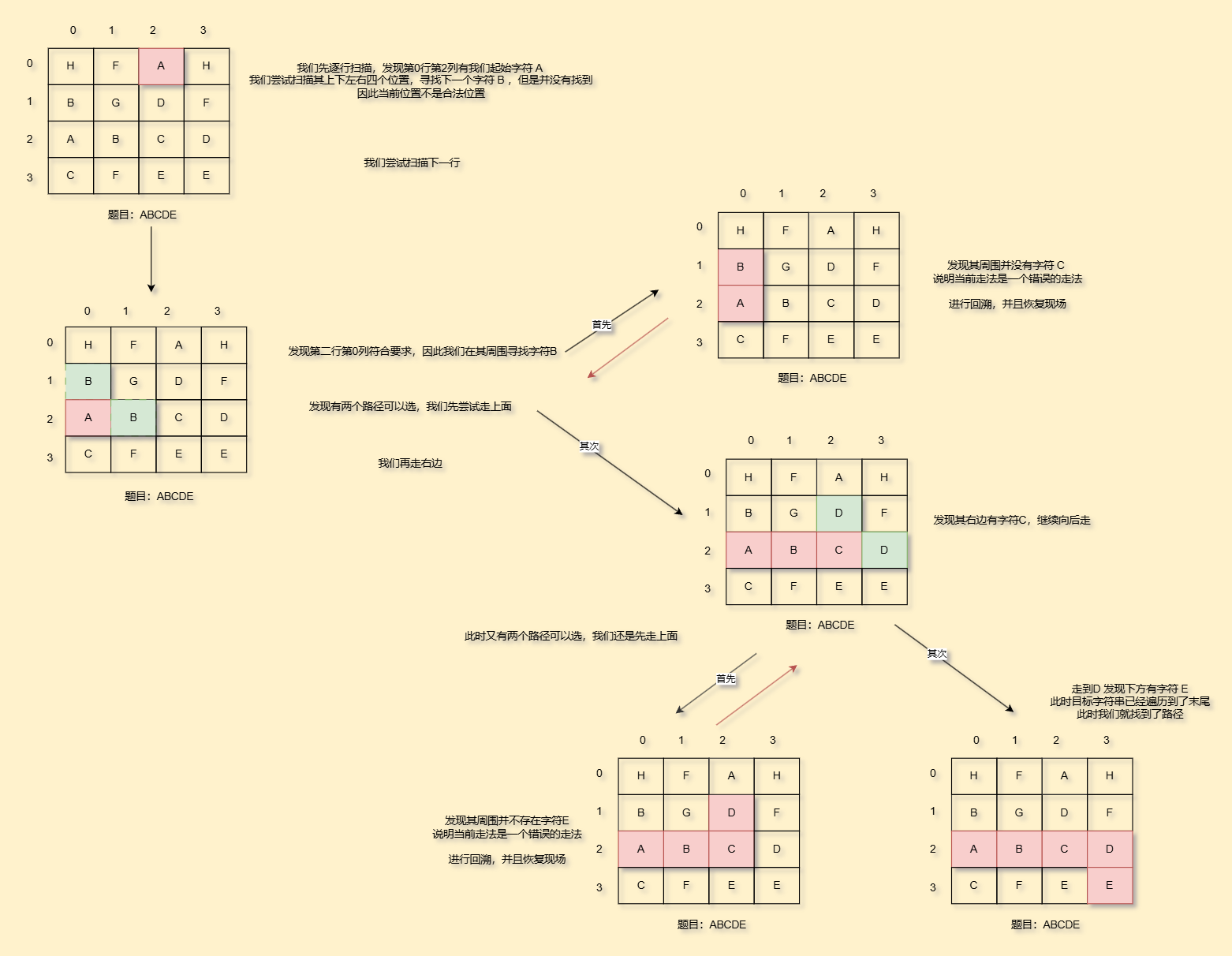
因此我们函数设计就可以变成每一次递归的时候,尝试去上下左右四个方位寻找目标字符,找到了就递归,找不到就回溯
并且我们搜索也是不能走重复路径的,因此同样使用一个boolean标记当前位置是否走过
但是我们要进行四个位置递归,开销太大,我们可以搞两个向量数组,表示四个方位,循环就循环四次就好
向量数组x方向:{0,0,1,-1} y方向:{1,-1,0,0},注意x和y方向数组要一一对应,能够表示当前位置的上下左右四个位置
你肯定想说,我不一定要用到向量数组啊,但是如果题目要求不能修改原数组呢
java
class Solution {
boolean [][] isUse;
char [][] boards;
int wordLength;
char[] words;
int wide;
int height;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word){
wide = board[0].length;
height = board.length;
if(height == 0){
return false;
}
wordLength = word.length();
words = word.toCharArray();
isUse = new boolean[height][wide];
//使用全局棋盘,为了在参数传递的时候节省递归开销
boards = board;
for(int i = 0;i < height;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < wide;j++){
//寻找字符串中第一个字符
if(board[i][j] == word.charAt(0)){
//就从此位置开始找,从字符串的第二个字符开始找
//先标记这个位置使用过
isUse[i][j] = true;
if(dfs(i,j,1)){
//如果从此位置开始后续的字符都可以被找到
//我们就直接返回true
return true;
}
//说明上面判断不合法,继续往后寻找
isUse[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
//到了这里说你整个表中并不存在和字符串中第一个字符匹配的字符
//直接返回false表示结果
return false;
}
//为避免多次递归,对于矩阵,我们使用一个向量数组表示各个位置
//上下两组一一对应
int [] x = {0,0,1,-1};
int [] y = {1,-1,0,0};
//posX表示第几行,poxY表示第几列
private boolean dfs(int posx,int posy,int strPos){
if(strPos == wordLength){
//说明此时到了字符串的最后一个字符,返回true
return true;
}
//使用循环直接去枚举四个方向
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++){
//此时的位置,我们使用向量作为偏移量
int curX = posx+x[i];
int curY = posy+y[i];
//判断当前位置的合法性
if(curX >= 0 && curX < height && curY >= 0 && curY < wide && !isUse[curX][curY] && boards[curX][curY] == words[strPos]){
//标记当前位置被使用过了
isUse[curX][curY] = true;
//进行递归
if(dfs(curX,curY,strPos+1)){
//说明后续的都是正确的,我们直接向上返回
return true;
}
//说明此时是一种错误的走法,恢复现场
isUse[curX][curY] = false;
}
}
//到了这里说明四个方向都不符合要求,再一次回退
return false;
}
}十三、黄金矿工
这题和单词搜索简直是一模一样,因此就不啰嗦了
java
class Solution {
//同理使用一个bool数组表示当前位置是否被使用过
boolean[][] isUse;
int wide;
int height;
int ret;
public int getMaximumGold(int[][] grid) {
wide = grid[0].length;
height = grid.length;
isUse = new boolean[height][wide];
//选取一个不为0的地点开始挖矿
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < wide; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] != 0) {
//从这个地方开始挖,先标记当前位置状态
isUse[i][j] = true;
//先把当前位置黄金加上
dfs(grid, i, j, grid[i][j]);
//恢复现场,从其他位置开始挖掘
isUse[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
//同理为避免多次递归,我们使用向量数组
int[] x = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
int[] y = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
//posX表示第几行,posYB表示第几列
private void dfs(int[][] grid, int posx, int posy, int path) {
ret = Math.max(ret, path);
//同理使用循环枚举四个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int curX = posx + x[i];
int curY = posy + y[i];
if (curX >= 0 && curX < height && curY >= 0 && curY < wide && !isUse[curX][curY] && grid[curX][curY] != 0) {
//先统计结果
path += grid[curX][curY];
//再设置状态
isUse[curX][curY] = true;
//递归下一次
dfs(grid, curX, curY, path);
//恢复现场
isUse[curX][curY] = false;
//不要忘记path也要恢复
path -= grid[curX][curY];
}
}
}
}十四、不同路径III
这题难就难在要把所有0的位置都走一遍,并且还不能重复,并且-1的位置还不能走
这题我们采用暴力搜索方式,先扫描整个表,寻找开始位置和结束位置
再去统计0的个数,这决定了我们走到终点时,我们实际走到步数和理想步数能不能对的上
java
class Solution {
//标记某个位置是否已经走过
boolean [][] isUse;
//起始位置
int startX,startY;
int endX,endY;
//统计0的个数,也就是预期走多少步
int step;
//定义计数器
int count;
int wide;
int height;
public int uniquePathsIII(int[][] grid) {
//废话不多说,直接开始暴力搜索枚举
height = grid.length;
wide = grid[0].length;
isUse = new boolean[height][wide];
step = 0; // 重置step
count = 0; // 重置count
//先扫描一遍整个表,统计0的个数,并且明确起始位置
for(int i = 0;i < height;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < wide;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 0){
step++;
}else if(grid[i][j] == 1){
startX = i;
startY = j;
}else if(grid[i][j] == 2){
endX = i;
endY = j;
}
}
}
isUse[startX][startY] = true;
//开始递归,从开始位置开始
dfs(grid,startX,startY,0);
return count;
}
//同样地使用向量数组
int [] x = {0,0,1,-1};
int [] y = {1,-1,0,0};
//同理posx表示行,posy表示列,path表示路径上0的个数
private void dfs(int [][] grid,int posx,int posy,int path){
// 先检查是否到达终点
if(posx == endX && posy == endY){
//如果遇到了数字2,就到了终点,检查结果
if(path == step){
count++;
}
return;
}
//枚举四个方向
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++){
int curX = posx+x[i];
int curY = posy+y[i];
// 检查边界、是否访问过、是否是障碍物
if(curX >= 0 && curX < height && curY >= 0 && curY < wide &&
!isUse[curX][curY] && grid[curX][curY] != -1){
// 标记为已访问
isUse[curX][curY] = true;
// 计算新的路径长度:如果是0则加1,否则保持不变
int newPath = path;
if(grid[curX][curY] == 0) {
newPath = path + 1;
}
// 递归到下一个位置
dfs(grid, curX, curY, newPath);
//恢复现场
isUse[curX][curY] = false;
}
}
}
}十五、找出所有子集异或总和再求和
决策树就不用画了,这一题就是子集那道题的综合版本
找子集就是我们刚开始传入0下标,我们每一次递归这个下标++就好
然后我们在回溯的时候,要记得恢复现场,可以再异或当前位置的数字,达到消除的效果
java
class Solution {
int sum;
int path;
public int subsetXORSum(int[] nums) {
subsetXORSumChild(nums,0);
return sum;
}
private void subsetXORSumChild(int [] nums,int pos){
//统计每一层的异或和
sum += path;
for(int i = pos;i < nums.length;i++){
path ^= nums[i];
subsetXORSumChild(nums,i+1);
//向上回溯的时候,要把当前层多余的元素消除
//因为刚刚在sum中就已经把每一层的结果都统计到了
path ^= nums[i];
}
}
}十六、全排列II
这题就是全排列I的升级版本,要求同一个位置不能选择重复的数字,我们还是来换一个决策树
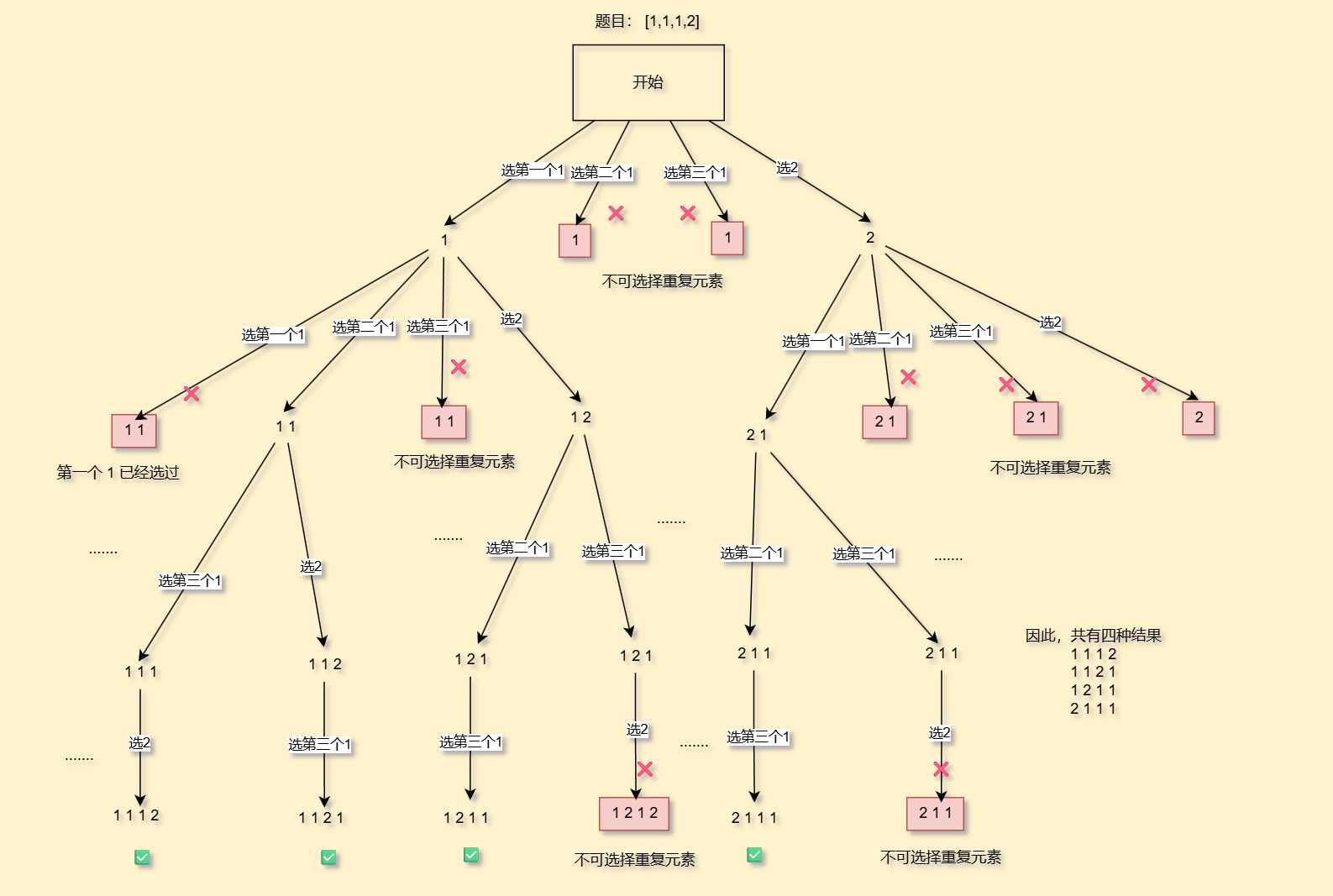
代码实在看不明白可以看我画的决策树,自己找几种情况带入就好了
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret;
List<Integer> path;
boolean [] isUse;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
isUse = new boolean[nums.length];
ret = new ArrayList<>();
path = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
permuteUniqueChild(nums,0);
return ret;
}
private void permuteUniqueChild(int [] nums,int pos){
if(pos == nums.length){
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
//正常遍历数组
for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){
if((isUse[i] == true || (i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && isUse[i-1] == false))){
//剪去不合法分支,其中i != 0 是为了保证i-1不越界
continue;
}
path.add(nums[i]);
isUse[i] = true;
permuteUniqueChild(nums,pos+1);
//恢复现场
isUse[i] = false;
//剪枝
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
/*
for循环也可以这样写,即只看合法分支
for(int i = 0;i < nums.length;i++){
if(!isUse[i] && *i == 0 || nums[i] != nums[i-1] && isUse[i-1]){
path.add(nums[i]);
isUse[i] = true;
permuteUniqueChild(nums,pos+1);
//恢复现场
isUse[i] = false;
//剪枝
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
*/
}
}希望本篇文章对您有帮助,有错误您可以指出,我们友好交流
END