29、删除链表倒数第n个节点
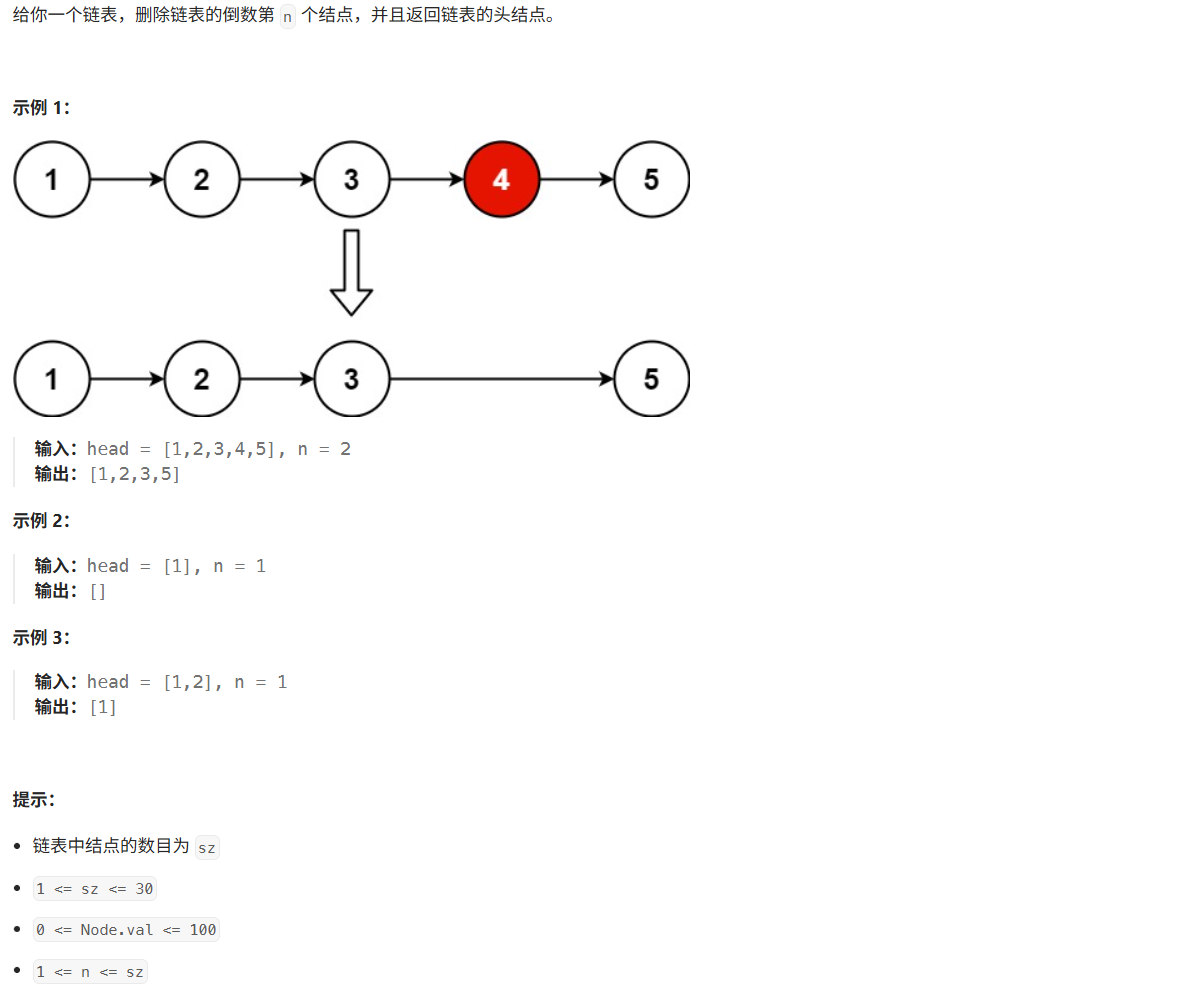
思路:使用快慢指针,快指针先走n步,之后快慢指针一起走直到快指针走到底,这时候慢指针指向的便是要删除节点的前一个,进行后一个删除即可。同时注意到有可能第一个节点便是要删除的节点,所以使用一个前置节点指向头节点进行链表存储。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
int fast = n;
// 前置节点
ListNode* pre_head = new ListNode();
pre_head->next = head;
ListNode* fast_cur = pre_head, *slow_cur = pre_head;
while(n--){
fast_cur = fast_cur->next;
}
while(fast_cur->next){
slow_cur = slow_cur->next;
fast_cur = fast_cur->next;
}
slow_cur->next = slow_cur->next->next;
return pre_head->next;
}
};30、两两交换链表中的节点
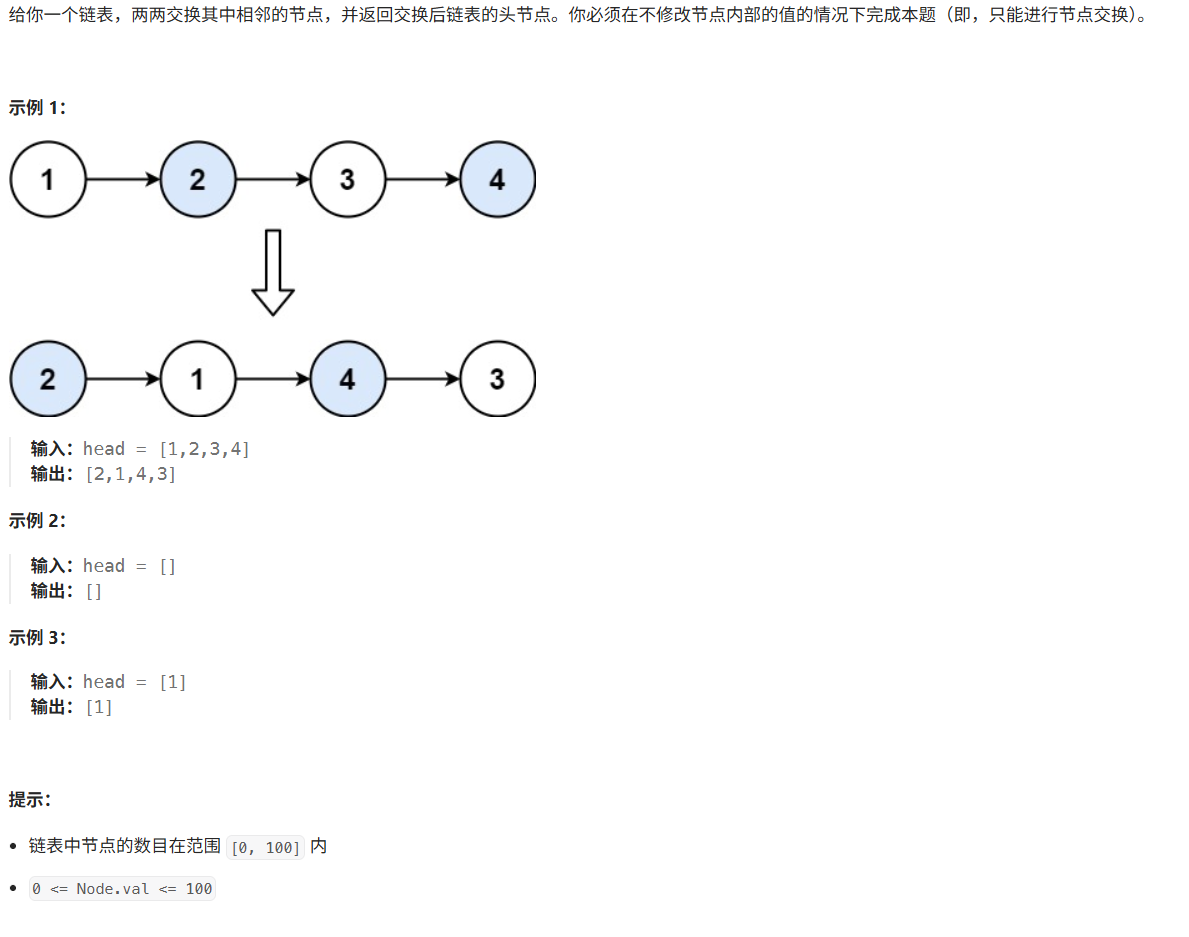 思路:递归算法进行节点交换
思路:递归算法进行节点交换
cpp
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next)
return head;
ListNode *node1 = head;
ListNode *node2 = head->next;
ListNode *node3 = node2->next;
node1->next = swapPairs(node3);
node2->next = node1;
return node2;
}
};31、k个一组翻转链表
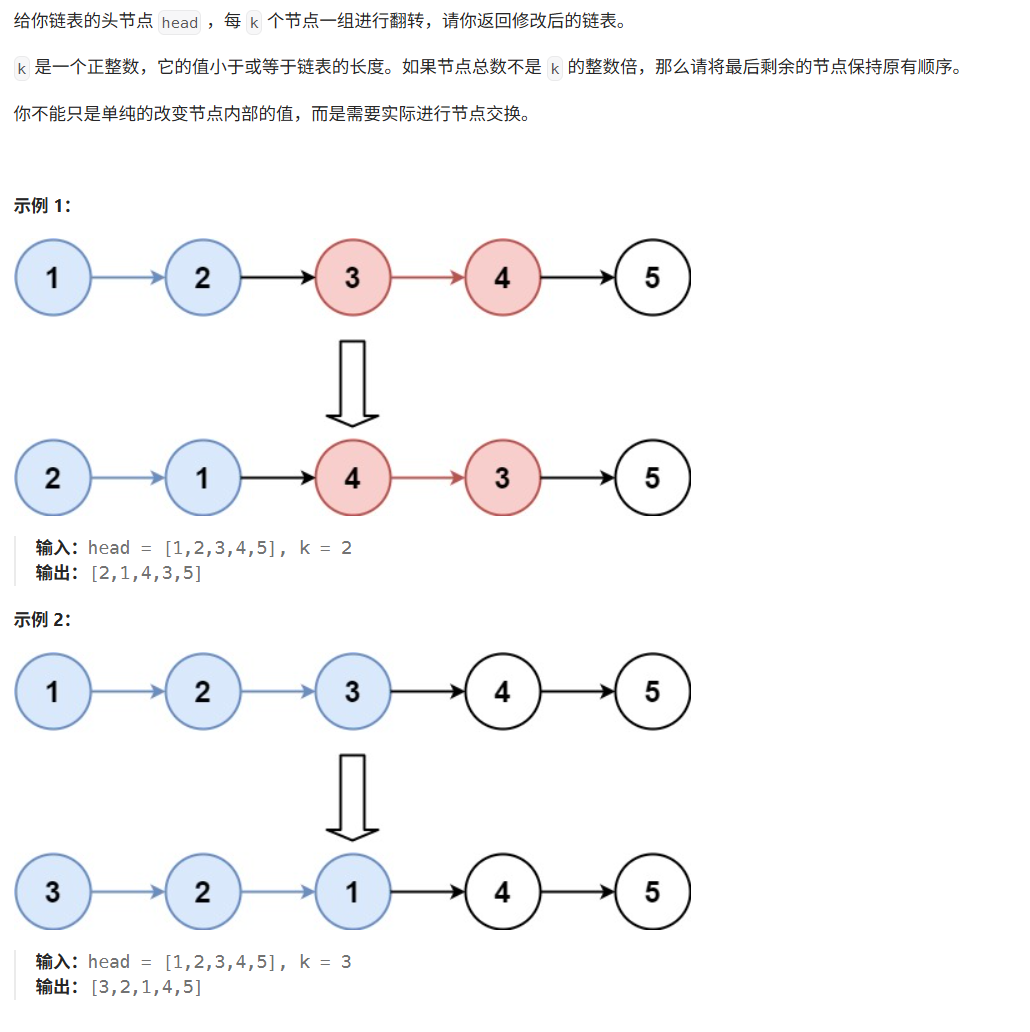
思路:迭代法,分组翻转链表
cpp
class Solution {
void reverseList(ListNode* head, ListNode *tail){
ListNode *stop = tail->next;
ListNode *pre = stop;
ListNode *cur = head;
while(cur != stop){
ListNode *tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
}
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *pre_head = new ListNode(0, head), *l = pre_head, *r = pre_head;
while(1){
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
r = r->next;
if(!r) return pre_head->next;
}
ListNode *nextl = l->next;
reverseList(nextl, r);
l->next = r;
l = r = nextl;
}
}
};32、随机链表的复制

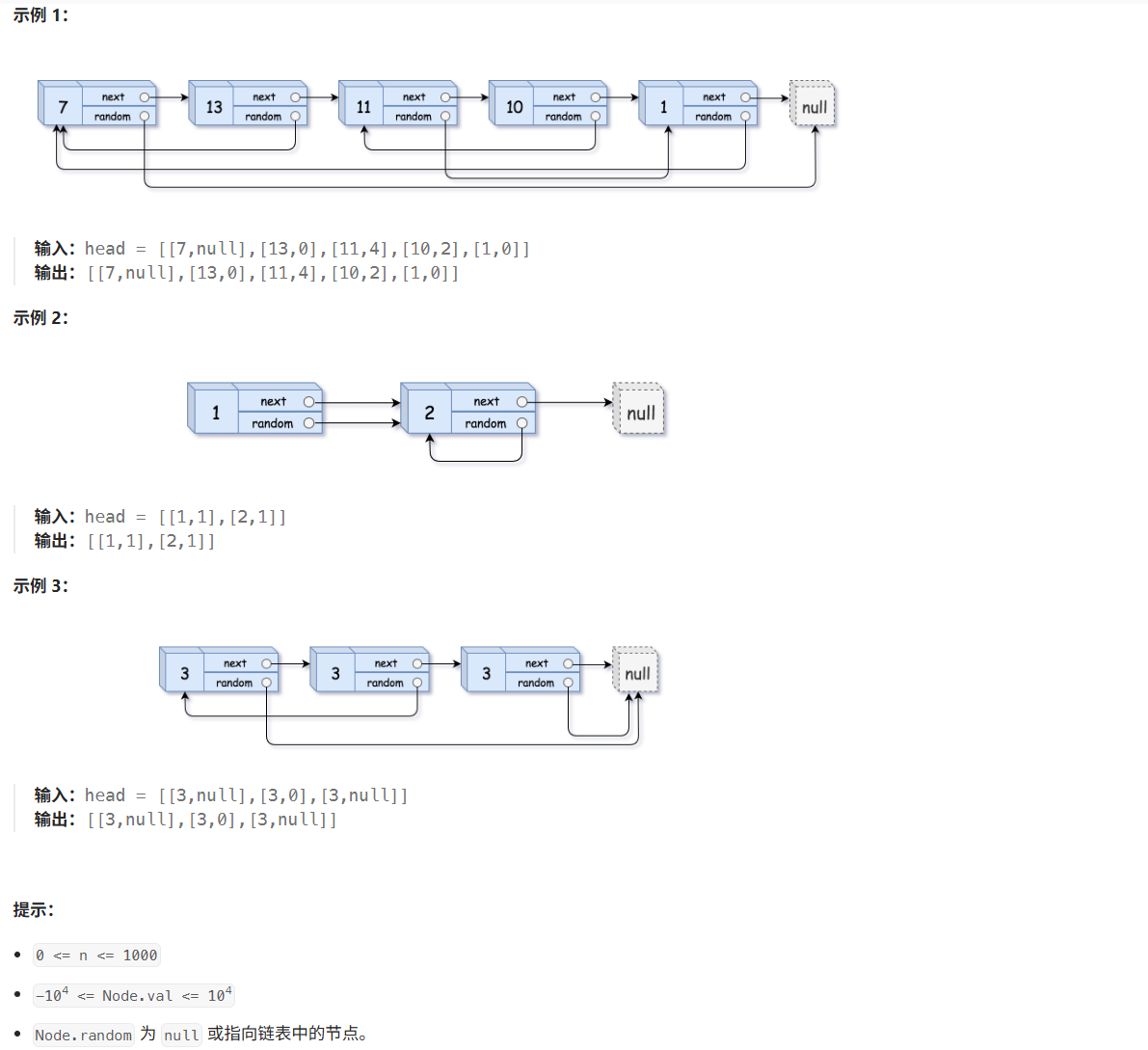
思路:链表拼接拆分,复制每个节点接入,再拆分。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if(!head) return nullptr;
Node *cur = head;
while(cur){
Node* tmp = new Node(cur->val);
tmp->next = cur->next;
cur->next = tmp;
cur = tmp->next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur){
if(cur->random)
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
cur = head->next;
Node* pre = head, *res = cur;
while(cur->next){
pre->next = pre->next->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
pre = pre->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
pre->next = nullptr;
return res;
}
};33、排序链表
思路:归并排序,采用递归的方式将左侧和右侧链表进行排序合并。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode *middle = getMiddle(head);
ListNode *rightHead = middle->next;
middle->next = nullptr;
ListNode *left = sortList(head);
ListNode *right = sortList(rightHead);
ListNode *pre_head = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode *cur = pre_head;
while(left && right){
if(left->val <= right->val){
cur->next = left;
left = left->next;
} else {
cur->next = right;
right = right->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
if(left) cur->next = left;
if(right) cur->next = right;
return pre_head->next;
}
ListNode* getMiddle(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head->next;
while(fast && fast->next){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
};34、合并k个升序链表
思路:迭代法,可以参考之前的合并两个升序链表,不断进行两两合并,比如lists[0]和lists[1]合并放在lists[0],lists[2]和lists[3]合并放在lists[2],之后再lists[0]和lists[2]合并,以此内推。最终合并的链表都放在lists[0],返回即可。
cpp
class Solution {
ListNode *mergeTowLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2){
ListNode *pre_head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode *cur = pre_head;
while(list1 && list2){
if(list1->val < list2->val){
cur->next = list1;
list1 = list1->next;
}else{
cur->next = list2;
list2 = list2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = list1 ? list1 : list2;
return pre_head->next;
}
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
int m = lists.size();
if(m == 0) return nullptr;
for(int step = 1; step < m; step *=2) {
for(int i = 0; i < m - step; i += step * 2){
lists[i] = mergeTowLists(lists[i], lists[i + step]);
}
}
return lists[0];
}
};