1、
struct qwe {
char itable;
int num[20];
char *togs;
}; 2、
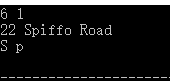
3、
struct year {
char month[10];
char MONTH[4];
int days;
int numbers;
}; 4、
struct year months[12] ={
{"January", "Jan", 31, 1},
{"February", "Feb", 28, 2},
{"March", "Mar", 31, 3},
{"April", "Apr", 30, 4},
{"May", "May", 31, 5},
{"June", "Jun", 30, 6},
{"July", "Jul", 31, 7},
{"August", "Aug", 31, 8},
{"September", "Sep", 30, 9},
{"October", "Oct", 31, 10},
{"November", "Nov", 30, 11},
{"December", "Dec", 31, 12}
}; 5、
int days(const struct year months[], int month)
{
int i, total = 0;
if(month < 1 || month > 12)
return 1;
else
{
for(i = 0; i < month; i++)
total += months[i].days;
return total;
}
}6、
a.
#include <string.h>
typedef struct lens {
float foclen;
float fstop;
char brand[30];
} LENS;
LENS arry[10];
arry[2].foclen = 500;
arry[2].fstop = 2.0;
strcpy(arry[2].brand ,"Remarkata");
/*
因为数组名在C语言中是个常量指针,表示数组首元素的地址。而字符串也是个常量指针,
直接赋值数组的话会改变地址,故可以选择给数组一个字符一个字符赋值,
或者用 strcpy() 函数把字符串拷贝到数组中
*/b.
#include <string.h>
typedef struct lens {
float foclen;
float fstop;
char brand[30];
} LENS;
LENS arry[10];
LENS arry[10] =
{
[2] = {
.foclen = 500.0,
.fstop = 2.0,
.brand = "Remarkata" // 注意:这里可以写字符串常量
}
};
/*
①与其它初始化方式混合:
LENS arry[10] = {
[2].foclen = 500.0, // 只为特定元素的特定成员赋值
[2].fstop = 2.0,
[2].brand = "Remarkata",
[5].brand = "Nikon" // 可以只初始化部分成员
};
*/
/*
②全部使用指定初始化器:
LENS arry[10] = {
[0] = {.foclen = 50.0, .fstop = 1.8, .brand = "Sigma"},
[1] = {.foclen = 85.0, .fstop = 1.4, .brand = "Sony"},
[2] = {.foclen = 500.0, .fstop = 2.0, .brand = "Remarkata"},
[3] = {.foclen = 35.0, .fstop = 1.4, .brand = "Zeiss"}
};
*/
/*
③部分初始化 + 传统初始化:
LENS arry[10] = {
[2] = {500.0, 2.0, "Remarkata"}, // 指定索引,传统顺序
{100.0, 4.0, "Tamron"}, // 没有指定索引,就是[0]
[4] = {200.0, 2.8, "Tokina"}
};
*/ 7、
a.
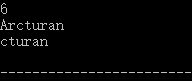
b.
①
deb.title.last
②
pb->title.lastc.
#include <stdio.h>
#include "starfolk.h"
struct name {
char first[20];
char last[20];
};
struct bem {
int limbs;
struct name title;
char type[30];
};
void show(const struct bem *ptr);
int main(void)
{
struct bem *pb;
struct bem deb = {
6,
{"Berbnazel", "Gwolkapwolk"},
"Arcturan"
};
pb = &deb;
show(pb);
return 0;
}
void show(const struct bem *fp)
{
printf("%s %s is a %d-limbed %s.\n",fp->title.first,
fp->title.last, fp->limbs, fp->type);
}8、
a.
willie.born
b.
pt->born
c.
scanf(%d, &willie.born);
d.
scanf(%d, &pt->born);
e.
scanf(%s, willie.name.lname);
f.
scanf(%s, pt->name.lname);
g.
willie.name.fname[2];
h.
strlen(willie.name.fname) + strlen(willie.name.lname);9、
struct car {
char name[20];
float horsepower;
float EAPMPG;
float wheelbase;
int year;
};10、
a.
struct gas mpgs(struct gas *fp)
{
if(fp.gals > 0)
fp.mpg = fp.distance / fp.gals;
else
fp.mpg = -1.0;
return fp;
}b.
void set_mpgs(struct gas *fp)
{
if(fp->gals > 0)
fp->mpg = fp->distance / fp->gals;
else
fp->mpg = -1.0;
}11、

12、

13、
double function1(double , double );
double function2(double , double );
double function3(double , double );
double function4(double , double );
double (*fp[4])(double , double)= {
function1,
function2,
function3,
function4
};
function1(10.0, 2.5);
(*fp[2])(10.0, 2.5);