写在开头的话
学习了今天的基础知识,让我们来做几道题来练练手吧。(题目是别的地方扒来的,参考答案是我自己写的,肯定不是最优解,有更好的方法欢迎评论区交流)
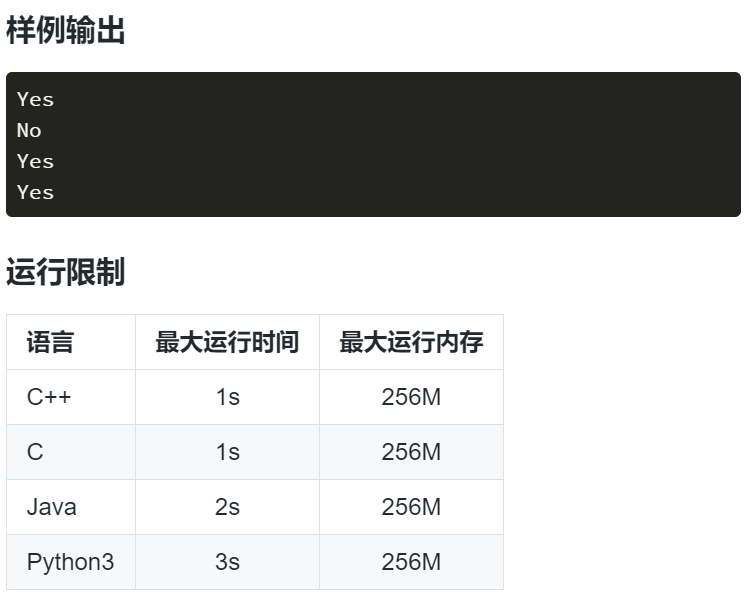
第一题------并查集

第二题------岛屿的数量

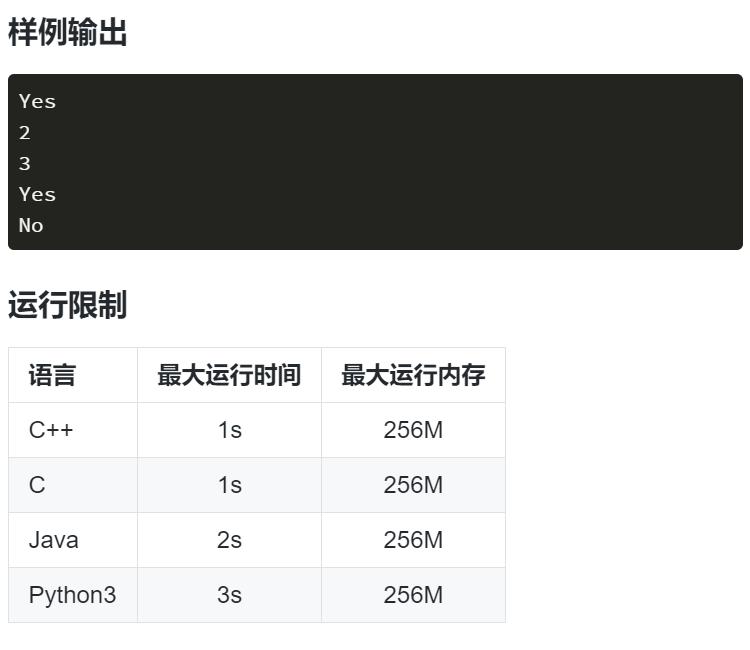
第三题------连通块中点的数量

参考答案
第一题参考答案(Python版)
python
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000000)
def main():
data = sys.stdin.read().strip().split()
n, m = int(data[0]), int(data[1])
parent = list(range(n + 1))
rank = [0] * (n + 1)
def find(x):
while parent[x] != x:
parent[x] = parent[parent[x]]
x = parent[x]
return x
def union(x, y):
root_x = find(x)
root_y = find(y)
if root_x == root_y:
return
if rank[root_x] < rank[root_y]:
parent[root_x] = root_y
elif rank[root_x] > rank[root_y]:
parent[root_y] = root_x
else:
parent[root_y] = root_x
rank[root_x] += 1
idx = 2
results = []
for _ in range(m):
op = data[idx]
a = int(data[idx + 1])
b = int(data[idx + 2])
idx += 3
if op == 'M':
union(a, b)
elif op == 'Q':
if find(a) == find(b):
results.append("Yes")
else:
results.append("No")
sys.stdout.write("\n".join(results))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()第二题参考答案(Python版)
python
import sys
def main():
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000000)
# 读取输入
n = int(sys.stdin.readline().strip())
matrix = []
for _ in range(n):
row = list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()))
matrix.append(row)
# 并查集初始化
parent = list(range(n * n))
rank = [0] * (n * n)
def find(x):
# 路径压缩
if parent[x] != x:
parent[x] = find(parent[x])
return parent[x]
def union(x, y):
root_x = find(x)
root_y = find(y)
if root_x != root_y:
# 按秩合并
if rank[root_x] < rank[root_y]:
parent[root_x] = root_y
elif rank[root_x] > rank[root_y]:
parent[root_y] = root_x
else:
parent[root_y] = root_x
rank[root_x] += 1
# 方向数组:上、下、左、右
directions = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
# 遍历矩阵,合并相邻的陆地
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if matrix[i][j] == 1:
index = i * n + j
for di, dj in directions:
ni, nj = i + di, j + dj
# 检查相邻格子是否在矩阵内且为陆地
if 0 <= ni < n and 0 <= nj < n and matrix[ni][nj] == 1:
neighbor_index = ni * n + nj
union(index, neighbor_index)
# 统计岛屿数量:收集所有陆地块的根节点
roots = set()
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if matrix[i][j] == 1:
roots.add(find(i * n + j))
print(len(roots))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()第三题参考答案(Python版)
python
import sys
sys.setrecursionlimit(300000)
def find(x, parent):
if parent[x] != x:
parent[x] = find(parent[x], parent)
return parent[x]
def union(a, b, parent, size):
root_a = find(a, parent)
root_b = find(b, parent)
if root_a != root_b:
if size[root_a] < size[root_b]:
root_a, root_b = root_b, root_a
parent[root_b] = root_a
size[root_a] += size[root_b]
def main():
import sys
input = sys.stdin.read
data = input().split()
n = int(data[0])
m = int(data[1])
parent = list(range(n + 1))
size = [1] * (n + 1)
idx = 2
results = []
for _ in range(m):
op = data[idx]
idx += 1
if op == 'C': # Connect
a = int(data[idx]); idx += 1
b = int(data[idx]); idx += 1
union(a, b, parent, size)
elif op == 'Q1': # Query 1
a = int(data[idx]); idx += 1
b = int(data[idx]); idx += 1
root_a = find(a, parent)
root_b = find(b, parent)
results.append("Yes" if root_a == root_b else "No")
elif op == 'Q2': # Query 2
a = int(data[idx]); idx += 1
root_a = find(a, parent)
results.append(str(size[root_a]))
sys.stdout.write("\n".join(results))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()