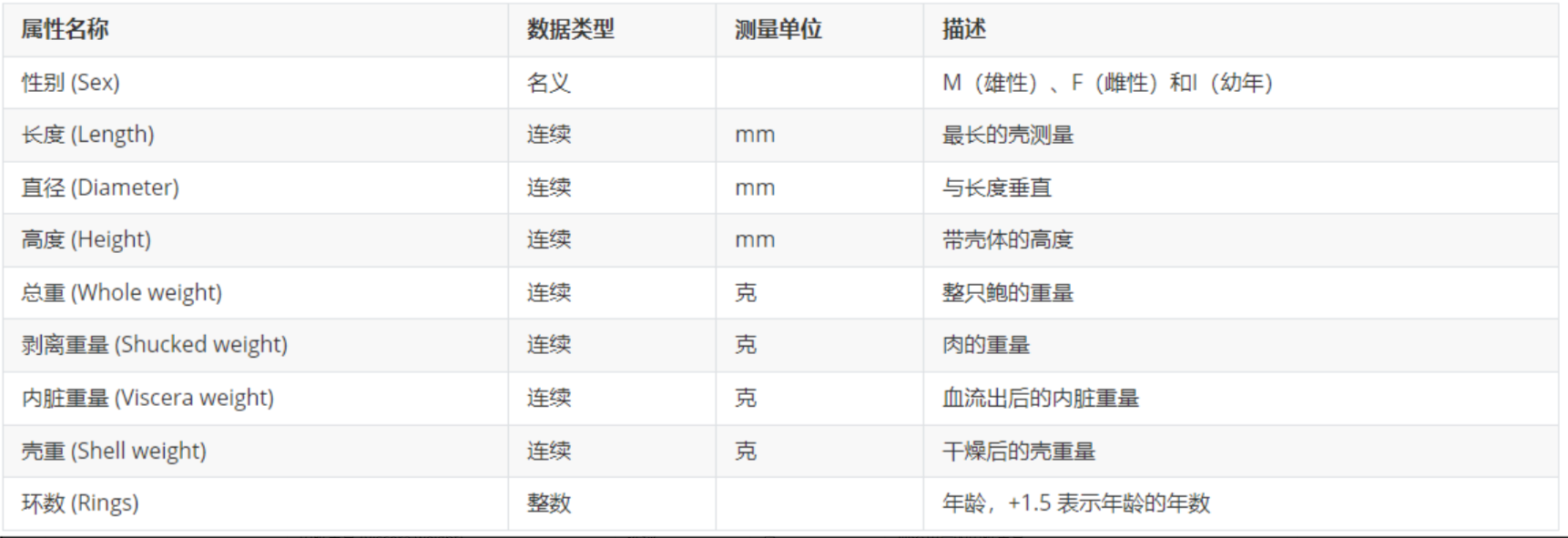
本例使用了一个Abalone(https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/1/abalone)数据集(已经下载好的数据集->📎abalone.zip),其中abalone.data是数据,abalone.names是本案例数据的英文解释。以下是数据集的中文解释:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
data = pd.read_csv(r'C:\Users\86198\Downloads\abalone (1)\abalone.data', sep=',')
# print(data.head())
column_names = ['Sex', 'Length', 'Diameter', 'Height', 'Whole_weight',
'Shucked_weight', 'Viscera_weight', 'Shell_weight', 'Rings']
data.columns = column_names
data = pd.get_dummies(data, columns=['Sex'])
print(data.keys())
X = data[['Sex_F', 'Sex_M', 'Sex_I', 'Length', 'Diameter',
'Height', 'Whole_weight', 'Shucked_weight', 'Viscera_weight', 'Shell_weight']]
# 选取 'Rings' 列作为目标变量,即模型要预测的对象,通常代表了鲍鱼的年龄相关信息 y = data['Rings']
y = data['Rings']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test_scaled = scaler.transform(X_test)
X_train_tensor = torch.tensor(X_train_scaled, dtype=torch.float32)
X_test_tensor = torch.tensor(X_test_scaled, dtype=torch.float32)
y_train_tensor = torch.tensor(y_train.values, dtype=torch.float32).view(-1, 1)
y_test_tensor = torch.tensor(y_test.values, dtype=torch.float32).view(-1, 1)
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size):
super(LinearRegressionModel, self).__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_size, 1)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
input_size = X_train_tensor.shape[1]
model = LinearRegressionModel(input_size)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
num_epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model.train()
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(X_train_tensor)
loss = criterion(outputs, y_train_tensor)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
predictions = model(X_test_tensor)
test_loss = criterion(predictions, y_test_tensor)
predictions = predictions.detach().cpu().numpy()
y_test_numpy = y_test_tensor.detach().cpu().numpy()
plt.figure(0)
plt.scatter(y_test_numpy, predictions, c='blue')
plt.plot([min(y_test_numpy), max(y_test_numpy)], [min(y_test_numpy), max(y_test_numpy)],
linestyle='--', color='red', linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel('Actual Values')
plt.ylabel('Predicted Values')
plt.title('Regression Results')
plt.figure(1)
sorted_indices = X_test.index.argsort()
# 根据排序后的索引获取对应的实际值
y_test_sorted = y_test.iloc[sorted_indices]
# 将预测值转换为Series类型,并且根据排序后的索引获取对应的值
y_pred_sorted = pd.Series(predictions.squeeze()).iloc[sorted_indices]
# 绘制实际值的曲线,用圆形标记
plt.plot(y_test_sorted.values, label='Acatual Values', marker='o')
# 绘制预测值的曲线,用*标记
plt.plot(y_pred_sorted.values, label='Predicted Values', marker='*')
# 设置轴标签和标题
plt.xlabel('Sorted Index')
plt.ylabel('Values')
plt.title('Actual vs Predicted Values in Linear Regression')
plt.show()