目录
[三、模块 1:环境配置与基础库导入](#三、模块 1:环境配置与基础库导入)
[四、模块 2:核心工具函数(数据处理 + 激活函数)](#四、模块 2:核心工具函数(数据处理 + 激活函数))
[2.1 激活函数(神经网络核心)](#2.1 激活函数(神经网络核心))
[2.2 数据读取函数](#2.2 数据读取函数)
[2.3 文本预处理函数](#2.3 文本预处理函数)
[五、模块 3:BP 神经网络类(核心模型)](#五、模块 3:BP 神经网络类(核心模型))
[3.1 初始化方法(init)](#3.1 初始化方法(init))
[3.2 前向传播(forward)](#3.2 前向传播(forward))
[3.3 反向传播(backward)](#3.3 反向传播(backward))
[3.4 参数更新(update_params)](#3.4 参数更新(update_params))
[3.5 训练函数(train)](#3.5 训练函数(train))
[3.6 预测函数(predict)](#3.6 预测函数(predict))
[六、模块 4:可视化函数(模型分析核心)](#六、模块 4:可视化函数(模型分析核心))
[4.1 训练损失曲线(plot_train_loss)](#4.1 训练损失曲线(plot_train_loss))
[4.2 混淆矩阵热力图(plot_confusion_matrix)](#4.2 混淆矩阵热力图(plot_confusion_matrix))
[4.3 分类性能指标可视化(plot_classification_report)](#4.3 分类性能指标可视化(plot_classification_report))
[4.4 情感词云(generate_wordcloud)](#4.4 情感词云(generate_wordcloud))
[4.5 特征重要性(plot_feature_importance)](#4.5 特征重要性(plot_feature_importance))
[七、模块 5:主流程(整合所有功能)](#七、模块 5:主流程(整合所有功能))
[九、基于 BP 神经网络的中文文本情感分类的Python代码完整实现](#九、基于 BP 神经网络的中文文本情感分类的Python代码完整实现)
一、引言
本文的自然语言处理实战项目是基于 BP 神经网络的中文文本情感分类,覆盖"数据读取→文本预处理→特征提取→模型训练→评估→多维度可视化→新样本预测"全流程,适配小数据集场景(如小型企业 / 个人的情感分析需求)。下面将详细讲解基于 BP 神经网络的中文文本情感分类的Python代码实现过程。
二、整体架构与核心目标
| 核心目标 | 区分中文文本的「正面情感」(如好评、开心)和「负面情感」(如差评、生气) |
|---|---|
| 技术栈 | 纯 Numpy 实现 BP 神经网络 + TF-IDF 文本特征提取 + 中文分词(jieba) + 多维度可视化 |
| 数据流转 | 原始文本文件 → 文本预处理(分词 / 去停用词) → TF-IDF 数值特征 → BP 网络训练 → 模型评估 → 可视化分析 → 新样本预测 |
三、模块 1:环境配置与基础库导入
python
import numpy as np
import jieba
import os
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 可视化库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from wordcloud import WordCloud
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report, accuracy_score
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 设置中文字体(解决可视化中文乱码)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 黑体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题功能说明:
- 基础库导入 :
numpy:手动实现 BP 神经网络的核心(矩阵运算、梯度计算);jieba:中文文本分词(解决中文无天然分隔符的问题);os:读取文本文件(路径处理);warnings:屏蔽无关警告(提升运行体验)。
- 可视化库导入 :
matplotlib/seaborn:绘制损失曲线、混淆矩阵、特征重要性等图表;WordCloud:生成情感文本词云(直观展示核心词汇)。
- SKlearn 工具导入 :
- 特征提取:
TfidfVectorizer(将文本转为数值特征); - 数据划分:
train_test_split(拆分训练 / 测试集); - 模型评估:
confusion_matrix/classification_report/accuracy_score(量化模型性能)。
- 特征提取:
- 中文显示配置:解决 Matplotlib 可视化时中文乱码、负号显示异常的问题。
四、模块 2:核心工具函数(数据处理 + 激活函数)
2.1 激活函数(神经网络核心)
python
def sigmoid(z):
"""Sigmoid激活函数(数值稳定版)"""
z = np.clip(z, -500, 500) # 防止exp(-z)溢出(z过大/过小导致计算错误)
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def sigmoid_derivative(z):
"""Sigmoid导数(反向传播需计算激活函数梯度)"""
s = sigmoid(z)
return s * (1 - s)
def relu(z):
"""ReLU激活函数(隐藏层用,缓解梯度消失)"""
return np.maximum(0, z)
def relu_derivative(z):
"""ReLU导数(反向传播用)"""
return np.where(z > 0, 1, 0)| 函数 | 作用 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|
sigmoid |
将输出映射到 (0,1) 区间,适配二分类任务(情感分类的输出层) | 输出层激活(判断 0/1 情感) |
sigmoid_derivative |
计算 Sigmoid 的导数,用于反向传播的梯度计算 | 输出层误差项推导 |
relu |
隐藏层激活函数,计算快、缓解梯度消失(相比 Sigmoid 更适合深层网络) | 隐藏层激活 |
relu_derivative |
计算 ReLU 的导数,用于反向传播的梯度计算 | 隐藏层误差项推导 |
2.2 数据读取函数
python
def load_sentiment_data(data_dir):
"""读取情感分类文本数据(从txt文件读取)"""
texts = []
labels = []
# 读取正面文本(标签1)
pos_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'positive.txt')
with open(pos_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if line: # 跳过空行
texts.append(line)
labels.append(1)
# 读取负面文本(标签0)
neg_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'negative.txt')
with open(neg_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if line: # 跳过空行
texts.append(line)
labels.append(0)
return texts, np.array(labels).reshape(-1, 1)功能说明:
- 输入:数据文件夹路径(
sentiment_data); - 输出:文本列表(
texts)、标签数组(labels,1 = 正面,0 = 负面,形状为(n_samples, 1)); - 核心逻辑:
-
读取
positive.txt(正面文本),每行一条,标签设为 1;bash这家餐厅的菜品超好吃,服务也特别周到 今天收到了心仪的礼物,心情超级棒 这部电影剧情紧凑,演员演技在线,值得一看 新入手的手机续航超久,拍照效果也很好 周末和朋友去郊游,天气好风景美,太开心了 公司团建活动很有趣,同事们都玩得很尽兴 这家咖啡店的拿铁口感丝滑,环境也很温馨 网购的衣服尺码很准,面料也很舒服 终于通过了考试,付出的努力都值得了 家乡的变化真大,基础设施越来越完善了 -
读取
negative.txt(负面文本),每行一条,标签设为 0;bash这家外卖送得超级慢,饭菜都凉了 手机用了没几天就卡顿,体验太差了 餐厅的菜品又贵又难吃,性价比极低 今天上班迟到被批评,一整天心情都不好 电影剧情拖沓,特效粗糙,完全不值票价 网购的商品有瑕疵,客服还不处理,太气人了 下雨天出门没带伞,被淋成落汤鸡了 公交车晚点半小时,耽误了重要的约会 这家酒店卫生条件差,房间还有异味 快递员态度恶劣,包裹还破损了 -
跳过空行,避免无效数据;
-
标签转为 Numpy 数组并重塑为列向量(适配 BP 网络的矩阵运算)。
-
2.3 文本预处理函数
python
def preprocess_text(texts):
"""中文文本预处理:分词+去停用词"""
# 简单停用词表(无实际语义,需过滤)
stopwords = {'的', '了', '在', '是', '我', '你', '他', '她', '它', '们', '就', '都', '也', '还', '很', '太', '超',
'又', '和', '与', '及', '等', '有', '没', '不', '无', '为', '之', '于', '以', '对', '对于'}
processed_texts = []
for text in texts:
# 分词(jieba.lcut:精确分词,返回列表)
words = jieba.lcut(text)
# 去停用词+去空字符(保留有语义的词汇)
words = [w for w in words if w.strip() and w not in stopwords]
processed_texts.append(' '.join(words))
return processed_texts功能说明:
- 输入:原始文本列表(如
["这家餐厅超好吃", ...]); - 输出:预处理后的文本列表(如
["这家 餐厅 好吃", ...]); - 核心价值:
- 分词:将连续中文拆分为独立词汇(如 "超好吃"→"超 好吃"),适配 TF-IDF 特征提取;
- 去停用词:过滤无语义的虚词(如 "的""了"),减少噪声,提升特征有效性;
- 格式转换:用空格分隔分词结果(TF-IDF 要求输入为 "词汇 词汇" 格式)。
五、模块 3:BP 神经网络类(核心模型)
python
class BPNeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim, learning_rate=0.01):
# 初始化网络参数
self.input_dim = input_dim # 输入维度(TF-IDF特征数)
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim # 隐藏层神经元数
self.output_dim = output_dim # 输出维度(二分类=1)
self.lr = learning_rate # 学习率(控制参数更新步长)
# 权重初始化(Xavier初始化:适配ReLU,避免梯度消失/爆炸)
self.W1 = np.random.normal(0, np.sqrt(2 / input_dim), (hidden_dim, input_dim))
self.b1 = np.zeros((hidden_dim, 1)) # 隐藏层偏置(初始化为0)
self.W2 = np.random.normal(0, np.sqrt(2 / hidden_dim), (output_dim, hidden_dim))
self.b2 = np.zeros((output_dim, 1)) # 输出层偏置(初始化为0)
# 记录训练损失(用于可视化损失曲线)
self.train_loss_history = []3.1 初始化方法(__init__)
- 核心参数:
input_dim:输入层维度(如 TF-IDF 的 100 维特征);hidden_dim:隐藏层神经元数(如 64,控制模型复杂度);output_dim:输出层维度(二分类 = 1);learning_rate:学习率(默认 0.01,控制参数更新速度);
- 关键逻辑:
- 权重初始化:采用 Xavier 初始化(针对 ReLU 优化),避免全 0 初始化(导致神经元输出相同);
- 偏置初始化:初始化为 0(不影响梯度计算,训练中自动调整);
- 损失记录:初始化空列表,保存每轮训练的损失值(用于可视化)。
3.2 前向传播(forward)
python
def forward(self, X):
"""前向传播:输入→隐藏层→输出层,计算预测值"""
Z1 = np.dot(self.W1, X) + self.b1 # 隐藏层净输入(线性变换)
H = relu(Z1) # 隐藏层输出(ReLU激活)
Z2 = np.dot(self.W2, H) + self.b2 # 输出层净输入(线性变换)
Y = sigmoid(Z2) # 输出层预测值(Sigmoid激活,范围0~1)
return H, Y- 输入:单个样本的特征向量(形状
(input_dim, 1)); - 输出:隐藏层输出(
H)、输出层预测值(Y,0~1 之间); - 核心逻辑:模拟信号在神经网络中的正向传递,公式对应:
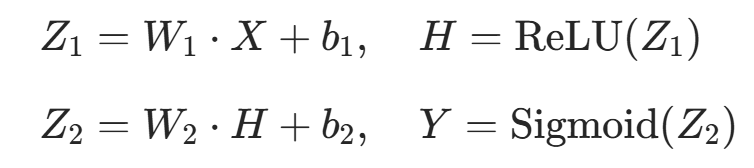
3.3 反向传播(backward)
python
def backward(self, X, H, Y, Y_true):
"""反向传播:计算损失对权重/偏置的梯度"""
delta2 = Y - Y_true # 输出层误差项(二元交叉熵+Sigmoid简化版)
Z1 = np.dot(self.W1, X) + self.b1 # 重新计算隐藏层净输入
delta1 = np.dot(self.W2.T, delta2) * relu_derivative(Z1) # 隐藏层误差项
# 计算各参数的梯度
dW2 = np.dot(delta2, H.T) # W2的梯度
db2 = delta2 # b2的梯度
dW1 = np.dot(delta1, X.T) # W1的梯度
db1 = delta1 # b1的梯度
return dW1, db1, dW2, db2- 输入:输入向量
X、隐藏层输出H、预测值Y、真实标签Y_true; - 输出:权重 / 偏置的梯度(
dW1, db1, dW2, db2); - 核心逻辑(链式法则):
- 输出层误差项:
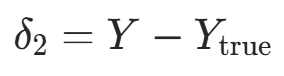 (二元交叉熵 + Sigmoid 的简化结果,无需复杂计算);
(二元交叉熵 + Sigmoid 的简化结果,无需复杂计算); - 隐藏层误差项:
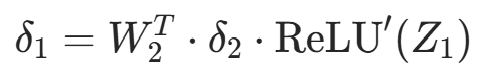 (通过输出层误差反向推导);
(通过输出层误差反向推导); - 梯度计算:损失对每个参数的偏导数(用于后续参数更新)。
- 输出层误差项:
3.4 参数更新(update_params)
python
def update_params(self, dW1, db1, dW2, db2):
"""梯度下降更新权重/偏置(沿梯度负方向调整,减小损失)"""
self.W1 -= self.lr * dW1
self.b1 -= self.lr * db1
self.W2 -= self.lr * dW2
self.b2 -= self.lr * db2- 核心公式:
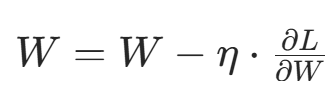 (η= 学习率,梯度负方向);
(η= 学习率,梯度负方向); - 作用:通过梯度下降最小化损失,让模型逐渐拟合数据规律。
3.5 训练函数(train)
python
def train(self, X_train, y_train, epochs=50, batch_size=4):
"""迭代训练网络,记录每轮损失"""
n_samples = X_train.shape[0]
self.train_loss_history = [] # 重置损失记录
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 打乱训练集(避免顺序影响,提升泛化)
indices = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X_shuffled = X_train[indices]
y_shuffled = y_train[indices]
epoch_loss = 0.0
batch_count = 0
# 批量训练(按batch_size切分)
for i in range(0, n_samples, batch_size):
batch_X = X_shuffled[i:i + batch_size]
batch_y = y_shuffled[i:i + batch_size]
batch_count += 1
batch_batch_loss = 0.0
for X, y_true in zip(batch_X, batch_y):
# 重塑为列向量(适配矩阵运算)
X = X.reshape(self.input_dim, 1)
y_true = y_true.reshape(self.output_dim, 1)
# 前向传播
H, Y = self.forward(X)
# 计算损失(加1e-7避免log(0))
loss = -y_true * np.log(Y + 1e-7) - (1 - y_true) * np.log(1 - Y + 1e-7)
batch_batch_loss += loss.item()
# 反向传播+参数更新
dW1, db1, dW2, db2 = self.backward(X, H, Y, y_true)
self.update_params(dW1, db1, dW2, db2)
# 累加批量损失
epoch_loss += batch_batch_loss / len(batch_X)
# 记录每轮平均损失
avg_epoch_loss = epoch_loss / batch_count
self.train_loss_history.append(avg_epoch_loss)
# 每5轮打印损失(监控训练进度)
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}, Average Loss: {avg_epoch_loss:.4f}")- 核心参数:
epochs:训练轮数(默认 50,遍历训练集的次数);batch_size:批量大小(默认 4,小批量训练提升泛化);
- 核心逻辑:
- 每轮训练前打乱数据(避免顺序偏差);
- 按
batch_size切分训练集,逐批处理; - 对每个样本:重塑为列向量→前向传播→计算损失→反向传播→更新参数;
- 计算每轮平均损失并记录(用于可视化);
- 每 5 轮打印损失(方便监控训练收敛情况);
- 损失计算时加
1e-7(避免log(0)导致数值错误)。
3.6 预测函数(predict)
python
def predict(self, X):
"""预测函数:输入特征→输出情感标签(0/1)"""
predictions = []
for x in X:
x = x.reshape(self.input_dim, 1) # 重塑为列向量
_, Y = self.forward(x) # 前向传播获取预测值
pred = 1 if Y > 0.5 else 0 # 阈值0.5:>0.5=正面,否则=负面
predictions.append(pred)
return np.array(predictions)- 输入:测试集 / 新样本的特征矩阵(
n_samples, input_dim); - 输出:预测标签数组(0 = 负面,1 = 正面);
- 核心逻辑:
- 对每个样本前向传播,得到 0~1 的预测值;
- 以 0.5 为阈值,将连续值转为离散标签(二分类)。
六、模块 4:可视化函数(模型分析核心)
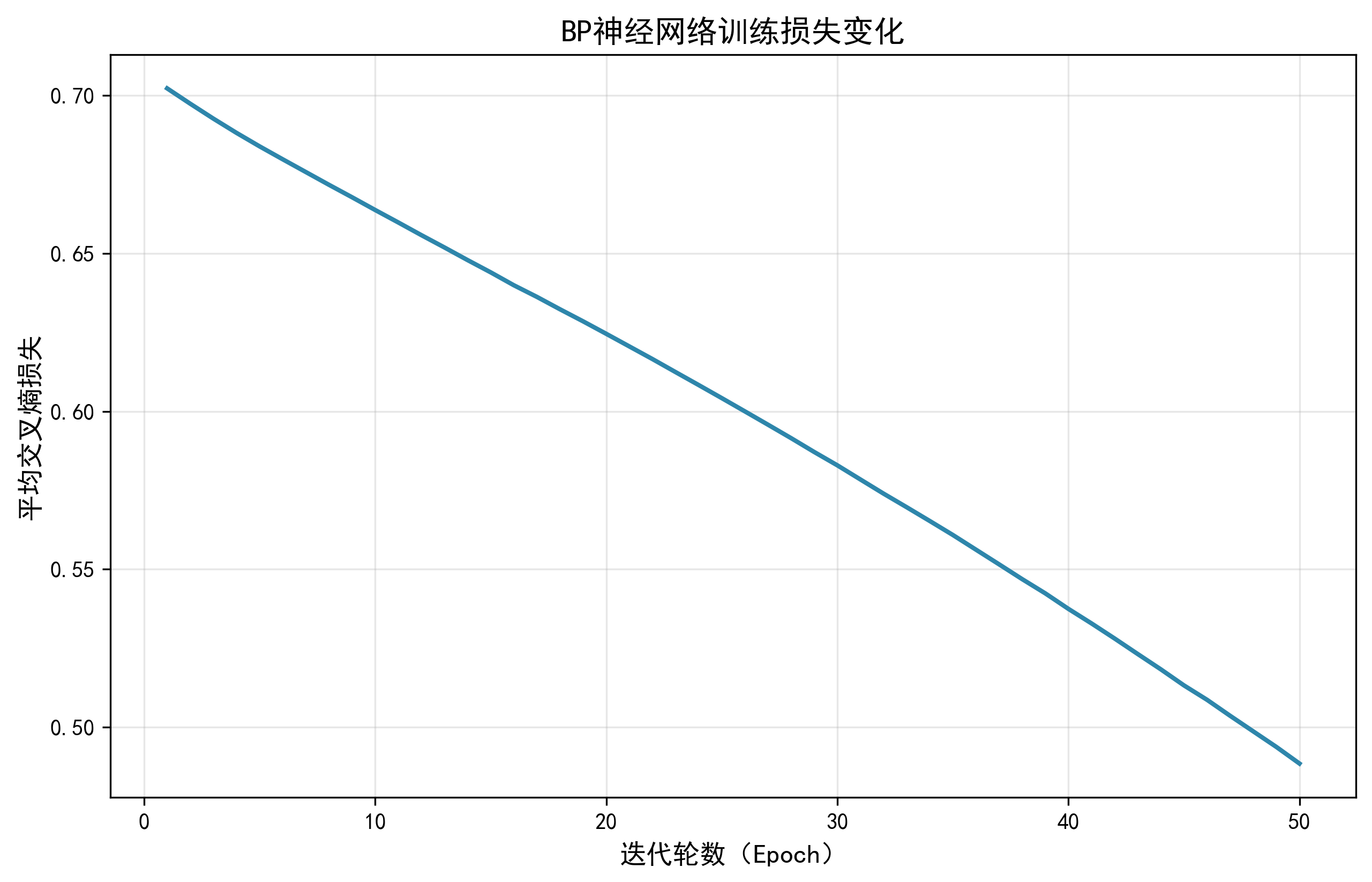
4.1 训练损失曲线(plot_train_loss)
python
def plot_train_loss(loss_history):
"""绘制训练损失曲线(监控模型收敛)"""
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(range(1, len(loss_history) + 1), loss_history, color='#2E86AB', linewidth=2)
plt.title('BP神经网络训练损失变化', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('迭代轮数(Epoch)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('平均交叉熵损失', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.savefig('train_loss_curve.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()- 功能:绘制 "迭代轮数→损失值" 曲线;
- 核心价值:
- 查看损失是否下降并收敛(损失逐渐降低→模型学习有效);
- 判断过拟合 / 欠拟合(损失骤降后反弹→过拟合;损失不降→欠拟合);
- 保存高清图片(
dpi=300),便于分析。
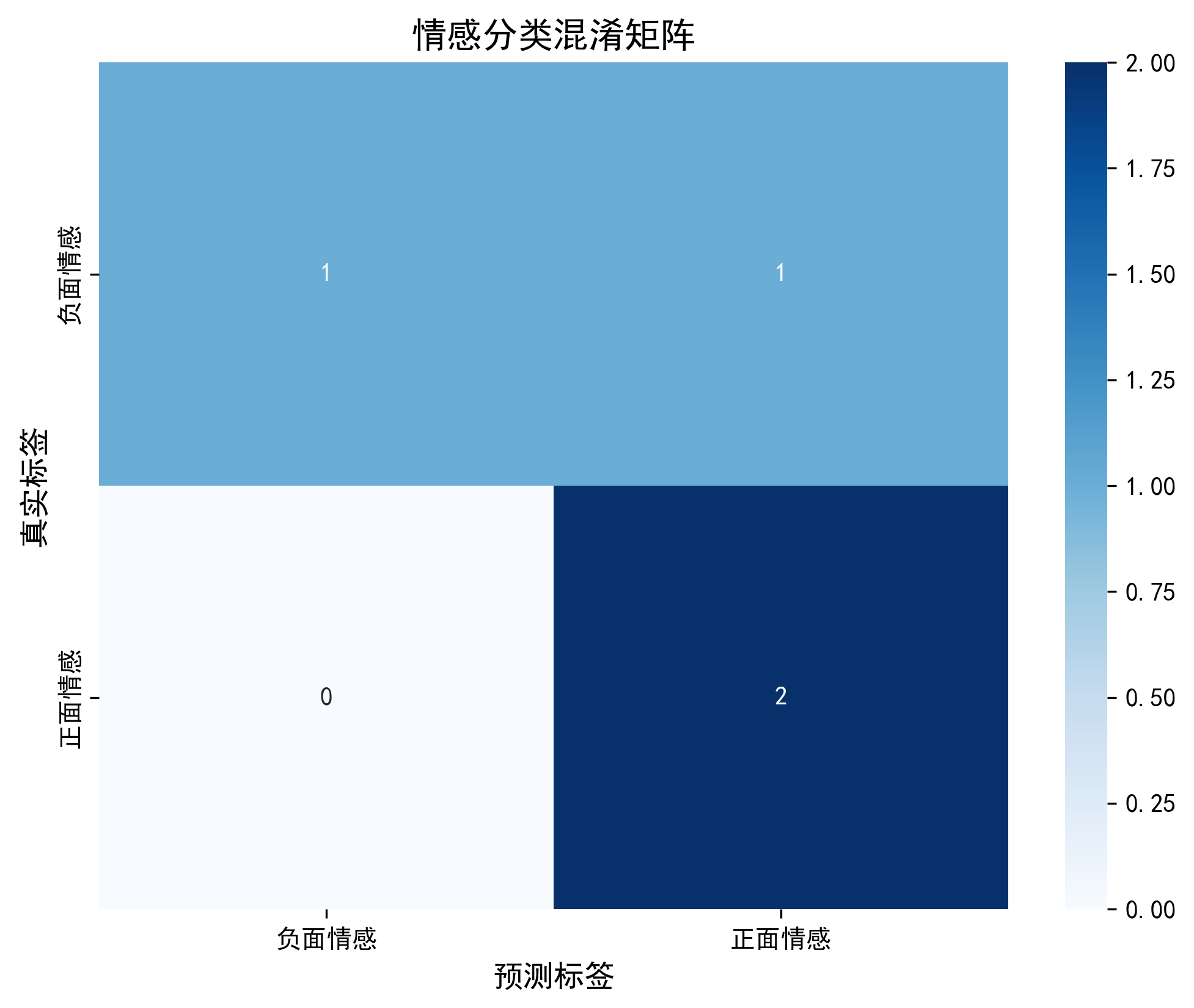
4.2 混淆矩阵热力图(plot_confusion_matrix)
python
def plot_confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred):
"""绘制混淆矩阵(查看分类错误类型)"""
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues',
xticklabels=['负面情感', '正面情感'],
yticklabels=['负面情感', '正面情感'])
plt.title('情感分类混淆矩阵', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('预测标签', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('真实标签', fontsize=12)
plt.savefig('confusion_matrix.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()- 功能:可视化混淆矩阵(行 = 真实标签,列 = 预测标签);
- 核心价值:
- 直观查看 "真阳性(正面预测正确)、真阴性(负面预测正确)、假阳性(负面误判为正面)、假阴性(正面误判为负面)";
- 定位模型薄弱点(如假阴性多→模型漏判正面情感)。
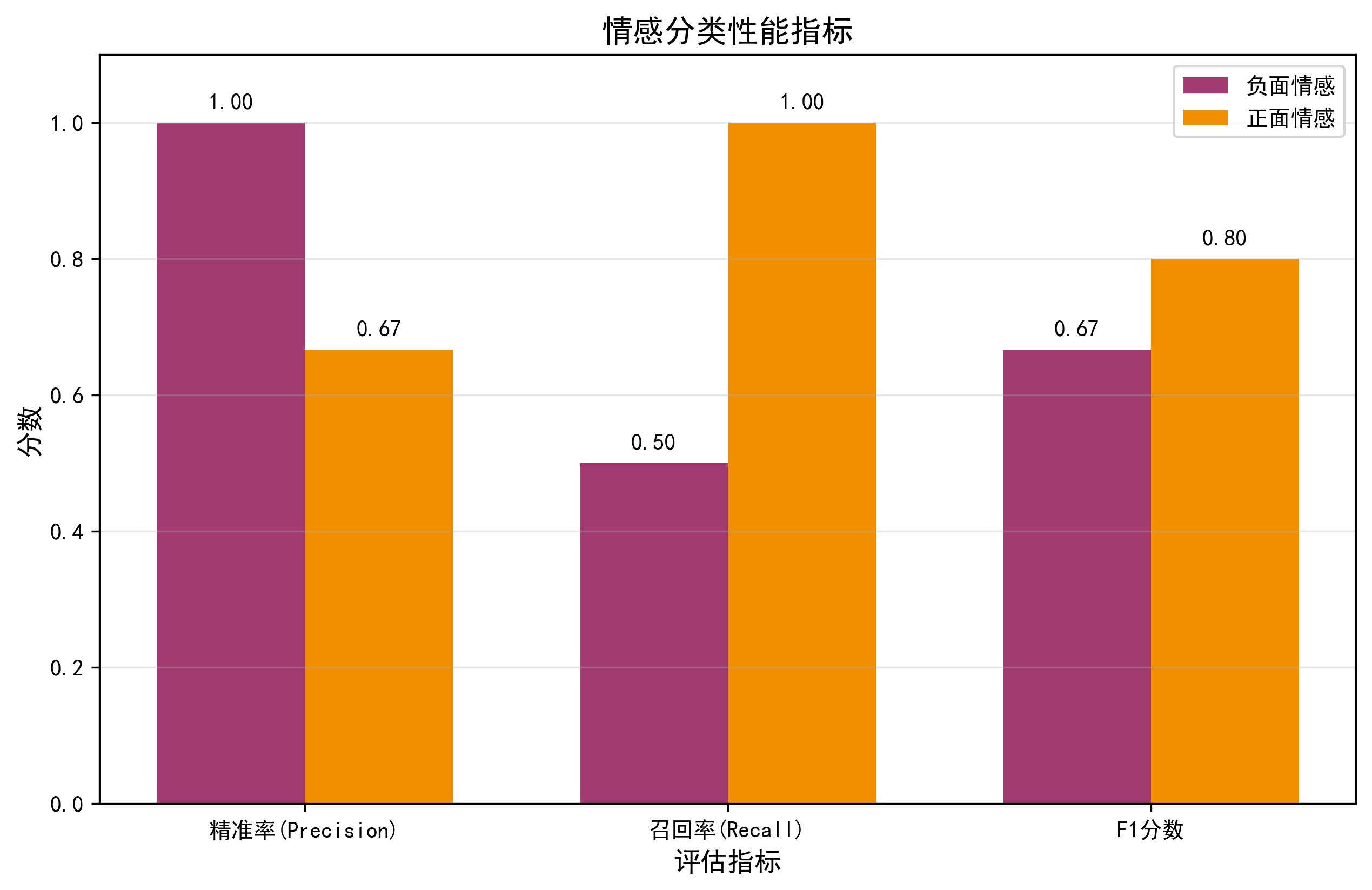
4.3 分类性能指标可视化(plot_classification_report)
python
def plot_classification_report(y_true, y_pred):
"""可视化精准率、召回率、F1分数(量化模型性能)"""
report = classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=['负面情感', '正面情感'], output_dict=True)
metrics = ['precision', 'recall', 'f1-score']
pos_scores = [report['正面情感'][m] for m in metrics]
neg_scores = [report['负面情感'][m] for m in metrics]
x = np.arange(len(metrics))
width = 0.35
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.bar(x - width / 2, neg_scores, width, label='负面情感', color='#A23B72')
plt.bar(x + width / 2, pos_scores, width, label='正面情感', color='#F18F01')
plt.title('情感分类性能指标', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('评估指标', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('分数', fontsize=12)
plt.xticks(x, ['精准率(Precision)', '召回率(Recall)', 'F1分数'])
plt.ylim(0, 1.1)
plt.legend()
# 添加数值标签(直观查看分数)
for i, v in enumerate(neg_scores):
plt.text(i - width / 2, v + 0.02, f'{v:.2f}', ha='center')
for i, v in enumerate(pos_scores):
plt.text(i + width / 2, v + 0.02, f'{v:.2f}', ha='center')
plt.grid(alpha=0.3, axis='y')
plt.savefig('classification_report.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()- 核心指标解释:
- 精准率(Precision):预测为某类的样本中,真实为该类的比例(如正面精准率 = 正面预测正确 / 所有预测为正面);
- 召回率(Recall):真实为某类的样本中,预测正确的比例(如正面召回率 = 正面预测正确 / 所有真实正面);
- F1 分数:精准率 + 召回率的调和平均(综合评估,越接近 1 越好);
- 核心价值:量化对比正负情感的分类效果(如正面 F1=0.95,负面 F1=0.90→模型对正面分类更准)。
4.4 情感词云(generate_wordcloud)
python
def generate_wordcloud(texts, label, save_path):
"""生成正负情感文本词云(直观展示核心词汇)"""
text = ' '.join(texts)
wc = WordCloud(
font_path='simhei.ttf', # 中文分词字体(需系统有该字体)
width=800, height=600,
background_color='white',
max_words=100,
colormap='RdYlGn' if label == 1 else 'RdYlBu_r' # 正面=绿红,负面=蓝红
).generate(text)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.imshow(wc, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title(f'{"正面" if label == 1 else "负面"}情感文本词云', fontsize=14)
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()- 功能:生成正负情感文本的词云(词汇越大→出现频率越高);
- 核心价值:
- 直观展示情感文本的核心词汇(如正面 ="好吃、开心、棒";负面 ="慢、差、气");
- 验证预处理效果(停用词是否过滤干净);
- 辅助业务分析(如负面词云多为 "慢"→优化配送效率)。
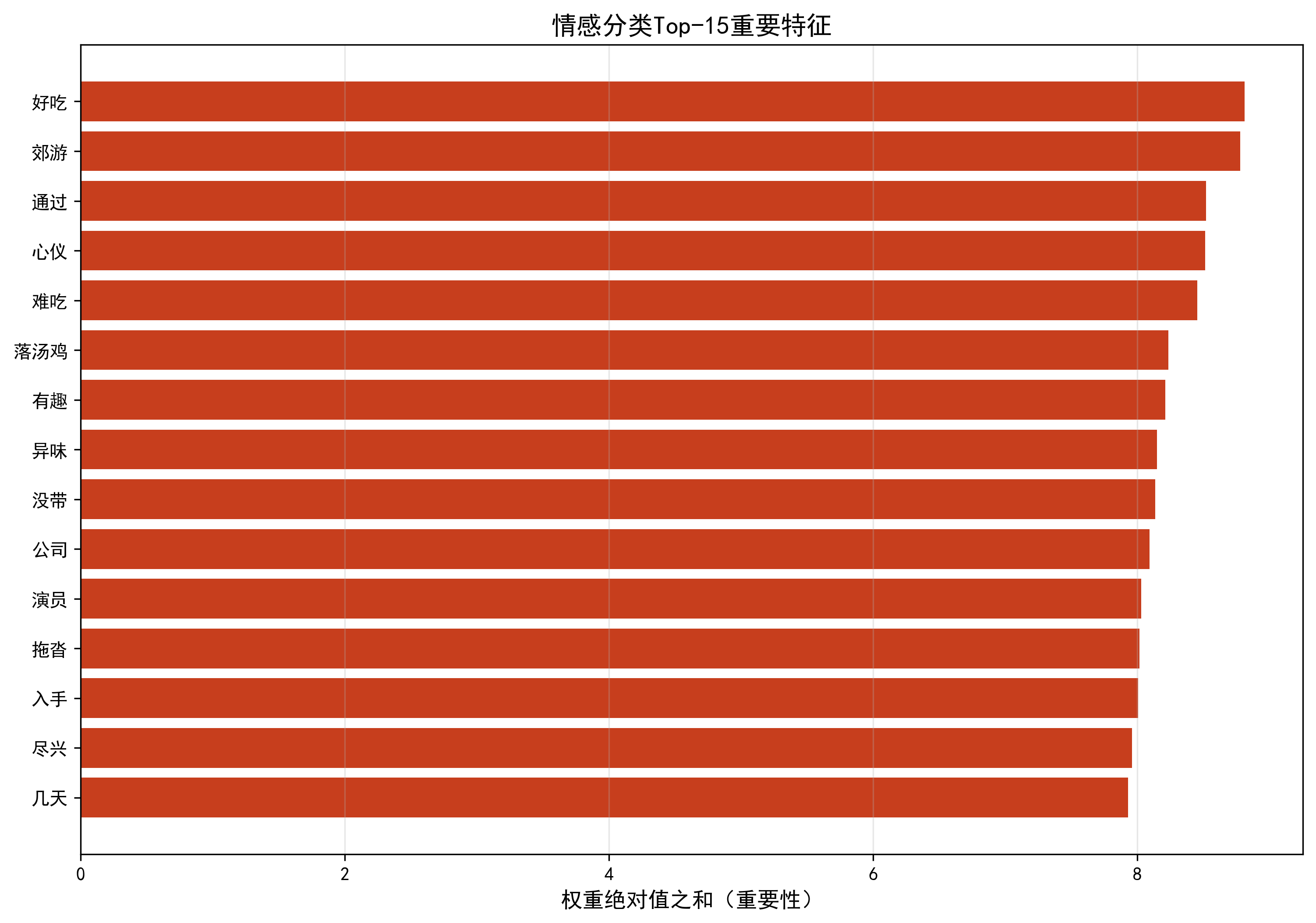
4.5 特征重要性(plot_feature_importance)
python
def plot_feature_importance(tfidf, model, top_k=15):
"""绘制Top-K重要特征(基于BP网络第一层权重)"""
# 计算每个特征的权重绝对值之和(代表重要性)
feature_importance = np.sum(np.abs(model.W1), axis=0)
feature_names = tfidf.get_feature_names_out() # 获取特征对应的词汇
# 排序取Top-K
indices = np.argsort(feature_importance)[-top_k:]
top_importance = feature_importance[indices]
top_features = feature_names[indices]
# 绘制水平条形图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.barh(range(len(top_features)), top_importance, color='#C73E1D')
plt.yticks(range(len(top_features)), top_features)
plt.title(f'情感分类Top-{top_k}重要特征', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('权重绝对值之和(重要性)', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3, axis='x')
plt.savefig('feature_importance.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()- 核心逻辑:BP 网络第一层权重的绝对值之和越大→该特征(词汇)对情感分类的影响越大;
- 核心价值:
- 找出对情感分类最关键的词汇(如 "好吃""难吃""开心""生气");
- 验证特征提取的有效性(关键词汇是否被选中)。
七、模块 5:主流程(整合所有功能)
python
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置参数
DATA_DIR = 'sentiment_data' # 数据文件夹
HIDDEN_DIM = 64 # 隐藏层神经元数
LEARNING_RATE = 0.01 # 学习率
EPOCHS = 50 # 训练轮数
BATCH_SIZE = 4 # 批量大小
TEST_SIZE = 0.2 # 测试集比例
# 2. 加载并预处理数据
print("===== 加载情感数据 =====")
texts, labels = load_sentiment_data(DATA_DIR)
print(f"总样本数:{len(texts)}(正面:{sum(labels)[0]},负面:{len(labels) - sum(labels)[0]})")
print("===== 文本预处理 =====")
processed_texts = preprocess_text(texts)
# 3. TF-IDF特征提取
print("===== 提取TF-IDF特征 =====")
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer(max_features=100) # 限制特征数(适配小数据集)
X = tfidf.fit_transform(processed_texts).toarray()
# 划分训练/测试集(分层抽样,保证正负样本比例)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, labels, test_size=TEST_SIZE, random_state=42, stratify=labels
)
print(f"训练集样本数:{X_train.shape[0]},测试集样本数:{X_test.shape[0]}")
print(f"特征维度:{X_train.shape[1]}")
# 4. 训练BP网络
print("\n===== 训练BP神经网络 =====")
bp_model = BPNeuralNetwork(
input_dim=X_train.shape[1],
hidden_dim=HIDDEN_DIM,
output_dim=1,
learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE
)
bp_model.train(X_train, y_train, epochs=EPOCHS, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
# 5. 模型评估
print("\n===== 模型评估 =====")
y_pred = bp_model.predict(X_test)
y_test_flat = y_test.flatten()
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test_flat, y_pred)
print(f"测试集准确率:{accuracy:.4f}")
print("\n分类报告:")
print(classification_report(y_test_flat, y_pred, target_names=['负面情感', '正面情感']))
# 6. 可视化
print("\n===== 生成可视化图表 =====")
plot_train_loss(bp_model.train_loss_history) # 损失曲线
plot_confusion_matrix(y_test_flat, y_pred) # 混淆矩阵
plot_classification_report(y_test_flat, y_pred) # 性能指标
# 词云
pos_texts = [processed_texts[i] for i in range(len(texts)) if labels[i] == 1]
neg_texts = [processed_texts[i] for i in range(len(texts)) if labels[i] == 0]
generate_wordcloud(pos_texts, 1, 'positive_wordcloud.png')
generate_wordcloud(neg_texts, 0, 'negative_wordcloud.png')
# 特征重要性
plot_feature_importance(tfidf, bp_model, top_k=15)
# 7. 新样本预测演示
print("\n===== 新样本情感预测 =====")
new_texts = [
"这家奶茶店的饮品甜度适中,用料很实在",
"今天打车遇到了绕路的司机,特别生气",
"新上映的动画电影画面精美,剧情感人",
"网购的水果烂了一半,售后还不处理"
]
new_processed = preprocess_text(new_texts)
new_X = tfidf.transform(new_processed).toarray()
new_pred = bp_model.predict(new_X)
for text, pred in zip(new_texts, new_pred):
sentiment = "正面情感" if pred == 1 else "负面情感"
print(f"文本:{text} → 预测结果:{sentiment}")核心流程拆解:
- 参数配置:定义数据路径、模型超参数(隐藏层神经元数、学习率等);
- 数据加载 + 预处理:读取 txt 文件→分词 + 去停用词;
- TF-IDF 特征提取:将预处理后的文本转为 100 维数值特征(限制维度,适配小数据集);
- 数据划分 :按 20% 比例拆分训练 / 测试集,
stratify=labels保证正负样本比例一致; - 模型训练:初始化 BP 网络→迭代训练 50 轮,记录损失;
- 模型评估:计算测试集准确率、打印分类报告(精准率 / 召回率 / F1);
- 可视化:生成 5 类图表(损失曲线、混淆矩阵、性能指标、词云、特征重要性);
- 新样本预测:对 4 个新文本预处理→提取特征→预测情感→输出结果。
八、代码的扩展与适配能力
- 数据集扩展 :只需向
positive.txt/negative.txt添加更多文本,无需修改核心代码; - 多分类适配:修改输出层为 Softmax 激活、标签为多分类(如 0 = 负面,1 = 中性,2 = 正面);
- 模型优化:调整隐藏层神经元数、学习率、训练轮数,或添加 Dropout(防过拟合);
- 预处理增强:扩展停用词表、加入词性过滤(如只保留名词 / 形容词)、同义词替换;
- 部署适配:可将训练好的模型权重保存为 NPY 文件,部署时直接加载(无需重新训练)。
九、基于 BP 神经网络的中文文本情感分类的Python代码完整实现
python
import numpy as np
import jieba
import os
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# 可视化库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
from wordcloud import WordCloud
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report, accuracy_score
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 设置中文字体(解决可视化中文乱码)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 黑体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# ======================== 1. 核心工具函数 ========================
def sigmoid(z):
"""Sigmoid激活函数(数值稳定版)"""
z = np.clip(z, -500, 500) # 防止exp溢出
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def sigmoid_derivative(z):
"""Sigmoid导数"""
s = sigmoid(z)
return s * (1 - s)
def relu(z):
"""ReLU激活函数"""
return np.maximum(0, z)
def relu_derivative(z):
"""ReLU导数"""
return np.where(z > 0, 1, 0)
def load_sentiment_data(data_dir):
"""
读取情感分类文本数据
:param data_dir: 数据文件夹路径
:return: texts(list) - 文本列表, labels(list) - 标签列表(1=正面,0=负面)
"""
texts = []
labels = []
# 读取正面文本
pos_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'positive.txt')
with open(pos_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if line: # 跳过空行
texts.append(line)
labels.append(1)
# 读取负面文本
neg_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'negative.txt')
with open(neg_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if line: # 跳过空行
texts.append(line)
labels.append(0)
return texts, np.array(labels).reshape(-1, 1)
def preprocess_text(texts):
"""
中文文本预处理:分词+去停用词
:param texts: 原始文本列表
:return: 预处理后的文本列表(空格分隔的分词结果)
"""
# 简单停用词表(可扩展)
stopwords = {'的', '了', '在', '是', '我', '你', '他', '她', '它', '们', '就', '都', '也', '还', '很', '太', '超',
'又', '和', '与', '及', '等', '有', '没', '不', '无', '为', '之', '于', '以', '对', '对于'}
processed_texts = []
for text in texts:
# 分词
words = jieba.lcut(text)
# 去停用词+去空字符
words = [w for w in words if w.strip() and w not in stopwords]
processed_texts.append(' '.join(words))
return processed_texts
# ======================== 2. BP神经网络类(适配情感分类) ========================
class BPNeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim, learning_rate=0.01):
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.lr = learning_rate
# 初始化权重和偏置(Xavier初始化)
self.W1 = np.random.normal(0, np.sqrt(2 / input_dim), (hidden_dim, input_dim))
self.b1 = np.zeros((hidden_dim, 1))
self.W2 = np.random.normal(0, np.sqrt(2 / hidden_dim), (output_dim, hidden_dim))
self.b2 = np.zeros((output_dim, 1))
# 记录训练损失(用于可视化)
self.train_loss_history = []
def forward(self, X):
"""前向传播"""
Z1 = np.dot(self.W1, X) + self.b1
H = relu(Z1)
Z2 = np.dot(self.W2, H) + self.b2
Y = sigmoid(Z2)
return H, Y
def backward(self, X, H, Y, Y_true):
"""反向传播计算梯度"""
delta2 = Y - Y_true
Z1 = np.dot(self.W1, X) + self.b1
delta1 = np.dot(self.W2.T, delta2) * relu_derivative(Z1)
dW2 = np.dot(delta2, H.T)
db2 = delta2
dW1 = np.dot(delta1, X.T)
db1 = delta1
return dW1, db1, dW2, db2
def update_params(self, dW1, db1, dW2, db2):
"""参数更新"""
self.W1 -= self.lr * dW1
self.b1 -= self.lr * db1
self.W2 -= self.lr * dW2
self.b2 -= self.lr * db2
def train(self, X_train, y_train, epochs=50, batch_size=4):
"""训练网络,记录损失"""
n_samples = X_train.shape[0]
self.train_loss_history = [] # 重置损失记录
for epoch in range(epochs):
indices = np.random.permutation(n_samples)
X_shuffled = X_train[indices]
y_shuffled = y_train[indices]
epoch_loss = 0.0
batch_count = 0
for i in range(0, n_samples, batch_size):
batch_X = X_shuffled[i:i + batch_size]
batch_y = y_shuffled[i:i + batch_size]
batch_count += 1
batch_batch_loss = 0.0
for X, y_true in zip(batch_X, batch_y):
X = X.reshape(self.input_dim, 1)
y_true = y_true.reshape(self.output_dim, 1)
H, Y = self.forward(X)
# 计算损失
loss = -y_true * np.log(Y + 1e-7) - (1 - y_true) * np.log(1 - Y + 1e-7)
batch_batch_loss += loss.item()
# 反向传播+更新
dW1, db1, dW2, db2 = self.backward(X, H, Y, y_true)
self.update_params(dW1, db1, dW2, db2)
epoch_loss += batch_batch_loss / len(batch_X)
# 记录每轮平均损失
avg_epoch_loss = epoch_loss / batch_count
self.train_loss_history.append(avg_epoch_loss)
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}, Average Loss: {avg_epoch_loss:.4f}")
def predict(self, X):
"""预测函数"""
predictions = []
for x in X:
x = x.reshape(self.input_dim, 1)
_, Y = self.forward(x)
pred = 1 if Y > 0.5 else 0
predictions.append(pred)
return np.array(predictions)
# ======================== 3. 可视化函数 ========================
def plot_train_loss(loss_history):
"""绘制训练损失曲线"""
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(range(1, len(loss_history) + 1), loss_history, color='#2E86AB', linewidth=2)
plt.title('BP神经网络训练损失变化', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('迭代轮数(Epoch)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('平均交叉熵损失', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.savefig('train_loss_curve.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def plot_confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred):
"""绘制混淆矩阵热力图"""
cm = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues',
xticklabels=['负面情感', '正面情感'],
yticklabels=['负面情感', '正面情感'])
plt.title('情感分类混淆矩阵', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('预测标签', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('真实标签', fontsize=12)
plt.savefig('confusion_matrix.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def plot_classification_report(y_true, y_pred):
"""可视化分类报告(准确率、召回率、F1)"""
report = classification_report(y_true, y_pred, target_names=['负面情感', '正面情感'], output_dict=True)
metrics = ['precision', 'recall', 'f1-score']
pos_scores = [report['正面情感'][m] for m in metrics]
neg_scores = [report['负面情感'][m] for m in metrics]
x = np.arange(len(metrics))
width = 0.35
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.bar(x - width / 2, neg_scores, width, label='负面情感', color='#A23B72')
plt.bar(x + width / 2, pos_scores, width, label='正面情感', color='#F18F01')
plt.title('情感分类性能指标', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('评估指标', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('分数', fontsize=12)
plt.xticks(x, ['精准率(Precision)', '召回率(Recall)', 'F1分数'])
plt.ylim(0, 1.1)
plt.legend()
# 添加数值标签
for i, v in enumerate(neg_scores):
plt.text(i - width / 2, v + 0.02, f'{v:.2f}', ha='center')
for i, v in enumerate(pos_scores):
plt.text(i + width / 2, v + 0.02, f'{v:.2f}', ha='center')
plt.grid(alpha=0.3, axis='y')
plt.savefig('classification_report.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def generate_wordcloud(texts, label, save_path):
"""
生成情感类别词云
:param texts: 文本列表
:param label: 标签(1=正面,0=负面)
:param save_path: 保存路径
"""
# 拼接所有文本
text = ' '.join(texts)
# 生成词云
wc = WordCloud(
font_path='simhei.ttf', # 中文分词字体(系统需有该字体)
width=800, height=600,
background_color='white',
max_words=100,
colormap='RdYlGn' if label == 1 else 'RdYlBu_r' # 正面用绿红,负面用蓝红
).generate(text)
# 绘制词云
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.imshow(wc, interpolation='bilinear')
plt.axis('off')
plt.title(f'{"正面" if label == 1 else "负面"}情感文本词云', fontsize=14)
plt.savefig(save_path, dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
def plot_feature_importance(tfidf, model, top_k=15):
"""
绘制TF-IDF特征重要性(基于BP网络第一层权重)
:param tfidf: TF-IDF向量化器
:param model: 训练好的BP模型
:param top_k: 显示前k个特征
"""
# 计算每个特征的权重绝对值之和(代表重要性)
feature_importance = np.sum(np.abs(model.W1), axis=0)
# 获取特征名称(词汇)
feature_names = tfidf.get_feature_names_out()
# 排序
indices = np.argsort(feature_importance)[-top_k:]
top_importance = feature_importance[indices]
top_features = feature_names[indices]
# 绘制条形图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
plt.barh(range(len(top_features)), top_importance, color='#C73E1D')
plt.yticks(range(len(top_features)), top_features)
plt.title(f'情感分类Top-{top_k}重要特征', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('权重绝对值之和(重要性)', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3, axis='x')
plt.savefig('feature_importance.png', dpi=300, bbox_inches='tight')
plt.show()
# ======================== 4. 主流程:情感分类+可视化 ========================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置参数
DATA_DIR = 'sentiment_data' # 数据文件夹路径
HIDDEN_DIM = 64 # 隐藏层神经元数
LEARNING_RATE = 0.01 # 学习率
EPOCHS = 50 # 训练轮数
BATCH_SIZE = 4 # 批量大小
TEST_SIZE = 0.2 # 测试集比例
# 2. 加载并预处理数据
print("===== 加载情感数据 =====")
texts, labels = load_sentiment_data(DATA_DIR)
print(f"总样本数:{len(texts)}(正面:{sum(labels)[0]},负面:{len(labels) - sum(labels)[0]})")
print("===== 文本预处理 =====")
processed_texts = preprocess_text(texts)
# 3. TF-IDF特征提取
print("===== 提取TF-IDF特征 =====")
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer(max_features=100) # 限制特征数,适配小数据集
X = tfidf.fit_transform(processed_texts).toarray()
# 划分训练集/测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, labels, test_size=TEST_SIZE, random_state=42, stratify=labels
)
print(f"训练集样本数:{X_train.shape[0]},测试集样本数:{X_test.shape[0]}")
print(f"特征维度:{X_train.shape[1]}")
# 4. 初始化并训练BP网络
print("\n===== 训练BP神经网络 =====")
bp_model = BPNeuralNetwork(
input_dim=X_train.shape[1],
hidden_dim=HIDDEN_DIM,
output_dim=1,
learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE
)
bp_model.train(X_train, y_train, epochs=EPOCHS, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
# 5. 模型评估
print("\n===== 模型评估 =====")
y_pred = bp_model.predict(X_test)
y_test_flat = y_test.flatten()
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test_flat, y_pred)
print(f"测试集准确率:{accuracy:.4f}")
print("\n分类报告:")
print(classification_report(y_test_flat, y_pred, target_names=['负面情感', '正面情感']))
# 6. 可视化(核心功能)
print("\n===== 生成可视化图表 =====")
# 6.1 训练损失曲线
plot_train_loss(bp_model.train_loss_history)
# 6.2 混淆矩阵
plot_confusion_matrix(y_test_flat, y_pred)
# 6.3 分类性能指标
plot_classification_report(y_test_flat, y_pred)
# 6.4 词云(正面/负面)
# 分离正面/负面文本
pos_texts = [processed_texts[i] for i in range(len(texts)) if labels[i] == 1]
neg_texts = [processed_texts[i] for i in range(len(texts)) if labels[i] == 0]
generate_wordcloud(pos_texts, 1, 'positive_wordcloud.png')
generate_wordcloud(neg_texts, 0, 'negative_wordcloud.png')
# 6.5 特征重要性
plot_feature_importance(tfidf, bp_model, top_k=15)
# 7. 新样本预测演示
print("\n===== 新样本情感预测 =====")
new_texts = [
"这家奶茶店的饮品甜度适中,用料很实在",
"今天打车遇到了绕路的司机,特别生气",
"新上映的动画电影画面精美,剧情感人",
"网购的水果烂了一半,售后还不处理"
]
# 预处理新样本
new_processed = preprocess_text(new_texts)
new_X = tfidf.transform(new_processed).toarray()
# 预测
new_pred = bp_model.predict(new_X)
# 输出结果
for text, pred in zip(new_texts, new_pred):
sentiment = "正面情感" if pred == 1 else "负面情感"
print(f"文本:{text} → 预测结果:{sentiment}")十、程序运行结果展示
===== 加载情感数据 =====
总样本数:20(正面:10,负面:10)
===== 文本预处理 =====
===== 提取TF-IDF特征 =====
训练集样本数:16,测试集样本数:4
特征维度:100
===== 训练BP神经网络 =====
Epoch 5/50, Average Loss: 0.6839
Epoch 10/50, Average Loss: 0.6638
Epoch 15/50, Average Loss: 0.6440
Epoch 20/50, Average Loss: 0.6246
Epoch 25/50, Average Loss: 0.6042
Epoch 30/50, Average Loss: 0.5829
Epoch 35/50, Average Loss: 0.5609
Epoch 40/50, Average Loss: 0.5375
Epoch 45/50, Average Loss: 0.5133
Epoch 50/50, Average Loss: 0.4885
===== 模型评估 =====
测试集准确率:0.7500
分类报告:
precision recall f1-score support
负面情感 1.00 0.50 0.67 2
正面情感 0.67 1.00 0.80 2
accuracy 0.75 4
macro avg 0.83 0.75 0.73 4
weighted avg 0.83 0.75 0.73 4
===== 生成可视化图表 =====


===== 新样本情感预测 =====
文本:这家奶茶店的饮品甜度适中,用料很实在 → 预测结果:负面情感
文本:今天打车遇到了绕路的司机,特别生气 → 预测结果:负面情感
文本:新上映的动画电影画面精美,剧情感人 → 预测结果:正面情感
文本:网购的水果烂了一半,售后还不处理 → 预测结果:正面情感
十一、总结
本文介绍了一个基于BP神经网络的中文文本情感分类实战项目,完整实现了从数据预处理到模型评估的全流程。通过jieba分词、TF-IDF特征提取和纯NumPy实现的BP神经网络,构建了一个能够区分中文文本正负面情感的分类模型。项目包含数据预处理、模型训练、评估指标计算和多维度可视化(包括损失曲线、混淆矩阵、词云和特征重要性分析)等功能模块。实验结果显示模型在测试集上达到75%的准确率,并通过可视化工具直观展示了分类效果和关键特征。该方案特别适合小数据集场景,具有代码简洁、可解释性强等特点,为中小企业或个人开发者提供了实用的情感分析解决方案。