目录
[1. 图的基本概念](#1. 图的基本概念)
[2. 图的类型](#2. 图的类型)
[有向图(Directed Graph):](#有向图(Directed Graph):)
[无向图(Undirected Graph):](#无向图(Undirected Graph):)
[简单图(Simple Graph):](#简单图(Simple Graph):)
[加权图(Weighted Graph):](#加权图(Weighted Graph):)
[完全图(Complete Graph):](#完全图(Complete Graph):)
[3. 图的术语](#3. 图的术语)
一、图的相关概念
在数据结构与算法中,图是一种常见且重要的数据结构,用于表示实体之间的关系。图由一组节点(或称为顶点)和一组边组成。每条边连接两个节点,可以表示不同类型的关系。图广泛应用于网络、社交媒体、推荐系统、路径规划等领域。
1. 图的基本概念
顶点(Vertex):
图中的基本元素,通常表示对象。
边(Edge):
连接两个顶点的线,表示两个对象之间的关系。边可以是有向的,也可以是无向的。
2. 图的类型
分类1:是否有箭头
有向图(Directed Graph):
边有方向,即从一个顶点指向另一个顶点。
无向图(Undirected Graph):
边没有方向,连接两个顶点的边表示双向关系。
分类2:是否有重边和自边
简单图(Simple Graph):
图中每对顶点之间最多只有一条边,没有自环(即顶点自己与自己相连的边)。
多重图(Multigraph):
允许多条边连接同一对顶点。
分类3:是否带权值:
加权图(Weighted Graph):
每条边都有一个权重,表示从一个顶点到另一个顶点的代价或距离。
其他
完全图(Complete Graph):
任意两点之间都有边相连,分为有向完全图和无向完全图
3. 图的术语
3.1度(Degree):
一个顶点的度是指与该顶点直接相连的边的数量。对于有向图,分为入度(指向该顶点的边的数量)和出度(从该顶点出发的边的数量)。
3.2连通性(Connectivity):
一个图是连通的,如果存在一条从任意一个顶点到另一个顶点的路径。
对于有向图,存在强连通和弱连通的概念。
连通分量(即极大连通图):
注意,极大而不是最大,极大的可以有多个,而最大的只能有一个。
路径(Path):
从一个顶点到另一个顶点的顶点序列,路径中的每一对相邻顶点通过一条边连接。
环(Cycle):
一条路径的起点和终点是同一个顶点,并且路径中的边没有重复。
树(Tree):
一种特殊的图,满足无环且连通的性质。树的一个重要特性是任何两点之间存在唯一的路径。
二、图的存储结构
1.边集数组
顺序存储
假设该图有n个点,m条边(n=100,m<1000)
点的存储:v[100+5](v[i]=x)
边的存储: 用结构体数组存储struct{起点编号,重点编号,边权};
假设现在数据的边权关系如下图所示:
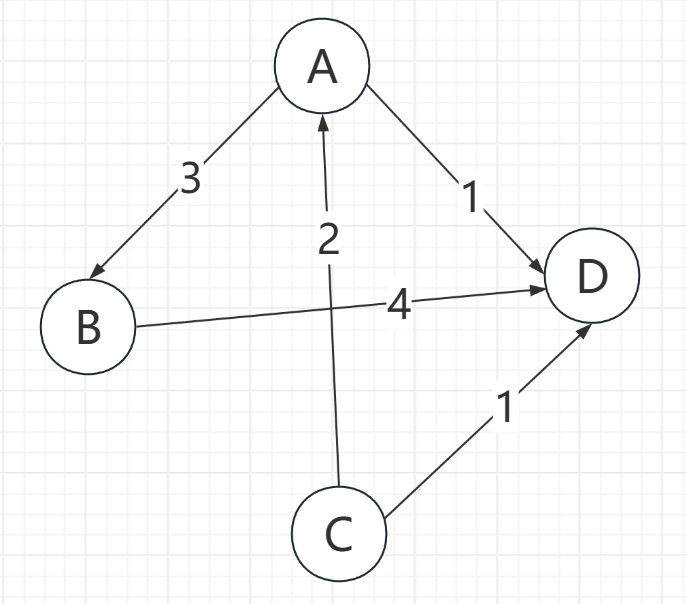
存储代码如下(不涉及操作):
关键代码(简略掉输出):
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
char v[100+5];
typedef struct {
int start;
int end;
int w;
} Edge;
Edge e[10000+5];
//也可以直接都用char类型,这样就不需要用到find函数
//但为了方便说明下一种方法,这里用到int来标号
int find(char x) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(v[i] == x) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
cout << "请输入n和m(点数和边数)" << endl;
cin >> n >> m;
// 输入顶点
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> v[i];
}
char x, y;
int w;
cout << "请输入" << m << "条边(格式:起点 终点 权值)" << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> x >> y >> w;
int xi = find(x);
int yi = find(y);
e[i].start = xi;
e[i].end = yi;
e[i].w = w;
}
return 0;
}完全代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 105; // 使用常量定义最大顶点数
const int MAX_M = 10005; // 使用常量定义最大边数
int n, m;
char v[MAX_N]; // 顶点数组,存储字符型顶点
// 边结构体
typedef struct {
int start; // 起点的编号
int end; // 终点的编号
int w; // 权值
} Edge;
Edge e[MAX_M]; // 边集数组
// 查找顶点在顶点数组中的索引
int find(char x) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(v[i] == x) {
return i;
}
}
return -1; // 找不到返回-1,增强健壮性
}
int main() {
cout << "请输入n和m(点数和边数): ";
cin >> n >> m;
// 验证输入范围
if(n > MAX_N || m > MAX_M) {
cout << "超出最大限制!最大顶点数:" << MAX_N
<< ",最大边数:" << MAX_M << endl;
return 1;
}
// 输入顶点
cout << "请输入" << n << "个顶点: ";
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> v[i];
}
// 输入边信息
cout << "请输入" << m << "条边(格式:起点 终点 权值):" << endl;
char x, y;
int w;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cout << "第" << i << "条边: ";
cin >> x >> y >> w;
int xi = find(x);
int yi = find(y);
// 检查顶点是否存在
if(xi == -1) {
cout << "错误:顶点 " << x << " 不存在!" << endl;
return -1;
}
if(yi == -1) {
cout << "错误:顶点 " << y << " 不存在!" << endl;
return -1;
}
// 存储边
e[i].start = xi;
e[i].end = yi;
e[i].w = w;
}
// 输出验证信息
cout << "\n========== 图信息 ==========" << endl;
cout << "顶点(" << n << "个): ";
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "\n边集数组(" << m << "条边):" << endl;
cout << "编号\t起点\t终点\t权值" << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cout << i << "\t"
<< v[e[i].start] << "\t"
<< v[e[i].end] << "\t"
<< e[i].w << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出结果
bash
请输入n和m(点数和边数): 4 5
请输入4个顶点: A B C D
请输入5条边(格式:起点 终点 权值):
第1条边: A B 3
第2条边: A D 1
第3条边: B D 4
第4条边: C A 2
第5条边: C D 1
========== 图信息 ==========
顶点(4个): A B C D
边集数组(5条边):
编号 起点 终点 权值
1 A B 3
2 A D 1
3 B D 4
4 C A 2
5 C D 1邻接矩阵存储
假设该图有n个点,m条边(n=100,m<1000)
点的存储:v[100+5](v[i]=x)

边的存储: 用二维数组g[ 100+5 ] [ 100+5 ]
g[ i ][ j ]=1 表示存储在一条由 i 到 j 的有向边
g[ i ][ j ]=0 表示没有
代码如下:
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
char v[100+5];
int g[100+5][100+5]; // 邻接矩阵
int find(char x) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(v[i] == x) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
cout << "请输入n和m(点数和边数)" << endl;
cin >> n >> m;
// 初始化邻接矩阵
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
g[i][j] = 0;//0表示不存在
}
}
// 输入顶点
cout<<"请输入"<<n<<"个顶点"<<endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> v[i];
}
char x, y;
int w;
cout << "请输入" << m << "条边(格式:起点 终点 权值)" << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> x >> y >> w;
int xi = find(x);
int yi = find(y);
// 存储到邻接矩阵
g[xi][yi] = w;
}
// 输出验证 - 从邻接矩阵提取边信息
cout << "\n边集数组(" << m << "条边):" << endl;
cout << "编号\t起点\t终点\t权值" << endl;
int edge_count = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if(g[i][j] != -1) { // 有边存在
edge_count++;
cout << edge_count << "\t"
<< v[i] << "\t"
<< v[j] << "\t"
<< g[i][j] << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}输出效果:
bash
请输入n和m(点数和边数)
4 5
请输入4个顶点
a b c d
请输入5条边(格式:起点 终点 权值)
a b 3
a d 1
b d 4
c a 2
c d 1
边集数组(5条边):
编号 起点 终点 权值
1 a b 3
2 a d 1
3 b d 4
4 c a 2
5 c d 1如果是想要无向图,只需要改成 g [ i ] [ j ] = g [ j ] [ i ] = w 即可
然后我们观察这个矩阵
| 终点 起点 | a | b | c | d |
| a | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
| b | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| c | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| d | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|---|
如果求有向图的出入度,
出度:横向之和
入度:纵向之和
则需要加入代码:
cpp
cout << "\n====== 顶点出度和入度 ======" << endl;
cout << "顶点\t出度\t入度\t总度" << endl;
// 计算每个顶点的出度和入度
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int out_degree = 0; // 出度
int in_degree = 0; // 入度
// 计算出度:统计第i行的非零元素个数
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if(g[i][j] != 0) {
out_degree++;
}
}
// 计算入度:统计第i列的非零元素个数
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if(g[j][i] != 0) {
in_degree++;
}
}
cout << v[i] << "\t"
<< out_degree << "\t"
<< in_degree << "\t"
<< out_degree + in_degree << endl;
}邻接表(类似孩子表示,只是记录出度)
假设该图有n个点,m条边(n=100,m<1000)
点的存储:v[100+5](v[i]=x)

边的存储:
用类似树的孩子表示法来记录每个节点的出度
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
char v[100+5];
//孩子表示法相关定义
typedef struct ChildNode {
int child; // 孩子节点(终点)的编号
int weight; // 边的权值
struct ChildNode *next; // 指向下一个孩子
} ChildNode, *ChildList;
ChildList childLists[100+5]; // 每个顶点的孩子链表(记录出边)
int find(char x) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(v[i] == x) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
cout << "请输入n和m(点数和边数)" << endl;
cin >> n >> m;
// 初始化孩子链表
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
childLists[i] = NULL; // 初始化孩子链表为空
}
// 输入顶点
cout << "请输入" << n << "个顶点" << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> v[i];
}
char x, y;
int w;
cout << "请输入" << m << "条边(格式:起点 终点 权值)" << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> x >> y >> w;
int xi = find(x);
int yi = find(y);
// 创建新的孩子节点
ChildNode *newChild = new ChildNode;
newChild->child = yi; // 终点节点编号
newChild->weight = w; // 边的权值
newChild->next = NULL;
// 插入到起点的孩子链表末尾
if(childLists[xi] == NULL) {
childLists[xi] = newChild;
} else {
ChildNode *p = childLists[xi];
while(p->next != NULL) {
p = p->next;
}
p->next = newChild;
}
}
// 输出边集数组信息
cout << "\n边集数组(" << m << "条边):" << endl;
cout << "编号\t起点\t终点\t权值" << endl;
int edge_count = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ChildNode *p = childLists[i];
while(p != NULL) {
edge_count++;
cout << edge_count << "\t"
<< v[i] << "\t"
<< v[p->child] << "\t"
<< p->weight << endl;
p = p->next;
}
}
// ============= 使用孩子链表输出出度信息 =============
cout << "\n====== 孩子表示法统计出度 ======" << endl;
cout << "顶点\t出度\t可达节点(权值)" << endl;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int out_degree = 0;
ChildNode *p = childLists[i];
cout << v[i] << "\t";
// 遍历孩子链表计算长度(出度)
while(p != NULL) {
out_degree++;
p = p->next;
}
cout << out_degree << "\t";
// 重新遍历输出可达节点和权值
p = childLists[i];
while(p != NULL) {
cout << v[p->child] << "(" << p->weight << ") ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}如果我们反过来记录入度,那就叫做逆邻接矩阵
十字链表
已知在邻接矩阵或者逆邻接矩阵中,分别可以记录出入度,如果在表的存储中,两种方式都用的话,有些数据其实是重复记录了,所以将二者结合,就产生了一种新的方法:十字链表
那下图作为示例(红色表示编号,从1开始)
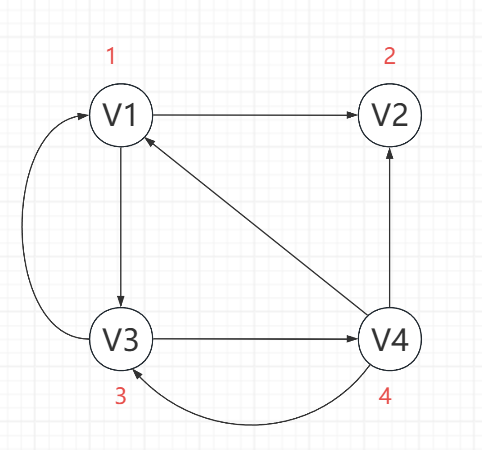
首先是顶点节点(显示每个节点的信息)
|---------|---------|----------|
| data | firstin | firstout |
| 数据(V1等) | 入度 | 出度 |
cpp
typedef struct VexNode {
char data; // 顶点数据
ArcNode *firstIn; // 第一条入边
ArcNode *firstOut; // 第一条出边
} VexNode;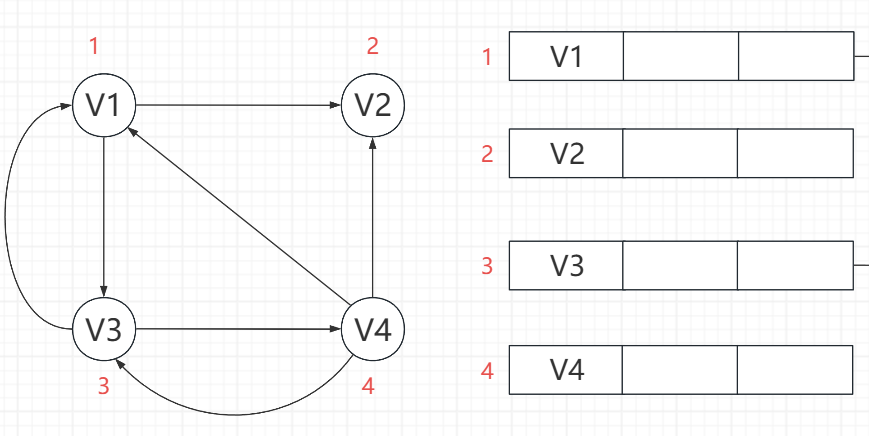
然后是弧节点(显示边的信息)这里的权值相当于info
|---------|---------|-------|-----------|----------|
| tailvex | headvex | hlink | tlink | ( info ) |
| 当前节点编号 | 下一个节点编号 | | | |
cpp
// 边节点(弧节点)
typedef struct ArcNode {
int tail; // 弧尾(起点)在顶点数组中的下标
int head; // 弧头(终点)在顶点数组中的下标
struct ArcNode *tlink; // 指向下一条相同起点的边
struct ArcNode *hlink; // 指向下一条相同终点的边
int weight; // 边的权值
} ArcNode;这里可以一步一步看,首先找到每个节点的出度(firstout------>指向整个结构体),从代码里就能看出来
cs
ArcNode *firstOut; // 第一条出边tlink 用来链接和他一样是出度的(找他兄弟,指向的是整个结构体),这里讲解先不考虑权值
|---------|---------|----------|
| data | firstin | firstout |
| 数据(V1等) | 入度 | 出度 |
|---------|---------|-------|-----------|
| tailvex | headvex | hlink | tlink |
| 当前节点编号 | 下一个节点编号 | | 同样是出度 |
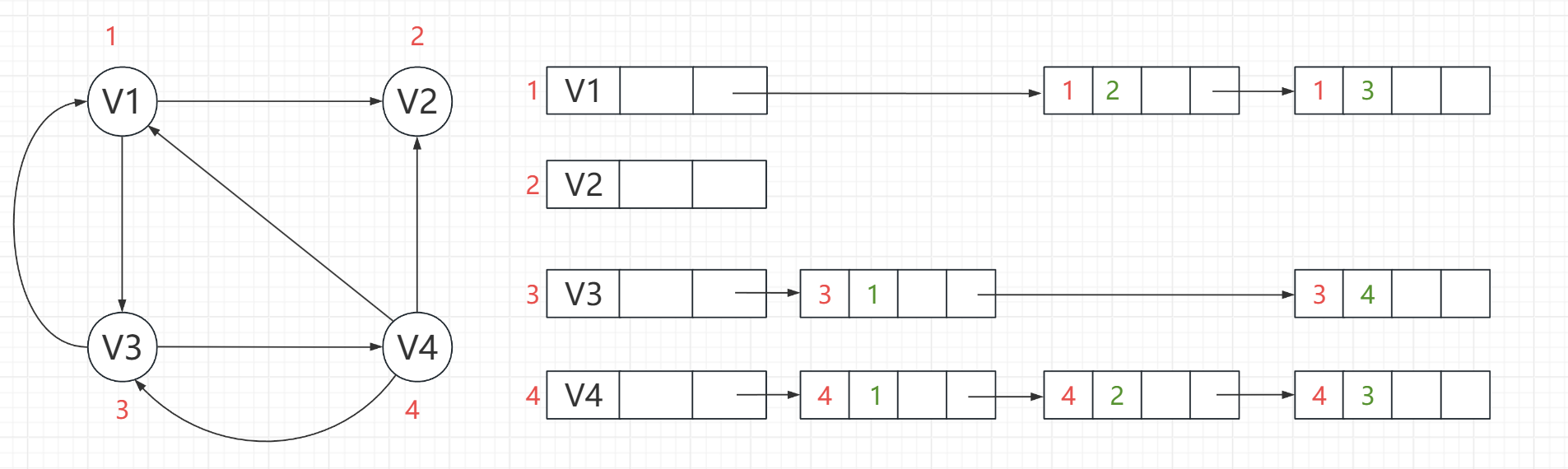
仔细看图,像是这种在方块里头的,说明是这个结构体中的一项去指向某个东西,可如果只是指向方框的边边上的,说明是指向整个结构体(从两个结构体的代码也可以看出来)
然后再找入度(firstin------>指向整个结构体)
tlink 用来链接和他一样是入度的(找他兄弟,指向的是整个结构体)
|---------|---------|----------|
| data | firstin | firstout |
| 数据(V1等) | 入度 | 出度 |
|---------|---------|-----------|-------|----------|
| tailvex | headvex | hlink | tlink | ( info ) |
| | | 同样是入度 | | |
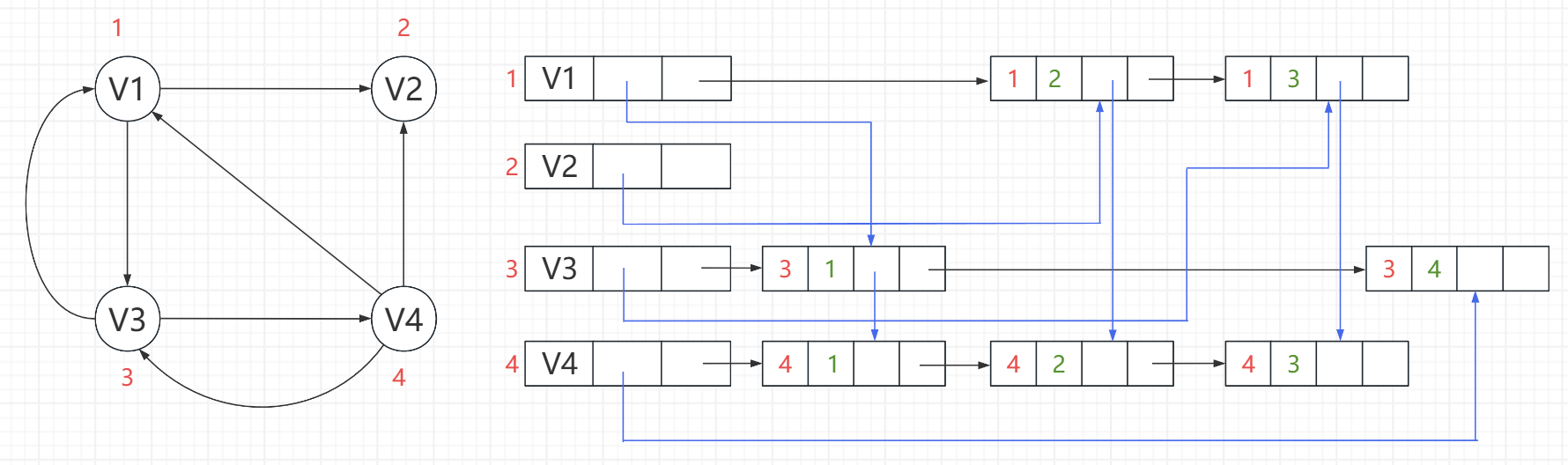
然后再把没有用到的地方用 ^ 表示空
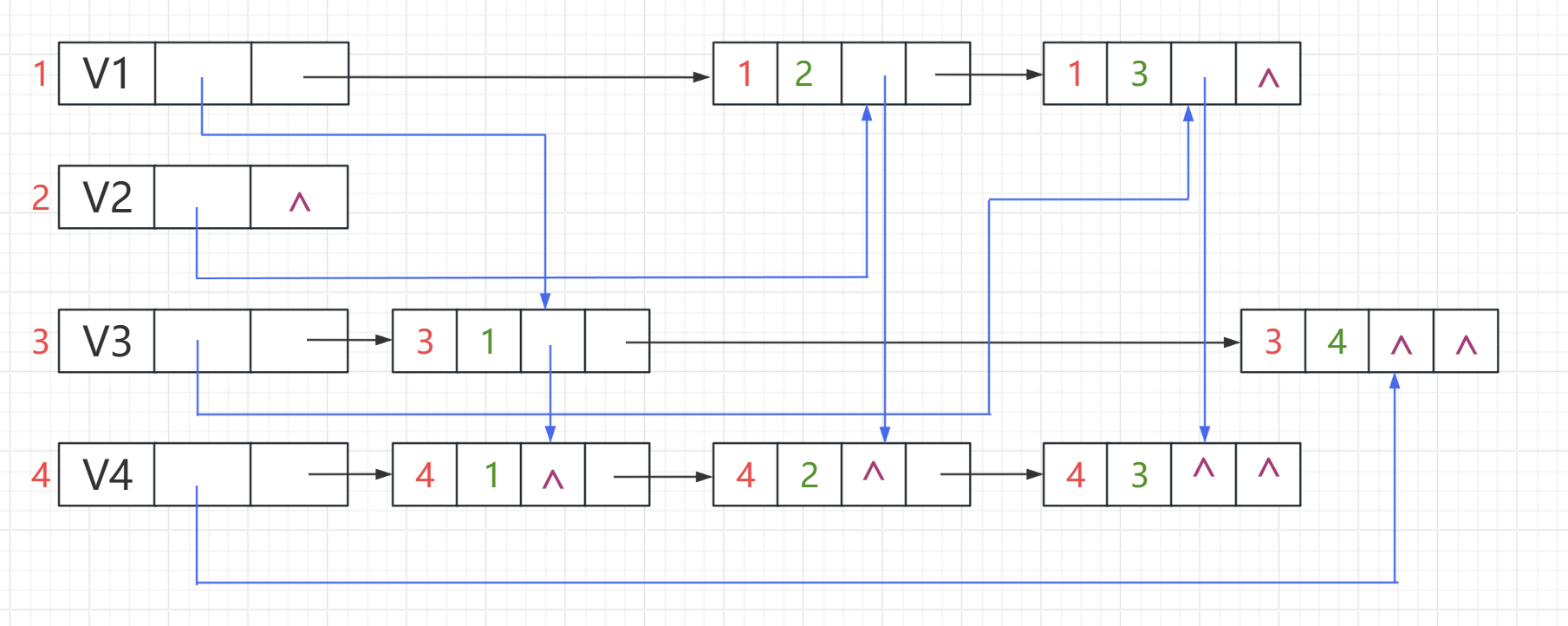
整体代码(带上权重)
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_VERTEX_NUM = 100;
// 边节点(弧节点)
typedef struct ArcNode {
int tail; // 弧尾(起点)在顶点数组中的下标
int head; // 弧头(终点)在顶点数组中的下标
struct ArcNode *tlink; // 指向下一条相同起点的边
struct ArcNode *hlink; // 指向下一条相同终点的边
int weight; // 边的权值
} ArcNode;
// 顶点节点
typedef struct VexNode {
char data; // 顶点数据
ArcNode *firstIn; // 第一条入边
ArcNode *firstOut; // 第一条出边
} VexNode;
// 十字链表图结构
typedef struct {
VexNode vexs[MAX_VERTEX_NUM]; // 顶点数组
int vexnum, arcnum; // 顶点数和边数
} OLGraph;
// 查找顶点位置
int locateVex(OLGraph &G, char v) {
for(int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {
if(G.vexs[i].data == v) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 创建十字链表
void createOLGraph(OLGraph &G) {
cout << "请输入顶点数和边数: ";
cin >> G.vexnum >> G.arcnum;
// 输入顶点
cout << "请输入" << G.vexnum << "个顶点: ";
for(int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {
cin >> G.vexs[i].data;
G.vexs[i].firstOut = NULL;
G.vexs[i].firstIn = NULL;
}
cout << "请输入" << G.arcnum << "条边(格式:起点 终点 权值):" << endl;
for(int k = 0; k < G.arcnum; k++) {
char v1, v2;
int weight;
cin >> v1 >> v2 >> weight;
int i = locateVex(G, v1); // 起点位置
int j = locateVex(G, v2); // 终点位置
if(i == -1 || j == -1) {
cout << "顶点不存在!" << endl;
k--;
continue;
}
// 创建新的边节点
ArcNode *p = new ArcNode;
p->tail = i;
p->head = j;
p->weight = weight;
// ========== 插入到出边链表(按起点) ==========
// 找到在出边链表中的正确插入位置(保持有序)
ArcNode *q = G.vexs[i].firstOut;
ArcNode *prevOut = NULL;
// 找到插入位置:保持按终点顺序
while(q != NULL && q->head < j) {
prevOut = q;
q = q->tlink;
}
// 插入到出边链表中
if(prevOut == NULL) {
// 插入到链表头部
p->tlink = G.vexs[i].firstOut;
G.vexs[i].firstOut = p;
} else {
// 插入到中间或尾部
p->tlink = prevOut->tlink;
prevOut->tlink = p;
}
// ========== 插入到入边链表(按终点) ==========
q = G.vexs[j].firstIn;
ArcNode *prevIn = NULL;
// 找到插入位置:保持按起点顺序
while(q != NULL && q->tail < i) {
prevIn = q;
q = q->hlink;
}
// 插入到入边链表中
if(prevIn == NULL) {
// 插入到链表头部
p->hlink = G.vexs[j].firstIn;
G.vexs[j].firstIn = p;
} else {
// 插入到中间或尾部
p->hlink = prevIn->hlink;
prevIn->hlink = p;
}
}
}
// 输出十字链表
void printOLGraph(OLGraph &G) {
cout << "\n========== 十字链表结构 ==========" << endl;
// 输出顶点表
cout << "顶点表:" << endl;
cout << "下标\t顶点\tfirstOut\tfirstIn" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {
cout << i << "\t" << G.vexs[i].data << "\t";
if(G.vexs[i].firstOut) {
cout << "→边" << G.vexs[i].firstOut->tail
<< "→" << G.vexs[i].firstOut->head;
} else {
cout << "NULL";
}
cout << "\t\t";
if(G.vexs[i].firstIn) {
cout << "←边" << G.vexs[i].firstIn->tail
<< "←" << G.vexs[i].firstIn->head;
} else {
cout << "NULL";
}
cout << endl;
}
// 输出边集数组格式
cout << "\n边集数组(" << G.arcnum << "条边):" << endl;
cout << "编号\t起点\t终点\t权值" << endl;
int edge_count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {
ArcNode *p = G.vexs[i].firstOut;
while(p != NULL) {
edge_count++;
cout << edge_count << "\t"
<< G.vexs[p->tail].data << "\t"
<< G.vexs[p->head].data << "\t"
<< p->weight << endl;
p = p->tlink;
}
}
// 输出每个顶点的出边和入边
cout << "\n========== 顶点出边和入边详情 ==========" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {
cout << "\n顶点 " << G.vexs[i].data << ":" << endl;
// 出边
cout << " 出边: ";
ArcNode *p = G.vexs[i].firstOut;
if(p == NULL) {
cout << "无";
} else {
while(p != NULL) {
cout << G.vexs[p->tail].data << "→"
<< G.vexs[p->head].data << "("
<< p->weight << ") ";
p = p->tlink;
}
}
cout << endl;
// 入边
cout << " 入边: ";
p = G.vexs[i].firstIn;
if(p == NULL) {
cout << "无";
} else {
while(p != NULL) {
cout << G.vexs[p->tail].data << "→"
<< G.vexs[p->head].data << "("
<< p->weight << ") ";
p = p->hlink;
}
}
cout << endl;
// 计算度
int out_degree = 0, in_degree = 0;
p = G.vexs[i].firstOut;
while(p != NULL) {
out_degree++;
p = p->tlink;
}
p = G.vexs[i].firstIn;
while(p != NULL) {
in_degree++;
p = p->hlink;
}
cout << " 出度: " << out_degree
<< ", 入度: " << in_degree
<< ", 总度: " << (out_degree + in_degree) << endl;
}
}
// 查找边
void findEdge(OLGraph &G, char v1, char v2) {
int i = locateVex(G, v1);
int j = locateVex(G, v2);
if(i == -1 || j == -1) {
cout << "顶点不存在!" << endl;
return;
}
// 从起点的出边链表中查找
ArcNode *p = G.vexs[i].firstOut;
while(p != NULL && p->head != j) {
p = p->tlink;
}
if(p != NULL) {
cout << "找到边: " << v1 << "→" << v2
<< " 权值: " << p->weight << endl;
} else {
cout << "边 " << v1 << "→" << v2 << " 不存在" << endl;
}
}
// 销毁十字链表
void destroyOLGraph(OLGraph &G) {
for(int i = 0; i < G.vexnum; i++) {
ArcNode *p = G.vexs[i].firstOut;
while(p != NULL) {
ArcNode *temp = p;
p = p->tlink;
delete temp;
}
G.vexs[i].firstOut = NULL;
G.vexs[i].firstIn = NULL;
}
}
int main() {
OLGraph G;
createOLGraph(G);
printOLGraph(G);
// 测试查找功能
cout << "\n========== 测试查找功能 ==========" << endl;
findEdge(G, 'a', 'b');
findEdge(G, 'b', 'a');
findEdge(G, 'c', 'd');
findEdge(G, 'd', 'c');
// 销毁图
destroyOLGraph(G);
return 0;
}