引言
stack和queue有一点需要注意的是,虽然stack和queue中也可以存放元素,但在STL中并没有将其划分在容器的行列,而是将其称为容器适配器,这是因为stack和queue只是对其他容器的接口进行了包装,STL中stack和queue默认使用deque容器。
在stack和queue的类模板声明当中我们就可以看到,它们的模板参数有两个,第一个是stack和queue当中所存储的元素类型,而另一个就是指定使用的容器类型。只不过当我们不指定使用何种容器的情况下,stack和queue都默认使用deque作为指定容器。


stack的模拟实现
有了容器适配器的思路后,stack的模拟实现就显得相当简单,我们只需要调用所指定容器的各个成员函数即可实现stack的各个函数接口。
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
namespace wzn
{
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& val)
{
_con.push_back(val);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_back();
}
// 库里引用的top后是可以修改的,不用+const
T& top()
{
return _con.back();
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void test1()
{
stack<int> s1;
s1.push(0);
s1.push(1);
s1.push(2);
s1.push(3);
s1.push(4);
cout << s1.size() << endl;
while (!s1.empty())
{
cout << s1.top() << endl;
s1.pop();
}
}
}queue的模拟实现
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
namespace wzn
{
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_front();
}
T& back()
{
return _con.back();
}
const T& back() const
{
return _con.back();
}
T& front()
{
return _con.front();
}
const T& front() const
{
return _con.front();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void test1()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(0);
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
q.push(4);
cout << q.size() << endl;
cout << q.back() << endl;
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.front() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}priority_queue的模拟实现
在模拟实现priority_queue前,我们得先了解仿函数
仿函数
- 概念:
仿函数,即函数对象。一种行为类似函数的对象,调用者可以像函数一样使用该对象,其实现起来也比较简单:用户只需要实现一种新类型,在类中重载operator()即可,参数根据用户所要进行的操作选择匹配。
上层调用者往往以仿函数operator()的结果为true,则进行运行代码为逻辑
- 样例:
内置类型比较大小关系:
cpp
//仿函数/函数对象 --- 对象可以像调用函数一样去使用
struct less
{
//()运算符重载--用于比较大小
bool operator()(int x, int y)
{
return x < y;
}
};自定义类型比较less:
cpp
template<class T>
struct less//用于 < 的比较
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) const
{
return x < y;
}
};自定义类型比较greater
cpp
template<class T>
struct greater//用于 > 的比较
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) const
{
return x > y;
}
};less和greater的测试:
cpp
//测试less
less<int> LessCom;
cout << LessCom(1, 2) << endl;//1
//测试greater
greater<int> GreaterCom;
cout << GreaterCom(1, 5) << endl;//0priority_queue的底层类似于堆
堆的向上调整算法
以小堆为例子,下面这张图的节点10,需要往上调整
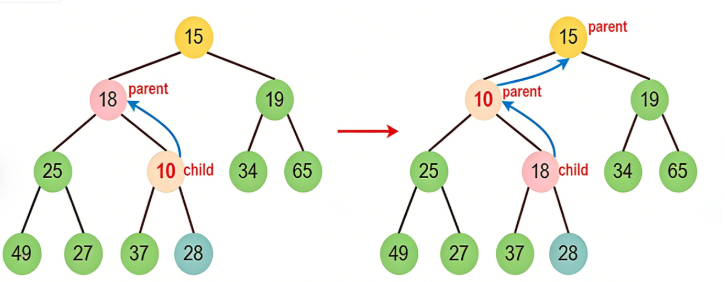
cpp
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com; // 仿函数对象
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}向下调整算法
cpp
// 向下调整
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
// 升序是大根堆,排升序,建大堆,然后和数组最后一个元素交换位置,这样才不会改变二叉树节点的父子关系
// less,升序,因此左右孩子找大的那个和parent比较
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
child += 1;
}
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}有了这两个算法的基础,就很好实现了
完整的priority_queue
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
namespace wzn
{
// less是升序,greater是升序,记法: less和greater 指的是 < 和 >
template<class T>
struct less
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
struct greater
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
// 向下调整
void AdjustDown(int parent)
{
Compare com;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
// 升序是大根堆,排升序,建大堆,然后和数组最后一个元素交换位置,这样才不会改变二叉树节点的父子关系
// less,升序,因此左右孩子找大的那个和parent比较
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
child += 1;
}
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
//向上调整
void AdjustUp(int child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
std::swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public:
priority_queue()
{}
//////////////////////////////////////////
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
// 先全部push进去再调整
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
//向上建堆,向下调整,O(N)
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i > 0; --i)
{
AdjustDown(i);
}
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
void push(const T& val)
{
_con.push_back(val);
AdjustUp(_con.size() - 1);
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
void pop()
{
std::swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
AdjustDown(0);
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
const T& top() const
{
return _con[0];
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
//////////////////////////////////////////
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
void test1()
{
priority_queue<int> q;
q.push(5);
q.push(1);
q.push(0);
q.push(7);
q.push(9);
cout << "size: " << q.size() << endl;
cout << "empty: " << q.empty() << endl;
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.top() << " ";
q.pop();
}
cout << endl;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> q1;
q1.push(5);
q1.push(1);
q1.push(0);
q1.push(7);
q1.push(9);
cout << "size: " << q1.size() << endl;
cout << "empty: " << q1.empty() << endl;
while (!q1.empty())
{
cout << q1.top() << " ";
q1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}