文章目录
- 前言
- 一、HQL基本介绍
- [二、Hive Set Operators](#二、Hive Set Operators)
-
- (一)基本介绍
-
- [1.UNION [DISTINCT] or UNION](#1.UNION [DISTINCT] or UNION)
- [2.UNION ALL](#2.UNION ALL)
- [(二)Hive Subqueries](#(二)Hive Subqueries)
-
- [1.Subqueries in FROM clause](#1.Subqueries in FROM clause)
- [2.Subqueries in WHERE clause](#2.Subqueries in WHERE clause)
- [(三)Partition-Based Query 基于分区的查询](#(三)Partition-Based Query 基于分区的查询)
- [三、Joins in Hive](#三、Joins in Hive)
-
- [(一)joins Introduction](#(一)joins Introduction)
- [(二)syntax of join](#(二)syntax of join)
-
- 1.使用相等连接来组合表
- [2.Using Outer Joins](#2.Using Outer Joins)
-
- [(1)Joining Tables in Hive Using Left Join](#(1)Joining Tables in Hive Using Left Join)
- [(2)Joining Tables in Hive Using Right Join](#(2)Joining Tables in Hive Using Right Join)
- [(3)Joining Tables in Hive Using a Full Outer Join](#(3)Joining Tables in Hive Using a Full Outer Join)
- [3.Using Largest Table Last](#3.Using Largest Table Last)
- [四、ORDER BY and SORT BY](#四、ORDER BY and SORT BY)
- [五、Hive common examples](#五、Hive common examples)
-
- (一)基本查询
- [(二) 过滤与分组](#(二) 过滤与分组)
- [(三) 实用功能](#(三) 实用功能)
- [(四) 子查询](#(四) 子查询)
- (五)分区查询
- (六)连接(JOIN)操作
- [六、Hive Views](#六、Hive Views)
-
- [(一)Apache Hive View on External Table](#(一)Apache Hive View on External Table)
- [(二)Creating a Hive View](#(二)Creating a Hive View)
- [七、Advanced Table Properties](#七、Advanced Table Properties)
-
- [(一)Skipping Header and Footer records while loading in table](#(一)Skipping Header and Footer records while loading in table)
- (二)如何操作
- [(三)Hive Immutable Table property](#(三)Hive Immutable Table property)
-
- [1.Mutable Table](#1.Mutable Table)
- [2.Immutable Table](#2.Immutable Table)
- [3.Insert into command on Non-Empty Immutable Table:](#3.Insert into command on Non-Empty Immutable Table:)
- [4.Insert Overwrite command on Non-Empty Immutable Table](#4.Insert Overwrite command on Non-Empty Immutable Table)
- [(四)Hive Null Format property](#(四)Hive Null Format property)
-
- [Data in the table with table Null format property](#Data in the table with table Null format property)
- 总结
前言
本章主要介绍如何在HQL中使用Hive的各种命令来完成在Hive中创建表、删除表、修改表等操作。 HIVE可以将SQL语句转换成MapReduce,在Hadoop上运行。 HQL语法与普通SQL语法略有不同。
一、HQL基本介绍
(一)概念
Hive提供了一种机制,将结构投射到Hadoop中的数据上,并使用类似sql的语言HiveQL (HQL)查询数据。 使用Hive是因为Hive中的表类似于关系数据库中的表。 如果您熟悉SQL,这是小菜一碟。 许多用户可以同时使用Hive-QL查询数据。
(二)基本命令
1.select
sql
SELECT Statement Syntax:
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ...
FROM table_reference
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY col_list [HAVING condition]]
[ CLUSTER BY col_list
| [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] [SORT BY| ORDER BY col_list]
]
[LIMIT number]2.ALL and DISTINCT clauses
ALL和DISTINCT选项指定是否返回重复的行 。如果未指定 ,则默认为ALL(返回所有行)。DISTINCT指定从结果集中删除重复的行。
ALL and DISTINCT options specify whether duplicate rows are returned. If not specified, the default is ALL (all rows are returned). DISTINCT specifies that duplicate rows are removed from the result set.
3.where clauses
sql
hive> select name,age from emp where gender='M' and salary>9000;
OK
Bernard 55.98
Burton 41.43
Lauren 38.32
Carter 51.75
Isaiah 57.98
Time taken: 1.596 seconds, Fetched: 5 row(s)4.group by clauses
Group by与聚合函数一起使用 ,按一个或多个列 对结果进行分组。 GROUP BY子句用于使用特定的集合列对结果集中的所有记录进行分组。 用于查询一组记录。
Group by is used with aggregate functions to group results by one or more columns. The GROUP BY clause is used to group all the records in a result set using a particular collection column. It is used to query a group of records.
sql
select gender, count(*) from emp group by gender;5.HAVING clause
它类似于where子句,我们将它与group by子句一起用于过滤数据。
It's similar to where clause, we use it with group by clause for filtering the data.
sql
select gender, count(*) from emp group by gender having gender='F';6.limit
典型查询的结果可以返回大量的行。 LIMIT子句对返回的行数设置了上限:
The results of a typical query can return a large number of rows. The LIMIT clause puts an upper limit on the number of rows returned:
sql
select name, age from emp limit 3;7.Column alias
我们可以使用排序名作为列名。 我们使用as关键字作为列别名。
We can use sort name as column names. We use as keyword for column alias.
sql
select name, salary as sal from emp limit 2;8.Like and RLike
Like是一个标准的SQL语句。 RLike是Hive的扩展。 通过java正则表达式可以指定匹配条件 。 LIKE是一个类似于SQL中的LIKE的操作符。 我们使用LIKE来搜索具有相似文本的字符串。
sql
select emp_id,name,salary from emp where name like '_u%';- we can use '_' and '%' in Like statement
- '_' :- only one letter
- '%' :- zero or more letters
RLIKE (Right-Like)是Hive中的一个特殊函数 ,如果a的任何子字符串与B匹配,则计算结果为true。 它还遵循Java正则表达式模式。 在RLIKE中,用户不需要为简单的匹配添加%符号。
sql
select emp_id,name,salary from emp where name rlike '(Hugh|Deane)';二、Hive Set Operators
(一)基本介绍
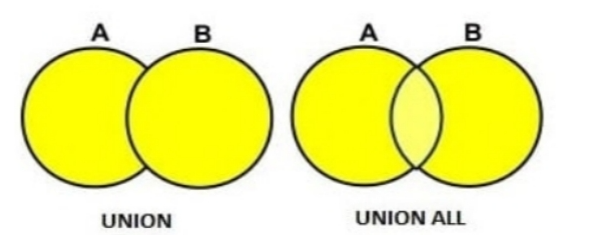
1.UNION [DISTINCT] or UNION
UNION集操作从结果集中删除重复的行。
A UNION set operation removes duplicate rows from the result set.
2.UNION ALL
UNION ALL集合操作不会从结果集中删除重复的行。
A UNION ALL set operation does not remove duplicate rows from the result set.
(二)Hive Subqueries
在查询中出现的查询称为子查询 。 主查询将依赖于子查询返回的值。
1.Subqueries in FROM clause
sql
SELECT <column names 1, 2...n>From (SubQuery) <TableName_Main >
SELECT col1 FROM (SELECT a+b AS col1 FROM t1) t22.Subqueries in WHERE clause
sql
SELECT <column names 1, 2...n> From<TableName_Main>WHERE col1 IN (SubQuery);
SELECT name,age FROM emp WHERE emp.emp_id IN (SELECT id FROM dept);- 应用场景:
- 从来自不同表的两个列值中获得组合的特定值
- 一个表值对其他表的依赖性
- 比较检查来自其他表的列值
(三)Partition-Based Query 基于分区的查询
通常,SELECT查询扫描所有表(抽样除外)。 如果表是用PARTITIONED BY子句创建的,则可以对查询进行分区和剪枝,并根据查询指定的分区范围扫描表的一部分。 目前Hive在JOIN的where子句或ON子句中指定分区,并执行分区修剪。 例如,如果根据列日期对表page_views进行分区,下面的查询只返回日期从2008-03-01到2008-03-31的行。
sql
SELECT page_views.* FROM page_views WHERE page_views.date >= '2008-03-01' AND
page_views.date <= '2008-03-31'如果连接了表page_views和其他表dim_users,可以在ON子句中指定分区的范围,如下所示:
sql
SELECT page_views.* FROM page_views JOIN dim_users ON (page_views.user_id =
dim_users.id AND page_views.date >= '2008-03-01' AND page_views.date <=
'2008-03-31')三、Joins in Hive
(一)joins Introduction
Hive中的join与传统RDBMS中的join用途相同 。 连接用于根据公共值或字段 从两个或多个表中获取有意义的数据。 换句话说,连接用于组合来自多个表的数据。 只要在FROM子句中指定了多个表,就会执行连接。
A join in Hive is used for the same purpose as in a traditional RDBMS. A join is used to fetch meaningful data from two or more tables based on a common value or field. In other words, a join is used to combine data from multiple tables. A join is performed whenever multiple tables are specified inside the FROM clause.
到目前为止,Hive只支持基于相等条件的连接。 它不支持任何基于非相等条件的连接条件。
(二)syntax of join
1.使用相等连接来组合表
sql
SELECT table_fields
FROM table_one
JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one
AND table_one.key_two = table_two.key_two);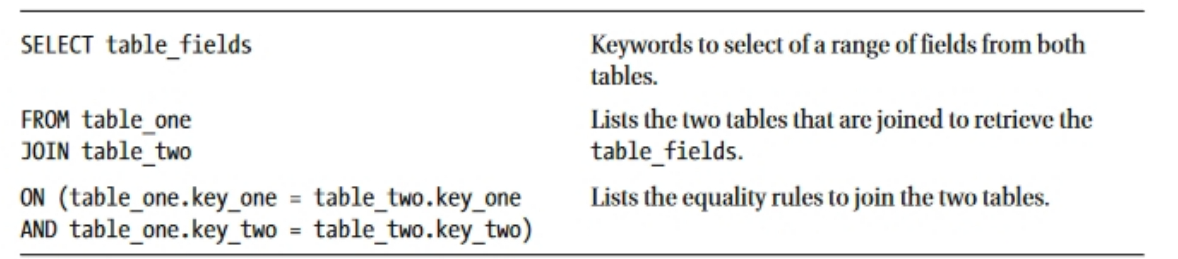
2.Using Outer Joins
Hive支持表之间使用LEFT、RIGHT和FULL OUTER连接的相等连接,其中键没有匹配。 Hive的语法如下:
Hive supports equality joins between tables using LEFT, RIGHT, and FULL OUTER joins, where keys have no match.
sql
SELECT table_fields
FROM table_one [LEFT, RIGHT, FULL OUTER] JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one
AND table_one.key_two = table_two.key_two)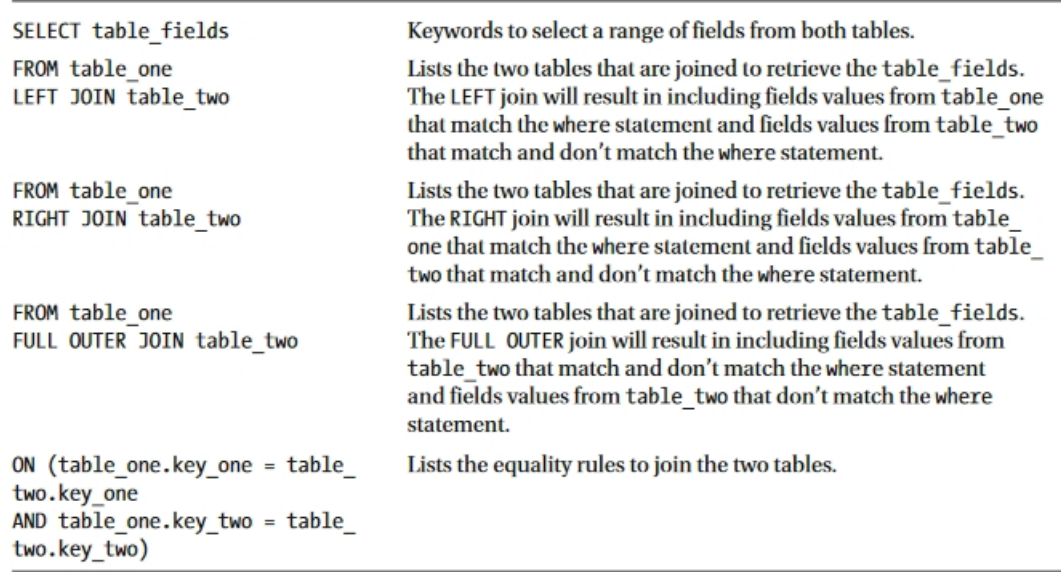
(1)Joining Tables in Hive Using Left Join
Hive支持表间的相等连接,可以将两个表中的数据合并。 本例使用脚本Script_OuterJoin.txt。
sql
USE census;
SELECT personname.firstname,
personname.lastname,
address.postname
FROM
census.personname
LEFT JOIN
census.address
ON (personname.persid = address.persid);
(2)Joining Tables in Hive Using Right Join
sql
SELECT personname.firstname,
personname.lastname,
address.postname
FROM
census.personname
RIGHT JOIN
census.address
ON (personname.persid = address.persid);
(3)Joining Tables in Hive Using a Full Outer Join
sql
SELECT personname.firstname,
personname.lastname,
address.postname
FROM
census.personname
FULL OUTER JOIN
census.address
ON (personname.persid = address.persid);
3.Using Largest Table Last
Hive通过缓冲连接的第一个表,然后将最后一个表映射到它们来执行连接。 最好总是把最大的表列在最后,因为这样可以加快处理速度。 Hive的语法如下:
Hive performs joins by buffering the first tables of the join and then mapping the last table against them.It's good practice to always list the biggest table last because this speeds up the processing.The Hive syntax one is as follows:
sql
SELECT table_one.key_one, table_two.key_one, table_three.key_one
FROM table_one JOIN table_two
ON (table_one.key_one = table_two.key_one)
JOIN table_three
ON (table_three.key_one = table_two.key_one);
四、ORDER BY and SORT BY
(一)介绍
在Hive中操作数据的另一个方面是对数据或结果集进行适当的排序 ,以清楚地识别重要的事实,例如前N值,最大值,最小值等。 Hive中主要使用以下关键字对数据进行排序:
Another aspect to manipulate data in Hive is to properly order or sort the data or result sets to clearly identify the important facts, such as top N values, maximum, minimum, and so on.There are the following keywords used in Hive to order and sort data:
(二)类型
1.ORDER BY (ASC|DESC)
这类似于RDBMS的ORDER BY语句 。 每个reducer的所有输出都保持有序 。 它只使用一个reducer执行全局排序 ,因此需要更长的时间来返回结果。 强烈建议对ORDER BY使用LIMIT。 可以这样使用:
This is similar to the RDBMS ORDER BY statement. A sorted order is maintained across all of the output from every reducer. It performs the global sort using only one reducer, so it takes a longer time to return the result. Usage with LIMIT is strongly recommended for ORDER BY. This can be used as follows:
sql
SELECT name FROM emp ORDER BY NAME DESC;2.SORT BY (ASC|DESC)
这表示在对reducer输入记录排序时要对哪些列进行排序。 这意味着它在将数据发送到reducer之前完成排序 。 SORT BY语句不执行全局排序 ,只确保数据在每个reducer中进行本地排序 ,除非我们设置mapred.reduce.tasks=1。
This indicates which columns to sort when ordering the reducer input records. This means it completes sorting before sending data to the reducer. The SORT BY statement does not perform a global sort and only makes sure data is locally sorted in each reducer unless we set mapred.reduce.tasks=1. In this case, it is equal to the result of ORDER BY.
- use more than 1 reducer
sql
SET mapred.reduce.tasks = n; // n=2, 3...
SELECT name FROM emp SORT BY NAME;- use only 1 reducer
sql
SET mapred.reduce.tasks = 1;
SELECT name FROM emp SORT BY NAME;3.DISTRIBUTE BY
具有匹配列值的行将被划分到同一个reducer中 。 当单独使用时,它不能保证对减速器的输入排序。 在决定将映射器输出分发到哪个reducer方面,DISTRIBUTE BY语句类似于RDBMS中的GROUP BY。 当与SORT BY一起使用时,必须在SORT BY语句之前指定DISTRIBUTE BY。 并且,用于分发的列必须出现在选择列列表中。
Rows with matching column values will be partitioned to the same reducer. When used alone, it does not guarantee sorted input to the reducer. The DISTRIBUTE BY statement is similar to GROUP BY in RDBMS in terms of deciding which reducer to distribute the mapper output to. When using with SORT BY,DISTRIBUTE BY must be specified before the SORT BY statement. And, the column used to distribute must appear in the select column list.
sql
SELECT name, emp_id FROM emp DISTRIBUTE BY emp_id;
-- Used with SORT BY
SELECT name, emp_id FROM emp DISTRIBUTE BY emp_id SORT BY name;4.CLUSTER BY
这是一个速记操作符,用于对同一列组执行DISTRIBUTE BY和SORT BY操作。 并且,它在每个reducer中都是局部排序的 。CLUSTER BY语句还不支持ASC或DESC 。 与全局排序的ORDER BY操作相比,CLUSTER BY操作在每个分布式组中排序。 为了在执行全局排序时充分利用所有可用的reducer,我们可以先执行CLUSTER BY,然后再执行ORDER BY。
This is a shorthand operator to perform DISTRIBUTE BY and SORT BY operations on the same group of columns. And, it is sorted locally in each reducer. The CLUSTER BY statement does not support ASC or DESC yet. Compared to ORDER BY, which is globally sorted, the CLUSTER BY operation is sorted in each distributed group. To fully utilize all the available reducers when doing a global sort, we can do CLUSTER BY first and then ORDER BY.
sql
SELECT name, emp_id FROM emp CLUSTER BY name;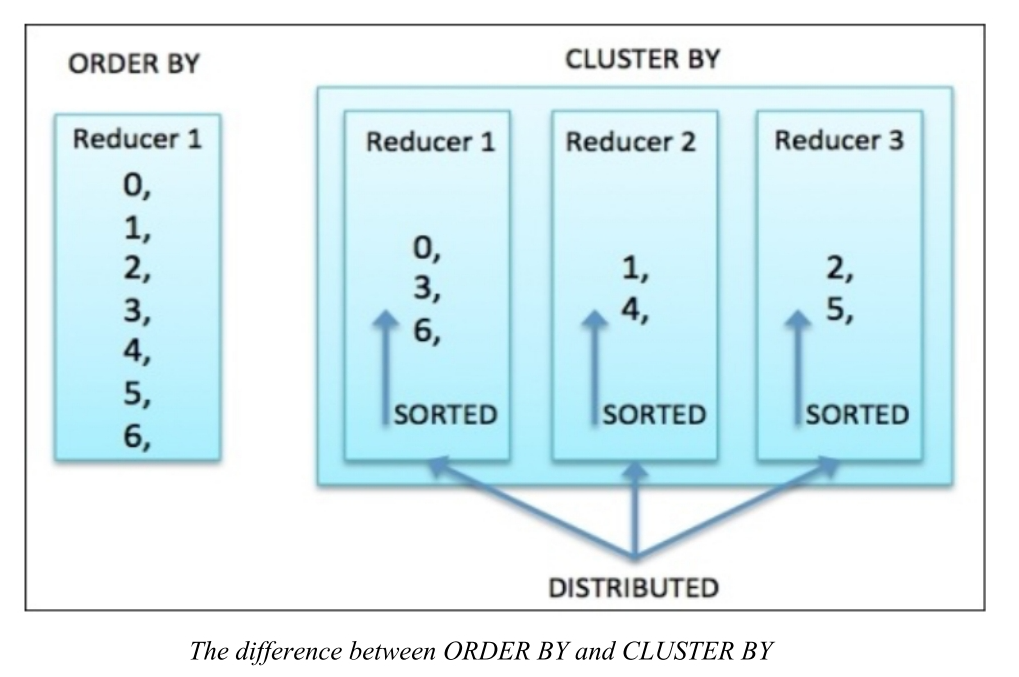
五、Hive common examples
以下是 Hive 中常见的查询操作示例,涵盖了基本查询、过滤、分组、子查询、分区和连接等场景。所有示例使用 SQL 语法,并在 Hive 环境中测试。
(一)基本查询
- 选择表中的所有行和列
sql
select * from table_nm;- 选择特定列的所有行
sql
select col_nm from table_nm;- 选择多个列的所有行
sql
select col_nm1, col_nm2, col_nm3 from table_nm;- 限制返回行数(仅显示样本数据)
sql
select * from table_nm limit 10;(二) 过滤与分组
- 基于条件过滤行(WHERE 子句)
sql
select col_nm1, col_nm2 from table_nm where salary > 100000;- 使用多个条件(AND, OR, BETWEEN, IN)
sql
select name, department, salary from emp_full where salary > 70000 and department='IT';
select name, department, salary from emp_full where salary between 70000 and 80000;
select name, department, salary from emp_full where department='IT' or salary < 70000;
select name, department, salary from emp_full where salary in (35962, 41922, 61407);
select name, department, salary from emp_full where department not in ('IT', 'HR', 'Sales');- 去除重复行(DISTINCT)
sql
select distinct col_nm1, col_nm2 from table_nm;- 分组聚合(GROUP BY)
sql
select count(*) from table_nm group by gender;- 分组后过滤(HAVING)
sql
SELECT department, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM emp_full
GROUP BY department
HAVING AVG(salary) > 70000;(三) 实用功能
- 设置列名显示
sql
set hive.cli.print.header=true;- 正则表达式匹配
sql
set hive.support.quoted.identifiers=none;
select `^yea.*` from emp_full;- 使用通配符(LIKE 和 RLIKE)
sql
select name, department, salary from table_nm where name like 'mat%';
select name, department, salary from emp_full WHERE name RLIKE 'Anth.*';- 列别名
sql
select department as dept from tbl_nm;(四) 子查询
- 查找部门内最高薪水的员工
sql
SELECT name, department, salary
FROM emp_full e1
WHERE salary = (
SELECT MAX(salary)
FROM emp_full e2
WHERE e1.department = e2.department
);- 薪水高于部门平均值的员工
sql
SELECT e.name, e.department, e.salary
FROM emp_full e
WHERE e.salary > (
SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM emp_full e2
WHERE e.department = e2.department
);- 薪水高于整体平均值的员工
sql
SELECT name, department, salary
FROM (
SELECT
name,
department,
salary,
AVG(salary) OVER () AS avg_salary_overall
FROM emp_full
) t
WHERE salary > avg_salary_overall;- 薪水高于 HR 部门最高薪水的员工
sql
SELECT name, department, salary
FROM (
SELECT
name,
department,
salary,
MAX(CASE WHEN department = 'HR' THEN salary ELSE NULL END) OVER () AS hr_max_salary
FROM emp_full
) t
WHERE salary > hr_max_salary;(五)分区查询
- 基于分区列过滤
sql
select * from employee where year = '2022';(六)连接(JOIN)操作
- 启用严格模式
sql
set hive.mapred.mode=STRICT;
set hive.mapred.mode;- 内连接(INNER JOIN)
sql
-- 示例:显示订单及客户和产品信息
SELECT
o.OrderID,
c.cust_name,
c.country,
p.productname,
o.quantity,
o.orderdate
FROM orders o
JOIN customer c
ON o.custsid = c.custid
JOIN products p
ON o.productid = p.productid;
-- 示例:列出订购 "Product_2004" 的客户
SELECT DISTINCT
c.cust_name,
c.Country
FROM customer c
JOIN orders o ON c.custid = o.custsid
JOIN products p ON o.ProductID = p.ProductID
WHERE p.ProductName = 'Product_2004';- 左连接(LEFT JOIN)
sql
-- 示例:显示所有客户及其订单(包括无订单客户)
SELECT
c.custid,
c.cust_name,
o.orderid,
o.OrderDate
FROM customer c
LEFT JOIN orders o ON c.custid = o.custsid;
-- 示例:显示所有客户,即使未下订单
SELECT
c.custid,
c.cust_name,
c.Country,
o.OrderID,
o.OrderDate
FROM customer c
LEFT JOIN orders o
ON c.custid = o.custsid;- 右连接(RIGHT JOIN)
sql
-- 示例:显示所有订单,即使客户记录缺失
SELECT
o.OrderID,
o.custsid,
c.cust_name,
o.ProductID,
o.Quantity
FROM customer c
RIGHT JOIN orders o
ON c.custid = o.custsid;
-- 示例:显示每个订单的产品详情(即使产品表缺失)
SELECT
o.OrderID,
o.custsid,
p.ProductName,
o.Quantity
FROM products p
RIGHT JOIN orders o ON p.ProductID = o.ProductID;- 全连接(FULL JOIN)
sql
-- 示例:显示所有订单和客户(即使一方缺失)
SELECT
o.OrderID,
c.custid,
c.cust_name
FROM orders o
FULL JOIN customer c ON o.custsid = c.custid;六、Hive Views
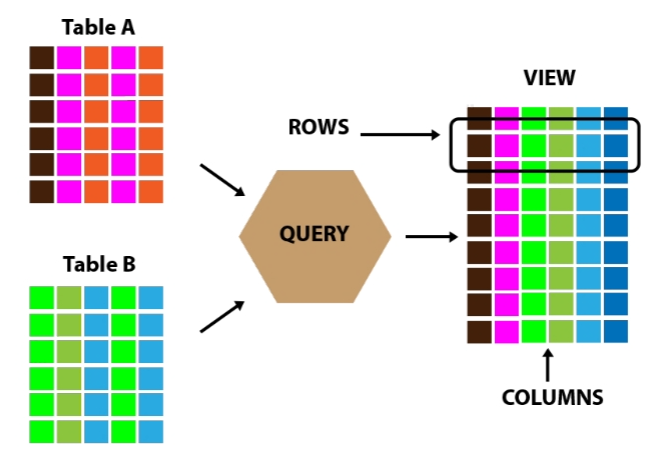
(一)Apache Hive View on External Table
- 作为Hive视图,我们可以保存任何结果集数据。
- 我们可以说它的用法和SQL中视图的用法一样。
- 虽然,我们可以在Hive视图上执行所有类型的DML操作。
换句话说,Apache Hive View是数据库中的一个可搜索对象,我们可以通过查询来定义它 。 但是,我们不能在视图中存储数据 。 尽管如此,有些人还是将视图称为"虚拟表"。 因此,我们可以像查询表一样查询视图。 此外,通过使用连接,可以组合来自或多个表的数据。 此外,它还包含一个信息子集。
(二)Creating a Hive View
sql
CREATE VIEW [IF NOT EXISTS] view_name [(column_name [COMMENT column_comment],
...)]
[COMMENT table_comment]
AS SELECT ...七、Advanced Table Properties
(一)Skipping Header and Footer records while loading in table
在许多源文件中,我们观察到一些行出现在顶部(页眉)和一些行出现在底部(页脚) ,它们不是实际数据,但包含有关数据或文件的信息。 因此,我们可以在文件上创建表之前,手动删除这些页眉和页脚行,这是不推荐的。 或者我们可以在使用表属性创建表时跳过这些页眉和页脚行。
考虑下面的文件作为源文件-我们可以观察到,前2行是头行,提供信息文件创建数据和文件名。 最后两行是页脚行,它提供了关于文件中的行数,最后修改日期的信息。
In many of the source files we have observed some lines present on the top (header) and some lines at the bottom (footer), which are not actual data but contains so information about the data or the file. So we can either go to file and manually delete these header and footer lines, before creating table on it, which is not recommended. Or we can skip these header and footer lines while creating table using table properties.Consider below file as a source file -- We can observe that first 2 rows are header rows which provide information File Creation Data and File Name. And last 2 rows are footer rows which provide information about number of rows in a File, last modified date.
(二)如何操作
我们创建了一个提到属性"skip.header.line.count " = " 2 ",因为我们想跳过文件的前两行,并且" skip.footer.line.count " = " 2 ",因为我们想从文件中跳过最后两行。
We created table mentioning property "skip.header.line.count"="2", since we want to skip the top 2 lines from the file and "skip.footer.line.count"="2", since we want to skip bottom 2 lines from the file.
sql
create table if not exists Tb_Employee (id int ,EMP_NAME string
,Department_ID int,Manager_ID int,Designation string,Location
string,Years_of_Experience double) row format delimited fields terminated by
',' lines terminated by '\n' stored as textfile tblproperties
("skip.header.line.count"="2", "skip.footer.line.count"="2");(三)Hive Immutable Table property
1.Mutable Table
默认情况下,所有表都是可变的。 可变表允许在数据已经存在于表中时追加数据。
All the tables by default are mutable. Mutable table allows to append the data when data
already present in table.
2.Immutable Table
通过将Table属性设置为True,可以将Table创建为不可变表。 默认情况下,此属性为false。
A Table can be created as immutable table, by setting its table property to True. By
default, this property is false.
sql
create table if not exists EMP1 (emp_id int, emp_name string, dept_id int)
row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines terminated by '\n' stored
as textfile tblproperties ("immutable"="true");3.Insert into command on Non-Empty Immutable Table:
如果我们尝试在不可变Hive表上使用insert into命令,那么我们将得到错误提示,不允许插入到非空的不可变表中。
If we will try to use insert into command on Immutable Hive table then we will get error saying, inserting into non-empty immutable table is not allowed.
4.Insert Overwrite command on Non-Empty Immutable Table
所有以前的数据从不可变表将被删除,新的数据将被插入 。
all the previous data from Immutable table will be removed and new data will be inserted.
(四)Hive Null Format property
此属性允许传递给此属性的给定值被视为空值。 让我们看一个例子。 下面的文件包含3列,但有3行(第2,第3和第5行),其中第二列的值缺失。 与第二行一样,在值20之后,第二列的值缺失。

现在,如果我们尝试将此文件加载到具有3列的hive表中,hive显然会成功加载此文件,但如果我们尝试从具有第二列值为NULL的表中捕获数据,则会返回零行 。 因为默认情况下,分隔符之间没有空。 分隔符之间的所有内容都是Hive的数据。 Hive不会将缺失的值视为NULL值。 它将是Hive的正常值,即使它是空的。
Data in the table with table Null format property
让我们创建另一个表------我们已经使用了表属性"serialization.null.format" is equals to "" (empty),因为我们想用null替换空字段。 如果我们想用null替换空格**,我们必须在设置表属性时更改值(在等于号之后),以便将其视为null。**
sql
create table if not exists DEPT_DET1 (Department_ID int,Started_on
string,Location string) row format delimited fields terminated by ',' lines
terminated by '\n' stored as textfile tblproperties
("serialization.null.format"="");总结
例如:以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了pandas的使用,而pandas提供了大量能使我们快速便捷地处理数据的函数和方法。