论文名称:DarkIR: Robust Low-Light Image Restoration
论文原文 (Paper) :https://arxiv.org/pdf/2412.13443
官方代码 (Code) :https://github.com/cidautai/DarkIR
超分辨率重建 | CVPR 2025 DarkIR:轻量级低光照图像增强与去模糊模型(论文精度)
摘要: 现有的目标检测和图像恢复模型在低光照、夜间或运动模糊场景下往往表现不佳。本文复现了CVPR 2024 最新论文 DarkIR 中的核心组件:EBlock (基于频域的低光增强编码块) 和 DBlock (基于大感受野的去模糊解码块) 。这两个模块设计轻量且高效,非常适合作为即插即用模块集成到网络中,用于提升模型在暗光增强 和去模糊任务中的鲁棒性。
目录
-
- [[超分辨率重建 | CVPR 2025 DarkIR:轻量级低光照图像增强与去模糊模型(论文精度)](https://editor.csdn.net/md/?articleId=154455320)](#超分辨率重建 | CVPR 2025 DarkIR:轻量级低光照图像增强与去模糊模型(论文精度))
- [一、 论文理论与模块解析](#一、 论文理论与模块解析)
-
- [1. 论文背景与痛点](#1. 论文背景与痛点)
- [2. 核心模块原理](#2. 核心模块原理)
-
- [(1) EBlock:基于频域的低光增强 (Encoder Block)](#(1) EBlock:基于频域的低光增强 (Encoder Block))
- [(2) DBlock:大感受野去模糊 (Decoder Block)](#(2) DBlock:大感受野去模糊 (Decoder Block))
- [二、 核心代码复现](#二、 核心代码复现)
- [三、 结果验证与引流](#三、 结果验证与引流)
-
- [1. 独立运行测试](#1. 独立运行测试)
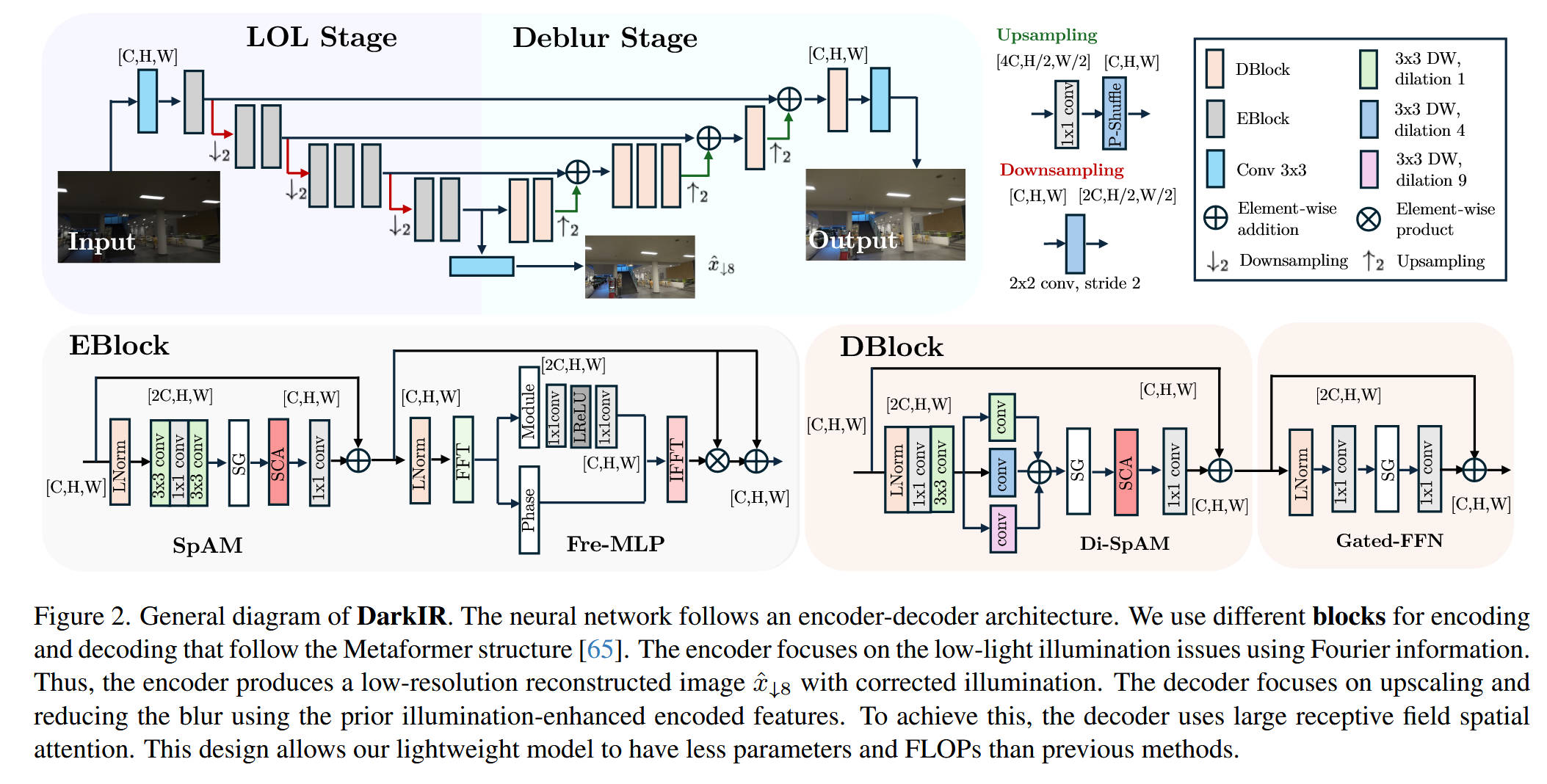
一、 论文理论与模块解析
1. 论文背景与痛点
在夜间摄影或安防监控中,图像通常面临"低光照(Low-light)"和"运动模糊(Blur)"的双重挑战。传统的图像增强方法通常将这两个问题分开处理,导致处理效率低且效果不连贯。
- 痛点: 目前主流的 YOLO 系列或 CNN 网络在处理夜间模糊图像时,特征提取能力会大幅下降,导致漏检或误检。
- DarkIR 的解决方案: 提出了一种多任务低光照图像恢复网络,通过在频域 处理光照信息,在空域处理模糊信息,实现了端到端的高效恢复。
2. 核心模块原理
本文提取了 DarkIR 中最核心的两个模块,均已封装为即插即用的 nn.Module,可直接替换主干网络(Backbone)或特征融合层(Neck)。
(1) EBlock:基于频域的低光增强 (Encoder Block)
- 核心原理: 论文指出,图像的"光照/亮度"信息主要集中在频域的**幅度谱(Amplitude)**中。
- 代码实现:
EBlock内部集成了 FreMLP (Frequency MLP)。它利用 FFT (快速傅里叶变换) 将特征转换到频域,仅对幅度谱进行增强,保持相位谱(结构信息)不变,从而在不破坏物体结构的前提下提亮特征。 - 适用位置: 适合放置在网络的 浅层 Backbone,用于在特征提取初期改善光照条件。
(2) DBlock:大感受野去模糊 (Decoder Block)
- 核心原理: 去模糊任务需要较大的感受野来捕捉上下文信息。
- 代码实现:
DBlock引入了多分支的 扩张卷积 (Dilated Convolution) 结构(代码中的dilations参数)。通过并行使用不同扩张率(如 1, 3, 5)的卷积,模块能够模拟"大核卷积"的效果,捕捉不同尺度的模糊特征,同时保持较低的计算量。 - 适用位置: 适合放置在网络的 深层 Backbone 或 Neck/Head 部分,用于细化特征并去除模糊干扰。
二、 核心代码复现
本部分提供了完整的、经过测试的 PyTorch 代码。代码包含 FreMLP(频域处理)、EBlock(编码块)和 DBlock(解码块)的完整实现,并附带了必要的 LayerNorm 和 Gate 机制。
python
"""
DarkIR模型的核心组件测试文件
包含编码块(EBlock)和解码块(DBlock)的定义和测试
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# LayerNorm2d: 2D层归一化实现
class LayerNormFunction(torch.autograd.Function):
"""自定义2D层归一化的前向和反向传播函数"""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, x, weight, bias, eps):
ctx.eps = eps
N, C, H, W = x.size()
mu = x.mean(1, keepdim=True)
var = (x - mu).pow(2).mean(1, keepdim=True)
y = (x - mu) / (var + eps).sqrt()
ctx.save_for_backward(y, var, weight)
y = weight.view(1, C, 1, 1) * y + bias.view(1, C, 1, 1)
return y
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
eps = ctx.eps
N, C, H, W = grad_output.size()
y, var, weight = ctx.saved_variables
g = grad_output * weight.view(1, C, 1, 1)
mean_g = g.mean(dim=1, keepdim=True)
mean_gy = (g * y).mean(dim=1, keepdim=True)
gx = 1. / torch.sqrt(var + eps) * (g - y * mean_gy - mean_g)
return gx, (grad_output * y).sum(dim=3).sum(dim=2).sum(dim=0), grad_output.sum(dim=3).sum(dim=2).sum(dim=0), None
class LayerNorm2d(nn.Module):
"""2D层归一化模块,对通道维度进行归一化"""
def __init__(self, channels, eps=1e-6):
super(LayerNorm2d, self).__init__()
self.register_parameter('weight', nn.Parameter(torch.ones(channels)))
self.register_parameter('bias', nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(channels)))
self.eps = eps
def forward(self, x):
return LayerNormFunction.apply(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.eps)
class SimpleGate(nn.Module):
"""简单门控机制:将输入通道分为两部分并逐元素相乘"""
def forward(self, x):
x1, x2 = x.chunk(2, dim=1)
return x1 * x2
class FreMLP(nn.Module):
"""频域MLP:在频域对幅度谱进行处理,保持相位不变"""
def __init__(self, nc, expand=2):
super(FreMLP, self).__init__()
self.process1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(nc, expand * nc, 1, 1, 0),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(expand * nc, nc, 1, 1, 0)
)
def forward(self, x):
_, _, H, W = x.shape
x_freq = torch.fft.rfft2(x, norm='backward')
mag = torch.abs(x_freq)
pha = torch.angle(x_freq)
mag = self.process1(mag)
real = mag * torch.cos(pha)
imag = mag * torch.sin(pha)
x_out = torch.complex(real, imag)
x_out = torch.fft.irfft2(x_out, s=(H, W), norm='backward')
return x_out
class Branch(nn.Module):
"""多分支结构中的单个分支:使用深度可分离卷积,支持不同的空洞率"""
def __init__(self, c, DW_Expand, dilation=1):
super().__init__()
self.dw_channel = DW_Expand * c
self.branch = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.dw_channel, out_channels=self.dw_channel, kernel_size=3, padding=dilation, stride=1, groups=self.dw_channel,
bias=True, dilation=dilation)
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.branch(input)
class DBlock(nn.Module):
"""解码块:包含多头分支注意力机制和前馈网络(FFN)"""
def __init__(self, c, DW_Expand=2, FFN_Expand=2, dilations=[1], extra_depth_wise=False):
super().__init__()
self.dw_channel = DW_Expand * c
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=c, out_channels=self.dw_channel, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=1, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
self.extra_conv = nn.Conv2d(self.dw_channel, self.dw_channel, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, groups=c, bias=True, dilation=1) if extra_depth_wise else nn.Identity()
self.branches = nn.ModuleList()
for dilation in dilations:
self.branches.append(Branch(self.dw_channel, DW_Expand=1, dilation=dilation))
assert len(dilations) == len(self.branches)
self.dw_channel = DW_Expand * c
self.sca = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.dw_channel // 2, out_channels=self.dw_channel // 2, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=1,
groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1),
)
self.sg1 = SimpleGate()
self.sg2 = SimpleGate()
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.dw_channel // 2, out_channels=c, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=1, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
ffn_channel = FFN_Expand * c
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=c, out_channels=ffn_channel, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=1, groups=1, bias=True)
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=ffn_channel // 2, out_channels=c, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=1, groups=1, bias=True)
self.norm1 = LayerNorm2d(c)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm2d(c)
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((1, c, 1, 1)), requires_grad=True)
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((1, c, 1, 1)), requires_grad=True)
def forward(self, inp, adapter=None):
y = inp
x = self.norm1(inp)
x = self.extra_conv(self.conv1(x))
z = 0
for branch in self.branches:
z += branch(x)
z = self.sg1(z)
x = self.sca(z) * z
x = self.conv3(x)
y = inp + self.beta * x
x = self.conv4(self.norm2(y))
x = self.sg2(x)
x = self.conv5(x)
x = y + x * self.gamma
return x
class EBlock(nn.Module):
"""编码块:包含多头分支注意力机制和频域处理模块"""
def __init__(self, c, DW_Expand=2, dilations=[1], extra_depth_wise=False):
super().__init__()
self.dw_channel = DW_Expand * c
self.extra_conv = nn.Conv2d(c, c, kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, groups=c, bias=True, dilation=1) if extra_depth_wise else nn.Identity()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=c, out_channels=self.dw_channel, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=1, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
self.branches = nn.ModuleList()
for dilation in dilations:
self.branches.append(Branch(c, DW_Expand, dilation=dilation))
assert len(dilations) == len(self.branches)
self.dw_channel = DW_Expand * c
self.sca = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.dw_channel // 2, out_channels=self.dw_channel // 2, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=1,
groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1),
)
self.sg1 = SimpleGate()
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.dw_channel // 2, out_channels=c, kernel_size=1, padding=0, stride=1, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
self.norm1 = LayerNorm2d(c)
self.norm2 = LayerNorm2d(c)
self.freq = FreMLP(nc=c, expand=2)
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((1, c, 1, 1)), requires_grad=True)
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros((1, c, 1, 1)), requires_grad=True)
def forward(self, inp):
y = inp
x = self.norm1(inp)
x = self.conv1(self.extra_conv(x))
z = 0
for branch in self.branches:
z += branch(x)
z = self.sg1(z)
x = self.sca(z) * z
x = self.conv3(x)
y = inp + self.beta * x
x_step2 = self.norm2(y)
x_freq = self.freq(x_step2)
x = y * x_freq
x = y + x * self.gamma
return x
# 测试代码:验证EBlock和DBlock的输入输出形状
# 输入输出格式: B C H W (Batch, Channels, Height, Width)
if __name__ == "__main__":
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
x = torch.randn(1, 32, 64, 64).to(device)
# 创建编码块和解码块实例
eblock = EBlock(32, DW_Expand=2, dilations=[1, 3, 5], extra_depth_wise=True).to(device)
dblock = DBlock(32, DW_Expand=2, FFN_Expand=2, dilations=[1, 3], extra_depth_wise=True).to(device)
y_e = eblock(x)
y_d = dblock(x)
# print("\n", eblock)
print("EBlock input:", x.shape)
print("EBlock output:", y_e.shape)
# print("\n", dblock)
print("DBlock input:", x.shape)
print("DBlock output:", y_d.shape)
print("\n")三、 结果验证与引流
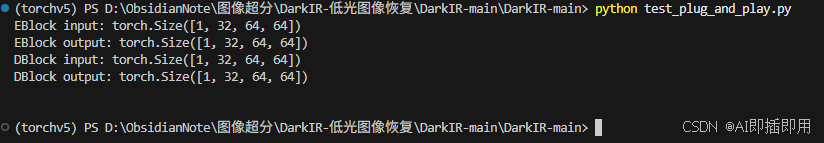
1. 独立运行测试
将上述代码保存并运行。可以看到模块成功处理了 (1, 32, 64, 64) 的输入,且输出尺寸保持不变,证明了其即插即用的特性。
声明: 本专栏提供的均为 独立、可运行 的 Python 模块代码,旨在帮助大家快速复现论文、优化模型。