论文标题:Latent Space Super-Resolution for Higher-Resolution Image Generation with Diffusion Models
论文原文 (Paper) :https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.18446
代码 (code) :https://github.com/3587jjh/LSRNA
超分辨率重建(论文精读) | CVPR 2025 LSRNA:利用隐空间超分与噪声对齐,打破扩散模型生成 4K 图像的效率瓶颈
目录
-
- 第一部分:模块原理与实战分析
-
- [1. 论文背景与解决的痛点](#1. 论文背景与解决的痛点)
- [2. 核心模块原理揭秘](#2. 核心模块原理揭秘)
- [3. 架构图解](#3. 架构图解)
- [4. 适用场景与魔改建议](#4. 适用场景与魔改建议)
- 第二部分:核心完整代码
- 第三部分:结果验证与总结
摘要:
本文提取自 CVPR 2025 最新论文《Latent Space Super-Resolution for Higher-Resolution Image Generation with Diffusion Models》。针对现有扩散模型(如SDXL)在生成 2K/4K 超高分辨率图像时容易出现结构崩坏、内容重复以及细节平滑丢失的痛点,提供了两个核心即插即用模块:LSR(潜在空间超分辨率)和 RNA(区域自适应噪声添加)。代码已封装为独立模块,无需训练庞大的扩散模型,即可无缝集成到现有的推理流程中,显著提升大图生成的清晰度与纹理细节。
第一部分:模块原理与实战分析
1. 论文背景与解决的痛点
在 AIGC 领域,虽然 Stable Diffusion XL (SDXL) 已经很强,但在生成超过其训练分辨率(通常是 1024 2 1024^2 10242)的图像时,比如生成 4K 壁纸,我们经常面临两个棘手的问题:
- "鬼影"与重复:直接强制生成高分辨率,模型会因为没见过这么大的 Latent,导致画面出现多个主体或结构扭曲。
- 细节丢失与平滑:现有的解决方法(如 DemoFusion)通常采用"低分生成 -> 上采样 -> 高分重绘"的策略。但如果用双三次插值(Bicubic)直接上采样 Latent,会导致特征偏离流形(Manifold Deviation),生成的图虽然大了,但细节全是糊的,或者纹理很假。
2. 核心模块原理揭秘
为了解决上述问题,CVPR 2025 的这篇 LSRNA 提出了两个巧妙的模块:
- LSR (Latent Space Super-Resolution) - 潜在空间超分模块 :
- 对应代码类名 :
LIIF(Local Implicit Image Function) - 核心原理 :它不仅仅是简单的插值,而是引入了 LIIF(局部隐式图像函数) 技术。它将低分辨率的 Latent 特征视为坐标点,通过 MLP 预测任意高分辨率坐标下的 Latent 值。这使得低分 Latent 能被精准映射到高分辨率的特征流形上,保证了结构的连贯性。
- 作用 :替代
torch.nn.functional.interpolate,提供更高质量的 Latent 上采样,为大图生成打好"骨架"。
- 对应代码类名 :
- RNA (Region-wise Noise Addition) - 区域自适应噪声模块 :
- 对应代码类名 :
RegionWiseNoiseAddition - 核心原理 :为了解决上采样后细节过于平滑的问题,RNA 利用 Canny 边缘检测 提取图像的高频区域(边缘、纹理丰富处)。然后,根据边缘强度自适应地向 Latent 中注入高斯噪声。
- 作用:在去噪过程中,"诱导"扩散模型在边缘和纹理区域生成更多的高频细节,而在平滑区域保持干净,从而提升画面的锐利度和质感。
- 对应代码类名 :
3. 架构图解
建议参考论文中的 Figure 4,该图清晰展示了 LSR 如何对 Latent 进行超分,以及 RNA 如何通过 Edge Map(边缘图)来控制噪声注入的位置。
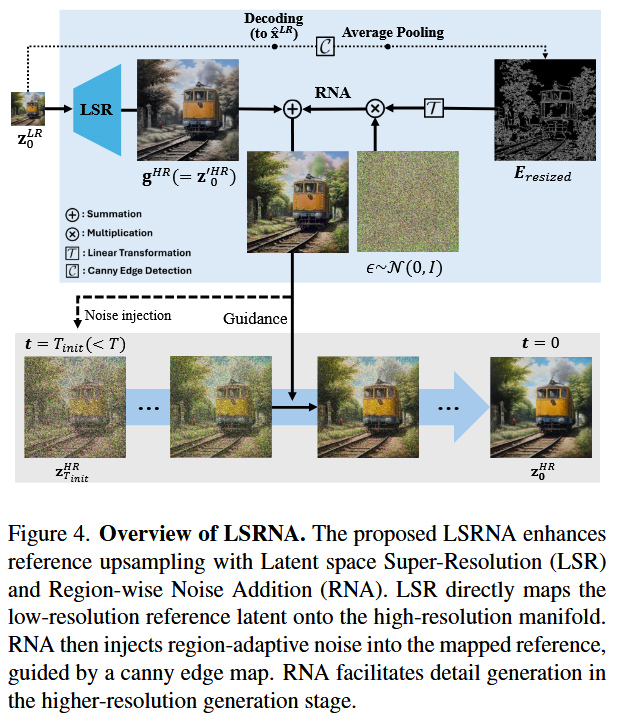
4. 适用场景与魔改建议
这套代码非常适合用于以下场景的改进:
- SDXL / SD1.5 的高分辨率生成脚本 :用于替代默认的
Upsample层。 - 图像超分辨率任务:作为特征域的增强模块。
- 图生图(Img2Img)流程:在放大图像重绘细节时,使用 RNA 模块可以显著增加细节丰富度。
第二部分:核心完整代码
python
"""
LSRNA Plug-and-Play Modules
提取自LSRNA项目的即插即用模块
主要模块:
1. LSR (Latent Space Super-Resolution): 基于LIIF的潜在空间超分辨率
2. RNA (Region-wise Noise Addition): 基于边缘检测的区域自适应噪声添加
Author: Extracted from LSRNA project
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# ==================== 工具函数 ====================
def make_coord(shape, ranges=None, flatten=True, device='cpu'):
"""
生成坐标网格
Args:
shape: 网格形状 (H, W)
ranges: 坐标范围,默认为 [-1, 1]
flatten: 是否展平坐标
device: 设备类型
Returns:
坐标张量
"""
coord_seqs = []
for i, n in enumerate(shape):
if ranges is None:
v0, v1 = -1, 1
else:
v0, v1 = ranges[i]
r = (v1 - v0) / (2 * n)
seq = v0 + r + (2 * r) * torch.arange(n, device=device).float()
coord_seqs.append(seq)
ret = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid(*coord_seqs, indexing='ij'), dim=-1)
if flatten:
ret = ret.view(-1, ret.shape[-1])
return ret
def gaussian_kernel(kernel_size=3, sigma=1.0, channels=3):
"""
生成高斯卷积核
Args:
kernel_size: 卷积核大小
sigma: 高斯标准差
channels: 通道数
Returns:
高斯卷积核
"""
x_coord = torch.arange(kernel_size)
gaussian_1d = torch.exp(-(x_coord - (kernel_size - 1) / 2) ** 2 / (2 * sigma ** 2))
gaussian_1d = gaussian_1d / gaussian_1d.sum()
gaussian_2d = gaussian_1d[:, None] * gaussian_1d[None, :]
kernel = gaussian_2d[None, None, :, :].repeat(channels, 1, 1, 1)
return kernel
def gaussian_filter(latents, kernel_size=3, sigma=1.0):
"""
对潜在表示应用高斯滤波
Args:
latents: 输入潜在张量
kernel_size: 卷积核大小
sigma: 高斯标准差
Returns:
滤波后的潜在张量
"""
channels = latents.shape[1]
kernel = gaussian_kernel(kernel_size, sigma, channels).to(latents.device, latents.dtype)
blurred_latents = F.conv2d(latents, kernel, padding=kernel_size//2, groups=channels)
return blurred_latents
def apply_canny_detection(image_np, low_threshold=100, high_threshold=200):
"""
应用Canny边缘检测
Args:
image_np: 输入图像 (numpy array, RGB)
low_threshold: 低阈值
high_threshold: 高阈值
Returns:
边缘图 (0或255)
"""
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image_np, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
filtered_image = cv2.Canny(gray_image, low_threshold, high_threshold)
return filtered_image
# ==================== MLP 模块 ====================
class MLP(nn.Module):
"""
简单的多层感知机
用于LIIF模块中的隐式函数
"""
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim, hidden_list):
"""
Args:
in_dim: 输入维度
out_dim: 输出维度
hidden_list: 隐藏层维度列表
"""
super().__init__()
layers = []
lastv = in_dim
for hidden in hidden_list:
layers.append(nn.Linear(lastv, hidden))
layers.append(nn.ReLU())
lastv = hidden
layers.append(nn.Linear(lastv, out_dim))
self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
shape = x.shape[:-1]
x = self.layers(x.view(-1, x.shape[-1]))
return x.view(*shape, -1)
# ==================== LSR 模块 (LIIF) ====================
class SimpleEncoder(nn.Module):
"""
简化的编码器
用于测试LIIF模块
"""
def __init__(self, in_dim=4, out_dim=64):
super().__init__()
self.out_dim = out_dim
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_dim, 32, 3, padding=1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, out_dim, 3, padding=1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.conv1(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv2(x))
return x
class LIIF(nn.Module):
"""
Local Implicit Image Function (LIIF)
潜在空间超分辨率模块
核心功能:
- 将低分辨率潜在表示映射到高分辨率潜在流形
- 支持任意分辨率的查询
- 使用局部集成提高重建质量
"""
def __init__(self, encoder=None, imnet_spec=None, feat_unfold=True, local_ensemble=True):
"""
Args:
encoder: 特征编码器
imnet_spec: 隐式函数网络配置
feat_unfold: 是否展开特征
local_ensemble: 是否使用局部集成
"""
super().__init__()
self.local_ensemble = local_ensemble
self.feat_unfold = feat_unfold
# 使用简化的编码器用于测试
if encoder is None:
self.encoder = SimpleEncoder(in_dim=4, out_dim=64)
else:
self.encoder = encoder
imnet_in_dim = self.encoder.out_dim
if self.feat_unfold:
imnet_in_dim *= 9
imnet_in_dim += 4 # attach coord, cell
# 使用简化的MLP
if imnet_spec is None:
self.imnet = MLP(imnet_in_dim, 4, [256])
else:
self.imnet = imnet_spec
def gen_feat(self, inp):
"""
生成特征表示
Args:
inp: 输入潜在张量 (B, C, H, W)
"""
self.inp = inp
feat = self.encoder(inp)
if self.feat_unfold:
feat = F.unfold(feat, 3, padding=1).view(
feat.shape[0], feat.shape[1] * 9, feat.shape[2], feat.shape[3])
self.feat = feat
self.feat_coord = make_coord(feat.shape[-2:], flatten=False, device=inp.device) \
.permute(2, 0, 1) \
.unsqueeze(0).expand(feat.shape[0], 2, *feat.shape[-2:])
def query_rgb(self, coord, cell):
"""
查询RGB值
Args:
coord: 查询坐标 (b, h, w, 2)
cell: 单元大小 (b, h, w, 2)
Returns:
RGB值 (b, c, h, w)
"""
feat = self.feat
feat_coord = self.feat_coord
if self.local_ensemble:
vx_lst = [-1, 1]
vy_lst = [-1, 1]
eps_shift = 1e-6
else:
vx_lst, vy_lst, eps_shift = [0], [0], 0
# field radius (global: [-1, 1])
rx = 2 / feat.shape[-2] / 2
ry = 2 / feat.shape[-1] / 2
preds = []
areas = []
for vx in vx_lst:
for vy in vy_lst:
coord_ = coord.clone()
coord_[:, :, :, 0] += vx * rx + eps_shift
coord_[:, :, :, 1] += vy * ry + eps_shift
coord_.clamp_(-1 + 1e-6, 1 - 1e-6)
q_feat = F.grid_sample(feat, coord_.flip(-1),
mode='nearest', align_corners=False).permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
q_coord = F.grid_sample(feat_coord, coord_.flip(-1),
mode='nearest', align_corners=False).permute(0, 2, 3, 1)
rel_coord = coord - q_coord
rel_coord[:, :, :, 0] *= feat.shape[-2]
rel_coord[:, :, :, 1] *= feat.shape[-1]
inp = torch.cat([q_feat, rel_coord], dim=-1)
rel_cell = cell.clone()
rel_cell[:, :, :, 0] *= feat.shape[-2]
rel_cell[:, :, :, 1] *= feat.shape[-1]
inp = torch.cat([inp, rel_cell], dim=-1)
pred = self.imnet(inp.contiguous())
preds.append(pred)
area = torch.abs(rel_coord[:, :, :, 0] * rel_coord[:, :, :, 1])
areas.append(area + 1e-9)
tot_area = torch.stack(areas).sum(dim=0)
if self.local_ensemble:
t = areas[0]; areas[0] = areas[3]; areas[3] = t
t = areas[1]; areas[1] = areas[2]; areas[2] = t
ret = 0
for pred, area in zip(preds, areas):
ret = ret + pred * (area / tot_area).unsqueeze(-1)
ret = ret.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
if ret.shape[1] != self.inp.shape[1]:
ret[:, :-1, :, :] += F.grid_sample(self.inp, coord.flip(-1), mode='bicubic',
padding_mode='border', align_corners=False)
else:
ret += F.grid_sample(self.inp, coord.flip(-1), mode='bicubic',
padding_mode='border', align_corners=False)
return ret
def forward(self, inp, coord, cell):
"""
前向传播
Args:
inp: 输入潜在张量 (B, C, H_in, W_in)
coord: 目标坐标 (1, H_out, W_out, 2)
cell: 单元大小 (1, H_out, W_out, 2)
Returns:
上采样后的潜在张量 (1, C, H_out, W_out)
"""
self.gen_feat(inp)
H, W = coord.shape[1:3]
n = H * W
coord = coord.view(1, 1, n, 2)
cell = cell.view(1, 1, n, 2)
ql = 0
preds = None
bsize = 512 * 512 # 批处理大小
while ql < n:
qr = min(ql + bsize, n)
pred = self.query_rgb(coord[:, :, ql:qr, :], cell[:, :, ql:qr, :])
preds = pred if preds is None else torch.cat([preds, pred], dim=-1)
ql = qr
preds = preds.view(1, -1, H, W)
return preds
# ==================== RNA 模块 ====================
class RegionWiseNoiseAddition(nn.Module):
"""
Region-wise Noise Addition (RNA)
区域自适应噪声添加模块
核心功能:
- 基于Canny边缘检测生成区域权重
- 根据边缘强度自适应调整噪声强度
- 在高频区域添加更多噪声以引导细节生成
"""
def __init__(self, rna_min_std=0.0, rna_max_std=1.2, low_threshold=0, high_threshold=255):
"""
Args:
rna_min_std: 最小噪声标准差
rna_max_std: 最大噪声标准差
low_threshold: Canny低阈值
high_threshold: Canny高阈值
"""
super().__init__()
self.rna_min_std = rna_min_std
self.rna_max_std = rna_max_std
self.low_threshold = low_threshold
self.high_threshold = high_threshold
def forward(self, latents, reference_image):
"""
前向传播
Args:
latents: 输入潜在张量 (B, C, H, W)
reference_image: 参考图像用于边缘检测 (numpy array, RGB, shape: [H_img, W_img, 3])
Returns:
添加噪声后的潜在张量 (B, C, H, W)
"""
H, W = latents.shape[-2:]
# 应用Canny边缘检测
edge_map = apply_canny_detection(
reference_image,
low_threshold=self.low_threshold,
high_threshold=self.high_threshold
).astype(np.float32)
# 转换为张量并调整大小
edge_map = torch.tensor(edge_map).to(latents.device).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
edge_map = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(edge_map, (H, W))
# 归一化到 [rna_min_std, rna_max_std]
std = ((edge_map - edge_map.min()) / (edge_map.max() - edge_map.min() + 1e-8)) * \
(self.rna_max_std - self.rna_min_std) + self.rna_min_std
# 添加区域自适应噪声
noise = torch.randn_like(latents) * std
latents_with_noise = latents + noise
return latents_with_noise
# ==================== 测试代码 ====================
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 设备选择
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(f"使用设备: {device.upper()}")
# 输入参数
B, C, H, W = 1, 4, 32, 64
x = torch.randn(B, C, H, W).to(device)
# ========== 测试 LSR (LIIF) 模块 ==========
print("\n# 测试 LSR (LIIF) 模块")
liif = LIIF(feat_unfold=True, local_ensemble=True).to(device)
liif.eval()
# 2倍上采样
scale = 2
H_out, W_out = H * scale, W * scale
coord = make_coord((H_out, W_out), flatten=False, device=device).unsqueeze(0)
cell = torch.ones_like(coord)
cell[:, :, :, 0] *= 2 / H_out
cell[:, :, :, 1] *= 2 / W_out
print(f"LSR输入: {x.shape}")
with torch.no_grad():
y_lsr = liif(x, coord, cell)
print(f"LSR输出: {y_lsr.shape}")
# ========== 测试 RNA 模块 ==========
print("\n# 测试 RNA (Region-wise Noise Addition) 模块")
rna = RegionWiseNoiseAddition(rna_min_std=0.0, rna_max_std=1.2).to(device)
# 创建参考图像
img_size = 256
ref_img = np.random.rand(img_size, img_size, 3) * 255
ref_img = ref_img.astype(np.uint8)
ref_img[img_size//2-10:img_size//2+10, :] = 255 # 添加边缘
print(f"RNA输入: {y_lsr.shape}")
with torch.no_grad():
y_rna = rna(y_lsr, ref_img)
print(f"RNA输出: {y_rna.shape}")
# ========== 测试完整 LSRNA 流程 ==========
print("\n# 测试完整 LSRNA 流程")
print(f"流程: {x.shape} -> LSR -> {y_lsr.shape} -> RNA -> {y_rna.shape}")
print("\n✓ 所有测试完成!")第三部分:结果验证与总结
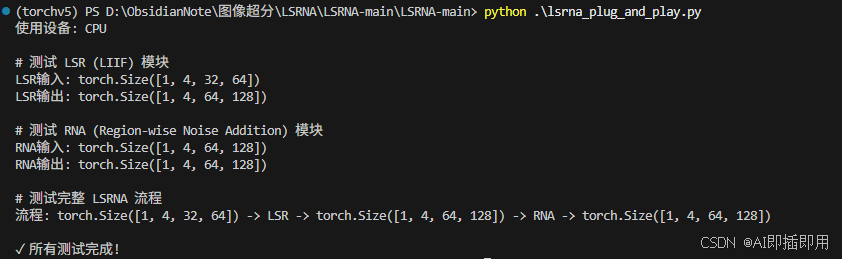
如下图所示,我们模拟了一个 Latent 输入进行测试:
- 经过 LSR 模块 后,成功超分 2 倍至
(1, 4, 64, 128),且通过 LIIF 机制处理,支持任意倍率。 - 经过 RNA 模块 后,结合参考图边缘信息,成功输出了带有自适应噪声的 Latent,尺寸保持不变。
到此,所有的内容就基本讲完了。如果觉得这篇文章对你有用,记得点赞、收藏并分享给你的小伙伴们哦😄。